Pulsed field ablation (PFA) is an emerging non-thermal ablation technique for treating cardiac arrhythmias. Unlike conventional radiofrequency ablation (RFA) which uses heat to ablate cardiac tissue, PFA uses pulsed electric fields to selectively disrupt cell membranes in the targeted cardiac tissue. The pulsed electric fields are generated using needle-like ablation electrodes that are inserted into the heart to deliver high-intensity, short-duration electric pulses. These pulses disrupt the cell membranes through electroporation without generating heat.
How Pulsed Field Ablation Works
When the ablation electrodes are placed in contact with cardiac tissue, short pulses of high voltage electricity in the range of hundreds to low thousands of volts are delivered through the electrodes. These pulses create small pores or holes in the cell membranes of the targeted cardiac cells through electroporation. The electroporated cells undergo apoptosis or programmed cell death without causing thermal damage to surrounding tissues. This non-thermal mechanism of ablation allows for more precise tissue disruption without collateral damage. The pulses can be precisely delivered to reshape cardiac conduction pathways and electrically isolate arrhythmogenic substrates.
Advantages over Conventional Ablation Techniques
PFA offers several potential advantages over conventional RFA for cardiac ablation procedures:
- Precision and control: PFA allows for targeted disruption of only the cardiomyocytes within the electric field generated by the ablation electrodes. This provides better precision and control over the ablation process compared to thermal technologies which rely on heat diffusion.
- Minimized collateral damage: Without generating heat, PFA can ablate target cardiac tissue with minimal damage to surrounding muscle and blood vessels. This helps reduce complications such as steam pops, thrombus formation, and cardiac wall necrosis seen with RFA.
- Faster procedure time: As PFA is a non-thermal technology, it does not require waiting for tissue cooling between successive ablation points. This helps reduce overall procedure time.
- Improved lesion formation: The non-thermal mechanism allows for more homogeneous lesion formation compared to heat-based techniques which are affected by blood flow cooling effects.
- Better assessment of lesion formation: Lesion formation through PFA can be monitored electrically during the procedure through impedance or conduction block confirmation. This enables better assessment compared to RFA where assessment relies on waiting for tissue cooling.
Clinical Development Status
Several companies are currently developing PFA systems for cardiac ablation. Notably, Acutus Medical has received FDA approval for its AcQBlate Force System, which utilizes a proprietary Pulsed Field Ablation technology, for treatment of recurrent lone atrial fibrillation.
Initial clinical studies comparing PFA to RFA have shown promising results. A 2018 study published in Heart Rhythm journal compared efficacy and safety of PFA versus RFA for atrial fibrillation ablation in 30 patients. The study demonstrated superior acute efficacy of PFA in achieving pulmonary vein isolation and similar procedure safety between the two technologies.
Larger clinical trials are currently underway to further evaluate safety, efficacy and outcomes of PFA compared to RFA in a variety of cardiac arrhythmias over longer follow-up periods. These include the PFA-SAFIRE study evaluating PFA for treatment of symptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and the TACCELERATE trial comparing PFA to cryoablation for treatment of ventricular arrhythmias. Results from pivotal clinical studies are expected in 2022-2023.
Overview and Future Trends
Within this, technologies such as cryoablation and pulsed field ablation are anticipated to displace some share from radiofrequency ablation over the coming years due to their technical advantages.
Specifically for pulsed field ablation, it is still in very early stages of development currently valued at less than $10 million globally according to analysts. However, its adoption is expected to increase exponentially over the next 5 years as ongoing clinical trials report results and more products receive regulatory approvals. Countries with established ablation like the United States and Europe are anticipated to be early adopters. By 2026, PFA technology is projected achieve around 5-10% share within the global cardiac ablation driven by its superior safety profile and efficacy.
In summary, pulsed field ablation represents an exciting emerging non-thermal ablation technology for treating cardiac arrhythmias. Positive early clinical data and technical advantages over RFA positions PFA for significant future growth over the coming years subject to outcomes from pivotal trials currently underway. Widespread adoption of PFA has the potential to reshape the cardiac ablation landscape.
Pulsed Field Ablation - A Promising Emerging Technology for Cardiac Ablation Procedures
Published Date: Nov 2024
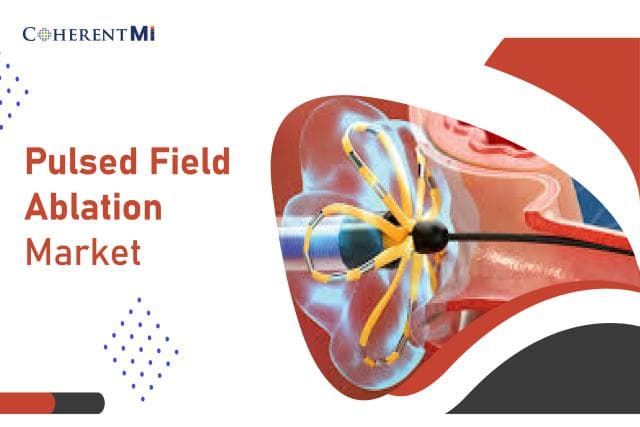
Pulsed field ablation (PFA) is an emerging non-thermal ablation technique for treating cardiac arrhythmias.
Unlike conventional radiofrequency ablation (RFA) which uses heat to ablate cardiac tissue, PFA uses pulsed electric fields to selectively disrupt cell membranes in the targeted cardiac tissue.
The pulsed electric fields are generated using needle-like ablation electrodes that are inserted into the heart to deliver high-intensity, short-duration electric pulses.
These pulses disrupt the cell membranes through electroporation without generating heat.
How Pulsed Field Ablation WorksWhen the ablation electrodes are placed in contact with cardiac tissue, short pulses of high voltage electricity in the range of hundreds to low thousands of volts are delivered through the electrodes.
These pulses create small pores or holes in the cell membranes of the targeted cardiac cells through electroporation.
The electroporated cells undergo apoptosis or programmed cell death without causing thermal damage to surrounding tissues.
This non-thermal mechanism of ablation allows for more precise tissue disruption without collateral damage.
The pulses can be precisely delivered to reshape cardiac conduction pathways and electrically isolate arrhythmogenic substrates.
Advantages over Conventional Ablation TechniquesPFA offers several potential advantages over conventional RFA for cardiac ablation procedures:- Precision and control: PFA allows for targeted disruption of only the cardiomyocytes within the electric field generated by the ablation electrodes.
This provides better precision and control over the ablation process compared to thermal technologies which rely on heat diffusion.- Minimized collateral damage: Without generating heat, PFA can ablate target cardiac tissue with minimal damage to surrounding muscle and blood vessels.
This helps reduce complications such as steam pops, thrombus formation, and cardiac wall necrosis seen with RFA.- Faster procedure time: As PFA is a non-thermal technology, it does not require waiting for tissue cooling between successive ablation points.
This helps reduce overall procedure time.
- Improved lesion formation: The non-thermal mechanism allows for more homogeneous lesion formation compared to heat-based techniques which are affected by blood flow cooling effects.
- Better assessment of lesion formation: Lesion formation through PFA can be monitored electrically during the procedure through impedance or conduction block confirmation.
This enables better assessment compared to RFA where assessment relies on waiting for tissue cooling.Clinical Development Status Several companies are currently developing PFA systems for cardiac ablation.
Notably, Acutus Medical has received FDA approval for its AcQBlate Force System, which utilizes a proprietary Pulsed Field Ablation technology, for treatment of recurrent lone atrial fibrillation.
Initial clinical studies comparing PFA to RFA have shown promising results.
A 2018 study published in Heart Rhythm journal compared efficacy and safety of PFA versus RFA for atrial fibrillation ablation in 30 patients.
The study demonstrated superior acute efficacy of PFA in achieving pulmonary vein isolation and similar procedure safety between the two technologies.
Larger clinical trials are currently underway to further evaluate safety, efficacy and outcomes of PFA compared to RFA in a variety of cardiac arrhythmias over longer follow-up periods.
These include the PFA-SAFIRE study evaluating PFA for treatment of symptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and the TACCELERATE trial comparing PFA to cryoablation for treatment of ventricular arrhythmias.
Results from pivotal clinical studies are expected in 2022-2023.
Overview and Future Trends Within this, technologies such as cryoablation and pulsed field ablation are anticipated to displace some share from radiofrequency ablation over the coming years due to their technical advantages.Specifically for pulsed field ablation, it is still in very early stages of development currently valued at less than $10 million globally according to analysts.
However, its adoption is expected to increase exponentially over the next 5 years as ongoing clinical trials report results and more products receive regulatory approvals.
Countries with established ablation like the United States and Europe are anticipated to be early adopters.
By 2026, PFA technology is projected achieve around 5-10% share within the global cardiac ablation driven by its superior safety profile and efficacy.
In summary, pulsed field ablation represents an exciting emerging non-thermal ablation technology for treating cardiac arrhythmias.
Positive early clinical data and technical advantages over RFA positions PFA for significant future growth over the coming years subject to outcomes from pivotal trials currently underway.
Widespread adoption of PFA has the potential to reshape the cardiac ablation landscape.