Europe Smart Water Meter Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2023 - 2030)
Europe Smart Water Meter Market is Segmented By Technology (Automatic Meter Reading, Advanced Metering Infrastructure, Others), By Type (One-way Water....
Europe Smart Water Meter Market Size
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR11.5%
| Study Period | 2023 - 2030 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2022 |
| CAGR | 11.5% |
| Largest Market | Europe |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Itron, Diehl Metering, Zenner International, Elster Group, Kamstrup and Among Others. |
please let us know !
Europe Smart Water Meter Market Analysis
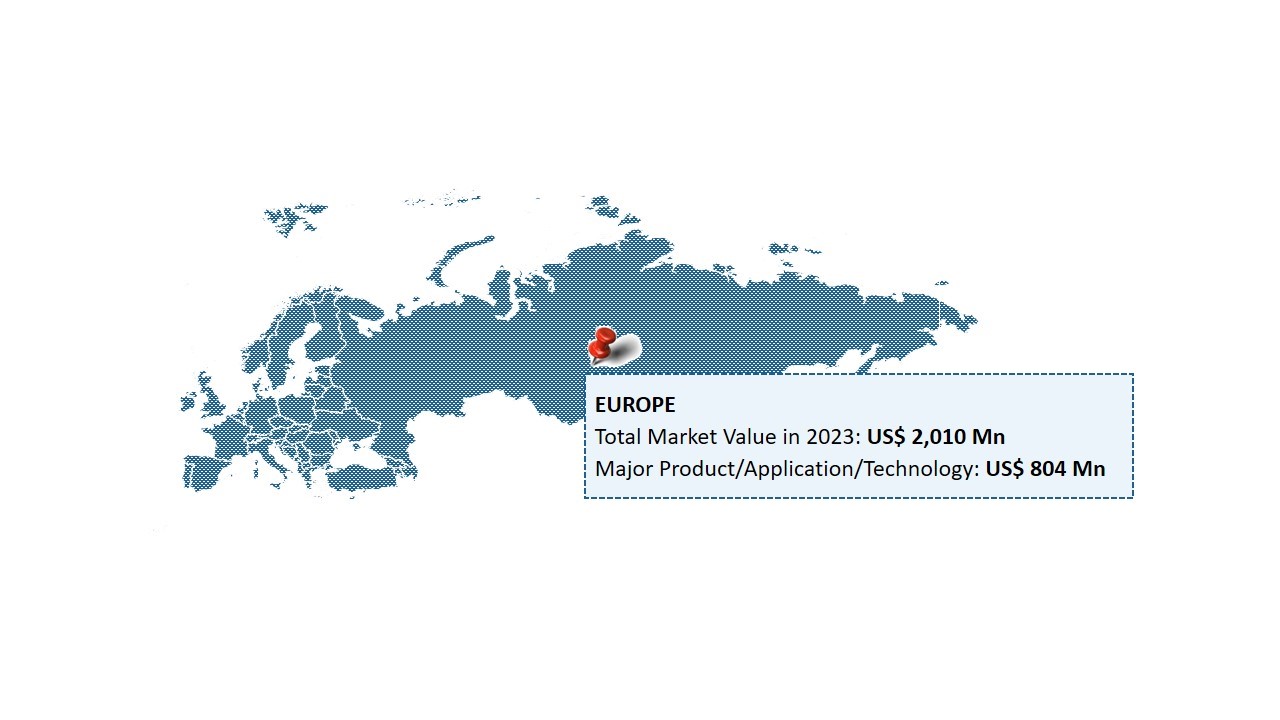
The Europe smart water meter market size is expected to reach US$ 4.30 Bn by 2030, from US$ 2.01 Bn in 2023, at a CAGR of 11.5% during the forecast period. Smart water meters are devices that measure and record water consumption data and communicate it back to the utility company for monitoring and billing. They provide real-time water usage data, detect leaks, and support water conservation efforts. The key drivers of the market include government policies, growing demand from emerging economies, increasing digitalization and automation, and rising awareness about water conservation.
The Europe smart water meter market is segmented by technology, type, component, application, and region. By technology, the market is segmented into Automatic Meter Reading, Advanced Metering Infrastructure, Others. The AMR segment held the largest share of the market in 2023. AMR technologies allow remote reading of meters through short-range radio frequency. It does not provide real-time usage data but offers cost benefits compared to AMI.
Europe Smart Water Meter Market Drivers
- Supportive government policies and regulations: Governments across Europe are undertaking initiatives to deploy smart water meters, which is driving market growth. For instance, The Energy Efficiency Directive, published by the European Union, established requirements for the installation of smart meters for gas and electricity. This mandate was increased by some member states to cover smart water meters as well. Countries like Italy, France, the U.K., Spain, and the Netherlands have already deployed millions of smart water meters or have plans to do so shortly. Supportive policies and mandates create strong demand for smart water metering technology.
- Need to reduce non-revenue water losses: Non-revenue water due to leaks, theft, and inaccuracies costs water utilities Bns yearly. Studies estimate Europe loses over $12 Bn worth of non-revenue water every year. Smart water meters allow precise measurement, leak alerts, and better monitoring to substantially curb such losses. Their adoption is growing as utilities aim to increase revenue collection and account for every drop of water. Advanced smart water meters also help detect underground leaks before they surface.
- Increased investments in smart city infrastructure: Many European cities are undertaking smart city projects involving revamping of water distribution infrastructure using smart technologies. These projects utilize IoT, cloud computing, big data analytics, and Artificial intelligence AI, along with smart meters, to deliver efficient, sustainable water management. Large-scale investments in smart city infrastructure create significant opportunities for smart water metering companies.
- Water conservation and sustainability goals: Reducing per capita water consumption and responsible water usage are key priorities for Europe. Smart water meters, by providing detailed consumption data and leakage alerts, play a crucial role in influencing consumer behavior and achieving conservation targets. Metering technology combined with customer engagement tactics can reduce water demand substantially. This is increasing adoption by utilities focused on sustainability.
Europe Smart Water Meter Market Opportunities
- New product development through technological innovation: The smart water metering space has seen continuous innovation in recent years. Companies are launching products like battery-free meters, LoRa-enabled meters for long-distance communication, and ultrasonic smart meters with no moving parts. Integrating smart meters with IoT and cloud platforms and adding capabilities like real-time analytics and control is an additional area of opportunity. Such innovation presents significant opportunities for manufacturers to gain market share.
- Geographic expansion to tap developing markets: Many parts of Eastern Europe, Russia, and Central Asia still use outdated water metering infrastructure. Modernizing water distribution is a priority for utilities in these territories. Companies can focus on expanding their presence in these markets. Local partnerships, distribution agreements, and cost-effective meters tuned to developing world requirements would be the keys.
- Mergers and acquisitions for enhanced product portfolio: The smart water metering space has seen some mergers and acquisitions activity recently. But there remains ample room for consolidation. Large meter makers can look at acquiring startups working in smart ultrasonic metering, AGIs, or communication modules. Such deals can allow access to new technologies and fast-track innovation. Vertical integration presents opportunities to provide complete smart water management solutions.
- Outsourcing of metering infrastructure operations: Many water utilities want to transfer the cost and complexity of operating smart metering infrastructure to specialists. This gives meter vendors the opportunity to provide metering-as-a-service, leveraging their expertise in meter rollout, communications, data integration, analytics, etc. Outcome-based contracts can be crafted around leakage reduction or revenue protection key performance indicators.
Europe Smart Water Meter Market Restraints
- High upfront costs of deployment: The upfront capital costs of large scale smart meter rollouts, along with investments in IT infrastructure, remain high for many utilities. The long ROI periods act as a barrier, especially for smaller utilities with limited budgets. Obtaining approvals for cost recovery through tariff hikes also presents challenges in the regulated utility space.
- Privacy and security concerns: A big challenge facing smart water metering is privacy and security concerns surrounding increased data collection. Consumer advocacy groups in some countries have opposed rollouts, citing the risks of location tracking, behavior profiling, and cyberattacks. Winning consumer confidence is essential for mainstream adoption.
- Technical knowledge and manpower limitations: Lack of in-house smart metering expertise can deter smaller utilities from attempting the technology transition. Moreover, managing the IT/OT convergence requires both technical skills and change management. Staff training and onboarding meter data management partners are key to overcoming this constraint.
Europe Smart Water Meter Market Trends
- Interoperability and open standards: One of the top priorities is interoperability between data systems, communications, and meter hardware. Lack of standards hampers large scale smart metering adoption. Efforts are ongoing to define open standards at every layer to allow components from different vendors to seamlessly integrate. Open architectures also prevent vendor lock-in and provide flexibility to water utilities.
- Advanced analytics and actionable insights: Smart water meters generate huge amounts of granular data. Recent years have seen the application of advanced analytics like machine learning to garner actionable insights from raw data. These include predictive modeling for demand forecasting, clustering to identify leakage zones, anomaly detection, and segmentation of customers. Such analytical capabilities help utilities maximize the ROI of smart metering.
- Cybersecurity enhancements: Smart water metering networks contain critical infrastructure, which makes them vulnerable to cyberattacks. Cybersecurity is a major concern impeding adoption. To mitigate risks, manufacturers are incorporating security features like data encryption, access controls, and remote software updates. Standards bodies are also working towards cybersecurity recommendations for smart metering systems.
- Transition to service-based business models: Vendors are transitioning from pure-play manufacturers to service-driven business models. This includes providing managed services, active monitoring and maintenance of meter networks, deploying analytics dashboards and mobile apps, and even building connectivity infrastructure. These value-added services beyond basic meter hardware deliver higher revenues.
Figure 1. Europe Smart Water Meter Market Size in US$ Bn
Competitive overview of Europe Smart Water Meter Market
Itron, Diehl Metering, Zenner International, Elster Group, Kamstrup, Landis+Gyr, Sensus, Aclara Technologies, Badger Meter, Neptune Technology Group
Europe Smart Water Meter Market Leaders
- Itron
- Diehl Metering
- Zenner International
- Elster Group
- Kamstrup
Europe Smart Water Meter Market - Competitive Rivalry, 2023

Europe Smart Water Meter Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Europe Smart Water Meter Market
New product launches
- In October 2022, Diehl Metering (global market leaders in water metering) launched HYDRUS IP, an ultrasonic smart water meter with built-in IP67 communication for IoT applications. It provides bidirectional communication and is suitable for residential and commercial buildings.
- In June 2021, Zenner (offers the complete value chain from project development to measurement data recording and processing up to applications for the end user) introduced the WIntesis smart water meter for IoT applications. It offers LoRaWAN connectivity and a battery lifetime of up to 16 years. It is designed for smart city projects.
- In May 2020, Badger Meter (leading manufacturer of metering products using flow measurement and control technologies) introduced the new Dynasonics TFM ultrasonic smart water meter. It provides enhanced accuracy and extended battery life for long-term performance.
Acquisition and partnerships
- In September 2021, Diehl Metering acquired majority stakes in two African meter manufacturers, GWI and Mimeta. The acquisitions expanded Diehl's market access in Sub-Saharan Africa.
- In November 2020, Itron (offers products and services for energy and water resource management) acquired mechanical flow meter specialist s::can. This allowed Itron to expand its smart water portfolio with flow monitoring solutions.
- In October 2019, Badger Meter acquired Innovative Metering Solutions, strengthening its position in the water utility market in the Southeast U.S.
Europe Smart Water Meter Market Segmentation
- By Technology
-
- Automatic Meter Reading
- Advanced Meter Infrastructure
- Others
- By Type
-
- One-way Water Meters
- Two-way Water Meters
- Smart Water Meters
- Others
- By Component
-
- Meters & Accessories
- IT Solutions
- Communications
- Others
- By Application
-
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
- Others

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
What are the key factors hampering growth of the Europe smart water meter market?
The major factors hampering the Europe smart water meter market growth are high upfront costs of deployment, privacy and security concerns, technical knowledge and manpower limitations.
What are the major factors driving the Europe smart water meter market growth?
The major factors driving the Europe smart water meter market growth are regulatory mandates, water conservation efforts, and advancements in IoT technology.
Which is the leading component segment in the Europe smart water meter market?
The leading component segment in the Europe smart water meter market is the meters & accessories segment.
Which are the major players operating in the Europe smart water meter market?
The major players operating in the Europe smart water meter market are Itron, Diehl Metering, Zenner International, Elster Group, Kamstrup, Landis+Gyr, Sensus, Aclara Technologies, Badger Meter, and Neptune Technology Group.
What will be the CAGR of Europe smart water meter market?
The CAGR of the Europe smart water meter market is projected to be 11.5% from 2023 to 2030.