Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market is segmented By Type (Intracerebral Hemorrhage, Subarachnoid Bleeding, Subdural Blood Hematoma, Epidural Hema....
Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market Size
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR8.1%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 8.1% |
| Market Concentration | Low |
| Major Players | Acasti Pharma, Alveron Pharma, NoNO Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb, Acticor Biotech and Among Others. |
please let us know !
Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market Analysis
The Global Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.9 Bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 3.4 Bn by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.1% from 2024 to 2031. With rising incidences of head injuries caused by road traffic accidents and fall-related injuries, especially among the geriatric population who are more prone to hypertension and cerebrovascular abnormalities, the demand for accurate and rapid diagnosis of intracranial hemorrhage is set to increase in the coming years.
The Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market is expected to witness positive growth over the forecast period. Key factors driving the market include technological advancements in diagnostic imaging modalities for improved detection capabilities, growing awareness about benefits of early diagnosis, and increasing healthcare expenditures. Advanced imaging technologies such as CT scans, MRI, and angiography are crucial for early detection and management of intracranial hemorrhages. The increasing demand for non-invasive, accurate diagnostic tools has driven innovation in this field, with AI-based diagnostic solutions enhancing detection accuracy. Factors such as the aging population and the prevalence of hypertension further contribute to the market’s expansion, making timely diagnosis essential for reducing mortality and improving patient outcomes in intracranial hemorrhage cases. However, high costs of specialized diagnostic equipment and procedures may limit market growth to some extent.
Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market Trends
Market Driver - Increasing Prevalence of Intracranial Hemorrhage Due to Lifestyle Factors and Aging Population Globally.
The prevalence of intracranial hemorrhage is increasing globally due to changing lifestyle patterns and an aging population. Risk factors such as hypertension, obesity, excessive alcohol consumption and smoking-related illnesses have become much more common in recent decades. Developed nations have witnessed a major shift towards more sedentary lifestyles with less physical activity and greater consumption of processed and fatty foods. This has translated to growing rates of conditions like metabolic syndrome, diabetes and cardiovascular disease - all of which are significant risk multipliers for hemorrhagic strokes.
At the same time, improvements in healthcare and living standards have allowed populations to age dramatically. As the proportion of elderly individuals expands worldwide, the incidence of age-related health issues is rising in tandem. The risk of intracranial hemorrhage, in particular, increases substantially with age since brain arteries tend to weaken as people grow older. This synergizes with the higher prevalence of comorbidities in advanced age to worsen outcomes. Longer life expectancies mean that more people will spend decades living with the threat of hemorrhagic complications.
The convergence of these lifestyle and demographic trends ensures that intracranial hemorrhages will continue impacting more families and communities in the future. As the underlying causes cannot be reversed quickly, focused efforts are needed to screen at-risk groups, modulate behaviors, control comorbid disease and improve post-event care. This growing clinical burden points to a definite need for better diagnostic techniques, new treatment approaches and preventive strategies customized for the changing healthcare needs of populations worldwide. Such medical innovations would help address a significant and expanding unmet need caused primarily by modern lifestyle shifts and aging societies.
Market Driver - Advancements in Drug Delivery Address Unmet Needs in Hemorrhagic Conditions.
While traditional drug and surgical approaches have made strides in stabilizing hemorrhagic events and reducing associated fatalities, there still remain major limitations and unaddressed needs in the management of intracranial hemorrhages. A key limitation is the inability to actively halt or reverse ongoing bleeding inside the brain after insult. Existing hemostatic agents cannot effectively penetrate hemorrhagic sites encased by the blood-brain barrier. Their systemic administration also risks unwanted side effects. Advancements in local drug delivery mechanisms could help surmount such roadblocks by ferrying therapeutic payloads directly to the source of bleeding intracranially.
Targeted drug carriers engineered at the nano or microscale, for instance, may be able to cross the blood-brain barrier when appropriately functionalized. They could then release hemostatic drugs, thrombin inhibitors or other molecules precisely within hemorrhagic lesions to achieve the desired local effect with minimal systemic exposure. Another innovation is the development of biocompatible, rapidly dissolving implants that can be placed directly into evacuation cavities after hemorrhage surgeries. Loaded with custom-formulated drug formulations and coated for controlled release, such temporary implants may be able to regulate healing and prevent re-bleeding more effectively than intermittent systemic therapies.
By devising solutions tailored to the unique pathological conditions within the brain, continued advances in local drug delivery promise to significantly improve outcomes for hemorrhagic stroke patients. It could help achieve ambitious technical targets like arresting bleeds already in progress or enabling functional recovery post-incident. This would fill critical gaps in addressing ischemic repercussions as well as the lifelong risks of recurrence or deterioration. Addressing such substantial unmet needs through innovative mechanisms holds immense potential for transforming the outlook from hemorrhagic conditions.
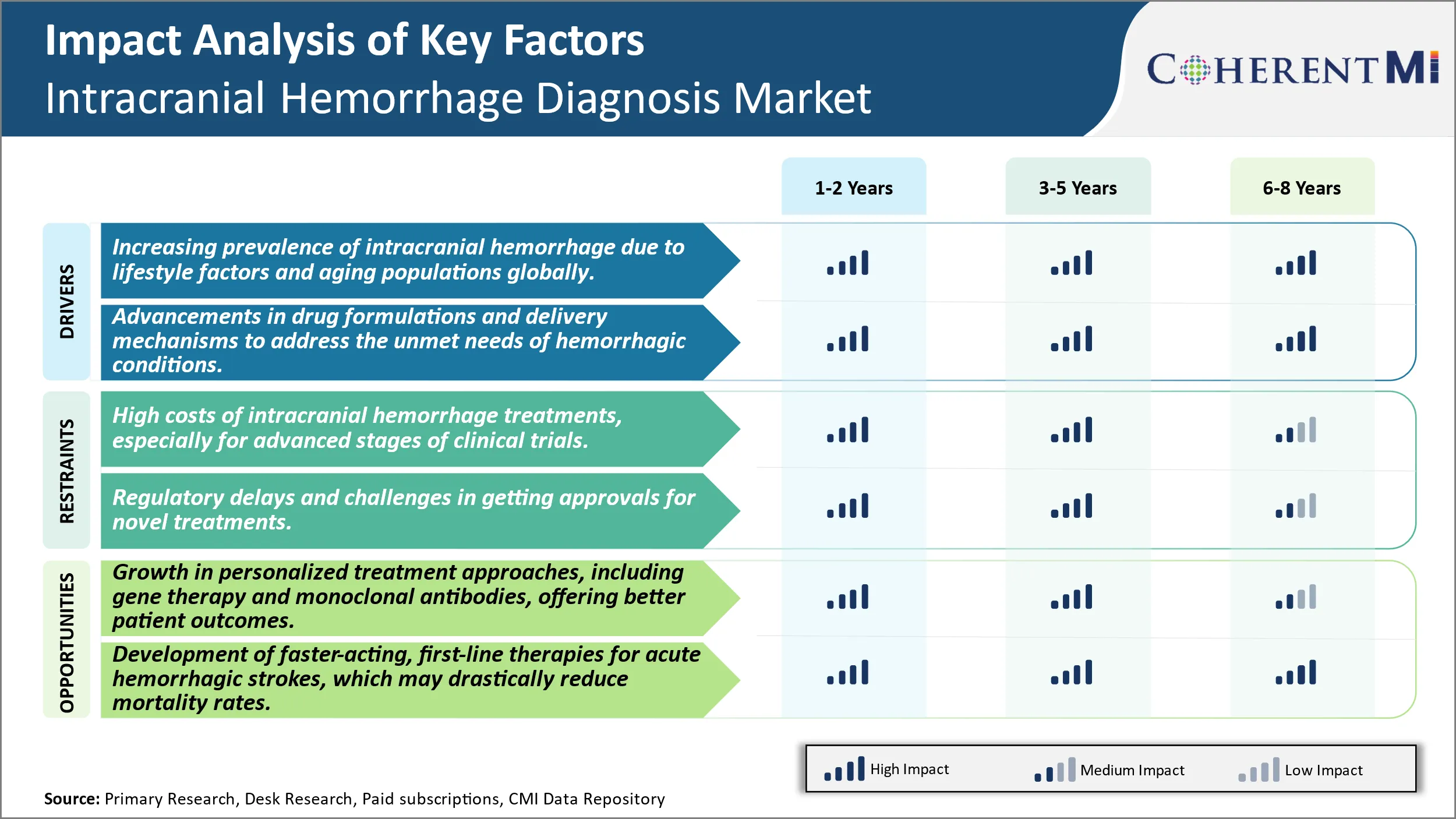
Market Challenge - High Costs of Intracranial Hemorrhage Treatments, Especially for Advanced Stages of Clinical Trials.
One of the major challenges faced by the intracranial hemorrhage diagnosis market is the extremely high costs associated with developing new treatments, particularly in the later stages of clinical trials. Conducting clinical trials from Phase-I through to Phase-III is an enormously expensive process, with costs running into the hundreds of millions of dollars or more. Intracranial hemorrhage is a relatively rare condition, with only a small patient population available for trials. This means pharmaceutical and medical device companies must spend vast amounts to recruit sufficient trial participants. The specialized medical equipment, facilities, monitoring and personnel required to study new diagnostic tools and therapies for this serious condition also contribute significantly to development costs. With an uncertain chance of regulatory approval and commercial success, many companies are discouraged from investing heavily in this market. Even successful new products may struggle to earn back expenses if the target population is small. This high-risk, high-cost environment poses a substantial barrier to innovation and growth within the intracranial hemorrhage diagnosis space.
Market Opportunity: Growth in Personalized Treatment Approaches, Including Gene Therapy and Monoclonal Antibodies, Offering Better Patient Outcomes.
One major opportunity in the intracranial hemorrhage diagnosis market is the advancement of personalized medicine approaches. Developments in areas such as gene therapy, monoclonal antibodies and targeted drug delivery systems are allowing for more customized treatment based on an individual's specific genetic profile and condition. This represents a shift away from traditional one-size-fits-all therapies. Personalized options offer the promise of more effective, longer lasting results tailored precisely to a patient's needs. They also enable targeting of therapies to molecular and cellular abnormalities driving different subtypes of intracranial hemorrhage. As these novel, personalized strategies demonstrate clearer benefits in clinical testing, such as reduced disability and mortality rates, their adoption is expected to grow significantly. This will both expand the market size and enhance outcomes for those suffering from this catastrophic illness. The ability to better match treatments to patients provides a tremendous opportunity for improved management of intracranial hemorrhage going forward.
Prescribers preferences of Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market
Intracranial Hemorrhage (ICH) can be treated via various lines of defense depending on the severity and stage of bleeding. For mild cases, initial management focuses on controlling risk factors like blood pressure and cholesterol through medications. Prescribers commonly opt for angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors like lisinopril and calcium channel blockers like amlodipine besylate to lower BP. Goals are set between 130-140/80-90 mmHg per guidelines.
As bleeding worsens, acute treatment becomes priority. Depending on location (lobar, deep), many opt for either craniotomy for clot removal via specialized techniques or conservative management if high surgical risk. During surgery, hemostatic agents like Surgicel and Tisseel are used. Post-op, anticonvulsants including Levetiracetam brands Keppra and Bricanyl are considered sufficient for seizure prophylaxis in eligible cases by 39% of prescribers.
However, recurrence remains a concern. Around 30 days, follow-up imaging and factor control is emphasized. Statins like Atorvastatin gain favor to reduce re-bleeding risk, along with antiplatelets if cardiovascular indication exists. Long-term, anticoagulant type and need is carefully weighed, factoring ICH etiology and procedure details. Surveillance also considers lifestyle management to control untreated comorbidities shown to increase risk such as diabetes, hypertension, and atrial fibrillation.
Treatment Option Analysis of Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market
Intracranial Hemorrhage can be categorized into four main stages based on severity - mild, moderate, severe, and critical. For mild cases, initial treatment focuses on controlling blood pressure through oral medications like acetazolamide or labetalol to prevent rebleeding. Moderate bleeding requires medical intervention. Minimally invasive procedures such as external ventricular drainage are preferred to relieve pressure by draining excess fluid from the brain. For severe bleeding, emergency surgery is needed. The hematoma is evacuated through a craniotomy to decompress the brain. Rebleeding risk remains high hence anti-hypertensives like nicardipine infusion are prescribed.
Critical bleeding with neurological deterioration warrants aggressive intervention. Decompressive craniectomy to temporarily remove part of the skull eases pressure. Blood products are administered to correct coagulopathy. Mannitol helps reduce swelling. Intensive care is imperative involving ventilation, ICP monitoring and sedation.
Overall, treatment approach varies based on severity but aims to control blood pressure, reduce mass effect on brain and prevent rebleeding through a combination of medications, minimally invasive procedures and surgeries. For any stage, close BP monitoring along with anti-hypertensives and anti-seizure drugs continue long-term to prevent complications and recurrence.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market
Product Innovation: Developing advanced diagnostic imaging techniques has been a major focus area for players. In 2016, GE Healthcare launched CT Angiography on its Revolution CT scanner which could accurately detect even very small bleeds in the brain within minutes. This helped clinicians triage patients and plan treatment faster. Similarly in 2018, Siemens Healthineers introduced Speeder, a unique post-processing software on its Somatom Definition Edge CT scanner. Speeder cuts brain hemorrhage scan time from one minute to just 20 seconds while providing high resolution images, a key differentiator.
Customer Partnerships: Players have partnered with major hospitals and clinical research organizations to validate new products and build clinical evidence. For example, in 2020 Philips partnered with multiple hospitals in Europe and USA to collect CT scan data from over 5000 hemorrhage patients treated on its IQON Elite CT system. This real-world clinical evidence helped Philips gain FDA approval and new large hospital contracts.
Geographic Expansion: To tap new growth markets, players have expanded into Asia, Middle East and Latin America in the last five years through acquisitions and new local manufacturing/R&D facilities. For instance, in 2017 Hitachi invested over USD 100 million to set up an MRI manufacturing plant in India. This helped Hitachi capture over 30% market share in India within 2 years, diversifying its revenue streams.
The above strategies of continuous product innovation, building clinical evidence through partnerships, and expanding into emerging markets have helped key players differentiate their offerings, increase adoption rates and achieve 5-10% annual revenue growth in the last decade despite price pressures in developed markets. This sustained leadership position and financial performance demonstrates the success of their strategies over competition.
Segmental Analysis of Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market
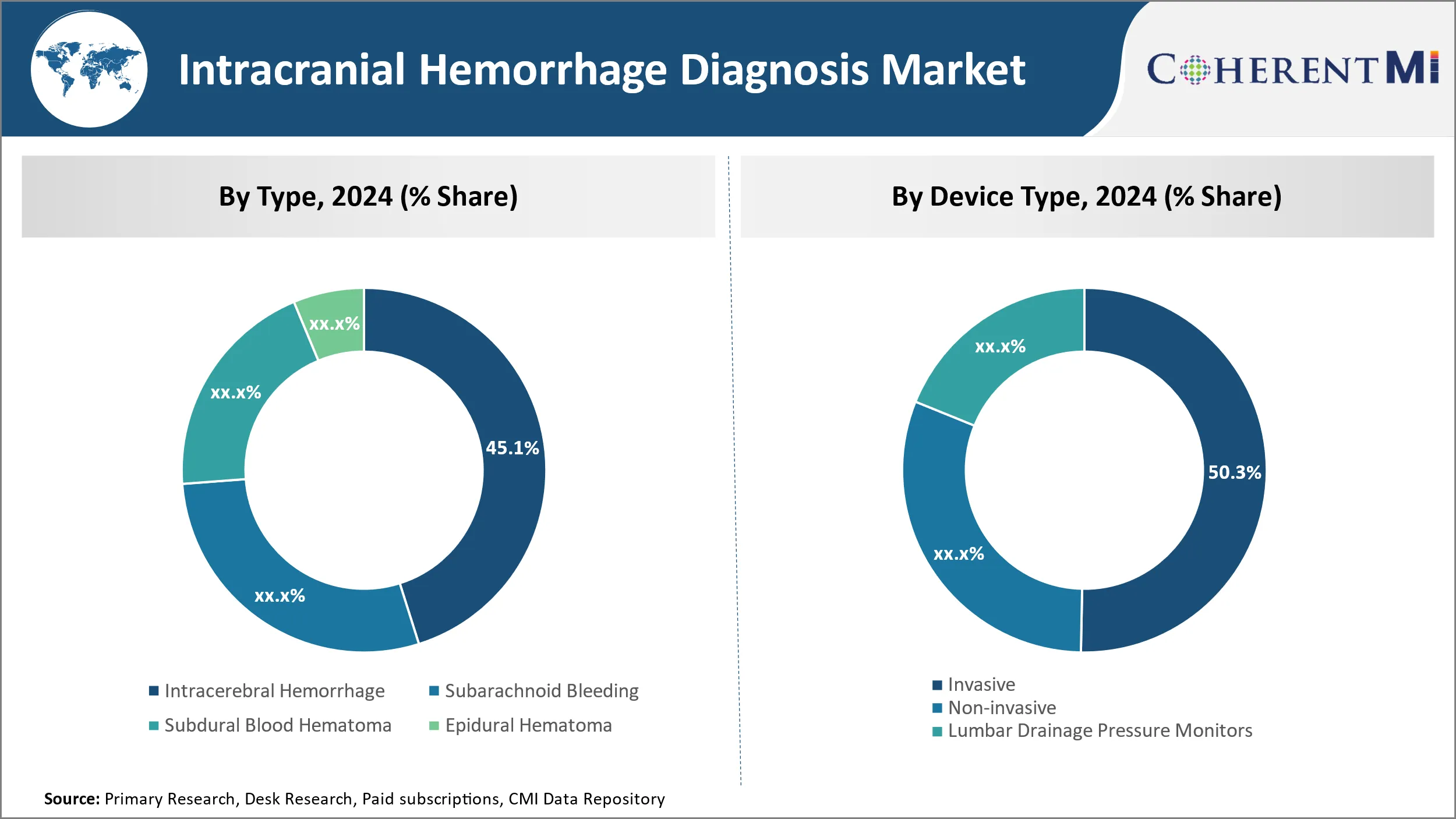
Insights, By Type, Rising Geriatric Population Drives Intracerebral Hemorrhage Segment.
By Type, Intracerebral Hemorrhage is expected to contribute the highest share 45.1% in 2024 of due to the rising risk of cerebral hemorrhages with age. Intracerebral hemorrhage, also known as deep brain hemorrhage, occurs within the brain tissue itself. It accounts for 10-15% of all strokes and tends to be more fatal than other types of hemorrhagic strokes. The risk of intracerebral hemorrhage doubles every decade after the age of 55. With increased life expectancy globally, the population aged 65 years and above is growing at an unprecedented rate. Moreover, lifestyle diseases like hypertension and diabetes which are major risk factors for hemorrhagic strokes are also on the rise. This has led to a surge in the number of Intracerebral Hemorrhage cases, driving the growth of this segment. Advanced diagnostic technologies help accurate detection and management of Intracerebral Hemorrhages in the elderly.
Insights, By Device Type, Invasive Devices Dominate Owing to Ability to Gather Real-Time Data.
By device type, invasive contributes the highest market share at 50.3% in 2024 due to their ability to provide real-time monitoring of intracranial pressure changes. Invasive devices such as intraventricular catheters and intraparenchymal probes are inserted directly into the brain tissue or ventricles. They help continuously track variables like ICP, brain oxygen levels and brain temperature which are critical for effective management of hemorrhagic strokes. This real-time data enabled by invasive monitoring helps surgeons and doctors make timely clinical decisions, improving patient outcomes. Though carried out on a smaller subset of critical patients, invasive monitoring forms the standard of care in neuro-intensive care units. Advancements in minimally invasive techniques and development of compact implantable devices are enhancing the adoption of invasive monitoring solutions.
Insights, By Diagnosis, Advanced Imaging Capabilities Boost Demand for CT-Scan.
By Diagnosis, CT-Scan contributes the highest share due to its high accuracy in detection of hemorrhages, evaluation of hemorrhage size and location. CT scans provide detailed images of the brain within minutes, aiding rapid diagnosis which is critical in hemorrhagic stroke management. Technological upgrades like multi-detector CT scans and perfusion CT have significantly improved the diagnostic ability of CT for hemorrhagic strokes. Multi-detector CT scans with wider coverage and higher resolution help detect even minuscule bleeds. Perfusion CT evaluates blood flow and volume, aiding distinction between old and new hemorrhages. In resource-poor settings, availability of affordable basic CT scanners makes them the preferred first-line diagnostic modality. With continued improvement in CT capabilities including low dose scans, this segment is expected to grow at a steady rate.
Additional Insights of Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market
Intracranial hemorrhage represents a critical condition requiring rapid diagnosis and intervention. Current treatment strategies include managing blood pressure, reversing anticoagulation, and surgically relieving brain pressure. Emerging pipeline drugs aim to tackle these challenges by providing faster-acting, more effective therapies with fewer side effects. For example, Acasti Pharma's GTX-104 offers an innovative nanoparticle-based approach that could improve outcomes in subarachnoid hemorrhage patients by ensuring stable drug concentrations and reduced adverse reactions. Meanwhile, Alveron Pharma's OKL-1111 holds the potential to become the first-line therapy for hemorrhagic stroke by rapidly reversing the effects of various anticoagulants. Both drugs highlight the growing focus on personalized and targeted approaches to treat intracranial hemorrhage, a field where survival and quality of life improvements are urgently needed. With increasing R&D activity, this market is expected to grow significantly, driven by the demand for safer, faster, and more efficient treatments.
Competitive overview of Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market
The major players operating in the Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market include Sanofi, Alveron Pharma, NoNO Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb, Acticor Biotech, Biogen, Sanofi, Hoffmann-La Roche, Canon Inc, Hitachi Ltd, Johnson & Johnson and Medtronic Plc.
Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market Leaders
- Acasti Pharma
- Alveron Pharma
- NoNO Inc.
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Acticor Biotech
Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market - Competitive Rivalry, 2024

Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market
- In May 2024, Acasti Pharma announced successful Phase III trials for GTX-104, a nanoparticle nimodipine formulation, showing increased efficacy in managing intracranial hemorrhage with fewer side effects.
- In March 2024, Alveron Pharma's OKL-1111, a rapid-response procoagulant, demonstrated positive early-stage results in Phase I trials, providing new hope for fast-acting treatments of hemorrhagic stroke.
Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market Segmentation
- By Type
- Intracerebral Hemorrhage
- Subarachnoid Bleeding
- Subdural Blood Hematoma
- Epidural Hematoma
- By Device Type
- Invasive
- Non-invasive
- Lumbar Drainage Pressure Monitors
- Tissue Resonance
- By Diagnosis
- CT-Scan
- MRI
- Others

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How Big is the Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market?
The Global Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.9 Bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 3.4 billion by 2031.
What will be the CAGR of the Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market?
The CAGR of the Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market is projected to be 8.1% from 2024 to 2031.
What are the major factors driving the Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market growth?
The increasing prevalence of intracranial hemorrhage due to lifestyle factors and aging populations globally and advancements in drug formulations and delivery mechanisms to address the unmet needs of hemorrhagic conditions are the major factors driving the Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market?
The high costs of intracranial hemorrhage treatments, especially for advanced stages of clinical trials and regulatory delays and challenges in getting approvals for novel treatments are the major factors hampering the growth of the Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market.
Which is the leading Type in the Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market?
Intracerebral Hemorrhage is the leading Type segment.
Which are the major players operating in the Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis Market?
Sanofi, Alveron Pharma, NoNO Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb, Acticor Biotech, Biogen, Sanofi, Hoffmann-La Roche, Canon Inc, Hitachi Ltd, Johnson & Johnson, Medtronic Plc are the major players.