Acute Intermittent Porphyria Market Size - Analysis
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR6.3%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 6.3% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Recordati Rare Diseases, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Dicerna Pharmaceuticals, Moderna and Among Others |
please let us know !
Acute Intermittent Porphyria Market Trends
With the advancement of technology and internet, awareness about rare diseases is rising exponentially. No longer are these diseases hidden due to lack of information. Doctors and researchers are also more vocal about these rare conditions. They publish research papers and give interviews to mainstream media. International rare disease day is marked every year with campaigns in various countries.
All these combined factors have significantly contributed to the growth of acute intermittent porphyria market. Early detection enables timely intervention techniques and symptom management approaches to be adopted. It prevents complications and deteriorating health conditions. Patients can get appropriate treatment instead of searching endlessly for proper diagnosis. Awareness removes the stigma around rare diseases and brings more funding as well as deeper research commitments from various stakeholders.
Market Driver - Development of RNA-based Therapies Offering Targeted Treatment
Several biotechs are conducting clinical trials of RNAi drugs for acute intermittent porphyria. If proven successful, they can achieve competitive edge over generic drug therapies given currently.
Therefore, the breakthroughs happening in RNA-based platforms for specifically targeting genetic rare diseases like acute intermittent porphyria are major drivers. They provide solutions directly addressing underlying causes and not just symptoms. This differentiated approach fulfilling unmet needs will have strong implications on market growth in coming times.
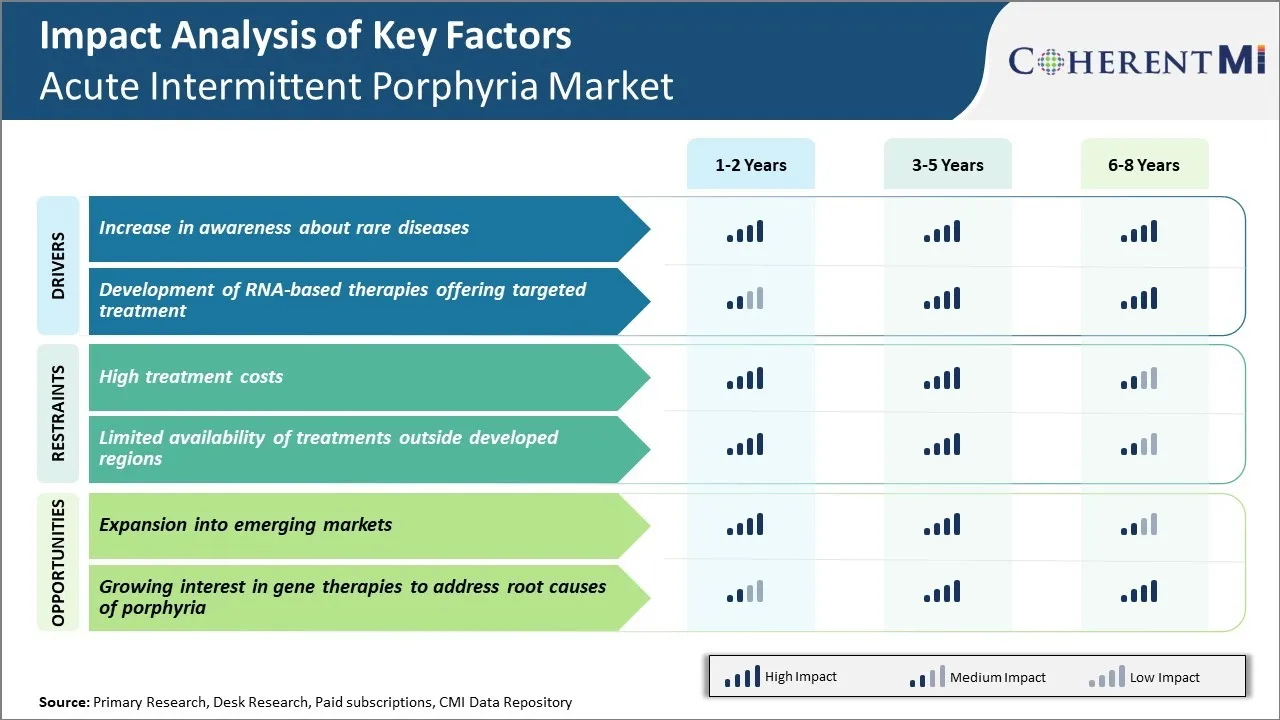
One of the major challenges faced by the Acute Intermittent Porphyria market is the high treatment costs associated with managing the condition. AIP requires costly lifelong management to prevent attacks and potential complications. The primary treatments for AIP attacks include intravenous hemin injections which can cost thousands of dollars per injection.
Drug manufacturers are hesitant to invest in developing more affordable treatment options due to the small potential market size. Unless awareness and appropriate diagnosis improves significantly, high costs will continue restricting patient access to care and impacting the growth of the AIP market.
Market Opportunity - Expansion into Emerging Markets
However, AIP has a global prevalence and remains underdiagnosed in many developing regions. There is immense potential to grow the market and improve patient outcomes by increasing diagnosis rates and access to existing therapies in emerging markets like Latin America, Asia Pacific and Middle Eastern countries. These countries represent rapidly growing healthcare sectors with rising income levels making treatment more affordable over time.
By expanding into new patient populations in emerging markets, companies can achieve significant revenue growth and economies of scale to help drive long term profitability and investments in developing next generation therapies.
Prescribers preferences of Acute Intermittent Porphyria Market
Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP) typically presents in three stages requiring different lines of treatment. The initial stage consists of less severe attacks and symptoms which can often be managed at home with diet modifications and carbohydrate supplementation. Prescribers may recommend glucose polymer products like Polycal to help prevent further buildup of toxic metabolites.
For severe, life-threatening attacks, the third stage involves intensive care support measures. In addition to hemin therapy, opioids may be needed to manage severe abdominal pain. Medications like Tramedo or Dilaudid are prescribed via intravenous drip. Close monitoring is essential at this stage to watch for complications affecting kidneys, liver or blood.
Treatment Option Analysis of Acute Intermittent Porphyria Market
Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP) has four main stages - remission, pre-crisis, acute attack, and convalescence. The preferred treatment depends on the stage.
If an acute attack occurs, hospitalization is usually required for intravenous hemin administration. Hemin, a branded product containing Panhematin, blocks the overproduction of porphyrins. It remains the first-line treatment for attacks as it significantly reduces attack duration from weeks to days and risk of permanent neurological damage.
During convalescence, care focuses on rest, tackling any nutritional deficiencies, and psychological support. Recovery can take weeks.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Acute Intermittent Porphyria Market
Focus on clinical development for new treatments - One of the main strategies adopted by companies has been investing aggressively in clinical research and development for new drugs to treat Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP). For example, Recordati Rare Diseases invested over $100 million between 2014-2018 in clinical trials for its oral drug rigosertib for AIP. The Phase 3 INSPIRE trial completed in 2018 showed promising results, reducing AIP attacks. If approved, rigosertib could become the first new treatment in over 20 years for AIP.
Acquisitions of promising pipeline assets - Acquisitions have enabled companies to gain access to mid-late stage clinical assets and expand their portfolios in this market. In 2020, Recordati acquired Orphan Europe, gaining the marketing rights to cysteamine bitartrate, a drug approved in Europe for AIP. This addition boosted Recordati's presence and commercialization capabilities for AIP treatments.
Segmental Analysis of Acute Intermittent Porphyria Market
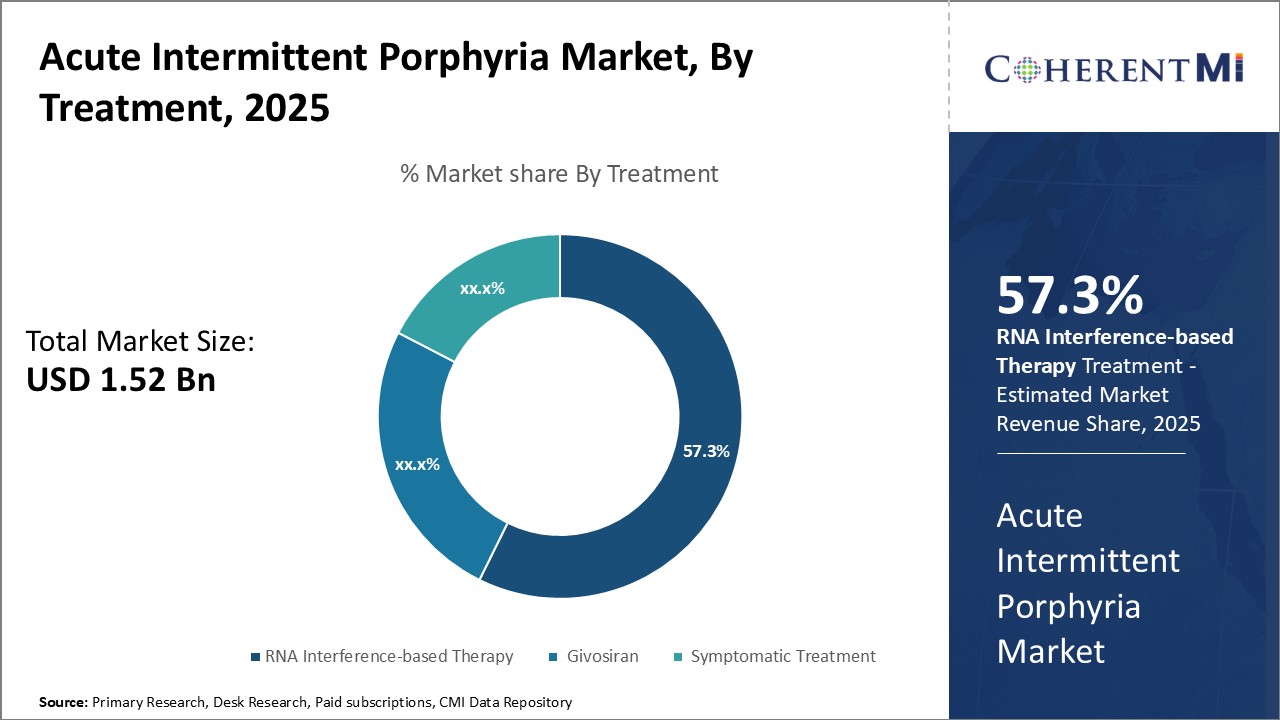 Insights, By Treatment: >RNA Interference-based Therapy - A Groundbreaking Option for Acute Intermittent Porphyria
Insights, By Treatment: >RNA Interference-based Therapy - A Groundbreaking Option for Acute Intermittent Porphyria
A key RNA interference-based drug, Givosiran, has shown significant reductions in hyperphenylalaninemia, the hallmark symptom of acute intermittent porphyria, in Phase 3 clinical trials. Patients receiving Givosiran experienced far fewer attacks than those on placebo. Its innovative modality and strong efficacy data have captured significant market interest from both physicians and patients. If approved, Givosiran is poised to become the first approved treatment that directly targets the underlying cause of acute intermittent porphyria.
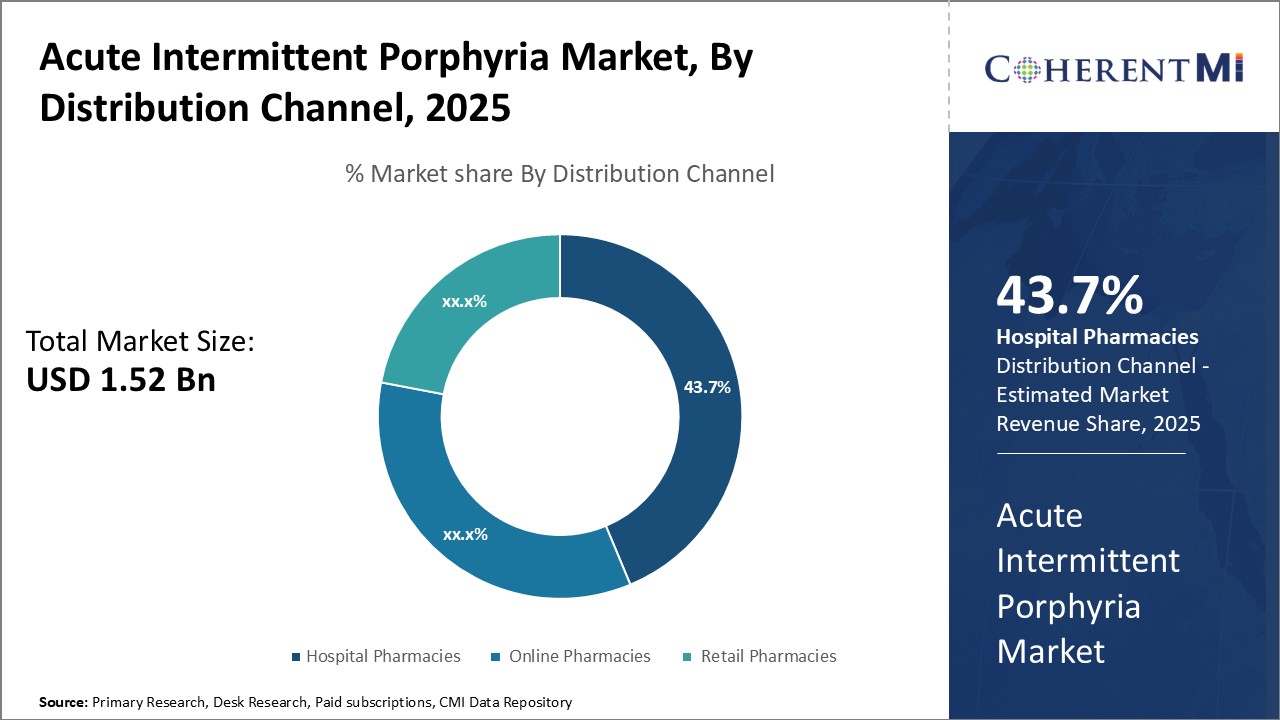
In terms of distribution channel, hospital pharmacies contribute the highest share of the market. This is because acute intermittent porphyria often requires inpatient care and management during severe attacks. Symptoms such as abdominal pain, vomiting, and neurological abnormalities may require hospital admission and around-the-clock monitoring until the attack subsides.
As the first point of contact during attacks, hospital pharmacies remain central to the treatment journey of many acute intermittent porphyria patients. Their availability 24/7 and expertise in handling specialized acute medications drive their prominence in the distribution landscape.
Additional Insights of Acute Intermittent Porphyria Market
- The market is witnessing a significant rise in patient awareness and diagnostic rates, particularly in the U.S. and Europe. Furthermore, the entry of new players in the market is creating a dynamic competitive environment.
- The increase in collaborations between pharmaceutical companies for rare disease research has accelerated progress in treatment options, especially in the areas of gene therapy and RNA-based solutions.
Competitive overview of Acute Intermittent Porphyria Market
The major players operating in the Acute Intermittent Porphyria Market include Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Recordati Rare Diseases, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Dicerna Pharmaceuticals, and Moderna.
Acute Intermittent Porphyria Market Leaders
- Alnylam Pharmaceuticals
- Recordati Rare Diseases
- Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma
- Dicerna Pharmaceuticals
- Moderna
Acute Intermittent Porphyria Market - Competitive Rivalry

Acute Intermittent Porphyria Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Acute Intermittent Porphyria Market
- In November 2019, Givosiran, branded as Givlaari, was approved by the FDA for the treatment of acute hepatic porphyria (AHP), a rare genetic disorder that causes severe and potentially life-threatening attacks. The drug has been shown to reduce porphyria attacks by about 70-74% based on clinical trials.
- In July 2023, Moderna announced its entry into the rare disease space with potential RNA therapies targeted for porphyria. This will enhance competition in the space. Moderna has been exploring various therapeutic areas beyond COVID-19 vaccines, including rare diseases. Their mRNA technology offers potential in treating genetic disorders like porphyria.
Acute Intermittent Porphyria Market Segmentation
- By Treatment
- RNA Interference-based Therapy
- Givosiran
- Symptomatic Treatment
- By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the acute intermittent porphyria market?
The acute intermittent porphyria market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.52 Billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 2.33 Billion by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the acute intermittent porphyria market?
The high treatment costs and limited availability of treatments outside developed regions are the major factors hampering the growth of the acute intermittent porphyria market.
What are the major factors driving the acute intermittent porphyria market growth?
The increase in awareness about rare diseases and development of RNA-based therapies offering targeted treatment are the major factors driving the acute intermittent porphyria market.
Which is the leading treatment in the acute intermittent porphyria market?
The leading treatment segment is RNA Interference-based therapy.
Which are the major players operating in the acute intermittent porphyria market?
Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Recordati Rare Diseases, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Dicerna Pharmaceuticals, and Moderna are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the acute intermittent porphyria market?
The CAGR of the acute intermittent porphyria market is projected to be 6.3% from 2025-2032.