Alopecia Areata Treatment Market Size - Analysis
The Global Alopecia Areata Treatment Market is estimated to be valued at USD 12.12 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 32.83 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.3% from 2025 to 2032. Increased spending on hair care products and rising number of patients susffering from alopecia areata are fueling the market growth. Various treatment options and new product launches are further anticipated to drive the market during the forecast period.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR15.3%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 15.3% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, Equillium, Maxinovel Pharmaceuticals and Among Others |
please let us know !
Alopecia Areata Treatment Market Trends
The approval of novel therapies targeting Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors like Deuruxolitinib is driving new treatment options for patients with alopecia areata. JAK inhibitor therapies has opened up a new avenue of treatment for patients suffering from alopecia areata. Alopecia areata is an autoimmune skin disease characterized by patchy hair loss on the scalp and sometimes other areas of the body. The exact cause of the condition is unknown but it is believed to be an autoimmune reaction where the immune system attacks the hair follicles. This leads to inhibition of hair growth and hair falling out, often in quite distinctive patches. For long alopecia areata was difficult to treat with limited treatment options available usually focused on care and not cures. However, in recent times research into the pathophysiology of the disease led to the identification of Janus kinases or JAK's which are enzymes involved in cellular signaling. Dysregulation of the JAK-STAT pathway was found to play an important role in the immune system attacking the hair follicles in alopecia areata. This opened up the possibility of using JAK inhibitors to mitigate the immune response and promote hair regrowth.
Alopecia areata has traditionally been under-diagnosed and under-recognized given its presentation of cosmetic patchy hair loss and lack of serious health consequences. However, in recent years greater awareness initiatives by patient advocacy groups as well as streamlining of diagnostic methods have enabled identification of higher numbers of people affected by the condition. Traditionally alopecia areata diagnosis relied on examination of characteristic patchy hair loss patterns under adequate lighting conditions. Now with the availability of specialized dermatoscopes even small patches and initial signs can be more readily detected. In addition, increased connectively between doctors through technology platforms has improved information sharing about updated diagnostic practices.
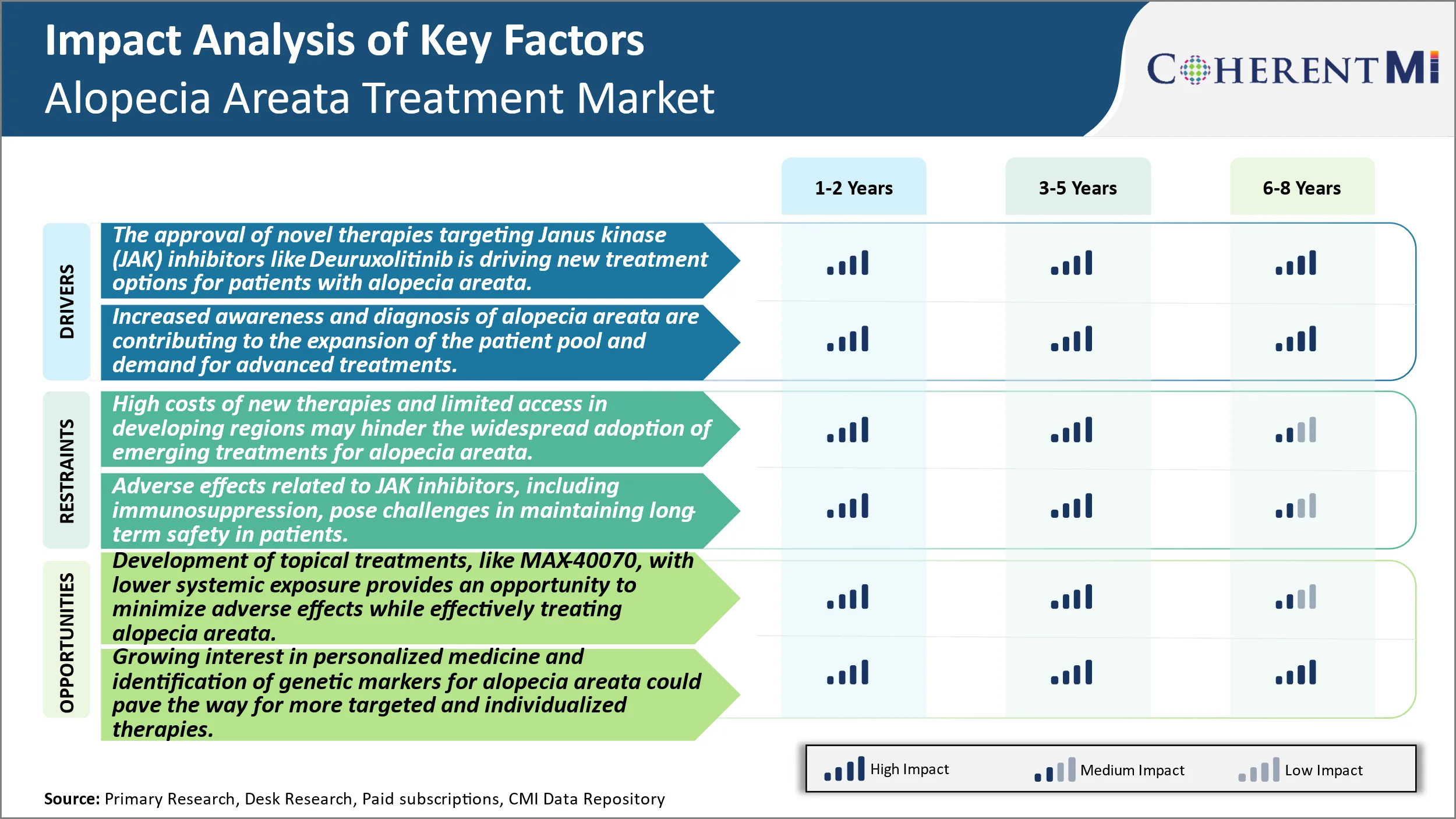
Market Challenge - High Costs of New Therapies and Limited Access in Developing Regions May Hinder the Widespread Adoption of Emerging Treatments for Alopecia Areata.
One promising opportunity in the alopecia areata treatment market is the development of topical therapies that minimize systemic exposure while effectively treating the condition locally. For example, Concert Pharmaceuticals' candidate MAX-40070 is a topical JAK inhibitor being evaluated for alopecia areata. Its topical formulation is designed to limit systemic absorption and exposure levels to reduce the risk of potential adverse effects seen with oral JAK inhibitors. If successful in trials, MAX-40070 could offer an efficacious treatment option with a improved safety profile compared to existing oral drugs. This has the potential to expand the addressable patient population by making the therapy a viable option even for patients’ intolerant of systemic medications' side effects. Additionally, topical treatments may be more convenient to administer on an ongoing basis versus oral pills. The lower complexity of topical therapies could also lower manufacturing costs and facilitate more reasonable product pricing.
Prescribers preferences of Alopecia Areata Treatment Market
Alopecia Areata is typically treated through a step-care approach based on the extent of hair loss and a patient's preferences. Mild cases involving small, localized patches are often first treated with topical corticosteroid solutions like clobetasol propionate (Clobex). If patches expand slightly or fail to regrow hair after 3-6 months, prescribing switches to topical immunotherapy with contact sensitizers like diphencyprone (DPCP).
In cases of full scalp/body hair loss (alopecia totalis/universalis), prescribers often trial immunomodulators next to restart hair growth. Popular choices are JAK inhibitors like ruxolitinib (Opzelura) and tofacitinib (Xeljanz), as well as lymphocyte stimulators like contact immunotherapy. Prescriber decisions also factor in a patient's age, risk factors, symptoms, and preferences regarding benefits, side effects and costs.
Treatment Option Analysis of Alopecia Areata Treatment Market
Alopecia Areata has varying stages from mild to extensive hair loss. Mild patches of hair loss are classified as AA1, while AA2 involves larger patches. Diffuse hair loss over the scalp is AA3, and complete scalp hair loss is AA4.
For more extensive shedding (AA2-3), the preferred first treatment is corticosteroid injections directly into scalp patches, such as triamcinolone acetonide. Response rates improve to 60-70% with injections allowing targeted high-dose treatment.
Alternative treatments for more severe/resistant cases include topical/oral immunotherapy using contact sensitizers like diphenylcyclopropenone or squaric acid dibutylester. Initial studies show monthly applications giving response rates of 40-60%. Off-label options involving rebamipide, tofacitinib and the JAK inhibitors also show promise.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Alopecia Areata Treatment Market
Research and Development: Companies have heavily invested in R&D to develop novel and effective treatment options for alopecia areata. For instance, Concert Pharmaceuticals invested over USD130 million between 2010-2017 in developing CTP-543, a JAK inhibitor for moderate-to-severe alopecia areata. In a Phase 2 trial, CTP-543 showed significant and rapid hair regrowth. This enhanced R&D capability allows companies to launch new products and maintain leadership in the market.
Geographic Expansion: Key companies are expanding globally through new product launches and partnerships to tap emerging markets. For instance, Pfizer launched its JAK inhibitor Olumiant in Japan for alopecia areata in 2021, a first of its kind approval in the country. Widening geographic presence helps achieve sales growth and market share gains.
Segmental Analysis of Alopecia Areata Treatment Market
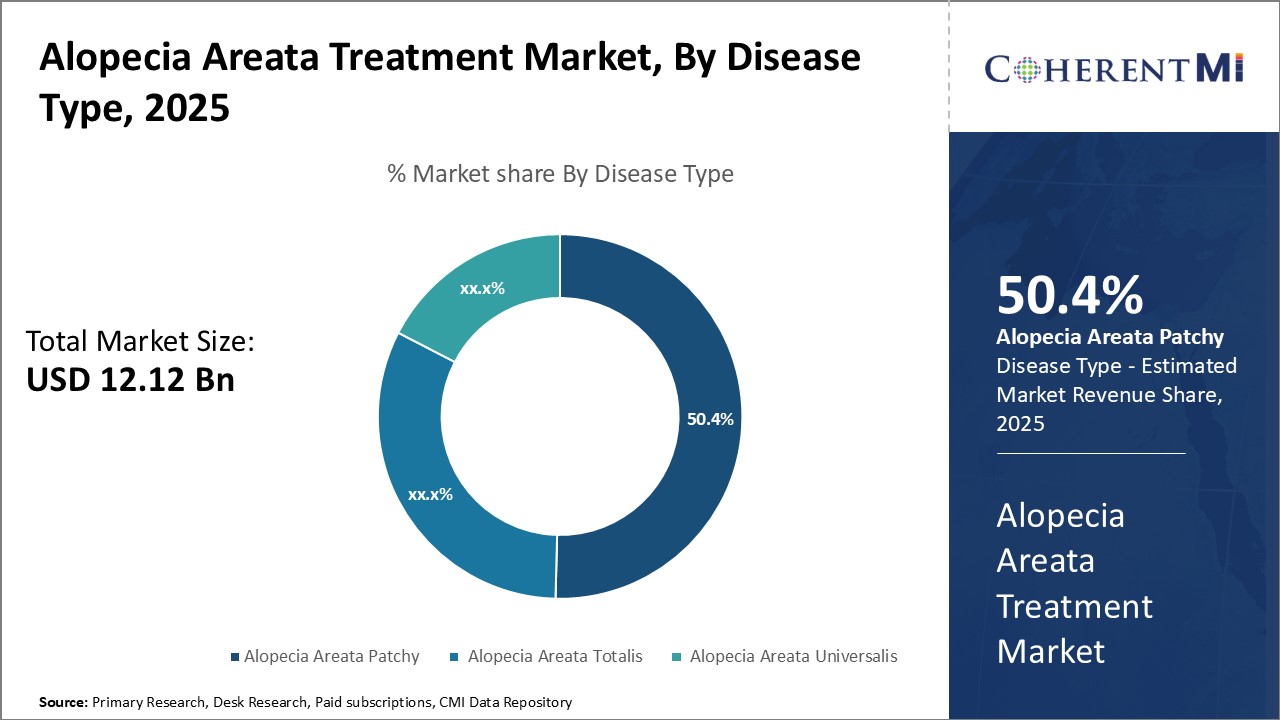 Insights, By Disease Type, Mild Nature Drives Alopecia Areata Patchy Dominance in the Forecast Period.
Insights, By Disease Type, Mild Nature Drives Alopecia Areata Patchy Dominance in the Forecast Period.By disease type, Alopecia Areata Patchy is expected to contribute the highest share 50.4% in 2025 owing to its relatively mild nature compared to other types. Patchy hair loss involves only small bald spots on the scalp, typically affecting less than 50% of the head. This makes it less psychologically stressful for patients compared to more severe forms. The mild symptoms also mean treatment is often not pursued as aggressively. Common triggers for Alopecia Areata Patchy include stressful life events and autoimmune disorders. However, the condition is generally not life-threatening or disfiguring. This helps drive its prevalence as patients may learn to accept the visible signs. Alopecia Areata Patchy treatment focuses on promoting hair regrowth in small, localized areas of hair loss. Common approaches include topical corticosteroids, minoxidil, and immunotherapy to stimulate the immune response. Emerging therapies, such as JAK inhibitors, show promise in reversing hair loss by targeting underlying autoimmune mechanisms, offering hope for more effective and lasting solutions.
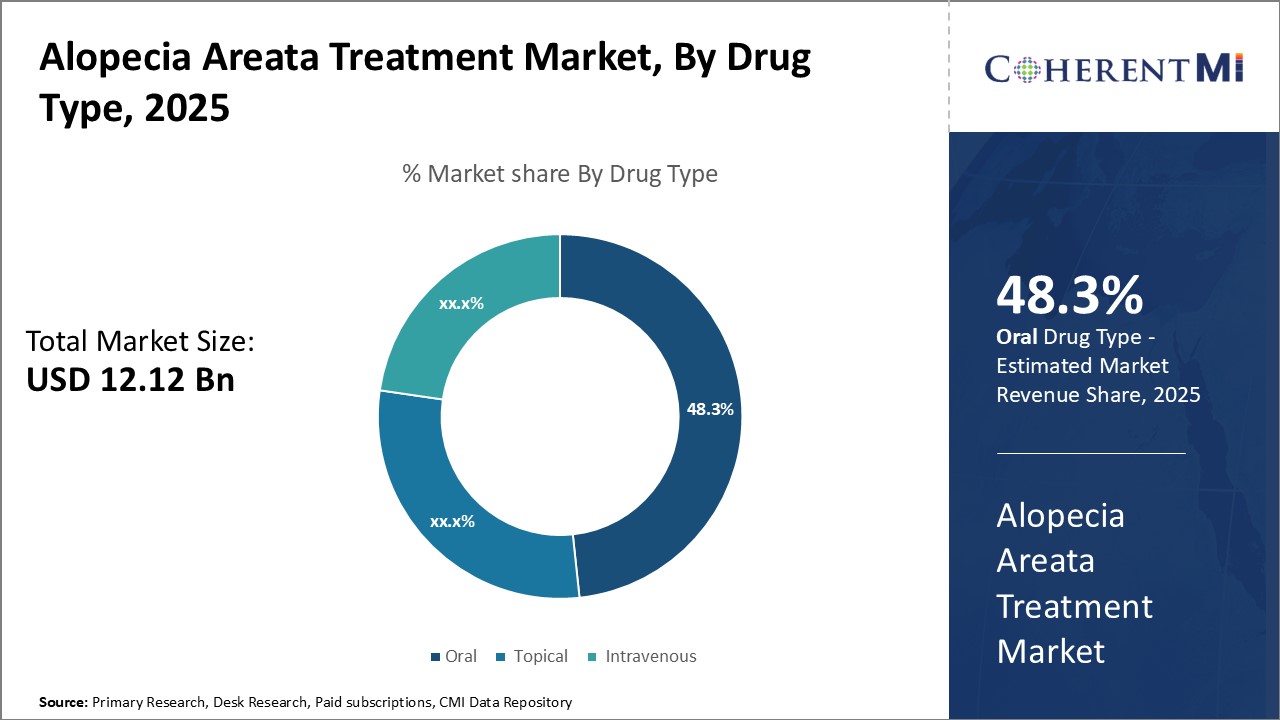
By drug type, oral segment is expected to contribute the highest share 48.3% in 2025 due to the convenience it offers patients. The oral route of administration for alopecia areata treatments is gaining traction due to its convenience and patient compliance. Oral medications, particularly JAK inhibitors like Baricitinib and Ritlecitinib are showing promise in clinical trials by effectively targeting autoimmune pathways. This non-invasive approach offers an appealing option for long-term management of alopecia areata. Oral medications like corticosteroids, immunomodulators and JAK inhibitors can be taken at home, eliminating the need for regular visits to a clinic or hospital for therapy. This is preferred especially by working individuals with busy schedules. The self-administration nature also provides patients a sense of control over their treatment. However, topical therapies may remain popular for minor cases due to lower risk of systematic side effects compared to oral options.
Insights, By End-user, Trusted healthcare Environment Fosters Patient Care in Hospitals
Additional Insights of Alopecia Areata Treatment Market
The landscape of alopecia areata treatment is evolving with a growing number of therapies targeting the underlying immune mechanisms of the disease. JAK inhibitors, such as Deuruxolitinib and Baricitinib, have demonstrated significant efficacy in regrowing hair in patients with moderate-to-severe alopecia areata. However, the safety of these treatments, especially in long-term use, remains a critical concern due to their immunosuppressive effects. In parallel, the development of topical formulations, like MAX-40070, offers a promising approach to mitigate these systemic risks. The market for alopecia areata therapies is expanding as new treatments advance through clinical trials, and pharmaceutical companies engage in strategic collaborations to accelerate development. The future of alopecia areata treatment lies in personalized approaches and targeted therapies, with the potential to offer patients more effective and safer options for managing their condition.
Competitive overview of Alopecia Areata Treatment Market
The major players operating in the Alopecia Areata Treatment Market include Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, Equillium, Maxinovel Pharmaceuticals, F.Hoffman, Mylan, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Pfizer Inc, AdvaCare Pharma and Reistone Biopharma.
Alopecia Areata Treatment Market Leaders
- Concert Pharmaceuticals
- Pfizer
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Equillium
- Maxinovel Pharmaceuticals
Alopecia Areata Treatment Market - Competitive Rivalry

Alopecia Areata Treatment Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Alopecia Areata Treatment Market
- In May 2024, Concert Pharmaceuticals announced positive topline results for Deuruxolitinib from its Phase III trials for treating moderate-to-severe alopecia areata, showing significant hair regrowth in patients. The company plans to submit a New Drug Application to the FDA by mid-2024.
- In April 2024, Equillium’s EQ101, a tri-specific inhibitor targeting IL-2, IL-9, and IL-15, continues to show promising results in Phase II trials for treating alopecia areata with a favorable safety profile.
- In March 2024, Maxinovel Pharmaceuticals initiated Phase I trials for MAX-40070, a topical JAK/Tyk2 inhibitor, aimed at treating alopecia areata with fewer systemic side effects compared to oral treatments.
Alopecia Areata Treatment Market Segmentation
- By Disease Type
- Alopecia Areata Patchy
- Alopecia Areata Totalis
- Alopecia Areata Universalis
- By Drug Type
- Oral
- Topical
- Intravenous
- By End-user
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Diagnostic Centers
- Drug Stores

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How Big is the Alopecia Areata Treatment Market?
The Global Alopecia Areata Treatment Market is estimated to be valued at USD 12.12 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 32.83 Bn by 2032.
What will be the CAGR of the Alopecia Areata Treatment Market?
The CAGR of the Alopecia Areata Treatment Market is projected to be 15.10% from 2024 to 2031.
What are the major factors driving the Alopecia Areata Treatment Market growth?
The approval of novel therapies targeting Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors like Deuruxolitinib is driving new treatment options for patients with alopecia areata. Increased awareness and diagnosis of alopecia areata are contributing to the expansion of the patient pool and demand for advanced treatments are the major factor driving the Alopecia Areata Treatment Market.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the Alopecia Areata Treatment Market?
The high costs of new therapies and limited access in developing regions may hinder the widespread adoption of emerging treatments for alopecia areata. Adverse effects related to JAK inhibitors, including immunosuppression, pose challenges in maintaining long-term safety in patients are the major factors hampering the growth of the Alopecia Areata Treatment Market.
Which is the leading Disease Type in the Alopecia Areata Treatment Market?
Alopecia Areata Patchy is the leading disease type segment.
Which are the major players operating in the Alopecia Areata Treatment Market?
Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, Equillium, Maxinovel Pharmaceuticals, F.Hoffman, Mylan, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Pfizer Inc, AdvaCare Pharma, Reistone Biopharma are the major players.