Autoimmune Hepatitis Market Size - Analysis
Market Size in USD Mn
CAGR5.8%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 5.8% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Novartis, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, Merck & Co., Bristol-Myers Squibb and Among Others |
please let us know !
Autoimmune Hepatitis Market Trends
The autoimmune hepatitis market is witnessing significant growth in recent years owing to the rising prevalence of the disease across global populations. As per various studies conducted by leading medical institutions, it is estimated that around 2 million people worldwide are currently suffering from autoimmune hepatitis. The occurrence of this chronic inflammatory disease is more common among women as compared to men. The female to male prevalence ratio is around 3:1.
Overall, with global population growing steadily and environmental exposures on the rise, it is expected that autoimmune hepatitis prevalence will continue climbing in the long-term. This upward trend presents significant expansion opportunities for players in the autoimmune hepatitis market catering to the treatment requirement of the growing patient base worldwide.
Market Driver - Advancements in Biologics and Immunosuppressants
Similarly, recent approvals of JAK inhibitors present additional treatment choices. By blocking the janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription protein pathway, they help control hepatic inflammation and prevent flare-ups. Compared to existing options, they have milder adverse effects and better tolerability. Their once-daily oral dosing also enhances treatment compliance and convenience for patients.
Thus, continuous evolutions in biologic and targeted synthetic drug platforms have significantly enhanced management of autoimmune hepatitis patients. They address prior limitations and expand treatment individualization. This in turn is proving instrumental in strengthening market growth trajectories.
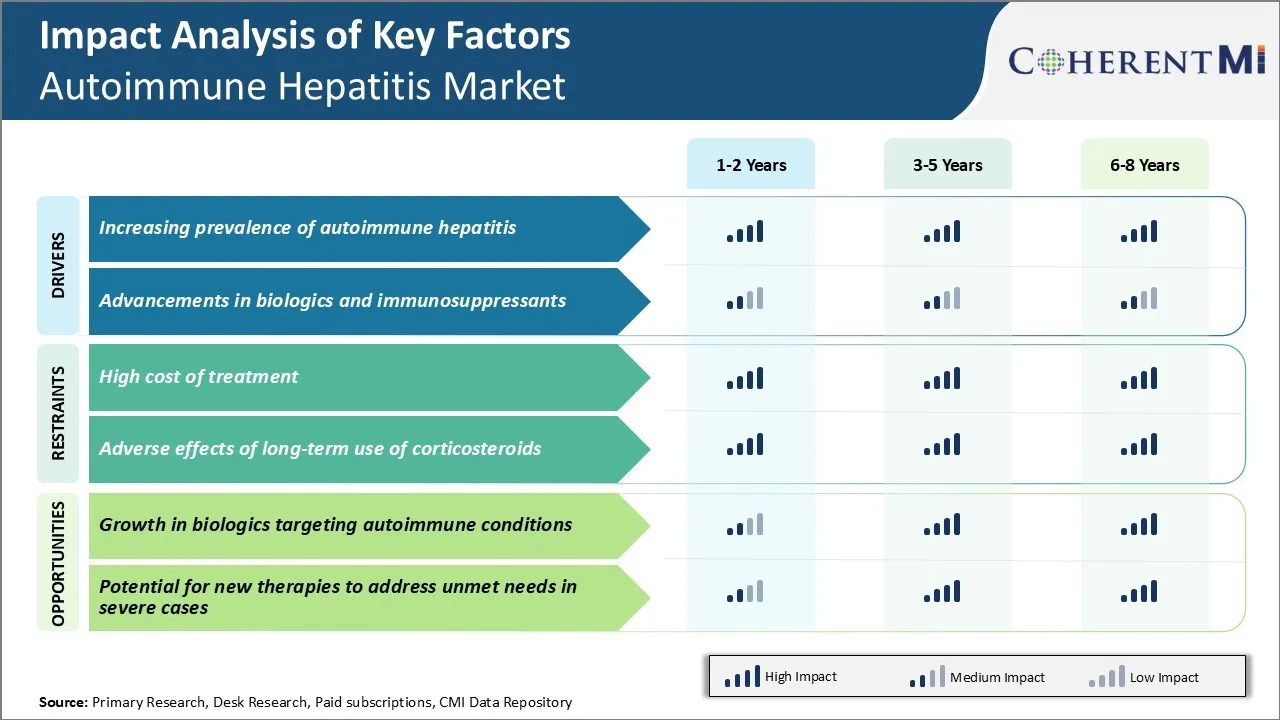
One of the major challenges faced by the autoimmune hepatitis market is the high cost of treatment options available. Autoimmune hepatitis requires long term treatment and management which increases the overall cost burden on patients significantly. The standard first line treatment includes immunosuppressant drugs such as prednisone and azathioprine which are quite effective but are also very expensive. The costs of these drugs increase greatly over the course of long-term therapy.
High healthcare costs can negatively impact access to life-saving therapies for a proportion of the patient population. Addressing issues related to the affordability of autoimmune hepatitis treatment options is a key challenge that needs to be resolved to drive growth in this market.
Market Opportunity - Growth in Biologics Targeting Autoimmune Conditions
Several biotechnology companies and pharmaceutical giants are investing heavily in developing biologics such as monoclonal antibodies, fusion proteins etc. that selectively interfere with certain cytokines, cell surface receptors or signaling molecules implicated in causing autoimmune response. These targeted therapy options have potential to be more effective than existing nonspecific immunosuppressants with lower treatment costs.
Prescribers preferences of Autoimmune Hepatitis Market
Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH) typically follows a stepwise treatment approach based on disease severity and stage of progression. For mild AIH without cirrhosis, monotherapy with glucocorticoids such as prednisone is preferred as a first-line treatment. However, for severe AIH or those with cirrhosis, immunosuppressants such as azathioprine (Imuran) are often added to prednisone for more potent suppression of the immune response.
For patients who fail two lines of immunosuppressive therapies, off-label options like cyclosporine (Neoral), tacrolimus (Prograf), or methotrexate may be considered. Liver transplantation is typically a last resort for those with decompensated cirrhosis non-responsive to medical therapies.
Treatment Option Analysis of Autoimmune Hepatitis Market
Autoimmune hepatitis has four stages - mild, moderate, severe and remission/inactive. For newly diagnosed mild disease, first-line treatment involves the use of corticosteroids like prednisone. This helps induce remission in most patients.
For patients with moderate to severe active disease, budesonide combined with azathioprine or mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) is prescribed. Budesonide, a locally acting corticosteroid, helps control liver inflammation rapidly with lesser risk of systemic side effects than prednisone. Early control of hepatic necroinflammatory activity is critical at this stage to prevent disease progression.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Autoimmune Hepatitis Market
Focus on early diagnosis and treatment: Early diagnosis and treatment is key to successful management of autoimmune hepatitis. Leaders like Pfizer have focused on awareness programs to educate physicians and patients on signs and symptoms of the disease. This helps in early identification and starting patients on treatments like immunosuppressants which can prevent progression to late stages.
Expand through acquisitions: Large players have expanded their pipeline and market reach through strategic acquisitions. For instance, in 2018 Bristol-Myers Squibb acquired Celgene for $74 billion, gaining a large portfolio including the blockbuster drug Otezla approved for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
Segmental Analysis of Autoimmune Hepatitis Market
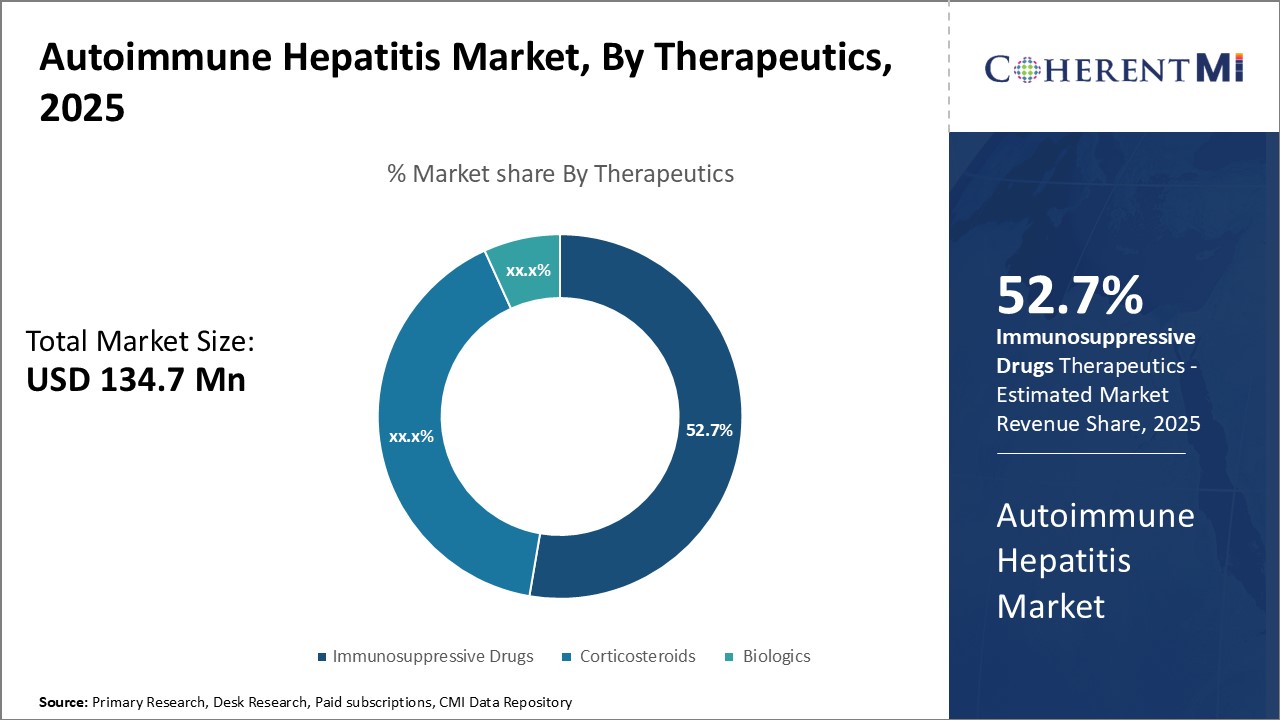
Insights, By Therapeutics: Promising Pipeline Drugs Drive Growth of Immunosuppressive Drugs Segment
For instance, Roche is evaluating an investigational compound called R0761 which is a next-generation calcineurin inhibitor with greater selectivity and improved pharmacokinetics. In pre-clinical studies, R0761 has shown potential to provide effective immunosuppression with fewer side effects compared to existing calcineurin inhibitors.
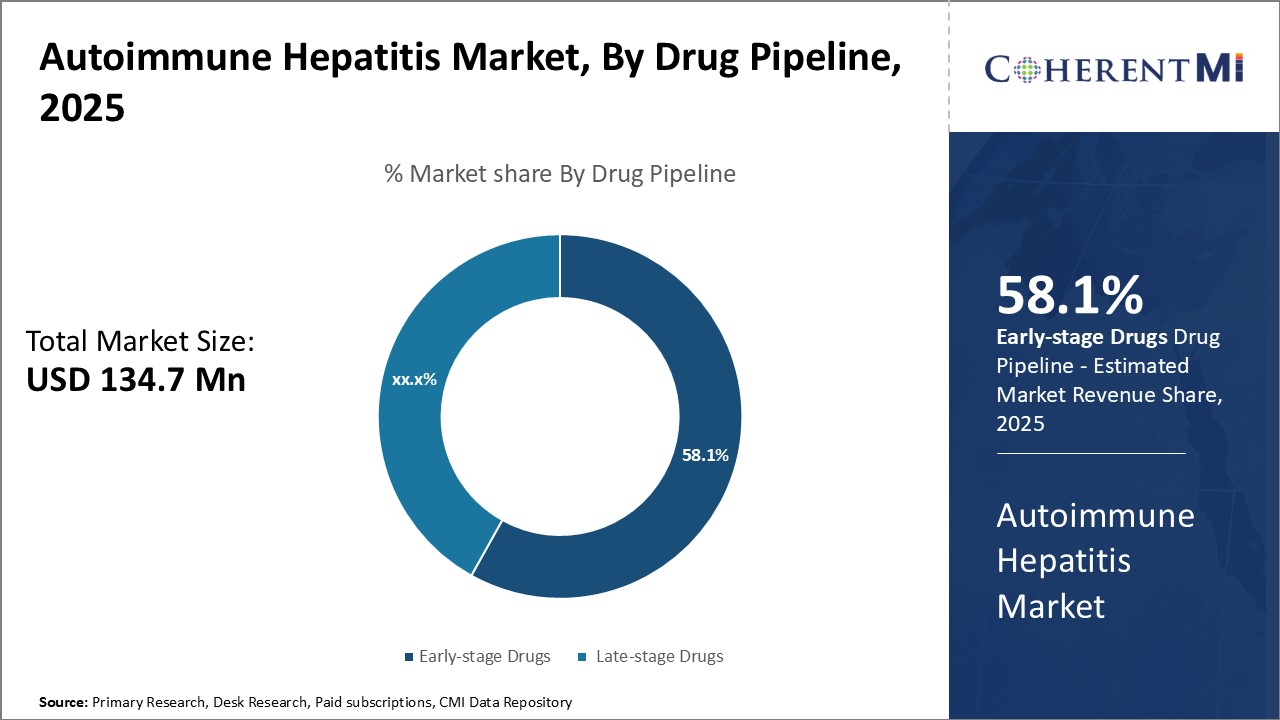 Insights, By Drug Pipeline: Promising Early Clinical Data Drives Interest in Early-Stage Pipeline
Insights, By Drug Pipeline: Promising Early Clinical Data Drives Interest in Early-Stage PipelineIn terms of drug pipeline, early-stage drugs are projected to account for 58.1% share of the market in 2025, owing to the promising early clinical data demonstrated by drugs in Phase I & Phase II trials. A majority of companies are focusing on developing novel targets and innovative mechanisms for treatment of autoimmune hepatitis.
The well-tolerated safety profile and encouraging biomarkers data in initial patients has generated significant interest among research organizations. The promising early clinical efficacy and safety demonstrated by these early-stage pipeline drugs is attracting high investment and collaborations, driving growth of the segment.
Insights, By Disease Progression: Favorable Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines Drive Growth in Acute Segment
Once diagnosed, the treatment generally involves high-dose corticosteroids along with azathioprine as the first line of treatment as recommended by guidelines. The well-defined diagnosis and management approach has ensured high treatment seeking rate for acute cases.
Additional Insights of Autoimmune Hepatitis Market
- Autoimmune hepatitis affects both adults and children, with a higher prevalence in females. Global research efforts are now focusing on improving immunosuppressive treatment options and reducing side effects associated with long-term use of corticosteroids.
- Autoimmune hepatitis is more prevalent in women, accounting for 80% of cases globally. The disease affects people of all ages, though the majority of diagnoses occur between ages 40 and 60. It is a rare but serious disease that, without treatment, can lead to liver failure.
- Autoimmune hepatitis can be misdiagnosed due to symptom overlap with viral hepatitis, making liver biopsy a critical tool for differentiation. Treatment involves corticosteroids and, in more severe cases, liver transplantation if the disease progresses despite medical intervention.
- Gilead and Pfizer lead the charge with innovative treatments that reduce the need for traditional corticosteroids, which have long-term side effects.
Competitive overview of Autoimmune Hepatitis Market
The major players operating in the autoimmune hepatitis market include Novartis, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, Merck & Co., Bristol-Myers Squibb, and TaiwanJ Pharmaceuticals.
Autoimmune Hepatitis Market Leaders
- Novartis
- Gilead Sciences
- Pfizer
- Merck & Co.
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
Autoimmune Hepatitis Market - Competitive Rivalry

Autoimmune Hepatitis Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Autoimmune Hepatitis Market
- In May 2024, Gilead Sciences announced the completion of a successful Phase II trial for a biologic targeting autoimmune hepatitis, with a significant reduction in liver inflammation. Gilead's recent activities in 2024 have focused more on its liver disease portfolio, particularly on seladelpar, a treatment for primary biliary cholangitis (PBC). This drug, acquired through Gilead's purchase of CymaBay Therapeutics, has shown promising results in reducing liver inflammation and symptoms such as pruritus in PBC patients during its Phase III trials.
- In May 2024, Novartis initiated Phase III trials for VAY736, a B-cell activating factor receptor (BAFF-R) antibody designed to treat autoimmune hepatitis. This advancement could significantly enhance the therapeutic landscape and target disease-specific pathways, reducing the reliance on broad-spectrum immunosuppressants. The clinical trials aim to assess its effectiveness in autoimmune hepatitis patients who do not respond to conventional treatments. The drug is still in the middle of its clinical development, with expected results for the ongoing trials over the next few years.
- In August 2023, Pfizer revealed a new immunosuppressive drug in Phase III trials that shows promise for treating refractory autoimmune hepatitis, aiming for regulatory approval by 2025. Pfizer's focus in 2023 has been on various other drugs in Phase III trials, such as treatments for different conditions, including hemophilia, sickle cell disease, and inflammatory bowel disease.
- In January 2019, TaiwanJ Pharmaceuticals reported positive results from Phase II trials for JKB-122, a TLR4 antagonist, showcasing its potential in reducing liver fibrosis and improving liver function in autoimmune hepatitis patients. The drug, a long-acting TLR4 antagonist, demonstrated improvements in liver function and reductions in key biomarkers associated with liver fibrosis. The trial successfully met its primary endpoint and indicated the drug's potential to address liver fibrosis and improve outcomes in AIH patients.
Autoimmune Hepatitis Market Segmentation
- By Therapeutics
- Immunosuppressive Drugs
- Corticosteroids
- Biologics
- By Drug Pipeline
- Early-stage Drugs
- Late-stage Drugs
- By Disease Progression
- Acute Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Chronic Autoimmune Hepatitis

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the autoimmune hepatitis market?
The autoimmune hepatitis market is estimated to be valued at USD 134.7 Mn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 199.9 Mn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the autoimmune hepatitis market?
High cost of treatment and adverse effects of long-term use of corticosteroids are the major factors hampering the growth of the autoimmune hepatitis market.
What are the major factors driving the autoimmune hepatitis market growth?
Increasing prevalence of autoimmune hepatitis and advancements in biologics and immunosuppressants are the major factors driving the autoimmune hepatitis market.
Which is the leading therapeutics segment in the autoimmune hepatitis market?
The leading therapeutics segment is immunosuppressive drugs.
Which are the major players operating in the autoimmune hepatitis market?
Novartis, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, Merck & Co., Bristol-Myers Squibb, and TaiwanJ Pharmaceuticals are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the autoimmune hepatitis market?
The CAGR of the autoimmune hepatitis market is projected to be 5.8% from 2025-2032.