

The Biologics Fill Finish Manufacturing Market is estimated to be valued at USD 5.83 Billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 9.80 Billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.7% from 2025 to 2032. This market is witnessing steady growth due to the rising demand for biologics drugs across major regions and increasing outsourcing of fill finish services by biologics drug manufacturers.
The trend in biologics fill finish manufacturing is positive with growth expected to continue through 2032. Major drivers include the biologics revolution and rising prevalence of chronic diseases globally. Additionally, capacity constraints and lack of infrastructure are prompting drug companies to outsource fill finish services to specialized contract service providers. These dynamics will likely sustain demand and support the high projected CAGR through the forecast period.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR7.7%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 7.7% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | AbbVie Contract Manufacturing, Boehringer Ingelheim BioXcellence, Catalent Biologics, Lonza, WuXi Biologics and Among Others |
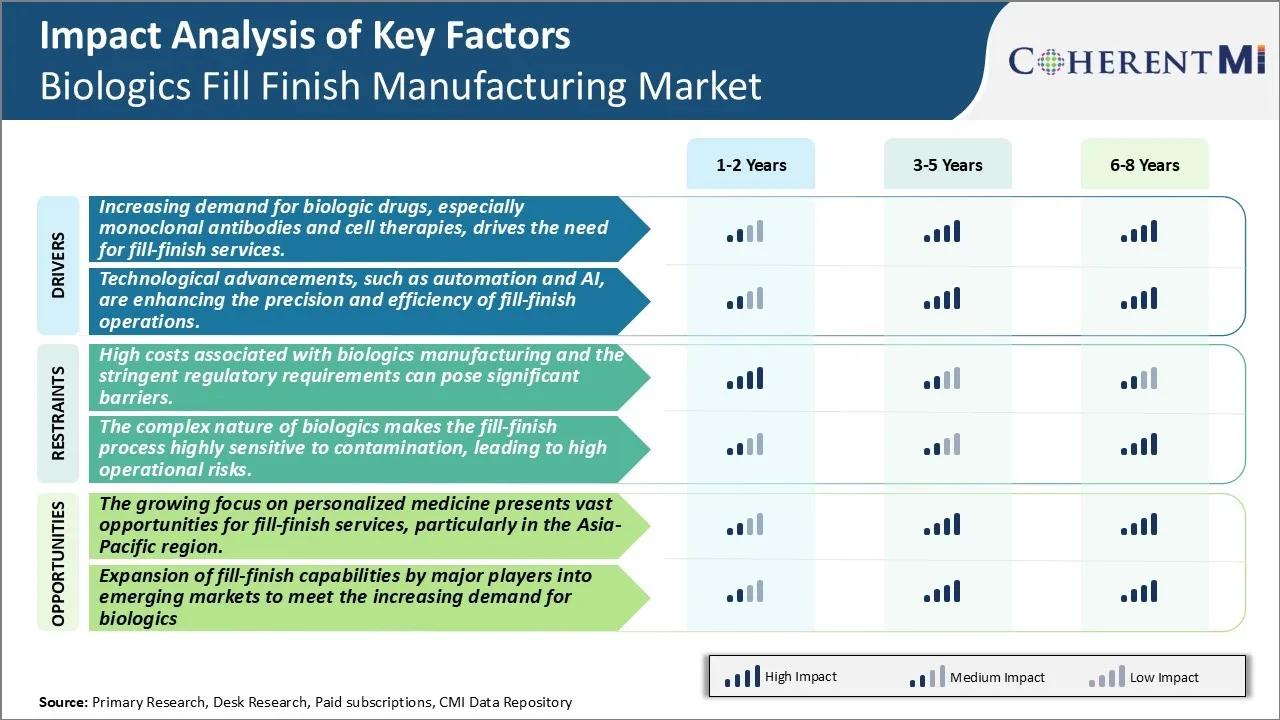
Market Driver - Increasing demand for biologic drugs, especially monoclonal antibodies and cell therapies, drives the need for fill-finish services.
The biologics fill finish manufacturing market is being driven heavily by the rising demand for advanced biologic drugs such as monoclonal antibodies and cell therapies. Biologics have revolutionized the treatment of various chronic and life-threatening diseases due to their high specificity and efficacy. As research continues to uncover new therapeutic targets and advance treatment methods, the development of novel biologic entities is growing rapidly. Over the last decade, biologics have dominated FDA approval numbers, with antibodies being the most prevalent biologic modality approved. These complex biologic drugs demand meticulous manufacturing processes and specialized fill-finish services to ensure the highest quality and safety.Fill-finish is considered the final crucial stage in biologics production where the drug substance is processed and filled into containers under aseptic conditions for packaging, labeling and distribution. With increasing biologics approvals and rising demand for personalized treatment options, fill-finish contractors are facing tremendous pressure to scale up operations and optimize production workflows to meet commercial supply requirements. Manufacturers also require specialized equipment, facilities, and technical know-how to handle the processing of different modalities such as antibody-drug conjugates, gene therapies and viral vectors. This has propelled substantial investments by fill-finish CMOs to expand their capabilities. Some notable expansion projects include the establishment of new aseptic suites equipped with state-of-the-art isolators and automation systems.
The proliferation of cell and gene therapies as promising treatment avenues has further accentuated the need for robust fill-finish infrastructure. These novel therapies rely on complex manufacturing processes and stringent environmental controls during formulation filling due to the use of living biological substances. Their fill-finish requires enhanced biocontainment and cleanroom facilities to prevent microbial contamination. Additionally, the short shelf-life and labile nature of these advanced modalities calls for centralized fill-finish facilities located near clinical trial sites for just-in-time manufacturing. As cell and gene therapies edge closer to commercialization, their mass-market production will strain existing fill-finish capacity, catapulting demand for specialized service providers.
Technological Transformation of Fill-Finish Operations
The biologics fill finish manufacturing industry is witnessing technological upgrades that are automating manual processes and enhancing precision to cope with growing therapeutic complexity and productivity requirements. The implementation of sophisticated automation equipment as well as digitalization trends such as artificial intelligence and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) are reshaping fill-finish workflows.
Automation allows for tighter process control and reduced human errors compared to conventional methods. Leading fill-finishers are adopting robotics for high-speed vial and syringe handling, inspection, labeling and packaging. This boosts line efficiency and accuracy while freeing up operators for value-added tasks. Liquid fillers integrated with automatic weight or volume inspection stations can perform homogenous filling of hundreds or thousands of containers per hour under validated conditions. Similarly, robotic visual inspection systems employing machine learning are being used to screen filled containers in real-time to identify defects, reduce reject rates and improve overall equipment effectiveness.
Digital technologies are also streamlining batch record management, data collection and quality oversight. IIoT sensors facilitate remote monitoring of critical process parameters to deliver real-time data for predictive maintenance and process optimization. AI-powered analytics of historical manufacturing datasets help predict failures and spot anomalies pre-emptively. The use of electronic batch records accessible via mobile devices enhances transparency, speed and compliance. Virtualization of equipment and process validation studies using digital twins further accelerates technology transfer between manufacturing sites as therapies are scaled globally. Such advanced technologies not only upgrade fill-finish quality but also make the contract services more cost-competitive, driving continued adoption.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High costs associated with biologics manufacturing and the stringent regulatory requirements can pose significant barriers.
The biologics fill finish manufacturing market faces significant challenges due to the high costs associated with biologics production and stringent regulatory compliance requirements. Biologics drug substances are produced from living cells and organisms, making their manufacturing process far more complex than traditional small molecule drugs. Living cells must be cultured and conditions controlled carefully to ensure product uniformity and safety. This complex manufacturing process is capital intensive requiring substantial investments in facilities, specialized equipment and a highly skilled workforce. Additionally, it is a long process taking two to four years from development to regulatory approval and commercial production. The stringent regulatory norms by agencies like FDA further drive up costs. Facilities and processes must be validated to meet CGMP standards with elaborate documentation and periodic inspections. Any change requires re-validation adding time and cost burdens. Significant investments must also be made in quality control testing to ensure therapeutic and immunogenic qualities of biologics throughout their shelf life. Meeting all these regulatory compliance requirements makes biologics manufacturing a high expense endeavor for companies.
Market Opportunities: The Growing Focus on Personalized Medicine Presents Vast Opportunities for Fill-Finish Services, particularly in the Asia-Pacific Region
The biologics fill finish manufacturing market is poised to harness substantial opportunities arising from the growing focus on personalized medicine. Personalized therapies tailor treatment based on an individual's genetic profile to improve therapeutic outcomes. They require smaller production runs to meet the needs of targeted patient subsets. This shifts demand to specialized contract service providers with flexible fill-finish capacity. Asia Pacific in particular presents a huge untapped market for fill-finish services. The region is home to over 60% of the global population with rising healthcare spends. However, high capital investments deter local pharma companies from establishing their own fill-finish capabilities. This provides opportunities for international contract organizations to set up facilities in emerging Asia Pacific markets through joint ventures or acquisitions. Additionally, favourable regulatory environment and availability of low-cost skilled workforce enhances Asia Pacific's attractiveness. The evolving personalized medicine sector coupled with Asia Pacific's unmet need for fill-finish capacity offers significant growth potential for services companies in the coming years.
For early stage NA, prescribers commonly rely on over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen (Advil) or naproxen (Aleve) to manage mild symptoms. However, for patients with more severe symptoms, guidelines recommend disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) as first-line treatment. Methotrexate is frequently the DMARD of choice due to its dual anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating properties. Brand names include Rheumatrex.
If a patient does not respond adequately to or cannot tolerate methotrexate, prescribers will often switch to another conventional DMARD such as leflunomide (Arava) or sulfasalazine (Azulfidine). For progressive disease, biologic DMARDs that target specific mechanisms like tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibition are introduced. Common choices include infliximab (Remicade), etanercept (Enbrel), and adalimumab (Humira).
Beyond pharmaceutical treatments, prescribers also consider non-drug factors such as disease severity, lifestyle, comorbidities, cost and insurance coverage when determining the optimal therapeutic approach. Generally, the treatment regimen becomes more aggressive as the disease advances to later stages and additional lines of therapy are required to control symptoms and protect joint integrity.
Lung cancer is typically classified into four main stages—Stage I through Stage IV—depending on the size and spread of the tumor. The appropriate treatment depends on the stage of cancer.
For early-stage (Stage I-II) non-small cell lung cancer (NSC), surgery is often the primary treatment and may be curative. Options include lobectomy (removal of a lung lobe), pneumonectomy (entire lung), or segmentectomy (portion of lobe). For patients who cannot undergo surgery, stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) may be used to precisely deliver high doses of radiation.
For more advanced localized NSC (Stage III), the standard treatment is usually a combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Common chemo regimens include platinum-based doublets containing drugs like cisplatin or carboplatin combined with other agents like paclitaxel, pemetrexed, gemcitabine or vinorelbine. Concurrent chemoradiation provides a survival benefit over sequential treatment.
For metastatic or late-stage NSC (Stage IV) where surgery is not an option, platinum-based chemotherapy remains first-line. Options include single agents like cisplatin/carboplatin or doublets like cisplatin/pemetrexed. For maintenance, pemetrexed alone is commonly used. Unfortunately, Stage IV NSCLC has a 5-year survival rate of only 5%. However, molecularly targeted therapies or immunotherapy may provide additional options.
This provides an overview of the different stages of NSC and recommended treatment options based on stage, from surgery and radiation to chemotherapy and targeted therapies.
Contract manufacturing: Many leading fill/finish service providers have adopted the strategy of contract manufacturing to cater to the growing demand from biotech companies. For example, Lonza, one of the top CMOs, generates over 50% of its Pharma & Biotech revenues from contract manufacturing. This allows biotech firms to focus on drug development while outsourcing production.
Expanding fill/finish capacities: To capture more market share, players are steadily expanding their manufacturing capacities. In 2018, Cobra Biologics invested US$100 million to double its viral vector production capacity. Similarly, IDT Biologika added 6 new production lines between 2017-19. Takeda acquired large scale facilities through the Shire acquisition in 2019.
Geographic expansion: Leading players are expanding their footprint globally through new facilities to address the demand from regional clients. For instance, Catalent invested US$250 million in 2018 to set up a 200,000 sq ft facility in Bloomington, Indiana to serve the US market. Last year, Samsung Biologics opened a plant in Incheon, South Korea which added 390,000 liters of biomanufacturing capacity.
Technology advancements: Adopting cutting-edge tech helps firms attract more business. For example, Fujifilm acquired Irvine Scientific’s cell banking facility in 2018 to boost its gene and cell therapy capabilities. Lonza implemented ultra high-capacity blow-fill-seal systems in 2018 reducing filling times manifold. These innovations enable manufacturing of more complex products.
Partnerships & acquisitions: Strategic tie-ups & acquisitions help strengthen expertise and capabilities. For instance, Thermo Fisher acquired Brammer Bio in 2019 for US$1.7 billion to gain important viral vector expertise and clients.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
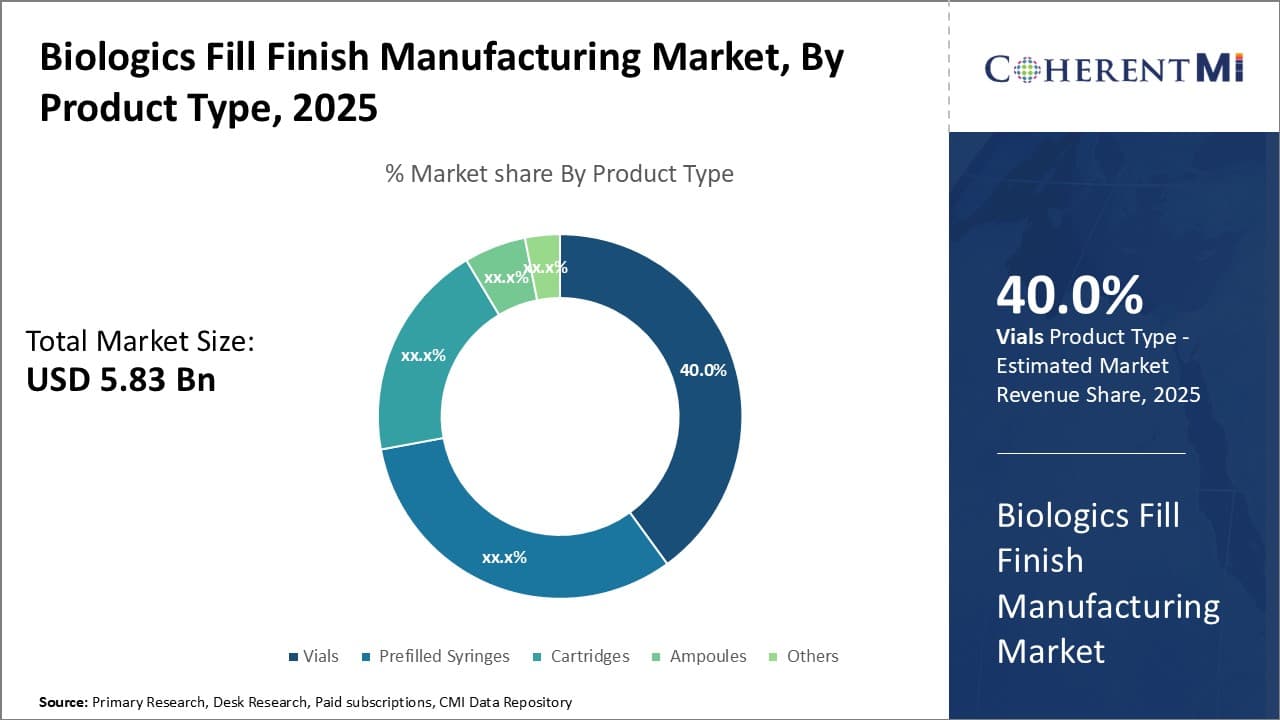
Product Type:- Growing Demand for Cost-effective Delivery Driving Vials Segment Growth
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Product Type:- Growing Demand for Cost-effective Delivery Driving Vials Segment Growth
In terms of Product Type:, Vials contributes the highest share of the market owning to their widespread adoption rate and cost-effectiveness as a delivery mechanism. Vials are simple to manufacture and provide substantial packaging efficacy at low costs compared to alternatives like prefilled syringes. Their low per-unit cost makes vials suitable for packaging high-volume biologics used in chronic therapies. A significant proportion of biologics sold are required for frequent or long-term dosing schedules, augmenting the demand for cost-effective vials. Hospitals and pharmacies also prefer vials packaging due to the lower storage space requirements and handling costs compared to cartridges or prefilled syringes. Several drug formulation technologies also enable maximizing the drug fill amount in vials, further boosting their economical appeal. Vials are likely to retain their popularity especially in developing markets where cost-sensitivity is paramount. The higher acceptance, combined with the ability to lower treatment expenditures, will continue promoting vials usage for biologics fill finish over the forecast period.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
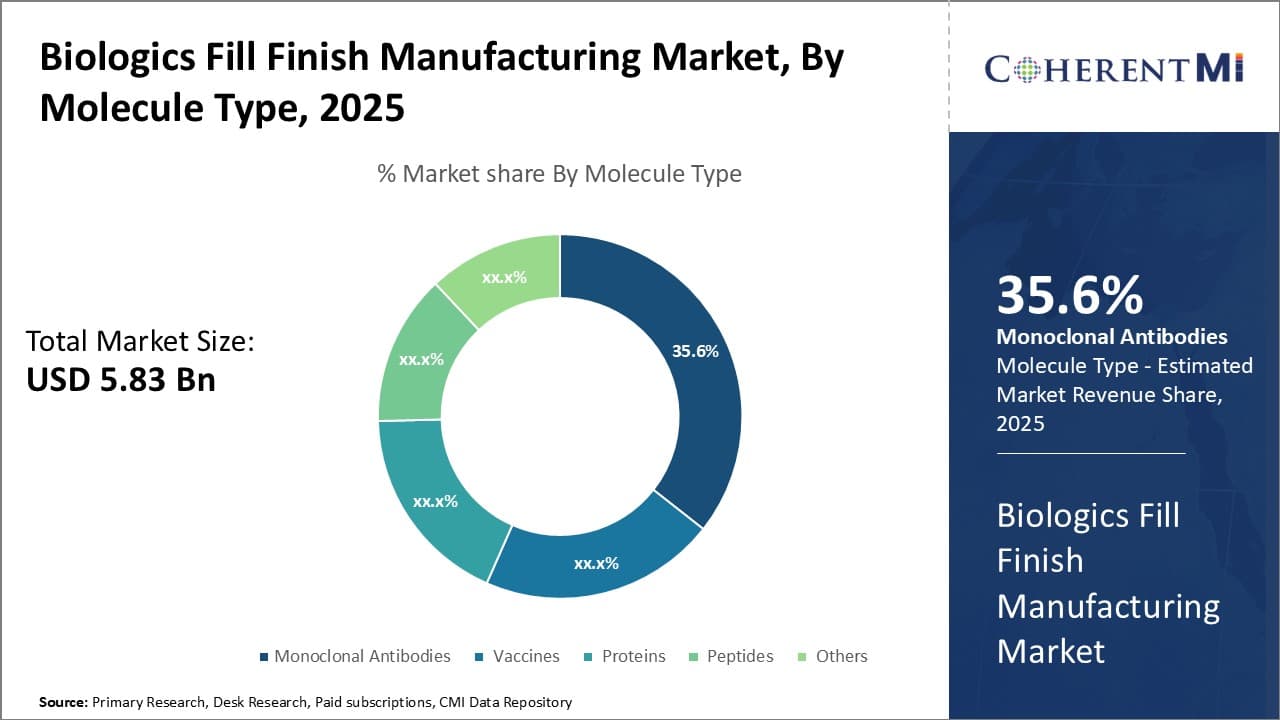
Molecule Type:- Dominant Monoclonal Antibodies Drive Monoclonal Antibodies Segment Growth
In terms of Molecule Type:, Monoclonal Antibodies contributes the highest share of the market. This can be attributed to the groundbreaking research in recent decades that has established monoclonal antibodies as a mainstay for treating various cancers and autoimmune disorders. A slew of blockbuster monoclonal antibodies have been commercialized, with many more in the drug development pipeline. These have vastly improved clinical outcomes while garnering high sales numbers. Their dominance in biologics revenues ensures that manufacturing capacity is consistently directed towards monoclonal antibodies. The fill finish of innovator mAbs also attract sophisticated solutions from CDMOs. Patent expiries of notable mAbs will see biosimilars further propelling this segment. Overall, the wide application scope and commercial successes of monoclonal antibodies have positioned them as the most prominent molecule class in biologics fill finish.
By Scale of Operation -Rising Outsourcing and Cost Optimization Drive Large-Scale Manufacturing Growth
In terms of By Scale of Operation the Biologics Fill Finish Manufacturing Market is segmented into Large-scale Manufacturing and Small-scale/Specialty Manufacturing. Large-scale Manufacturing contributes the highest share of the market owing to growing outsourcing of bioprocessing activities by biopharmaceutical companies. Contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) specializing in large-scale fill finish are capable of realizing economies of scale that optimize costs for both new and generic drug marketers. This makes outsourcing an attractive strategy for maintaining profit margins. Additionally, stringent regulatory requirements for advanced production technologies favor large equipment and integrated facilities over smaller operations. The sheer resource needs and capital expenses involved in expanding or establishing bioproduction sites also steers demand to specialized large-scale providers. As the biologics pipeline matures into high-selling brands, there will be greater reliance on CDMOs’ large plants to keep pace with rising commercial demands while minimizing per-unit costs. This helps consolidate large-scale manufacturing’s prominent position within the biologics fill finish arena.
The biologics fill-finish market is evolving rapidly, driven by the rising demand for biologic therapies such as monoclonal antibodies and cell and gene therapies. As the complexity of these therapies increases, so does the demand for advanced fill-finish capabilities that can ensure the safety and efficacy of these products. The market is expected to grow significantly, with a CAGR of 7.5% from 2024 to 2035, reaching $11.6 billion by 2035. This growth is supported by technological advancements, such as the integration of automation and artificial intelligence in manufacturing processes, which are helping companies improve efficiency and reduce contamination risks. The market is characterized by a mix of large and mid-sized players, with the leading companies expanding their capacities to meet the growing global demand, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region, which is anticipated to be the fastest-growing market. However, the market also faces challenges, including high operational costs and stringent regulatory requirements, which could impact the speed of growth.
The major players operating in the Biologics Fill Finish Manufacturing Market include WuXi Biologics, Lonza, Catalent Biologics, Boehringer Ingelheim BioXcellence, AbbVie Contract Manufacturing, Charles River, Evonik, Sandoz, Patheon Pharma Services, Recipharm, Pierre Fabre, Fresenius Kabi, GSK, Asymchem, Hetero, Syngene and WACKER.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Abhijeet Kale is a results-driven management consultant with five years of specialized experience in the biotech and clinical diagnostics sectors. With a strong background in scientific research and business strategy, Abhijeet helps organizations identify potential revenue pockets, and in turn helping clients with market entry strategies. He assists clients in developing robust strategies for navigating FDA and EMA requirements.
Biologics Fill Finish Manufacturing Market is Segmented By Product Type (Vials, Prefilled Syringes, ...
Biologics Fill Finish Manufacturing Market
How big is the Biologics Fill Finish Manufacturing Market?
The Biologics Fill Finish Manufacturing Market is estimated to be valued at USD 5.83 in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 9.80 Billion by 2032.
What are the major factors driving the Biologics Fill Finish Manufacturing Market growth?
The increasing demand for biologic drugs, especially monoclonal antibodies and cell therapies, drives the need for fill-finish services. and technological advancements, such as automation and ai, are enhancing the precision and efficiency of fill-finish operations. are the major factor driving the Biologics Fill Finish Manufacturing Market.
Which is the leading Product Type: in the Biologics Fill Finish Manufacturing Market?
The leading Product Type: segment is Vials.
Which are the major players operating in the Biologics Fill Finish Manufacturing Market?
WuXi Biologics, Lonza, Catalent Biologics, Boehringer Ingelheim BioXcellence, AbbVie Contract Manufacturing, Charles River, Evonik, Sandoz, Patheon Pharma Services, Recipharm, Pierre Fabre, Fresenius Kabi, GSK, Asymchem, Hetero, Syngene, WACKER are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the Biologics Fill Finish Manufacturing Market?
The CAGR of the Biologics Fill Finish Manufacturing Market is projected to be 7.7% from 2025-2032.