子宮頸部上皮内腫瘍市場 サイズ - 分析
グローバル頚部イントラピュリアル Neoplasia 市場は評価されると推定されます 2024年のUSD 670.1 Mn そして到達する予定 米ドル 971.5 によって Mn 2031, 化合物年間成長率で成長 (CAGR) 2024年~2031年
市場は、世界の子宮頸がんの上昇の蔓延に陥る予測期間にわたって肯定的な成長を目撃することが期待されます。 スクリーニングおよび予防接種プログラムによる早期がん検出に関する女性人口の認知度を高め、市場の成長にも貢献しています。 女性人口のスクリーニングに向けた様々な政府の取り組みやプログラムが市場拡大を支援しています。 開発途上国におけるヘルスケアの普及と健康増進などの他の要因は、計画された年の間に、頚部内視鏡市場で多くの成長機会を提供します。
市場規模(米ドル) Mn
CAGR5.4%
| 調査期間 | 2025-2032 |
| 推定の基準年 | 2024 |
| CAGR | 5.4% |
| 市場集中度 | High |
| 主要プレーヤー | 株式会社Pfizer, グラクソスミスクライン plc, ノバルティスAG, ジョンソン&ジョンソン プライベートリミテッド, マーク&株式会社 その他 |
お知らせください!
子宮頸部上皮内腫瘍市場 トレンド
市場ドライバー - 子宮頸がんの予防とHPVワクチンのワイドな実施の高度化が市場成長を促進しています。
子宮頸がんのリスクや政府によるタイムリーなスクリーニングの重要性や、さまざまな国の非営利団体に対する啓発キャンペーンの増加により、この病気について女性を教育することができました。 定期的な検査と試験は、治療されていない場合、癌に進行する可能性がある、子宮頸部の多発的な変化を検出することができます。 コミュニティのアウトリーチ活動、ソーシャルメディア、およびプライマリケアセンターを通じて、Pap smearsなどのスクリーニングテストに関するワイドなプロモーションは、より多くの女性がスクリーニングを受けることを奨励しています。
政府はまた、スクリーニングのガイドラインを形成し、推薦されたテストを手頃な価格にし、参加を高めるためにアクセス可能にするためにイニシアチブを取っています。 これは、以前の治療可能な段階における頸部病変の検出につながりました。 また、HPVに対する予防接種プログラム、子宮頸がんの主な原因はグローバルに展開されています。 国民の免疫プログラムの一環として、9〜14歳までの女子をワクチン接種しました。 非営利団体は、これらの取り組みを意識ドライブや、資源制限区域の予防接種をサポートする資金調達を通じて補います。
女性は、一般的なHPV感染がいかにあり、生命を脅かす子宮頸がんが時折行動しない場合は、より予防策を講じる喜んでいるかを理解しています。 自分の健康と他の女性の生活を守ることを望んでいます。 ヘルスケアの専門家は、適切な婦人科のケアポストの予防接種と成人を通じて維持の重要性にあまりにも応じています。 持続的かつ調整された努力により、子宮頸がんの病態と利用可能なスクリーニングオプションに関する意識は途上なく上昇しています。 これは、早期の検出と前癌の変化のタイムリーな管理を促進する重要な要因であり、患者の結果を大幅に改善します。
市場ドライバ-診断における技術的な進歩は、市場の成長を燃料化します。
診断技術の急速な進歩は前癌性の頚部の損害の検出を改良しました。 従来のPapテストは、液体ベースのPapスクリーニングとHPVテストなどのより敏感なテストで拡張されます。 液体ベースのパパは、従来のパパテストよりも多くの細胞異常を検出できるスライドのコンピュータ補助解析を可能にします。 HPV 検査は、HPV ウイルスの種類を引き起こす癌に感染した女性を識別することができるので、効率的な第一次スクリーニング方法として機能します。
酢酸やデジタル子宮内膜を用いた視覚検査などの高度なスクリーニング技術は、限られた資源開発途上国におけるスクリーニングの妥当性を上げてきました。 さらに、DNA検査やサイトロジーによる分子診断は、結果の特定性と精度を高めています。 バイオマーカーアッセイは、子宮頸部の分泌における腫瘍関連の抗原の検出も検討中です。 イメージング技術の革命により、衝突などの技術を用いた高解像度の頸部画像のキャプチャを可能にし、専門家による評価のための拡大とデジタル文書の遠隔化を実現します。
デジタル化したテレシトロジーの実践 パップスミアは、他の場所で資格のあるシトパストロジストによって分析され、農村の場所にスクリーニング品質が向上しています。 継続的な強化により、RNAシーケンシングやプロテオミクスなどの新しい診断法は、がん早期発見のためのバイオマーカーを発見する可能性があります。 Altogether、連続的な技術の改善は段階の悪性への進行前の敏速な介入のためのprecancerous損害の時機を得た同一証明を可能にします。 これは、診断および治療結果を大幅にアップリフトします。
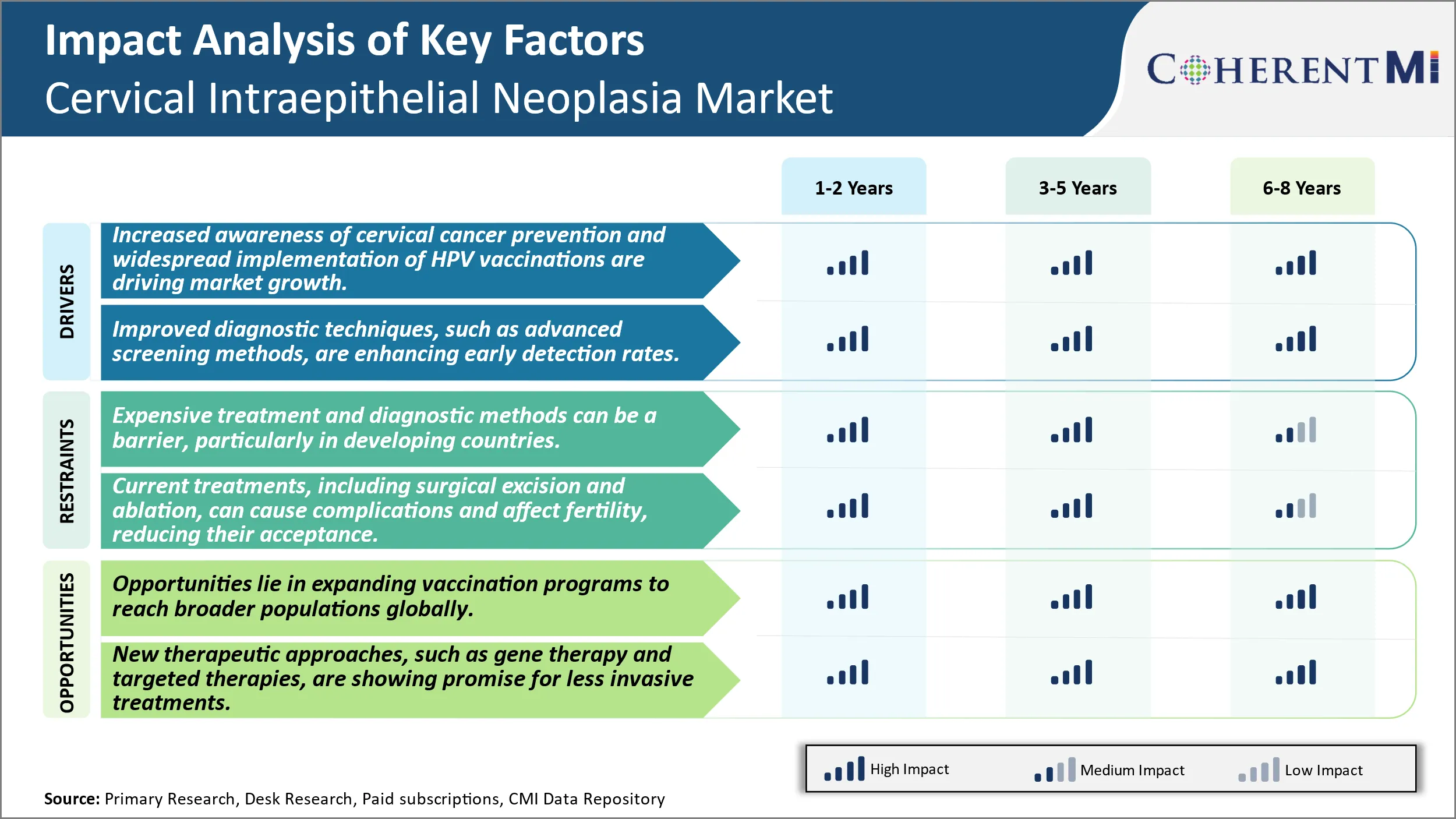
市場課題 - 高価な治療と診断方法は、国を特に開発する障壁であることができます。
子宮頸部内視鏡検査における主要な課題の1つは、治療とスクリーニング方法に関連する高いコストです。 子宮頸がんスクリーニングは、通常、早期の検出と介入を可能にし、HPV検査と通常のパックスマイヤーを含みます。 しかし、これらの診断テストは、米国の約USD 260の費用対効果の高い、高価であり得る。 LEEPのプロシージャ、cryotherapy、またはループ電気外科切除のプロシージャのような処置方法はまた重要なコストを伴います。 たとえば、LEEP手順の平均コストは約USD 1,500です。 このような高価な診断と治療コストは、特に限られた医療リソースで経済を発展させることで、子宮頸がん予防へのアクセスを制限することができます。 これは、早期発見と治療として大きな障壁は、子宮頸部内視神経症を管理し、侵襲性がんの進行を防ぐ上で重要です。 スクリーニングおよび治療に関連する費用は、公衆衛生プログラムおよび民間保険者に重大な負担をかけます。 この課題は、予防医療対策のより広い採用と、子宮頸部内視神経市場の全体的な成長可能性に影響を与える.
市場機会 - HPV予防接種プログラムの拡張は、将来の開発のための新しいアベニューを作成します。
ヒトパピローマウイルス(HPV)ワクチン接種プログラムをグローバルに展開する市場機会もかなりあります。 潜在的な暴露の前にHPVの予防接種は、単純で効果的で費用対効果の高い方法を提供し、子宮頸がんおよび骨頸部内視神経症の症例を防ぐことができます。 ワクチン接種率は多くの先進国で増加していますが、子宮頸がんが女性に影響を及ぼす地域では、カバレッジは比較的低いままです。 機会は、多国間パートナーシップと公平な価格の差別を通じて、これらの保護されたコミュニティでHPVワクチンへのアクセスを拡大することを信じています。 ワクチン接種アップテークの増加により、長期にわたる子宮頸部がんおよびがんの発生率が大幅に低下する可能性があります。 これは、関連する診断テストと治療の機会を作成します。 HPVワクチンをグローバルに提供することを目的としたプログラムを通じた予防医療の拡大により、子宮頸部内視鏡検査における将来の成長が著しい可能性があります。
処方者の好み 子宮頸部上皮内腫瘍市場
子宮頸部内腔内視神経内視鏡(CIN)は、子宮頸部内の異常な細胞変化を記述します。 通常、異常細胞の深さと、それらがどのように影響する子宮頸部の約3段階(CIN 1-3)に分類されます。 軽度または低グレードの変更(CIN 1) の場合、これらはしばしば自分自身でクリアするので、治療は必要ありません。 がんの進行を防止するために、より重度または高レベルな変化(CIN 2/3)がしばしば処理されます。
治療オプションはステージによって異なりますが、最初は侵襲的な選択肢が少なくなります。 CIN 2/3では、一般的な早期治療には、異常な細胞を除去したり、凍結したり、それらを破壊したりするレプが含まれます。 これらが不成功であるか、または病気が主張している場合は、コーンバイオプシーは、子宮頸部のより大きなセクションを削除するために実行することができます。 初期治療後の再発または持続的な高品位変化のために、子宮頸部および子宮を除去する催眠術が推奨されることがあります。
処方者は、年齢、変化の重症度、前処理の成功、フォローアップ、不妊欲求などのさまざまな要因を検討し、最高の管理アプローチを決定する。 オープンコミュニケーションは、患者と臨床医の間で通知された、共有された決定を確立するのに役立ちます。 未来の健康と生活の質を可能な限り維持しながら、目標は常に完全な決断です。
治療オプション分析 子宮頸部上皮内腫瘍市場
子宮頸部内膜ネオプラシア(CIN)には3つのステージがあります - CIN1、CIN2、CIN3は、異常細胞が子宮頸部にどれだけ深いかに基づいています。
CIN1では、好まれる最初のライントリートメントは、多くのCIN1の病変が自分自身で回帰するので、しばしば見栄えを監視しています。 1年後の持続的な場合、LEEP(ループ電気外科的排泄手続)やCryotherapyなどの外来の手順は使用することができます。 LEEPは、前方細胞を除去するために、電化ワイヤループを使用しており、局所麻酔下で同じ日に実行できます。 Cryotherapyは液体窒素を使用して異常な細胞を凍結し、破壊します。
CIN2およびCIN3のために、LEEPはprecrousance細胞を取除くために推薦される標準的な最初のライン処置です。 90%以上の成功率を持ち、組織の病理学的検査を可能にします。 証拠金が正の場合、LEEPを繰り返します。
LEEPの後の再発または持続的な高級CINのために、第2ライン処置の選択は化学療法の薬剤Cisplatinです。 それは通常より大きい効力のためのGoserelinのようなホルモン療法と共に単一の線量の注入によって管理されます。 この政権は70%以上の成功率を持っていますが、LEEPよりも多くの副作用に関連付けられています。
子宮摘出術(子宮の外科的除去)は、一般的には最初のライン治療として推奨されていませんが、再発後のCINまたは小児期を終わらせる女性のような特定のケースで検討されることがあります。
主要プレーヤーが採用した主な勝利戦略 子宮頸部上皮内腫瘍市場
ノベル医薬品および治療を開発するための研究開発投資: Roche、QIAGEN、およびHologicのような主要なプレーヤーは一貫してR & Dの重要な資源を投資し、高度の診断テスト、薬剤を開発し、頚部内視神経神経疾患のための最低の侵襲的な処置のアプローチを開発しました。 たとえば、Rocheは2020年に研究開発で9億米ドルに投資しました。 そのコバスHPVテストは2011年に承認され、米国の市場の70%以上を捕獲する第一次頚癌スクリーニングのための心配の標準になりました。
ポートフォリオを強化するための戦略的買収: 企業は、革新的な治療に取り組んでいる小企業を獲得し、製品の提供を急速に拡大します。 例えば、2019年、QIAGENはSTAT-Dxを買収し、そのポートフォリオに新しいE6/E7 mRNAテストを追加しました。 QIAGENは、成長する子宮頸がんスクリーニング市場のより大きなシェアを捕獲しました。 同様に、Rocheは診断および製薬部門を強化するために複数の買収を完了しました。
積極的なマーケティングキャンペーン: 定期的なスクリーニングの重要性を考えると、選手は積極的にヘルスケアプロバイダーや患者にソリューションを販売しています。 例えば、ホロジックは、HPVテストを自動化するためのFDA承認パンサーシステムの利点を強調2018年にマルチチャネル教育プログラムを開始しました。 これにより、2019年のシステムからHologicの収益が20%増加しました。
現代テストのための好ましい払い戻し: 政府機関と民間保険会社とのパートナーシップは、企業が新しい診断およびスクリーニング技術のための有利な償還コーディングと支払い率を受け取るのを助けました。 たとえば、QIAGENは米国でCMSと密接に連携し、E6/E7テスト用の独自の償還コードを確保し、クリニックの採用を迅速化しました。
セグメント分析 子宮頸部上皮内腫瘍市場

洞察, 現在の治療によって HPV の予防接種は、予測期間で市場シェアをリードするためのアカウントに期待されます.
現在の処置によって、HPV ワクチン接種は、予防の意識を高めるため、2024年に最高シェア54.3%に寄与することが期待されます。 HPVの予防接種は、ヒトパピローマウイルス(HPV)感染による子宮頸がんおよび前癌病変を防ぐための最も効果的な方法として登場しました。 多くの国で広く普及しているワクチン接種プログラムでは、HPVとその子宮頸がんへのリンクについて大幅に認知度を高めています。 公衆衛生当局は、性的に活動する前に、HPVワクチンをよく受け取ることの重要性について、人々、特に若い少女、女性を教育する上で重要な役割を果たしています。 HPVは、生命の後に癌の危険性に女性を置く非常に一般的な性感染症であるという事実は、予防接種を選ぶためにより説得力があります。
臨床研究では、ワクチンを対象とするHPVタイプからの感染を防ぐため、ほぼ100%効果的であることが実証されています。 非常に効果的な予防オプションを利用できると、子宮頸がんおよびその前の状態は、より多くの予防可能なと感じています。 このような病気を取り巻く歴史上の致命的な態度を伝えています。 また、2つの線量から成る予防接種スケジュールの短い期間は、他の予防接種シリーズよりも比較的簡単に完了しました。 一緒に、改善された意識、実証済みの有効性、および管理の利便性は、HPVタイプの子宮頸部疾患に対する前線防衛としてHPVの予防接種をセメントで行っています。
公共および民間企業からのさまざまな取り組みも引き続きHPV予防接種を促進します。 ヘルスケアプロバイダの教育は優先的にとどまり、対象となる患者にワクチンを強くお勧めします。 コミュニティ・アウトリーチの取り組みは、潜在的重病から女性の将来の世代を保護するための予防接種の能力を強調しています。 思春期のより多くのコホーツがHPVワクチンシリーズを完了するように、予防接種のための市場は、保護を維持するために定期的に必要な繰り返し用量で堅牢に保たれている。 ワクチンによる追加のHPVタイプのカバレッジも時間をかけて、その対処可能な集団を広げます。 全体的に、高められた防止焦点は現在の頚部疾患管理でHPVの予防接種のintegralをしました。
洞察, 魅惑的なセラピーによって, 遺伝子治療 2024年リードシェア登録
セラピスをエマージすることで、子宮内腔内視鏡市場、遺伝子 治療は、2024年に最も高いシェア65.3%を目標とするアプローチに貢献します。 子宮頸部内視鏡神経内視鏡検査のための新しい治療法の中で、遺伝子治療は重要な約束を実証しています。 遺伝子治療は、疾患を治療するために細胞や組織の内部または外側の遺伝子の意図的な導入、変更、または除去を含みます。 子宮頸がんおよびその前駆体の場合、遺伝子治療の研究者は、治療的遺伝的ペイロードをがんまたはdysplastic細胞に直接配信するために、標的ベクターの開発に取り組んでいます。 遺伝子治療の主な利点の1つは、ネオプラスチックの増殖、侵略および転移を根ざした分子経路を正確に干渉する可能性です。 より広い毒性作用を運ぶ従来の化学療法よりむしろ、遺伝子治療は最適化されたベクトル設計および遺伝子の沈黙のメカニズムによってローカル効果を作り出すかもしれません。 腫瘍抑制遺伝子のインサートや子宮頸部の腫瘍遺伝子のブロックを伴う早期臨床試験では、より少数の有害反応を伴う死体の再放出を達成するために遺伝子治療が示されている。
分子ターゲティング能力は、遺伝子治療が従来の薬理学的介入で見られる薬物抵抗のような問題を克服することを可能にします。 また、ウイルスおよび非ウイルス性ベクターエンジニアリングの進歩は、子宮頸部疾患に対する遺伝子配信の安全性と有効性を引き続き高めます。 トランスジェネレーション式の長さやベクトルの普及を制御するなどの要因に対するさらなる改良により、遺伝子治療技術は、頸部内視鏡下脳症にさらに戦略的に適用される可能性があります。 そのムーアの法則は、したがって、遺伝子治療は、この病気の風景の中で最も密接に見られた新興国の一つになります。 子宮頸部疾患管理におけるイノベーションの最前線でがん経路を正確に調節する全体的な能力。
追加の洞察 子宮頸部上皮内腫瘍市場
子宮頸部の内視鏡神経(CIN)は、一般に子宮頸部のdysplasiaとして知られており、子宮頸がんに対する重要な前駆体です。 子宮頸がんにおけるHPVの役割の拡大意識で、早期発見と予防策は世界中に勢いを上げています。 現在の治療オプションは、外科的切除または陽性技術によって異常な細胞を除去することに焦点を当てています。 しかし、HPVの予防接種を認めて、将来の世代におけるCINの発生率を削減する明確な機会があります。 CIN治療の市場展望は、より良い診断ツール、HPV予防接種プログラムのグローバル展開、および新しい治療革新によって駆動され、成長のために表彰されます。 当然のことながら、非侵襲的な遺伝子治療と分子標的治療は開発中であり、高品位のCINのより少ない侵入管理を期待しています。 進歩にもかかわらず、低所得国における治療へのアクセシビリティなどの課題や、CIN患者に必要な長期フォローアップは障壁を保ちます。 次の10年は、CIN市場における重要な変化が見込まれる可能性があり、新しい治療法が新しく、より優れた予防戦略が実装されている。
競合の概要 子宮頸部上皮内腫瘍市場
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Marketで動作する主要なプレーヤーには、Pfizer Inc.、GlaxoSmithKline Plc、Novatsis AG、ジョンソン&ジョンソン・プライベートリミテッド、メルク&Co.、株式会社、AstraZeneca、Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH、Bristol-Myers Squibb、Biocon、Amgenが含まれます。
子宮頸部上皮内腫瘍市場 リーダー
- 株式会社Pfizer
- グラクソスミスクライン plc
- ノバルティスAG
- ジョンソン&ジョンソン プライベートリミテッド
- マーク&株式会社
子宮頸部上皮内腫瘍市場 - 競合関係

子宮頸部上皮内腫瘍市場
(大手プレーヤーが支配)
(多くのプレーヤーが参入し、競争が激しい。)
最近の動向 子宮頸部上皮内腫瘍市場
- 2024年2月、ジョンソン・アンド・ジョンソンは、HPV株の広範な範囲をターゲットに、改善された効力の新HPVワクチンを発売し、グローバルにCIN症例を減らすことが可能になりました。
- 2023年3月、Pfizerが有望に発表 フェーズ III 臨床結果、新しい頚部内視鏡神経治療薬。 患者様の転帰を著しく改善することが期待されます。
子宮頸部上皮内腫瘍市場 セグメンテーション
- 現在の処置によって
- HPVのワクチン接種
- 外科エクスカーション
- アブレーションセラピー
- エマージセラピー
- 遺伝子治療
- ターゲット分子 セラピー

購入オプションを検討しますか?このレポートの個々のセクション?
Vipul Patil は、製薬業界で 6 年間の経験を積んだダイナミックな経営コンサルタントです。分析力と戦略的洞察力に優れた Vipul は、製薬会社と提携して業務効率の向上、より広範な拡大、収益性の高い市場での流通の複雑さへの対応に成功しています。
よくある質問 :
子宮内腔内視鏡のネオプラシア市場はどれくらいの大きさですか?
グローバル頚部イントラピュリアル ネオプラシア市場は米ドル670.1で評価されると推定される 2024年のMnは2031年までにUSD 971.5 Mnに達すると予想されます。
子宮内腔内視鏡のネオプラシア市場とは?
子宮頸部内腔内視鏡神経内視鏡のCAGR 市場は2024-2031から5.2%になるように計画されています。
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Marketの成長を運転する主要な要因は何ですか?
子宮頸がん予防の意識を高め、HPV予防ワクチンの普及が市場成長を推進しています。 高度のスクリーニング方法のような改善された診断技術は、早期の検出率を高めますCervical Intraepithelial Neoplasiaの市場を運転する主要な要因です。
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Marketの成長を妨げる重要な要因は何ですか?
広範囲の処置および診断方法は開発途上国で障壁、特にある場合もあります。 外科切除およびablationを含む現在の処置は、合併症を引き起こし、fertilityに影響を与えることができます。 これらは、Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Marketの成長を妨げる主要な要因です。
子宮頸部内腔内視鏡検査における主要な治療は?
HPVについて ワクチン接種は、現在の治療分野をリードする。
子宮内腔内視鏡市場で動作する主要な選手はどれですか?
Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Novartis AG, Johnson & Johnson Private Limited, Inc., AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, ブリストル・マイアス・スクイブ, バイオコン, Amgenは主要なプレーヤーです。