Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Market Size - Analysis
The Global Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Market is estimated to be valued at USD 706.3 Mn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 1020.6 Mn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% from 2025 to 2032.
The market is expected to witness positive growth over the forecast period owing to the rising prevalence of cervical cancer worldwide. Increasing awareness among women population regarding early cancer detection through screening and vaccination programs is also contributing to the growth of the market. Various government initiatives and programs targeted towards screening women population are further supporting market expansion. Other factors such as new product launches, rising healthcare expenditure and improving healthcare infrastructure in developing nations will provide numerous growth opportunities in the cervical intraepithelial neoplasia market during the projected years.
Market Size in USD Mn
CAGR5.4%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 5.4% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Novartis AG, Johnson & Johnson Private Limited, Merck & Co., Inc. and Among Others |
please let us know !
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Market Trends
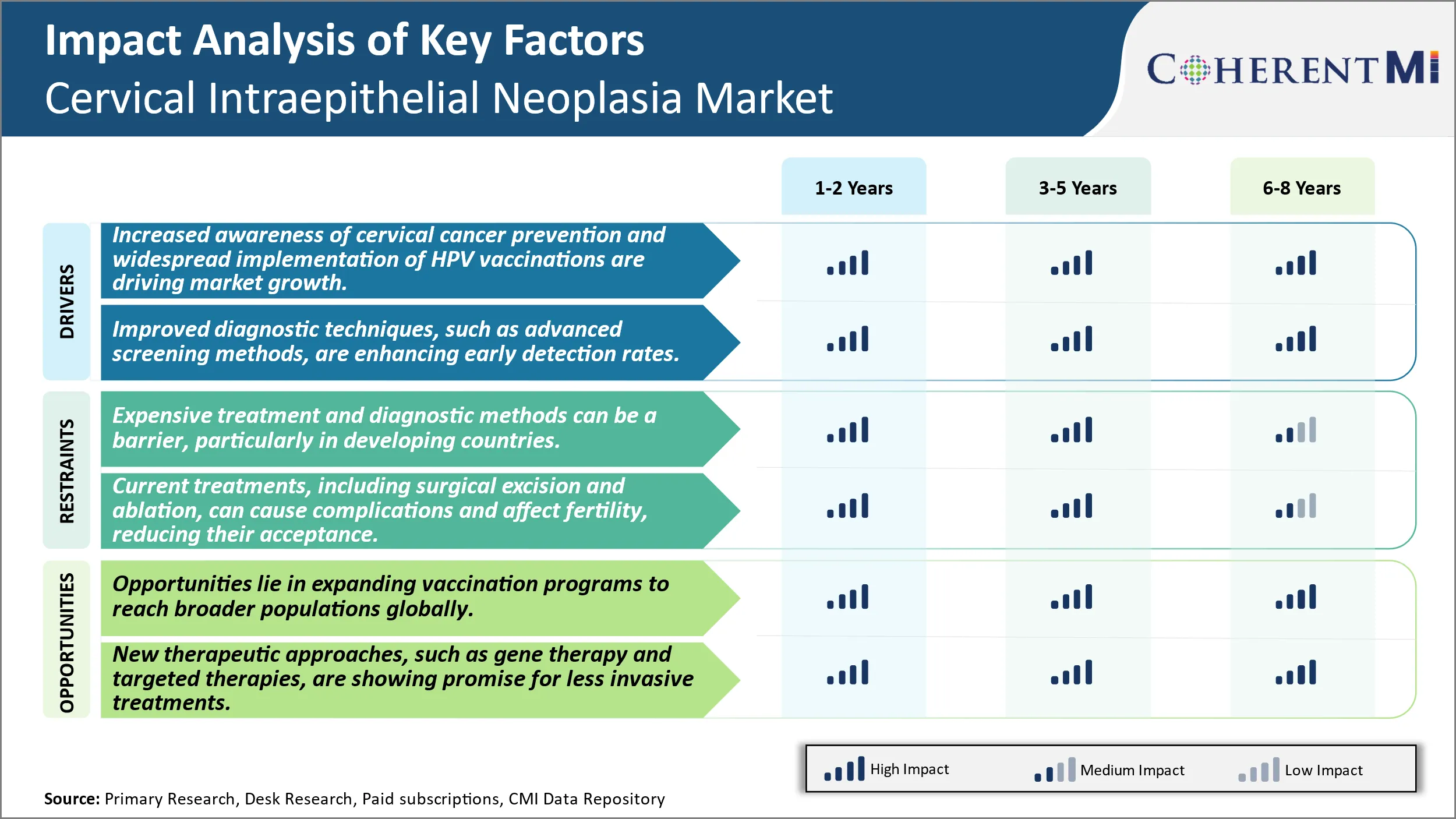
Market Driver - Increased Awareness of Cervical Cancer Prevention and Widespread Implementation of HPV Vaccinations are Driving Market Growth.
Increased awareness campaigns about the risks of cervical cancer and importance of its timely screening by governments as well as nonprofit organizations across various nations has helped educate women about this disease. Regular checkups and tests can detect pre-cancerous changes in the cervix that, if untreated, could progress into cancer. Widespread promotion about screening tests such as Pap smears through community outreach activities, social media, and primary care centers has encouraged more women to get screened.
Governments have also taken initiatives to form screening guidelines and make recommended tests affordable and accessible to boost participation. This has resulted in detection of cervical lesions at earlier treatable stages. Additionally, vaccination programs against HPV, the major cause of cervical cancer, have been expanded globally. Several countries now vaccinate girls between 9 to 14 years of age as part of national immunization programs. Nonprofits supplement these efforts through awareness drives as well as fundraising to support vaccination in resource limited areas.
As women understand how common HPV infection is and life-threatening cervical cancer can be if not acted upon in time, more are willing to take preventive measures. They wish to safeguard their health and that of other women in their lives. Healthcare professionals too stress on the importance of maintaining proper gynecological care post vaccination and through adulthood. With persistent and coordinated efforts, awareness regarding cervical cancer etiology and available screening options has risen tremendously. This is a key factor promoting early detection and timely management of pre-cancerous changes, greatly improving patient outcomes.
Market Driver- Technological Advancements in Diagnostics Fuels the Market Growth.
Rapid advancement in diagnostic technologies has enabled improved detection of pre-cancerous cervical lesions. Traditional Pap testing is now augmented by liquid-based Pap screening and more sensitive tests like HPV testing. Liquid-based Pap allows for computer assisted analysis of slides which can detect more cell abnormalities than conventional Pap tests. HPV testing acts as an efficient primary screening method as it can identify women infected with cancer causing types of HPV virus, who are then referred for colposcopy.
Advanced screening technologies like visual inspection with acetic acid and digital cervicography have raised screening adequacy in limited resource developing countries. Further, molecular diagnosis through DNA testing and cytology has enhanced specificity and accuracy of results. Biomarker assays allowing detection of tumor associated antigens in cervical secretions are also under study. Revolution in imaging technology enables capture of high-resolution cervical imagery using techniques like colposcopy, enabling magnification and digital documentation for assessment by experts remotely.
Telecytology practices where digitized Pap smears are analyzed by qualified cytopathologists elsewhere have improved screening quality in rural locations. With ongoing enhancements, novel diagnostic methods such as RNA sequencing and proteomics offer potential to discover biomarkers for early detection of cancer. Altogether, continuous tech improvements are enabling timely identification of precancerous lesions for prompt intervention before progression to late-stage malignancy. This significantly uplifts diagnosis and treatment outcomes.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - Expensive Treatment and Diagnostic Methods Can Be a Barrier, Particularly in Developing Countries.
One of the major challenges in the cervical intraepithelial neoplasia market is the high costs associated with treatment and screening methods. Cervical cancer screening typically involves regular pap smears and HPV testing, which allows for early detection and intervention. However, these diagnostic tests can be expensive, with the average pap smear costing around USD 260 in the United States. Treatment methods such as LEEP procedures, cryotherapy, or loop electrosurgical excision procedure also involve significant costs. For example, the average cost of a LEEP procedure is approximately USD 1,500. Such expensive diagnostic and treatment costs can limit access to cervical cancer prevention, especially in developing economies with limited healthcare resources. This is a major barrier as early detection and treatment is critical in managing cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and preventing progression to invasive cancer. The high costs associated with screening and treatment also place significant burdens on public health programs and private insurers. This challenges broader adoption of preventive healthcare measures and impacts the overall growth potential of the cervical intraepithelial neoplasia market.
Market Opportunity - Expansion of HPV Vaccination Programs Creates New Avenues for Future Developments.
There are also significant market opportunities in expanding human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination programs globally. HPV vaccination prior to potential exposure provides a simple, effective, and cost-efficient way to prevent cervical cancer and curb cervical intraepithelial neoplasia cases. While vaccination rates are increasing in many developed countries, coverage remains relatively low in developing regions where cervical cancer disproportionately impacts women. Opportunities lie in broadening access to HPV vaccines in these underserved communities through multilateral partnerships and equitable price differentiation. Increased vaccination uptake could dramatically reduce the incidence of cervical dysplasia and cancer over the long run. This would create opportunities for associated diagnostic testing and treatment. Expanding preventive healthcare through programs aimed at making HPV vaccines more accessible globally could drive considerable future growth in the cervical intraepithelial neoplasia market.
Prescribers preferences of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Market
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN) describes abnormal cell changes within the cervix. It is usually classified into three stages (CIN 1-3) based on how deep the abnormal cells are and how much of the cervix they affect. For mild or low-grade changes (CIN 1), treatment may not be needed since these often clear on their own. More severe or high-grade changes (CIN 2/3) are often treated to prevent progression to cancer.
Treatment options vary depending on the stage, with less invasive options tried first. For CIN 2/3, common early treatments include Leep, which removes the abnormal cells, or cryotherapy, which freezes and destroys them. If these are unsuccessful or the disease persists, a cone biopsy may be performed to remove a larger section of the cervix. For recurrent or persistent high-grade changes after initial treatment, a hysterectomy to remove the cervix and uterus may be recommended.
Prescribers consider various factors like age, severity of changes, success of prior treatments, ability to adhere to follow-up, fertility desires and more in determining the best management approach. Open communication helps establish informed, shared decisions between patients and their clinicians. The goal is always complete resolution while preserving future health and quality of life as much as possible.
Treatment Option Analysis of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Market
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN) has three stages - CIN1, CIN2 and CIN3 based on how deep the abnormal cells are in the cervix.
For CIN1, the preferred first line treatment is often monitored watchful waiting since many CIN1 lesions regress on their own. If persistent after a year, outpatient procedures like LEEP (Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure) or cryotherapy can be used. LEEP uses an electrified wire loop to remove the precancerous cells and can be performed as a same day procedure under local anesthesia. Cryotherapy freezes and destroys abnormal cells using liquid nitrogen.
For CIN2 and CIN3, LEEP is the standard first line treatment recommended to remove the precancerous cells. It has success rates over 90% and allows for histopathological examination of the excised tissue. If the margins are positive, a repeat LEEP may be required.
For recurrent or persistent high-grade CIN after LEEP, a second line treatment option is the chemotherapy drug Cisplatin. It is usually administered via a single dose injection in conjunction with a hormone therapy such as Goserelin for greater efficacy. This regime has over 70% success rate but is associated with more side effects than LEEP.
Hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus) is generally not recommended as first line treatment but may be considered in specific cases like recurrent CIN after repeated treatments or in women who have finished childbearing.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Market
R&D Investments to Develop Novel Drugs and Therapies: Major players like Roche, QIAGEN, and Hologic have consistently invested significant resources in R&D to develop advanced diagnostic tests, drugs, and minimally invasive treatment approaches for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. For example, Roche invested over USD 9.1 billion in R&D in 2020. Its cobas HPV test was approved in 2011 and has become the standard of care for primary cervical cancer screening, capturing over 70% of the U.S. market.
Strategic Acquisitions to Enhance Portfolios: Companies acquire smaller firms working on innovative therapies to rapidly expand their product offerings. For example, in 2019, QIAGEN acquired STAT-Dx, adding the novel E6/E7 mRNA test to its portfolio. This helped QIAGEN capture a larger share of the growing cervical cancer screening market. Similarly, Roche has completed multiple acquisitions to strengthen its diagnostic and pharma divisions.
Aggressive Marketing Campaigns: Given the importance of regular screening, players aggressively market their solutions to healthcare providers and patients. For example, Hologic launched multichannel education programs in 2018 highlighting the benefits of the FDA-approved Panther system for automating HPV tests. This led to a 20% increase in Hologic's revenue from the system in 2019.
Favorable Reimbursement for Modern Tests: Partnerships with government agencies and private insurers have helped companies receive favorable reimbursement coding and payment rates for novel diagnostic and screening technologies. For example, QIAGEN worked closely with CMS in the US to secure unique reimbursement codes for its E6/E7 test, expediting its adoption among clinics.
Segmental Analysis of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Market
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
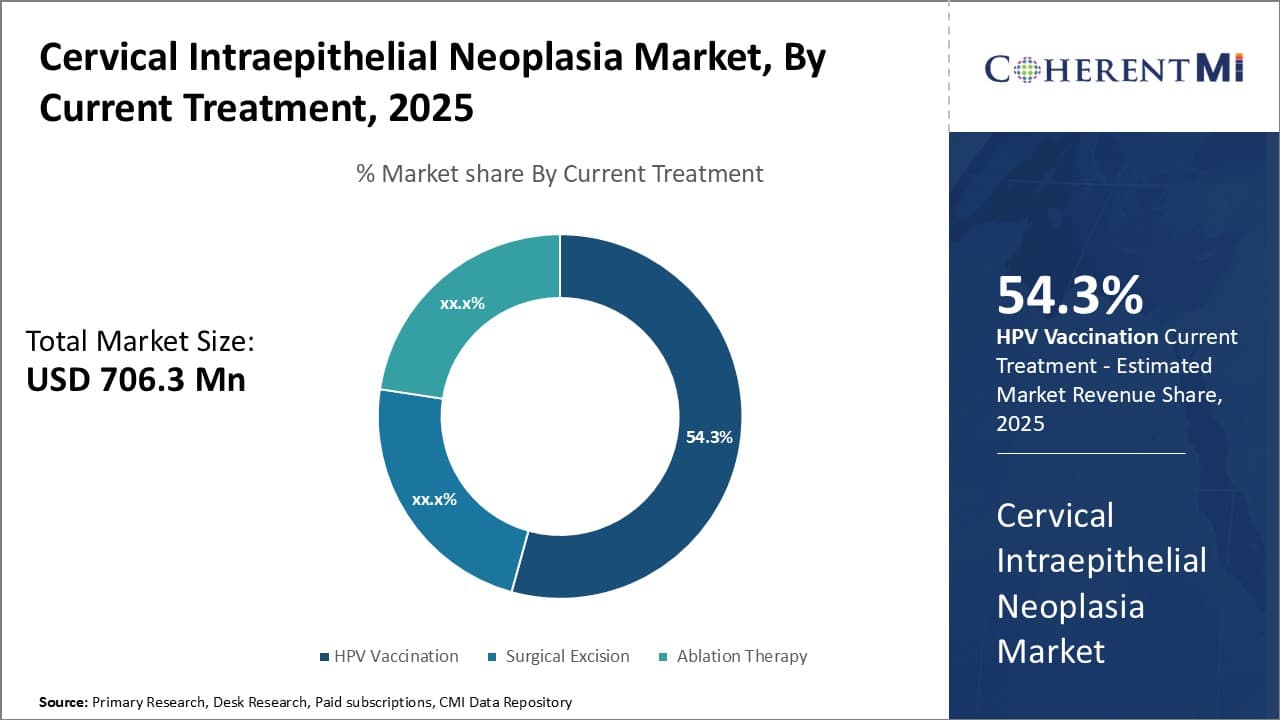
Insights, By Current Treatment HPV Vaccination Is Expected to Account for Leading Market Share in The Forecast Period.
By Current Treatment, HPV Vaccination is expected to contribute the highest share 54.3% in 2025 due to increased prevention awareness. HPV vaccination has emerged as the most effective method for preventing cervical cancer and pre-cancerous lesions caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. Widespread vaccination programs in many countries have substantially increased awareness about HPV and its link to cervical cancer. Public health authorities have played a key role in educating people, especially young girls and women, about the importance of receiving the HPV vaccine well before becoming sexually active. The fact that HPV is a very common sexually transmitted infection that puts women at risk of cancer later in life has compelled more to opt for vaccination.
Clinical studies have proven HPV vaccination to be nearly 100% effective at preventing infection from the HPV types targeted by the vaccines. Having a highly effective prevention option available has made cervical cancer and its preceding conditions feel more preventable to many. This has addressed historical fatalism surrounding such diseases. Additionally, the short duration of the vaccination schedule consisting of just two doses has made completion comparatively easier than other vaccination series. Together, improved awareness, proven efficacy, and convenience of administration have cemented HPV vaccination as the front-line defense against cervical disease for the covered HPV types.
Various initiatives from public and private entities also continue to promote HPV vaccination uptake. Educating healthcare providers remains a priority so they strongly recommend the vaccine to eligible patients. Community outreach efforts emphasize the ability of vaccination to safeguard future generations of women from a potentially grave disease. As more cohorts of adolescents complete the HPV vaccine series, the market for vaccination is poised to remain robust with repeat doses needed periodically to maintain protection. Coverage of additional HPV types by the vaccines also widens their addressable population over time. Overall, increased prevention focus has made HPV vaccination integral in current cervical disease management.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
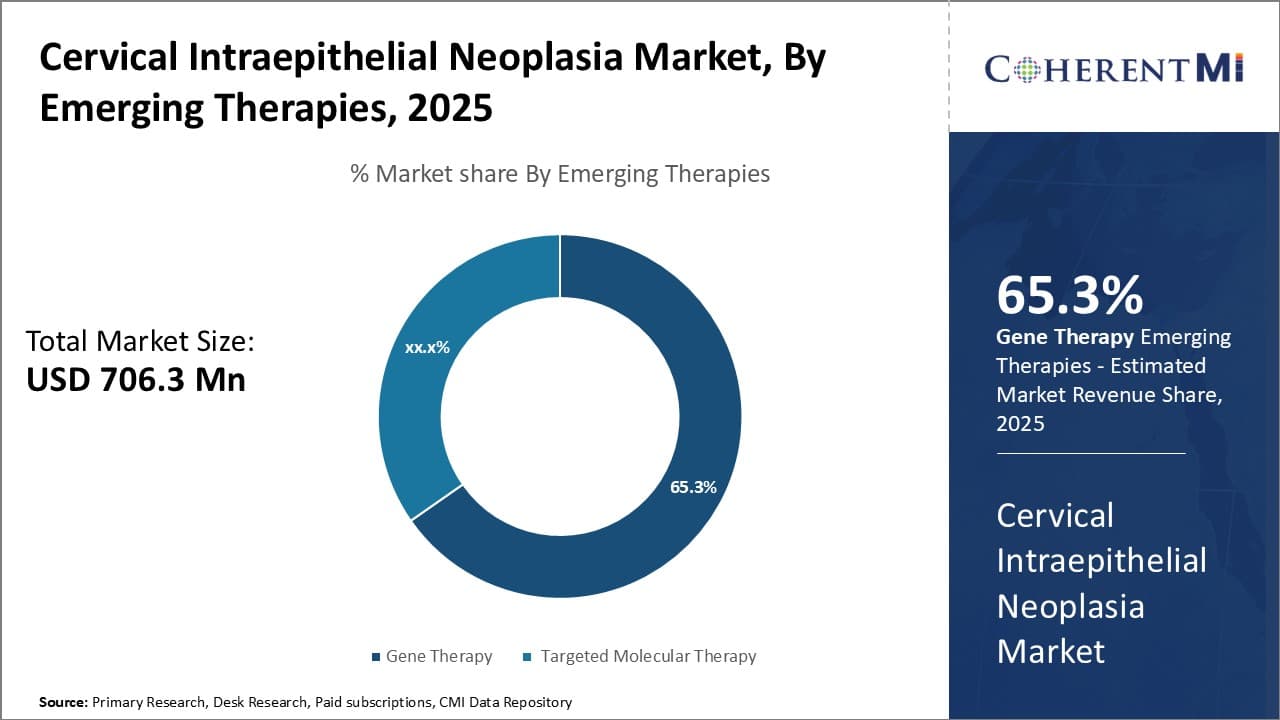
Insights, By Emerging Therapies, Gene Therapy Registered a Leading Share in 2024.
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Emerging Therapies, Gene Therapy Registered a Leading Share in 2024.
By Emerging Therapies, the Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Market, Gene Therapy contributes the highest share 65.3% in 2025 owing to its targeted approach. Among emerging novel treatment approaches for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, gene therapy is demonstrating significant promise. Gene therapy involves the deliberate introduction, alteration, or removal of genes inside or outside cells and tissues to treat disease. In the case of cervical cancer and its precursors, gene therapy researchers are working on developing targeted vectors to deliver therapeutic genetic payloads directly into cancer or dysplastic cells. One of the major advantages of gene therapy is its potential to precisely interfere with molecular pathways underlying neoplastic proliferation, invasion and metastasis. Rather than traditional chemotherapy which carries wider toxic effects, gene therapy may produce local effects through optimized vector design and gene silencing mechanisms. Early clinical trials involving insertion of tumor suppressor genes or blocking of oncogenes in cervical lesions have shown gene therapy to achieve remission of dysplasia with fewer adverse reactions.
The molecular targeting ability also allows gene therapy to better overcome issues like drug resistance seen with conventional pharmacological interventions over time. Additionally, advancements in viral and non-viral vector engineering continue to enhance the safety and efficacy of gene delivery for cervical disease. With more refinements to factors such as transgene expression duration and controlling vector dissemination, gene therapy techniques could become even more strategically applicable for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Its Moore's Law driven progress therefore makes gene therapy one of the most closely watched emerging modalities in this disease landscape. Overall ability to precisely downregulate cancer pathways at the genetic level positions gene therapy at the forefront of innovation in cervical disease management.
Additional Insights of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Market
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), commonly known as cervical dysplasia, is a significant precursor to cervical cancer. With the growing awareness of the role of HPV in cervical cancer, early detection and prevention measures are gaining momentum globally. Current treatment options focus on removing the abnormal cells through surgical excision or ablative techniques. However, with the advent of HPV vaccination, there is a clear opportunity to reduce the incidence of CIN in future generations. The market outlook for CIN treatment is poised for growth, driven by better diagnostic tools, the global expansion of HPV vaccination programs, and new therapeutic innovations. Notably, non-invasive gene therapies and molecular-targeted treatments are in development, providing hope for less intrusive management of high-grade CIN. Despite the advancements, challenges such as accessibility to treatment in lower-income countries and the long-term follow-up needed for CIN patients remain barriers. The next decade is likely to see significant shifts in the CIN market, with new therapies emerging and better preventative strategies being implemented.
Competitive overview of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Market
The major players operating in the Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Market include Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Novartis AG, Johnson & Johnson Private Limited, Merck & Co., Inc., AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Biocon and Amgen.
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Market Leaders
- Pfizer Inc.
- GlaxoSmithKline plc
- Novartis AG
- Johnson & Johnson Private Limited
- Merck & Co., Inc.
Recent Developments in Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Market
- In February 2024, Johnson & Johnson launched a new HPV vaccine with improved efficacy, targeting a broader range of HPV strains, potentially reducing CIN cases globally.
- In March 2023, Pfizer announced promising Phase III clinical results for their new cervical intraepithelial neoplasia treatment drug. This advancement is expected to improve patient outcomes significantly.
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Market Segmentation
- By Current Treatment
- HPV Vaccination
- Surgical Excision
- Ablation Therapy
- By Emerging Therapies
- Gene Therapy
- Targeted Molecular Therapy
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
