Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) Market Size - Analysis
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR6.9%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 6.9% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | NIHON KOHDEN CORPORATION, Koninklijke Philips N.V., GENERAL ELECTRIC COMPANY, Siemens Healthcare Private Limited, Natus Medical Incorporated and Among Others |
please let us know !
Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) Market Trends
Clinically Isolated Syndrome is often considered as the initial clinical presentation of Multiple Sclerosis. However, it can progress to MS in some cases while remain isolated in others. This brings a sense of uncertainty for patients experiencing CIS symptoms. In recent years, advocacy initiatives by non-profit organizations as well as social media influence have ensured dissemination of information about subtle yet significant symptoms of early signs of MS and other neurological conditions.
All this has prompted many to seek specialist opinions for even the slightest of sensory issues or visual disturbances in the past. Overall, growing health awareness is effectively reducing diagnostic delays and supports early identification of CIS cases. This plays a big role in clinical management and holds significance for long-term prognosis.
Market Driver - Increasing Diagnostic Capabilities and Advancements in Neuroimaging Techniques
MRIs are able to identify minute tissue abnormalities invisible on older, low-resolution machines. Availability of improved MRI equipment along with optimized scanning protocols at major hospitals have enabled radiologists and neurologists to detect even asymptomatic white matter lesions seen in early MS with a high degree of certainty.
Additionally, Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans examining biochemical and pathological brain changes at cellular level provide important disease insights beyond traditional MRI findings. Overall, ongoing innovations in neuroimaging sphere have elevated CIS and MS diagnostic abilities to an unprecedented level. This empowers clinicians worldwide to detect CIS at its onset and make well-informed management decisions promptly.
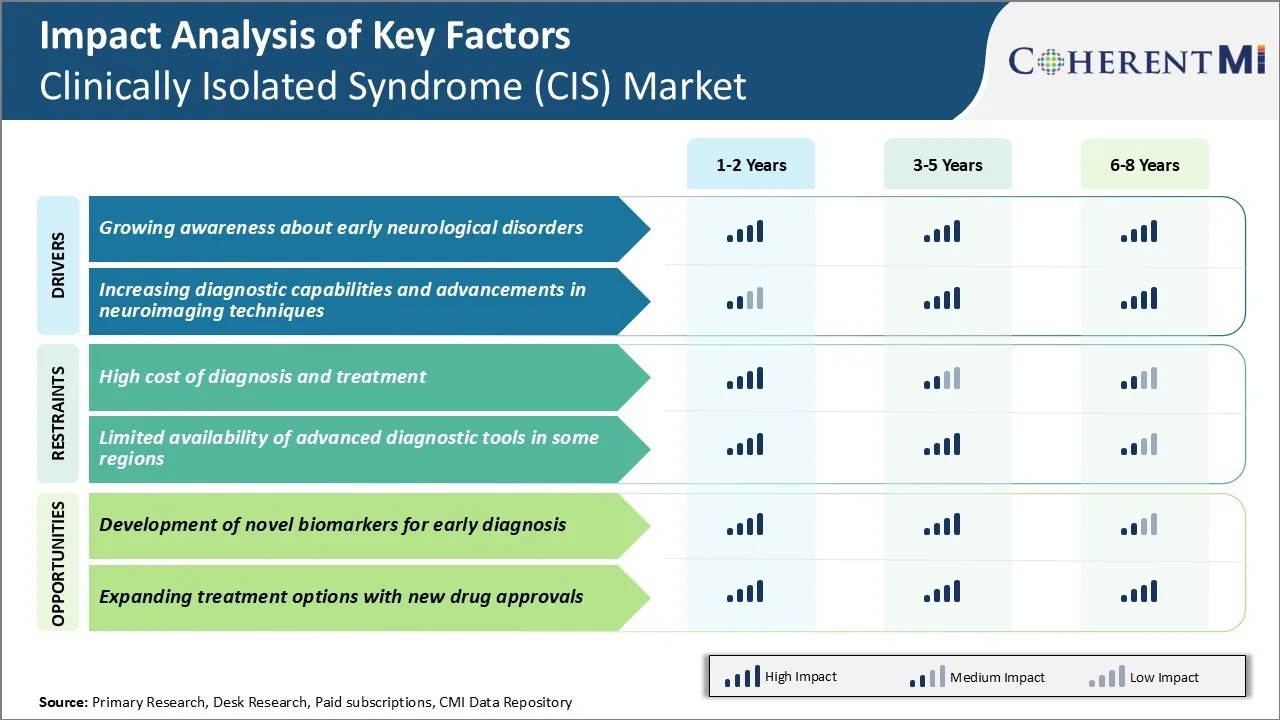
One of the key challenges faced by the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) market is the high cost associated with diagnosing and treating CIS patients. Diagnosing CIS requires advanced medical imaging techniques like MRI scans of the brain and spine to detect lesions. Performing detailed MRI scans regularly to monitor the progression of lesions in CIS patients contribute significantly to the overall cost of diagnosis.
While several highly effective disease-modifying therapies are available for CIS patients who progress to MS, their high drug prices restrict access for many patients. The out-of-pocket costs incurred for treatments especially for patients from lower socioeconomic backgrounds can be enormous and often prove to be unsustainable. Addressing these financial challenges surrounding diagnosis and treatment will be important for the long-term growth of the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) market.
Market Opportunity - Development of Novel Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis
However, MRI may not always be able to identify early lesions. The development of liquid biomarkers that can be detected through simple blood or CSF tests can help diagnose CIS at a much earlier stage before lesions appear on MRI. Biomarker research focused on identifying proteins, genes or metabolites specifically associated with the onset and progression of CIS can potentially enable detecting the disease even before the appearance of initial clinical symptoms.
Wider adoption of accurate and easy-to-use biomarkers for CIS diagnosis globally would significantly expand the addressable market size over the long term. Several companies are actively investing in biomarker research to tap into this high growth opportunity area within the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) market.
Prescribers preferences of Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) Market
CIS refers to the initial clinical presentation of multiple sclerosis (MS), characterized by an acute, clinically documented attack of neurologic symptoms. For patients diagnosed with CIS, prescribers generally consider disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) soon after the event to help prevent or delay progression to clinically definite MS.
For patients who continue experiencing relapses or show signs of disease progression on first-line therapies, prescribers may switch to second-line high-potency DMTs. Popular options include oral teriflunomide (Aubagio), which offers convenience, or injectable dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera), which has a milder side effect profile than some alternatives. Daclizumab (Zinbryta) was previously used but has been withdrawn from markets due to safety concerns.
Treatment Option Analysis of Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) Market
CIS represents the earliest stage of multiple sclerosis (MS), where patients present with a single clinical episode suggestive of demyelination in the central nervous system. There are typically three stages seen in CIS progression - CIS itself, relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS), and secondary progressive MS (SPMS).
If patients progress to RRMS, treatments aim to reduce relapse rate and new lesion formation. Highly effective therapies include glatiramer acetate (Copaxone), teriflunomide (Aubagio), dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera), and the monoclonal antibodies like alemtuzumab (Lemtrada) and ocrelizumab (Ocrevus). Selection depends on factors like efficacy evidence from trials, route of administration, side effect risks, insurance coverage and patient preference.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) Market
Product Innovation: Successful companies in this market have continuously innovated and launched new products to address unmet needs. In 2017, Roche launched Ocrevus, the first and only disease modifying treatment approved for both relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) and CIS. This was a breakthrough as it was the first drug approved for CIS treatment. Ocrevus saw strong uptake and achieved $1 billion in sales by 2019.
Expanded Indications: Obtaining approval for additional CIS/MS indications expands addressable markets. In 2019, Novartis gained FDA approval of Gilenya for treating CIS based on data from the FREEDOMS II trial. This grew Gilenya's revenue by 10% as it captured more CIS patients before progression to MS.
Segmental Analysis of Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) Market
-market-by-diagnosis.png) Insights, By Diagnosis: Neuroimaging Drives Diagnosis Segment Due to Precision and Early Detection Capabilities
Insights, By Diagnosis: Neuroimaging Drives Diagnosis Segment Due to Precision and Early Detection CapabilitiesThe neuroimaging segment is estimated to hold 55.3% market share in 2025, for CIS diagnosis due to its unique ability to detect lesions in the central nervous system with great precision. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can reveal even very small lesions that may not be detected through other diagnostic methods like neurological exams. This high resolution and sensitivity make neuroimaging the gold standard for CIS diagnosis.
New contrast agents further increase the visibility of lesions. These continual improvements boost the diagnostic value of neuroimaging, driving its uptake among clinicians. Overall, neuroimaging emerges as the preferred initial tool for CIS diagnosis due to its proven accuracy, sensitivity and reassurance it provides patients and physicians alike regarding the need for swift treatment intervention.
-market-by-treatment.webp)
Disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) is projected to constitute 47.7% of the market share in 2025, primarily due to their ability to potentially slow the progression to clinically definite multiple sclerosis (MS). DMTs target the underlying disease process in MS rather than just symptom relief. They work to reduce inflammation, prevent new lesions from forming, and limit existing lesion activity/growth. Evidence shows early treatment with effective DMTs after a CIS event can cut the risk of converting to MS by 30-50% within two years.
By modifying the underlying disease, clinicians aim to prevent or delay subsequent disabling relapses and onset of progressive disability that significantly impacts quality of life. This makes early DMT initiation post-CIS diagnosis crucial from both medical and economic perspectives. It underscores the dominance of the disease-modifying therapies segment in CIS treatment protocols due to its potential for slowing disease progression long-term.
Additional Insights of Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) Market
- In 2023, Spain had 826 CIS cases, expected to increase during the forecast period.
- Phenotype-specific prevalence data provided for multiple sclerosis subtypes in various countries.
- Early treatment after the first clinical event reduces the risk of progression to multiple sclerosis.
- Elevated NfL levels increase the likelihood of progression to MS, suggesting it could serve as a prognostic marker.
Competitive overview of Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) Market
The major players operating in the Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) Market include NIHON KOHDEN CORPORATION, Koninklijke Philips N.V., GENERAL ELECTRIC COMPANY, Siemens Healthcare Private Limited, Natus Medical Incorporated, and Compumedics Limited.
Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) Market Leaders
- NIHON KOHDEN CORPORATION
- Koninklijke Philips N.V.
- GENERAL ELECTRIC COMPANY
- Siemens Healthcare Private Limited
- Natus Medical Incorporated
Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) Market - Competitive Rivalry

Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) Market
- In April 2024, high blood levels of neurofilament light chain (NfL) were identified as a prognostic marker for the progression to multiple sclerosis (MS) in patients with Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS). Studies showed that CIS patients with elevated NfL levels had a higher risk of converting to MS and transitioned earlier than those with lower NfL levels. Early treatment following the first clinical event significantly reduced the risk of this transition.
- In August 2023, the FDA approved Tyruko® (natalizumab-sztn), the first biosimilar to Tysabri (natalizumab), for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS), including clinically isolated syndrome (CIS). The approval was based on robust Phase I and III clinical trials, demonstrating that Tyruko provides similar efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity as the reference medicine Tysabri. This makes Tyruko the first and only FDA-approved biosimilar for these indications.
Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) Market Segmentation
- By Diagnosis
- Neuroimaging
- Laboratory Tests
- Lumbar Puncture
- Neurological Examination
- By Treatment
- Disease-Modifying Therapies
- Symptomatic Treatment
- Corticosteroids

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) market?
The clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) market is estimated to be valued at USD 17.14 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 27.34 Bn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) market?
The high cost of diagnosis and treatment and limited availability of advanced diagnostic tools in some regions are the major factors hampering the growth of the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) market.
What are the major factors driving the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) market growth?
The growing awareness about early neurological disorders, increasing diagnostic capabilities, and advancements in neuroimaging techniques are the major factors driving the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) market.
Which is the leading diagnosis in the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) market?
The leading diagnosis segment is neuroimaging.
Which are the major players operating in the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) market?
NIHON KOHDEN CORPORATION, Koninklijke Philips N.V., GENERAL ELECTRIC COMPANY, Siemens Healthcare Private Limited, Natus Medical Incorporated, Compumedics Limited are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) market?
The CAGR of the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) market is projected to be 6.9% from 2025-2032.