Diarrhea Therapeutics Market Size - Analysis
The Global Diarrhea Therapeutics Market is estimated to be valued at USD 4.07 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 5.46 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2025 to 2032.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR4.3%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 4.3% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Vedanta Biosciences, Inc., RedHill Biopharma Limited, Hunazine Biotech, Eveliqure Biotechnologies GmbH, Cosmo Pharmaceuticals and Among Others |
please let us know !
Diarrhea Therapeutics Market Trends
Diarrheal diseases remain a significant cause of illness and death worldwide, especially in developing regions of Asia, Africa, and Latin America that have poor sanitation and limited access to clean drinking water. The World Health Organization estimates that diarrhea is responsible for over 1.5 million deaths annually, mostly among children under five years of age living in low-income settings. The main pathogens implicated in such endemic diarrhea cases include rotavirus, norovirus, Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, and pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli (E. coli). Rates of diarrhea morbidity and mortality have decreased in recent decades due to public health measures like improved water treatment and handwashing education. However, populations remain vulnerable, and outbreaks can still overwhelm weak health systems. The continuous threat posed by diarrheal illnesses is driving demand for preventive options like rotavirus vaccines as well as effective treatments that can help manage severe dehydration caused by watery stools and vomiting. Oral rehydration solution remains the standard of care, but many patients would benefit from anti-motility and anti-secretory drugs that can help control diarrhea episodes more quickly. Furthermore, if emerging pathogens acquire antibiotic resistance traits, newer anti-diarrheal drugs targeting virulence factors or immune modulation may be needed. The high disease burden associated with diarrhea in developing nations represents a substantial unmet need and commercial opportunity for manufacturers of innovative diarrhea therapeutics.
Market Driver - Advancements in Microbiome-Based Therapies Boosts Industry Growth.
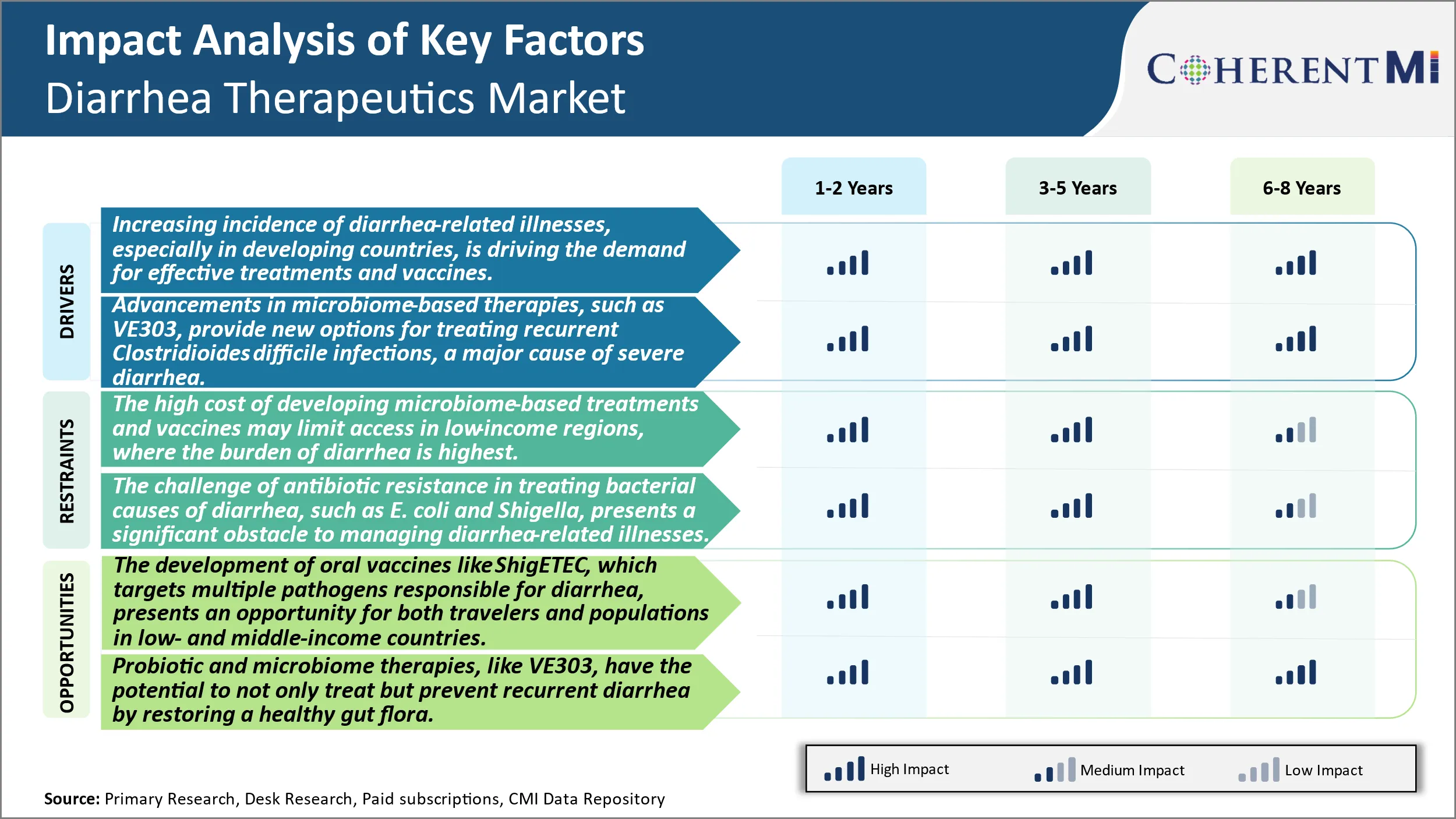
Market Challenge - The High Cost of Developing Microbiome-Based Treatments and Vaccines May Limit Access in Low-Income Regions, Where the Rate of Diarrhea is Highest.
The development of oral vaccines like ShigETEC, which targets multiple pathogens responsible for diarrhea, presents an opportunity for both travelers and populations in low- and middle-income countries. Oral vaccines have major advantages over injectables in terms of easier administration, which increases compliance and coverage. For travelers going to high- risk regions, an oral preventative solution could provide peace of mind without the need for visits to clinics. In vulnerable developing populations that experience frequent outbreaks, broad-spectrum diarrhea vaccines have the potential for major public health impacts if distribution challenges can be addressed. Successful implementation could help control endemic diarrhea and reduce the health burden on underfunded medical systems. Global health groups are keen to support trials and adoption of affordable diarrhea vaccines with the potential for widespread use.
Prescribers preferences of Diarrhea Therapeutics Market
Diarrhea is typically classified by its duration as acute or persistent. For acute diarrhea lasting less than 14 days, over-the-counter oral rehydration salts (ORS) are usually the first line of treatment. Example brands include Pedialyte and DripDrop.
Persistent diarrhea lasting 14 days or more is evaluated for underlying causes. Stool tests help identify parasitic (e.g. Giardia lambia), viral (e.g.norovirus) or bacterial (e.g. C. difficile) infections. Targeted antibiotic therapy follows based on confirmed pathogens.
Additional factors like patient age, comorbidities, tolerability, insurance approval and resistance patterns impact drug choice. Younger patients are less likely to receive antibiotics without clear causes identified. Brand availability and costs also guide prescribers towards similar generic alternatives when possible.
Treatment Option Analysis of Diarrhea Therapeutics Market
Diarrhea can range from mild to severe depending on the underlying cause and requires different lines of treatment. Mild cases are usually treated with oral rehydration therapy (ORT) using oral rehydration solutions (ORS) which replace lost electrolytes and fluids. ORS brands like Electral and Oraline are easily available and affordable options.
In case of persisting symptoms beyond 5-7 days despite ORS/antibiotics, the patient is evaluated for parasitic infestations. Altered blood reports or stool samples confirming Giardia lamblia or other parasites will warrant anti-parasitic treatment. Tinidazole 2g stat, a nitroimidazole derivative with broad spectrum anti-parasitic action is frequently prescribed.
Appropriate and timely management following established treatment guidelines is key to achieve positive outcomes in diarrhea. Choice of medication depends on severity, suspected cause and patient profile.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Diarrhea Therapeutics Market
One of the major strategies adopted by players has been focusing on developing innovative and improved treatment options. For example, in 2019, Salix Pharmaceuticals launched Xifaxan (rifaximin) 550 mg tablets to treat travelers' diarrhea caused by noninvasive strains of Escherichia coli in adults and children 12 years of age and older. Clinical trials demonstrated that Xifaxan was effective in significantly reducing the duration of travelers' diarrhea compared to placebo. This innovative product helped Salix gain a competitive advantage in the travelers' diarrhea segment.
Partnering and collaboration have also emerged as a vital strategy. In 2017, Shire partnered with Galapagos to develop novel cystic fibrosis treatments. This helped both companies to leverage their combined clinical development expertise. Shire also provided USD50 million upfront payment, signaling its commitment to developing novel treatments for cystic fibrosis. Such partnerships enable companies to reduce R&D costs and risks.
Segmental Analysis of Diarrhea Therapeutics Market
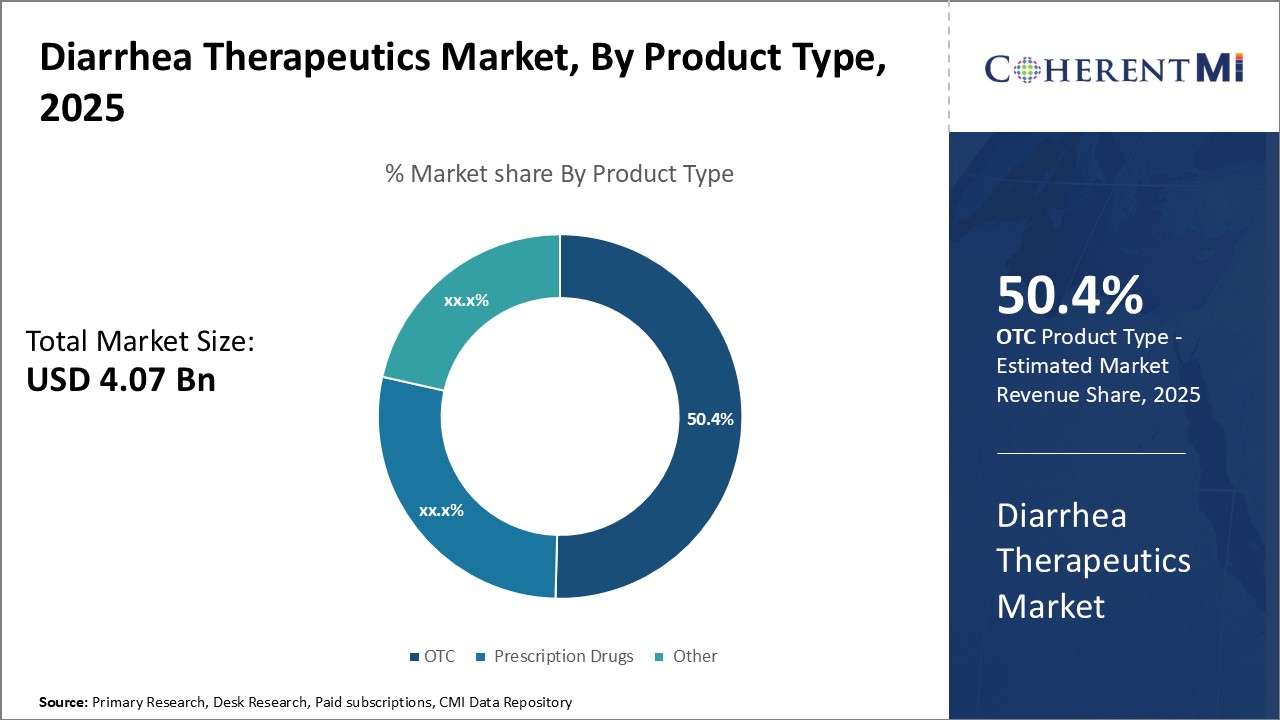 Insights, By Product Type, Convenience and Affordability Drive High OTC Share
Insights, By Product Type, Convenience and Affordability Drive High OTC ShareBy product type, OTC is expected to contribute the highest share 50.4% in 2025 based on convenience and affordability. People suffering from diarrhea often prefer OTC drugs as they are easily available without a prescription. This allows treatment to begin immediately without needing to visit a doctor. OTC drugs are also significantly more affordable than prescription medication. With diarrhea being a common ailment, affordability is an important factor for consumers. Many opt for OTC brands they are familiar with and trust to effectively treat symptoms. Their wide availability at all local drug stores and supermarkets makes them a highly convenient and cost-effective option. Common OTC products include anti-diarrheal medications like loperamide, bismuth subsalicylate, and oral rehydration solutions. These treatments are widely used for conditions such as traveler's diarrhea or food-related issues. The convenience and affordability of OTC medications make them a preferred choice for self-medication, driving their demand in the global market.
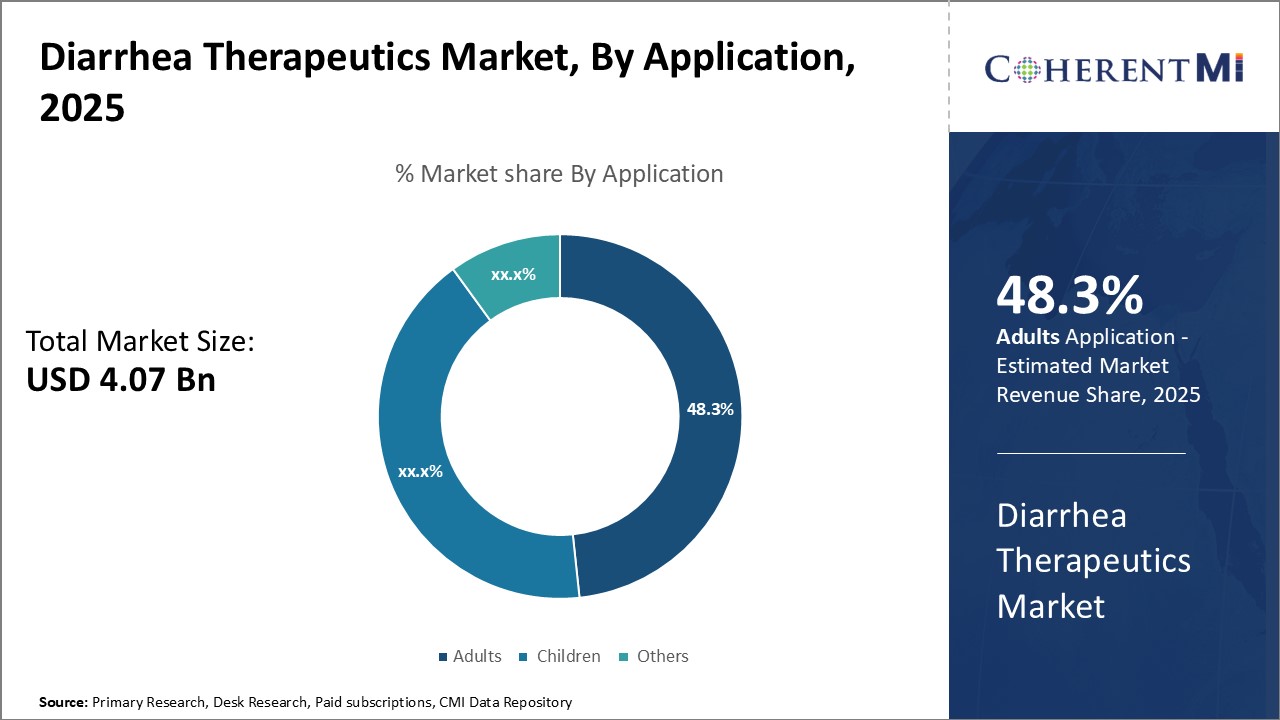
By application, adults contribute the highest share 48.3% in 2025 owing to having the highest incidence rate of diarrhea. Diarrhea affects people of all ages but is more commonly experienced by adults compared to children. Changes in diet, lifestyle and stress levels make adults more prone to gastrointestinal issues that can potentially lead to diarrhea. Risk is further heightened for older individuals with declining immunity. Adults also account for a larger demographic segment of the overall population. The adult segment in the diarrhea therapeutics market plays a significant role due to the prevalence of conditions like traveler's diarrhea, antibiotic-associated diarrhea, and chronic diarrhea linked to gastrointestinal disorders. Adults, especially immunocompromised individuals and the elderly, are susceptible to severe outcomes. Therapeutics, including oral rehydration solutions, antibiotics, probiotics, and microbiome-based treatments, are vital for managing acute and chronic diarrhea, improving patient outcomes, and reducing hospitalizations in this demographic.
Insights, By End-user, Hospitals Lead Due to Severe Cases and Insurance Coverage in the Forecast Period.
Additional Insights of Diarrhea Therapeutics Market
The pipeline for diarrhea-related treatments is expanding, with new therapies targeting both the prevention and treatment of severe diarrhea. Microbiome-based therapies, such as Vedanta Biosciences’ VE303, are advancing into late-stage clinical trials and show promise in preventing recurrent Clostridioides difficile infections, which can lead to chronic diarrhea. Similarly, oral vaccines like Eveliqure Biotechnologies’ ShigETEC, targeting both Shigella and E. coli, represent a new approach to preventing traveler’s diarrhea and other infectious diarrheal diseases. Despite these advances, significant challenges remain, including the high cost of developing new treatments and the growing threat of antibiotic resistance in managing bacterial diarrhea. However, the growing focus on preventive therapies, including vaccines and probiotic-based treatments, provides hope for reducing the global burden of diarrhea, particularly in low- and middle-income countries where the impact is most severe. The future prospects in diarrhea management will likely involve a combination of preventive strategies, targeted treatments, and new technologies aimed at restoring a healthy gut microbiome.
Competitive overview of Diarrhea Therapeutics Market
The major players operating in the Diarrhea Therapeutics Market include Vedanta Biosciences, Inc., RedHill Biopharma Limited, Hunazine Biotech, Eveliqure Biotechnologies GmbH, Cosmo Pharmaceuticals, Ipsen Corporate, Salix Pharmaceuticals, Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Napo Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals.
Diarrhea Therapeutics Market Leaders
- Vedanta Biosciences, Inc.
- RedHill Biopharma Limited
- Hunazine Biotech
- Eveliqure Biotechnologies GmbH
- Cosmo Pharmaceuticals
Diarrhea Therapeutics Market - Competitive Rivalry

Diarrhea Therapeutics Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Diarrhea Therapeutics Market
- In May 2024, Vedanta Biosciences’ VE303 entered Phase III trials. It is a defined bacterial consortium designed to prevent Clostridioides difficile infection, aiming to reduce the recurrence of diarrhea in high-risk patients.
- In April 2024, RedHill Biopharma advanced RHB-102 to Phase II trials, offering a once-daily oral formulation of ondansetron to alleviate nausea and vomiting associated with gastrointestinal conditions, including diarrhea.
- In March 2024, Hunazine Biotech continued Phase II trials for VR-AD-1005, targeting severe cholera-induced diarrhea by reducing liquid stool volume without affecting motility.
Diarrhea Therapeutics Market Segmentation
- By Product Type
- OTC
- Prescription Drugs
- Other
- By Application
- Adults
- Children
- Others
- By End-user
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Diagnostic Centers
- Drug Stores
- By Drug Class
- Absorbents
- Mucosal Protectants
- Motility Modifying Drugs

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How Big is the Diarrhea Therapeutics Market?
The Global Diarrhea Therapeutics Market is estimated to be valued at USD 4.07 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 5.46 billion by 2032.
What will be the CAGR of the Diarrhea Therapeutics Market?
The CAGR of the Diarrhea Therapeutics Market is projected to be 4.10% from 2024 to 2031.
What are the major factors driving the Diarrhea Therapeutics Market growth?
The increasing incidence of diarrhea-related illnesses, especially in developing countries, is driving the demand for effective treatments and vaccines. Advancements in microbiome-based therapies, such as ve303, provide new options for treating recurrent clostridioides difficile infections, a major cause of severe diarrhea are the major factors driving the Diarrhea Therapeutics Market.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the Diarrhea Therapeutics Market?
The high cost of developing microbiome-based treatments and vaccines may limit access in low-income regions, where the burden of diarrhea is highest and the challenge of antibiotic resistance in treating bacterial causes of diarrhea, such as E. coli and Shigella, presents a significant obstacle to managing diarrhea-related illnesses. These are the major factors hampering the growth of Diarrhea Therapeutics Market.
Which is the leading Product Type in the Diarrhea Therapeutics Market?
OTC is the leading product type segment.
Which are the major players operating in the Diarrhea Therapeutics Market?
Vedanta Biosciences, Inc., RedHill Biopharma Limited, Hunazine Biotech, Eveliqure Biotechnologies GmbH, Cosmo Pharmaceuticals, Ipsen Corporate, Salix Pharmaceuticals, Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Napo Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals are the major players.