EGFR Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) Market Size - Analysis
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR7.9%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 7.9% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | AstraZeneca, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Roche, Novartis and Among Others |
please let us know !
EGFR Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) Market Trends
The occurrence of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cases harboring epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations has witnessed a marked rise over the past decade. Statistics show lung cancer is now the most commonly diagnosed cancer as well as the leading cause of cancer death among both men and women in the United States. This genomic alteration is known to drive tumor growth and disease progression in NSCLC patients.
A majority of EGFR mutations occur in exons 18 to 21 of the gene which encodes the tyrosine kinase domain of EGFR. Widespread screening combined with growing NSCLC patient volumes has significantly raised the base number of new EGFR mutation-positive diagnoses every year. Rising incidence trend of targetable EGFR mutant NSCLC presents a sizable opportunity for pharmaceutical innovations in this space.
Market Driver - Strong Clinical Advancements in EGFR Inhibitors
Continued R&D in this field has led to second and third-generation compounds with enhanced efficacy. Osimertinib is a potent, irreversible EGFR-TKI targeting the T790M resistance mutation and was the first drug to demonstrate a progression-free and overall survival benefit over platinum-based chemotherapy in the second-line setting.
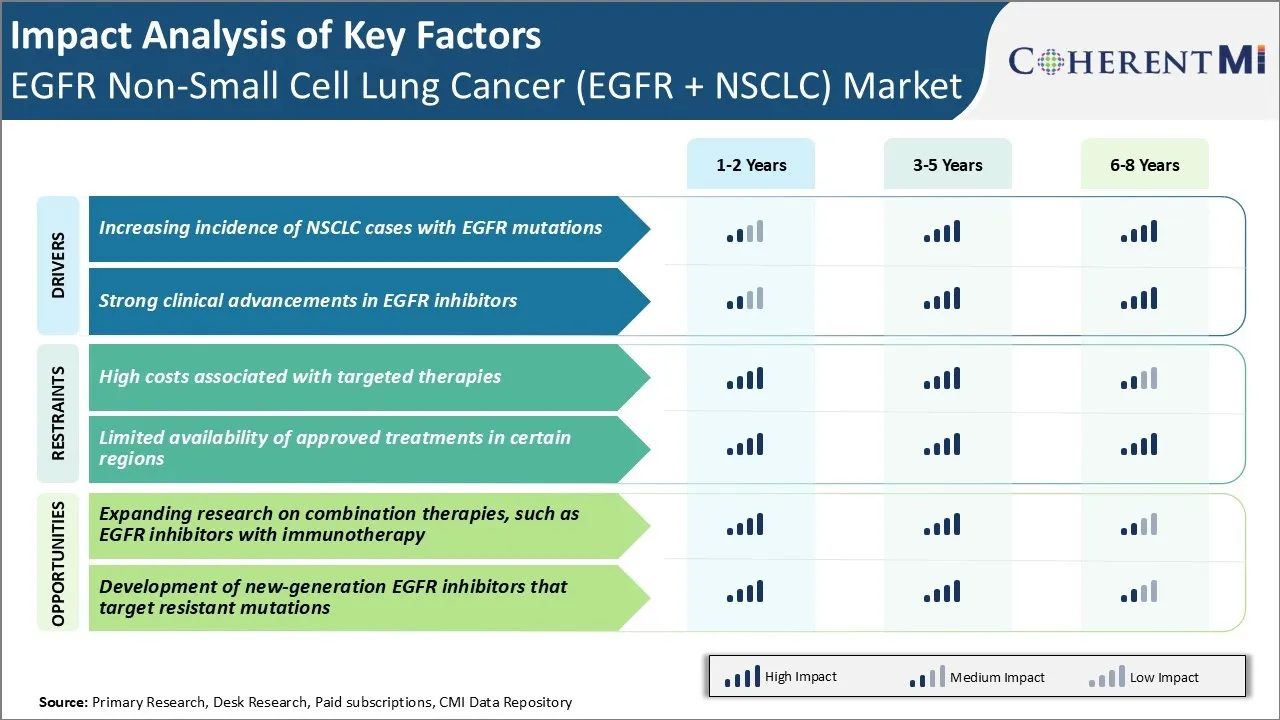
Market Challenge - High Costs Associated with Targeted Therapies
Additionally, the costs put a huge strain on public and private health insurance budgets. While targeted therapies have improved clinical outcomes compared to chemotherapy, the expense involved limits their widespread accessibility and adoption. Drug developers will need to explore strategies to make these life-saving drugs more affordable without compromising on their efficacy.
Market Opportunity - Expanding Research on Combination Therapies
Ongoing clinical trials are evaluating the safety and efficacy of combining EGFR inhibitors like osimertinib and gefitinib with immune checkpoint inhibitors like pembrolizumab. Positive results from such studies could establish EGFR inhibitor plus immunotherapy combinations as an important new standard of care.
Prescribers preferences of EGFR Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) Market
EGFR mutations are common in NSCLC, occurring in 10-15% of cases. Treatment approaches vary depending on disease stage and line of therapy. For early-stage EGFR+ NSCLC, surgical resection is the standard first-line treatment.
Upon disease progression, prescribers often consider second-generation EGFR TKIs like Tagrisso (osimertinib). Tagrisso selectively targets both common EGFR mutations as well as the resistant T790M mutation, making it an important second-line option. It has significantly improved outcomes versus platinum chemotherapy in this setting.
Overall treatment selection is influenced by mutation status, performance status, organ dysfunction, prior treatment history, and availability of clinical trial options.
Treatment Option Analysis of EGFR Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) Market
EGFR + NSCLC can be treated based on the stage of cancer. For stage I-IIIA disease, surgery is the standard first-line treatment with the goal of removing the tumor. For patients whose cancer has spread to distant areas (stage IV), systemic therapy is preferred.
For patients who progress on first-line TKI treatment, second-line options include chemo drugs like pemetrexed (Alimta) or docetaxel. Some may benefit from switching to a different TKI like osimertinib (Tagrisso) which is able to overcome common resistance mutations. For those who progress on second-line chemotherapy or TKI, third-line treatment choices consist of chemotherapy, clinical trials, or best supportive care depending on performance status and tumor burden. The goal at this stage is to improve quality of life by controlling cancer progression.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of EGFR Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) Market
Roche's acquisition of Genentech in 2009 was a strategic move to gain access to Genentech's biomarker testing capabilities and FDA-approved EGFR inhibitor Tarceva (erlotinib). This acquisition positioned Roche as the leading player in the EGFR + NSCLC market. Tarceva was the first FDA-approved EGFR TKI therapy and dominated the EGFR non-small cell lung cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) market until 2015. By acquiring Genentech, Roche combined drug development and diagnostic capabilities that helped drive personalized treatment of EGFR+ patients.
PFE/Merck's Tagrisso faced latest entry challenges but it adopted a two-pronged strategy - an 'umbrella' trial studying Tagrisso for all EGFR+ populations and providing comprehensive access programs. This helped communicate Tagrisso's broader utility and overcome access barriers. Between 2017-2019, Tagrisso's market share doubled to over 30% in the overall EGFR TKI market, demonstrating the success of PFE/Merck's strategy.
Segmental Analysis of EGFR Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) Market
-market-by-treatment.webp)
Insights, By Treatment: New Targeted Therapies Driving Growth of EGFR-TKI Inhibitors
The superior clinical efficacy demonstrated by EGFR-TKI inhibitors in improving progression-free survival as well as overall survival rates among NSCLC patients with activating EGFR mutations has made them the standard of care as first-line treatment for this specific patient subgroup.
-market-by-stages-of-the-disease.webp) Insights, By Stages of the Disease: Early Detection Fueling Dominance of Early-Stage NSCLC
Insights, By Stages of the Disease: Early Detection Fueling Dominance of Early-Stage NSCLCIn terms of stages of the disease, early-stage NSCLC is projected to hold 58.7% share of the EGFR non-small cell lung cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) market in 2025. This can be attributed to growing awareness programs that encourage regular lung screenings as well as advancements in diagnostic techniques that allow for earlier detection of NSCLC tumors. Technologies such as low-dose CT scans provide radiologists the ability to catch even tiny cancerous lesions in their initial stages before they metastasize to other organs.
In terms of therapy approvals, first-line treatments contribute the highest share of the EGFR non-small cell lung cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) market owing to the survival advantages conferred by these options when used upfront for newly diagnosed NSCLC patients. Landmark clinical trials have provided robust evidence establishing EGFR-TKI inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors as preferred first-line therapy protocols for specific molecular subclasses of NSCLC.
Further research validating the use of immunotherapy, chemo-immunotherapy and novel combinations in earlier treatment lines is propelling higher consumption of first-line approved therapies in the NSCLC market.
Additional Insights of EGFR Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) Market
- EGFR mutations are present in approximately 10-15% of NSCLC cases, with a higher prevalence in Asian populations, making Asia-Pacific a significant growth region for EGFR-targeted treatments.
- Unmet Needs: The development of therapies to address resistance mutations such as C797S is crucial in the NSCLC treatment landscape.
- EGFR Inhibitors Impact: EGFR inhibitors remain the first-line treatment for EGFR-mutant NSCLC but have limited efficacy against specific mutations, such as exon 20 insertions.
Competitive overview of EGFR Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) Market
The major players operating in the EGFR non-small cell lung cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) market include AstraZeneca, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Roche, Novartis, Cullinan Oncology, Bridge Biotherapeutics, ORIC Pharmaceuticals, BeiGene, Dizal Pharmaceuticals, Merck & Co., and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
EGFR Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) Market Leaders
- AstraZeneca
- Janssen Pharmaceuticals
- Pfizer
- Roche
- Novartis
EGFR Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) Market - Competitive Rivalry

EGFR Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in EGFR Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) Market
- In March 2024, AstraZeneca expanded its clinical trials for TAGRISSO (osimertinib) in combination with chemotherapy. The trial, known as FLAURA2, demonstrated a significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with advanced-stage EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The combination of TAGRISSO and chemotherapy showed better outcomes compared to TAGRISSO alone, potentially enhancing survival rates for patients with more aggressive forms of NSCLC.
- In September 2023, Janssen Pharmaceuticals reported positive results from the Phase 3 MARIPOSA trial. The trial evaluated the combination of amivantamab (RYBREVANT®) and lazertinib in patients with EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The study demonstrated a significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) compared to osimertinib, the current standard of care. Specifically, the combination therapy reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 30%, with a median PFS of 23.7 months for amivantamab and lazertinib, compared to 16.6 months for osimertinib.
- In August 2023, ORIC-114 announced that it is currently undergoing Phase I clinical trials, and significant findings indicate that the drug demonstrates promising CNS activity. Specifically, ORIC-114, a brain-penetrant EGFR and HER2 inhibitor, has shown notable activity against brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with EGFR exon 20 mutations. The trial revealed both systemic and intracranial responses, including the first reported confirmed complete response in a patient with untreated brain metastases. This highlights its potential in addressing CNS metastasis, a significant challenge in NSCLC treatments.
- In July 2023, BBT-176, developed by Bridge Biotherapeutics, demonstrated promising efficacy in its Phase I trials for treating non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with EGFR mutations. The drug specifically targets the complex EGFR mutations (including C797S mutations) that arise after resistance develops to third-generation EGFR inhibitors like osimertinib. In the interim results from the study reported significant tumor shrinkage in patients with advanced NSCLC. For instance, one patient from the 320 mg dosing cohort experienced a 30.3% reduction in tumor size, while another from the 480 mg cohort saw a 26.3% reduction.
- In January 2022, Zipalertinib (Cullinan Oncology) announced that the FDA granted breakthrough therapy designation for Zipalertinib (also known as CLN-081), specifically for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations who had already undergone prior platinum-based chemotherapy.
EGFR Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) Market Segmentation
- By Treatment
- EGFR-TKI Inhibitors
- Immunotherapy
- By Stages of the Disease
- Early-stage NSCLC
- Metastatic NSCLC
- By Therapy Approvals
- First-line Treatments
- Second-line Treatments

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the EGFR non-small cell lung cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) market?
The EGFR non-small cell lung cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) market is estimated to be valued at USD 4.65 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 7.92 Bn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the EGFR non-small cell lung cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) market?
High costs associated with targeted therapies and limited availability of approved treatments in certain regions are the major factors hampering the growth of the EGFR non-small cell lung cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) market.
What are the major factors driving the EGFR non-small cell lung cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) market growth?
Increasing incidence of NSCLC cases with EGFR mutations and strong clinical advancements in EGFR inhibitors are the major factors driving the EGFR non-small cell lung cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) market.
Which is the leading treatment in the EGFR non-small cell lung cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) market?
The leading treatment segment is EGFR-TKI inhibitors.
Which are the major players operating in the EGFR non-small cell lung cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) market?
AstraZeneca, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Roche, Novartis, Cullinan Oncology, Bridge Biotherapeutics, ORIC Pharmaceuticals, BeiGene, Dizal Pharmaceuticals, Merck & Co., and Bristol-Myers Squibb are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the EGFR non-small cell lung cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) market?
The CAGR of the EGFR non-small cell lung cancer (EGFR + NSCLC) market is projected to be 7.9% from 2025-2032.