Endometrial Cancer Market Size - Analysis
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR5.9%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 5.9% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals, Merck & Co, AstraZeneca, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Evergreen Therapeutics and Among Others |
please let us know !
Endometrial Cancer Market Trends
As per medical experts studying cancer trends, factors such as the increasing prevalence of obesity and diabetes are contributing contributors to the spike in endometrial cancer incidence rates worldwide. With obesity affecting a huge population globally due to sedentary lifestyles and consumption of unhealthy diets, the potential patient pool suffering from endometrial cancer is expanding rapidly.
Various non-profit organizations and medical institutions actively educate women on the signs to watch out for like abnormal vaginal bleeding and impart knowledge to seek prompt medical care. This, combined with widespread accessibility to diagnostic procedures like endometrial biopsy, facilitates identification of premalignant and early-stage cancer cases treatable with minimally invasive procedures. Greater screening thus expands the patient population eligible for treatment and management of endometrial cancer, driving higher market demand.
Market Driver - Evolving Treatment Approaches Expanding Scope
A key area attracting extensive research focus is targeted therapies blockading pathways essential for cancer progression. Drugs inhibiting hormones that fuel cancer growth like PARP inhibitors for BRCA mutated endometrial cancer have shown remarkable results in clinical trials. Angiogenesis inhibitors cutting tumor blood supply and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitors restricting signaling driving cell proliferation are other targeted agents demonstrating promise. Immunotherapies engineering the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells also hold potential for transforming treatment. Checkpoint inhibitors releasing brakes on immune response have yielded durable responses in endometrial cancer even after tumor recurrence post other modalities.
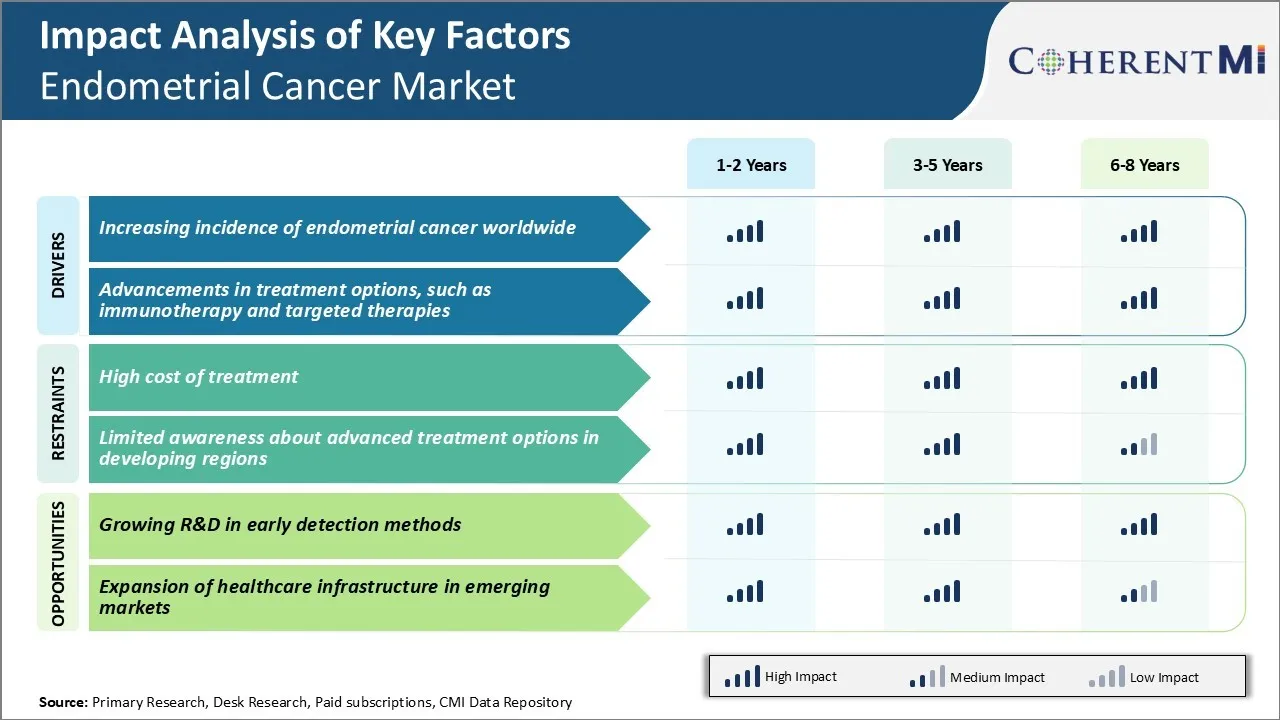
Market Challenge - High Cost of Treatment
Additionally, advanced stage treatments involving newer targeted therapies and immunotherapy drugs have even higher costs. The financial toxicity of treatment poses a huge burden on patients. It negatively impacts treatment adherence and outcomes. High out-of-pocket costs and lack of health insurance amplify the problem in many countries. From a business perspective, the potential for market growth is limited due to affordability issues.
One key opportunity for the endometrial cancer market lies in the growing research and development in the area of early detection methods. Currently, diagnosis is often late when the cancer has spread locally or metastasized. Late-stage diagnosis leads to poorer prognosis and higher treatment costs.
Researchers are also working on minimally invasive screening methods like ultrasound, hysteroscopy and genetic testing to better evaluate women at high risk of the disease. If successful, such early detection technologies can facilitate early treatment intervention when cure rates are highest. This presents an avenue to not just improve clinical outcomes but also reduce the financial burden of treatment.
Prescribers preferences of Endometrial Cancer Market
Endometrial cancer treatment varies based on disease stage and clinical guidelines. For early-stage (I-II) disease, prescribers typically recommend surgery to remove the uterus, ovaries, andFallopian tubes (total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy). For low-risk Stage I disease, adjuvant treatment is usually not needed.
For advanced or recurrent Stage III-IV disease, chemotherapy is the primary treatment. The preferred first-line regimen consists of dose-dense doxorubicin (Adriamycin) and cisplatin (Platinol) every 2-3 weeks for 6 cycles. For patients who cannot tolerate platinum-based therapy, prescribers may opt for liposomal doxorubicin (Doxil) alone.
Treatment Option Analysis of Endometrial Cancer Market
Endometrial cancer is generally categorized into four stages based on how far the cancer has spread from the uterus. Stage I cancer is confined to the uterus, Stage II has spread to the cervix, Stage III involves nearby tissues/organs, and Stage IV is an advanced stage with distant metastases.
For early-stage cancers where the disease is contained, adjuvant treatment with radiation therapy is often recommended after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence. External beam radiation targets the pelvis and vagina. Brachytherapy involves placing radioactive sources directly into the vagina or uterus for a higher localized dose.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Endometrial Cancer Market
Focus on R&D and innovation: Continuous investment in R&D has helped leading players develop novel treatment options for endometrial cancer. For example, Roche invested over $9 billion in R&D in 2020 to develop its pipeline of personalized medicines including giredestrant, a potential new treatment for endometrial cancer.
Partnerships and licensing deals: Companies often partner or license their drugs to other players for further development and commercialization in different regions. For instance, Clovis Oncology out-licensed rucaparib to Pfizer for development and commercialization outside of the US and certain Asian territories. Such deals help maximize a drug's revenue potential globally.
Segmental Analysis of Endometrial Cancer Market
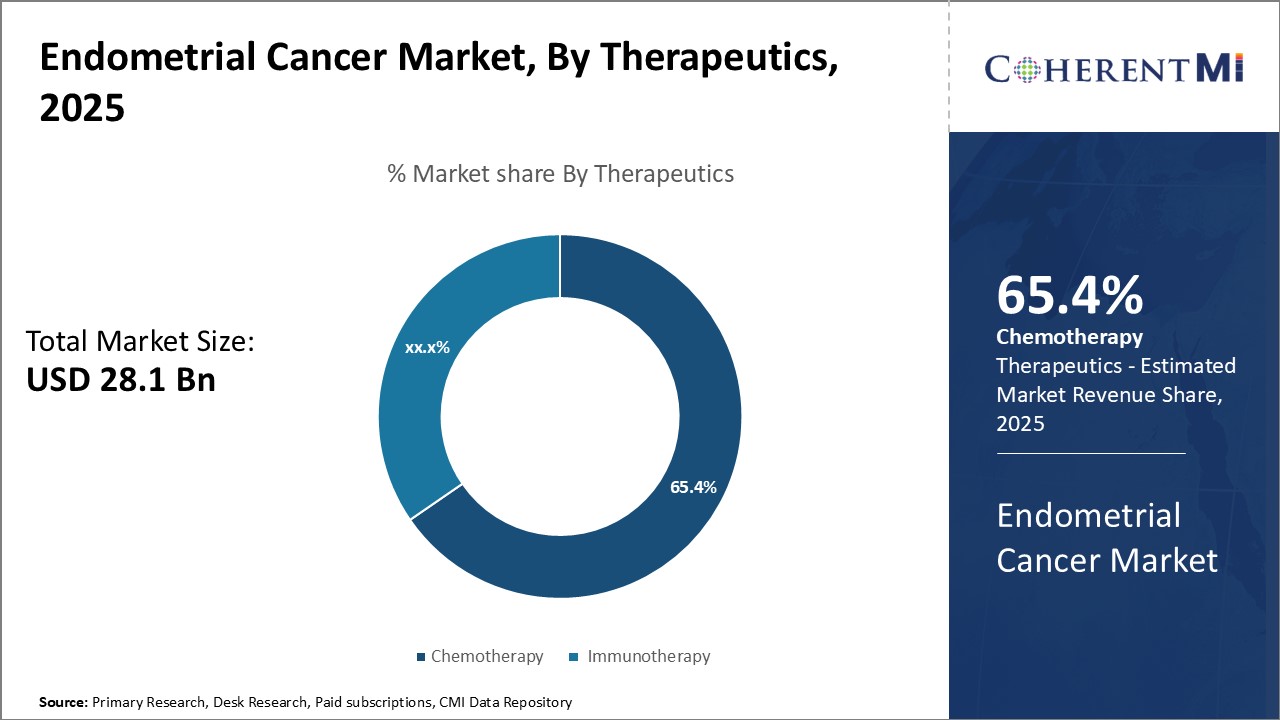 Insights, By Therapeutics: Chemotherapy Dominance - Aggressive Treatment Needs
Insights, By Therapeutics: Chemotherapy Dominance - Aggressive Treatment NeedsIn terms of therapeutics, chemotherapy contributes the 65.4% of market share in 2025, owning to its widespread acceptance for aggressive and advanced disease treatment. Chemotherapy leverages cytotoxic drugs to destroy fast-dividing cancer cells throughout the body. Given endometrial cancer is often detected at an early localized stage, chemotherapy serves as a key adjuvant therapy after hysterectomy to eliminate any remaining cancer cells and prevent recurrence.
Additionally, chemotherapy is generally more affordable and accessible than other options like targeted therapy or immunotherapy. This translates to chemotherapy's extensive use even in developing markets where cost remains a major consideration for patients.
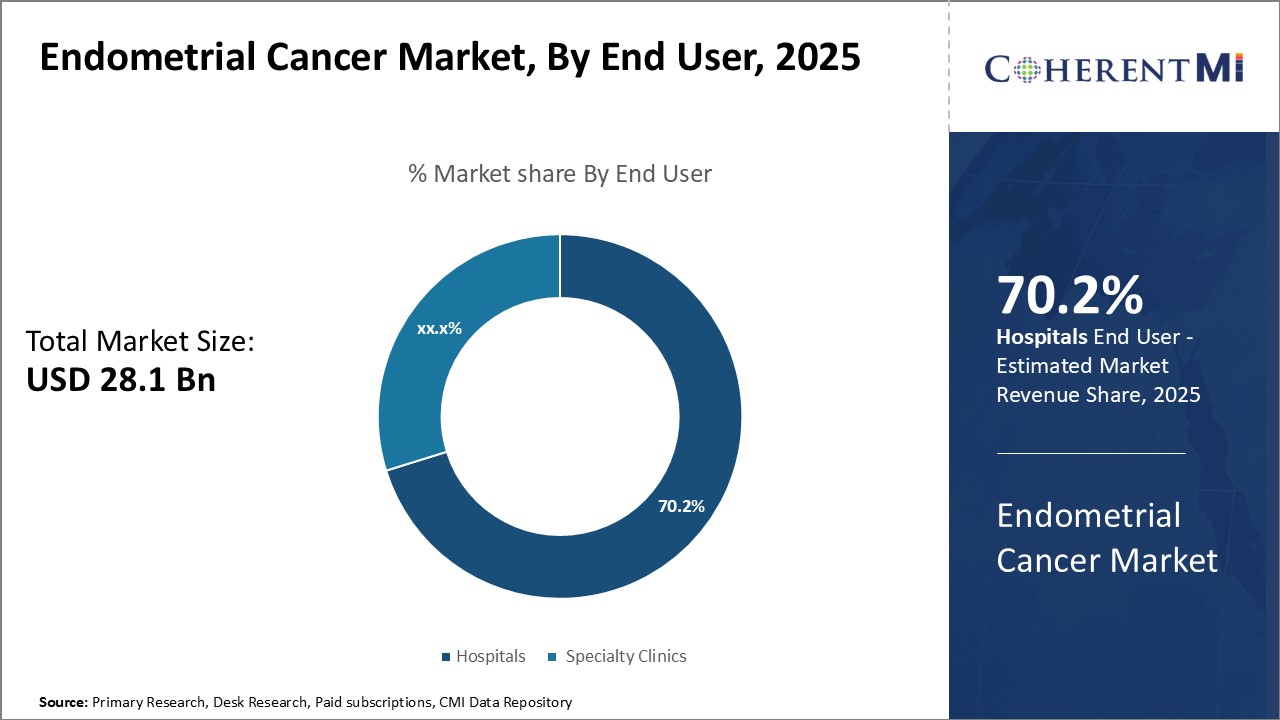
Insights, By End User: Hospitals Dominate Service Delivery - Centralized Expertise
For surgeries such as total hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and lymph node dissection, hospitals have dedicated operating theaters and support staff. They also offer on-site chemotherapy infusion units along with diagnostic and imaging capabilities for staging and monitoring disease. The centralization of resources and coordination of multimodality treatment maximizes quality of care.
In terms of cancer stage, early-stage endometrial cancer contributes the highest share of the market owing to potential for less morbid treatment approaches. Endometrial cancer is typically detected at an early stage due to the post-menopausal bleeding symptom.
The slow growth characteristics of early-stage cancer along with patients’ preference for organ/function-sparing options make hysterectomy the first-line standard of care. By allowing treatment with curative intent in an outpatient setting, early-stage cancer provides opportunities such as fertility-preserving therapies for select young patients. This has driven innovation around techniques such as laparoscopic hysteroscopic surgery. Therefore early-stage presents greater growth prospects than the limited adjuvant options available for advanced disease.
Additional Insights of Endometrial Cancer Market
- Endometrial cancer accounts for about 4% of all cancers in women globally.
- Approximately 3 in 100 women will be diagnosed with uterine cancer at some point in their lives.
- Efforts are underway to enhance research and treatment for endometrial cancer, focusing on understanding the disparity in outcomes for minority populations, particularly Black women.
- Various clinical trial results, partnership announcements, and government approvals are noted, each contributing to the growing market share of companies like Pfizer and Roche.
Competitive overview of Endometrial Cancer Market
The major players operating in the endometrial cancer market include GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals, Merck & Co, AstraZeneca, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Evergreen Therapeutics, and Incyte Corporation.
Endometrial Cancer Market Leaders
- GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals
- Merck & Co
- AstraZeneca
- Karyopharm Therapeutics
- Evergreen Therapeutics
Endometrial Cancer Market - Competitive Rivalry

Endometrial Cancer Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Endometrial Cancer Market
- In March 2024, AstraZeneca launched a new immunotherapy drug, which is expected to change the treatment landscape. Each development includes a detailed explanation of the impact on the market and potential changes in treatment protocols. AstraZeneca has been involved in advancing its immunotherapy portfolio, particularly with combination immunotherapies, such as the combination of durvalumab (Imfinzi) with other novel agents, which showed improved outcomes for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in studies.
- In November 2021, the UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center launched the Endometrial Cancer Center of Excellence. This initiative is aimed at advancing the understanding of endometrial cancer, particularly focusing on addressing disparities, such as the higher mortality rates among Black women in North Carolina, who are twice as likely to die from the disease. The center aims to develop new treatment paradigms, improve outcomes, and investigate the underlying factors contributing to these disparities.
- In March 2021, Eisai Inc. launched the "Spot Her" initiative to raise awareness about endometrial cancer and encourage advocacy for women's health. The initiative aimed to break the silence around endometrial cancer, inspire women to prioritize their health, and was launched in partnership with SHARE Cancer Support, FORCE, and Black Health Matters.
Endometrial Cancer Market Segmentation
- By Therapeutics
- Chemotherapy
- Immunotherapy
- By End User
- Hospitals
- Specialty Clinics
- By Cancer Stage
- Early-Stage Endometrial Cancer
- Advanced-Stage Endometrial Cancer

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the endometrial cancer market?
The endometrial cancer market is estimated to be valued at USD 28.10 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 41.97 Bn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the endometrial cancer market?
The high cost of treatment and limited awareness about advanced treatment options in developing regions are the major factor hampering the growth of the endometrial cancer market.
What are the major factors driving the endometrial cancer market growth?
The increasing incidence of endometrial cancer worldwide and advancements in treatment options, such as immunotherapy and targeted therapies are the major factor driving the endometrial cancer market.
Which is the leading therapeutics segment in the endometrial cancer market?
The leading therapeutics segment is chemotherapy.
Which are the major players operating in the endometrial cancer market?
GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals, Merck & Co, AstraZeneca, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Evergreen Therapeutics, and Incyte Corporation are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the endometrial cancer market?
The CAGR of the endometrial cancer market is projected to be 5.9% from 2025-2032.