Epithelioid Sarcoma Market Size - Analysis
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR9.3%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 9.3% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Epizyme, Eli Lilly and Company, Pfizer, Merck Sharp & Dohme, GlaxoSmithKline and Among Others |
please let us know !
Epithelioid Sarcoma Market Trends
Sarcomas are rare types of cancers that develop in various soft tissues like muscles, fat, and deep skin tissues. Among the different subtypes of sarcomas, epithelioid sarcoma is one of the rarest but aggressive forms especially found in young adults. According to recent studies and reports from cancer institutes as well as sarcoma foundations, the prevalence of sarcomas in general has seen consistent rise globally especially over the past decade. Doctors believe this is due to various factors like increasing life expectancy leading to aging population more prone to cancer, better diagnostic tools and improved data collection methods.
After years of limited treatment options for epithelioid sarcoma patients, the approval of tazemetostat in recent times has provided a ray of hope. Tazemetostat is an oral targeted therapy drug that works by specifically inhibiting a protein called EZH2 which is over-expressed in epithelioid sarcoma tumors. Since its approval by regulatory authorities in 2020 based on promising results from phase 2 clinical trials, the adoption of tazemetostat among physicians has increased steadily.
While its use still depends on various clinical parameters, surveys show growing familiarity and positive perception of tazemetostat treatment in medical community. We can thus expect its prescription rates to continue rising in coming years as more real-world efficacy and safety data becomes available from wider patient population.
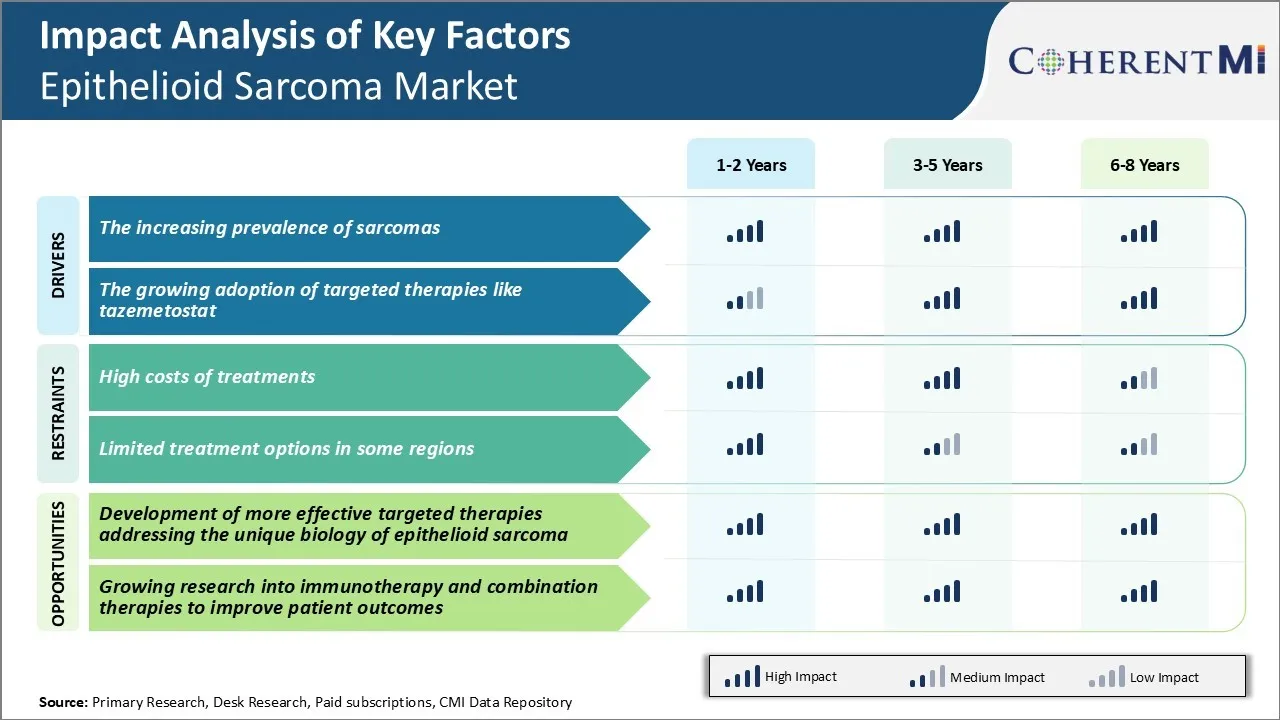
Market Challenge - High Costs of Treatments
Current treatments such as surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy regimens come with high price tags that are difficult for providers and patients to afford given the limited overall market size for this cancer. Further confounding the issue is the fact that multi-drug chemotherapy regimens are often needed, driving costs up substantially.
An important opportunity in the epithelioid sarcoma market lies in the development of more effective targeted therapies that address the unique biology of this disease. Recent advances in genomics and molecular research have expanded understanding of the underlying genetic drivers and anomalies present in epithelioid sarcoma cases. This enhanced knowledge of the disease pathogenesis creates opportunities for pharmaceutical firms to develop novel targeted therapies designed to interfere with specific molecular abnormalities fueling tumor growth and progression.
By zeroing in on molecular vulnerabilities, targeted drugs addressing the distinct tumor characteristics of epithelioid sarcoma could radically improve outcomes for this patient population while also commanding higher price points justified by their superior performance. This would make the overall market more attractive for sustained investment.
Prescribers preferences of Epithelioid Sarcoma Market
Epithelioid sarcoma is an aggressive soft tissue cancer that typically arises in the distal extremities. First-line treatment involves surgery to remove the tumor. For early-stage localized disease, wide local excision is usually sufficient. However, for later stages where there is risk of metastasis, amputation may be necessary to obtain clean margins.
Newer targeted therapies are also gaining acceptance, especially for later lines of treatment. Inhibitors of mTOR signaling, such as temsirolimus (Torisel), have shown promise in early trials. Immunotherapies like nivolumab (Opdivo) are being explored as well, as epithelioid sarcoma exhibits high levels of PD-L1 expression in many cases. Overall prognosis remains poor, emphasizing the need for novel therapies.
Treatment Option Analysis of Epithelioid Sarcoma Market
For localized disease, surgery remains the primary treatment option with wide local excision of the tumor. For tumors amenable to surgery, adjuvant radiation therapy may be recommended to reduce the risk of recurrence.
For patients who progress on or are intolerant to first-line treatment, pazopanib (Votrient) monotherapy remains a good second-line option. Pazopanib is an oral multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor that blocks tumor angiogenesis by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3). It has a manageable side effect profile and yields response rates of 10-15% in pre-treated advanced epithelioid sarcoma patients.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Epithelioid Sarcoma Market
Focus on targeted therapy drugs: One of the major strategies adopted by companies like Adaptimmune, Amphivena Therapeutics, and Immunocore is to focus on developing novel targeted therapy drugs for epithelioid sarcoma. For example, Adaptimmune is developing SPEAR T-cell therapies that target the NY-ESO-1 antigen expressed on epithelioid sarcoma tumors.
Invest in clinical trials: Leading players like Aadi Bioscience and Novartis have strategically invested in conducting robust clinical trials to generate positive efficacy and safety data for their drug candidates. For example, Aadi's nab-sirolimus achieved statistically significant improvement in pathological complete response rates in a phase 2b trial in 2020.
Segmental Analysis of Epithelioid Sarcoma Market
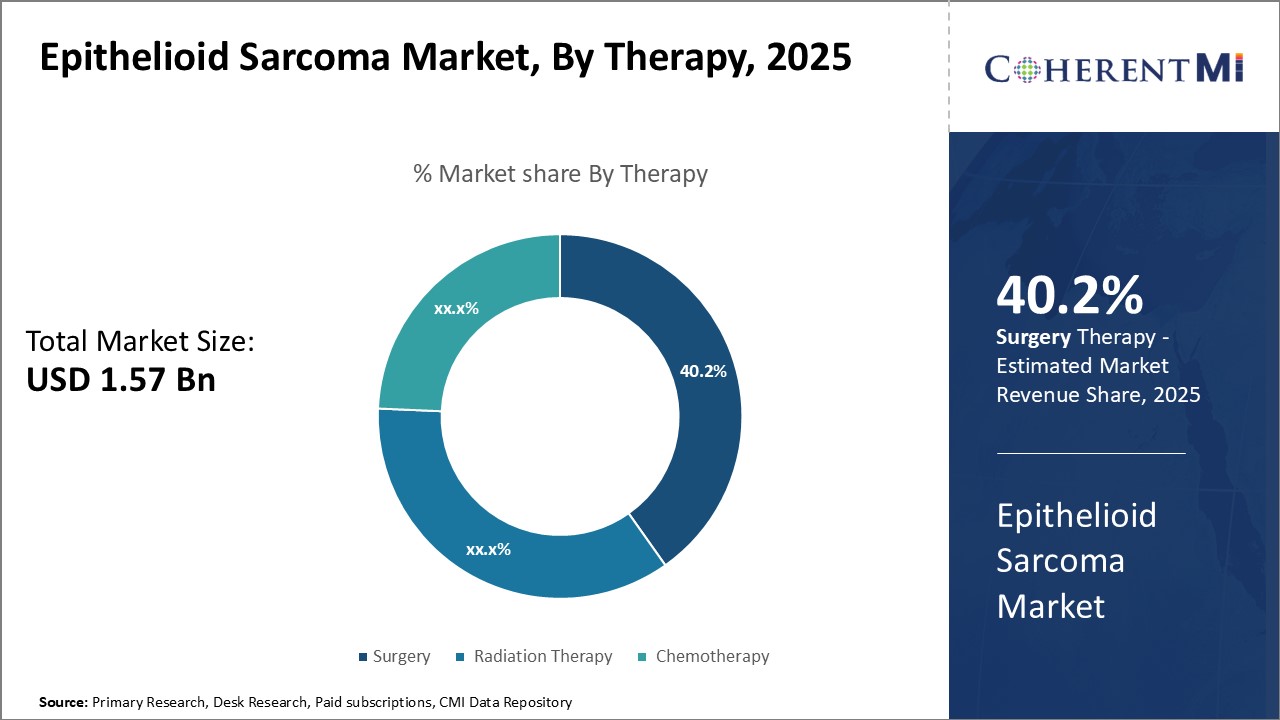 Insights, By Therapy: Technological Advancements Drive Surgery Segment
Insights, By Therapy: Technological Advancements Drive Surgery SegmentIn terms of therapy, surgery is projected account for 40.2% revenue share of the epithelioid sarcoma market in 2025, owning to ongoing technological advancements in surgical techniques and equipment. Surgery remains the standard of care treatment option for patients with localized epithelioid sarcoma.
The demand for advanced surgical oncology services has led to an increasing number of specialized cancer surgery centers opening in major cities. These centers are at the forefront of adopting and training surgeons on the latest surgical innovations. Manufacturers continue to develop new surgical tools like fluorescent tumor-tagging agents that allow surgeons to better visualize and delineate tumor margins during removal. Indocyanine green is an example of an agent recently approved for soft tissue tumor surgery that emits infrared light detectable by cameras to identify cancerous versus healthy tissues.
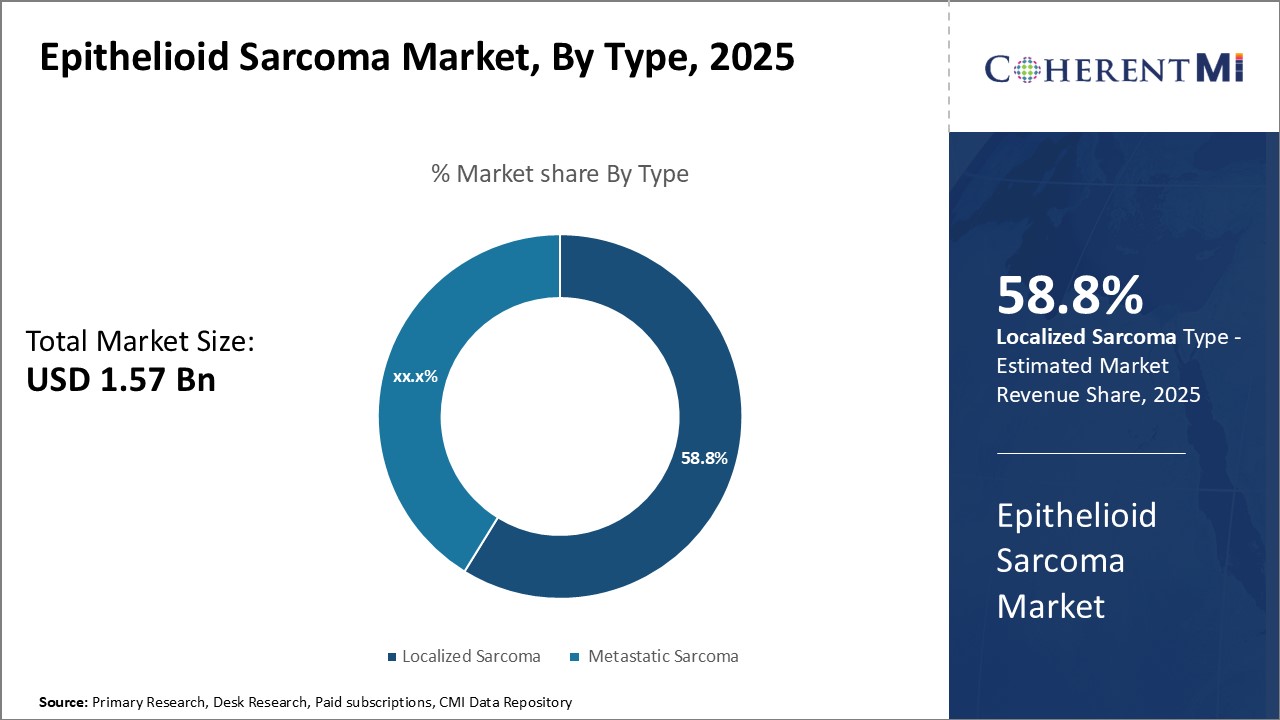
Insights, By Type: Genetic Understanding Fuels Localized Sarcoma Segment
Studies now demonstrate that localized Epithelioid Sarcoma arises from rearrangements in the YWHAE or FAM22A genes in the majority of cases. These gene fusions lead to activation of signaling networks controlling cell division and survival. Determining the specific genetic mutations present in an individual’s tumor allows for more precise diagnosis and classification of whether the sarcoma will behave in a localized or metastatic manner. It also opens avenues for developing targeted therapies directed at vulnerabilities in the genetic makeup of localized disease.
In terms of drug type, TK inhibitors contribute the highest share of the epithelioid sarcoma market as they address key mechanisms involved in metastatic disease progression. Tyrosine kinase receptors possess intrinsic enzymatic activity that phosphorylates other proteins upon binding extracellular signaling molecules. Epithelioid Sarcomas co-opt pathways regulated by these TKs to break away from primary tumors, invade locally, and potentially spread to distant sites via the bloodstream.
Meanwhile, immune modulating TKIs are an appealing new class due to findings that sarcomas evade the immune system partly through TK signaling. BTK and JAK inhibitors could restore anti-tumor immunity while also directly hindering sarcoma cell survival and migration. Combining these immunotherapy-enabling TKIs with immune checkpoint blockade is expected to yield favorable results. Their promising preclinical profiles and novel mechanisms of action support TK inhibitors currently dominating the drug type segment.
Additional Insights of Epithelioid Sarcoma Market
- In the US, 0.50% of soft tissue sarcoma cases are epithelioid sarcoma, highlighting its rarity but increasing market attention for therapeutic development. Additionally, ongoing research into molecular pathways like PI3K and MAPK is expected to drive the growth of the sarcoma treatment market.
- Epithelioid sarcoma is a rare form of soft tissue cancer with a high rate of recurrence and metastasis. Most patients are young males, and the disease primarily affects the upper extremities.
- The disease has a male predilection (2:1 ratio), and most cases occur between ages 10 and 45. Early detection and aggressive treatment are critical for patient survival, though recurrence is common.
Competitive overview of Epithelioid Sarcoma Market
The major players operating in the epithelioid sarcoma market include Epizyme, Eli Lilly and Company, Pfizer, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and GlaxoSmithKline.
Epithelioid Sarcoma Market Leaders
- Epizyme
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Pfizer
- Merck Sharp & Dohme
- GlaxoSmithKline
Epithelioid Sarcoma Market - Competitive Rivalry

Epithelioid Sarcoma Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Epithelioid Sarcoma Market
- In Q1 of 2023, Sarcoma Oncology Research Center announces early-stage research on a novel immunotherapy targeting rare sarcomas, including epithelioid sarcoma. Furthermore, research at various institutions, including the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), has focused on advancing immunotherapy approaches, including checkpoint inhibitors and T-cell therapies, for several types of sarcomas, although most research has centered on soft tissue and synovial sarcomas. It is possible that immunotherapies targeting rare sarcomas like epithelioid sarcoma are in the early stages of exploration.
- In January 2020, Epizyme received approval for tazemetostat, impacting the sarcoma market by offering a novel therapeutic approach that targets EZH2 mutations, commonly found in sarcoma patients. The approval opened new treatment options for patients previously limited to traditional chemotherapy. Tazemetostat was granted accelerated approval for the treatment of adults and pediatric patients aged 16 years and older with metastatic or locally advanced epithelioid sarcoma. This drug targets EZH2 mutations, providing a novel therapeutic approach for patients with limited treatment options who are not candidates for complete surgical resection.
Epithelioid Sarcoma Market Segmentation
- By Therapy
- Surgery
- Radiation Therapy
- Chemotherapy
- By Type
- Localized Sarcoma
- Metastatic Sarcoma
- By Drug Type
- TK Inhibitors
- mTOR Inhibitors

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the epithelioid sarcoma market?
The epithelioid sarcoma market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.57 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 2.93 Bn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the epithelioid sarcoma market?
The high costs of treatments and limited treatment options in some regions are the major factors hampering the growth of the epithelioid sarcoma market.
What are the major factors driving the epithelioid sarcoma market growth?
The increasing prevalence of sarcomas and the growing adoption of targeted therapies like tazemetostat are the major factors driving the epithelioid sarcoma market.
Which is the leading therapy in the epithelioid sarcoma market?
The leading therapy segment is surgery.
Which are the major players operating in the epithelioid sarcoma market?
Epizyme, Eli Lilly and Company, Pfizer, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and GlaxoSmithKline are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the epithelioid sarcoma market?
The CAGR of the epithelioid sarcoma market is projected to be 9.3% from 2025-2032.