Exosome Therapeutics Market Size - Analysis
The exosome therapeutics market is estimated to be valued at USD 299.4 Mn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 1961.1 Mn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 30.8% from 2025 to 2032.
Market Size in USD Mn
CAGR30.8%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 30.8% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Evox Therapeutics, ExoCoBio, ILIAS Biologics, Coya Therapeutics, Rion and Among Others |
please let us know !
Exosome Therapeutics Market Trends
The therapeutic arena has seen a tremendous evolution over the past few decades. Where earlier therapies targeted diseases in a broad manner, the recent focus has been on developing precision medicines that address the core pathways driving a disease. Exosomes being extracellular vesicles that aid intercellular communication, researchers have been actively exploring their potential to be utilized as targeted therapies, specifically for conditions where conventional drugs have limitations.
For conditions where the exact disease-causing changes are not fully clear, exosomes open possibilities for personalized profiling approaches. Scientists are learning to analyze a patient's bodily fluid exosomes to glean molecular signatures reflective of their disease state. This detailed information can then guide selection of optimal exosome therapies best suited to counter observed aberrations. Several startup companies are collaborating with clinical organizations to validate such strategies, hoping to eventually support precision care approaches.
Strengthened by the successes seen so far in validating exosome's therapeutic potential, research in this domain has intensified significantly. Both private business entities as well as academic institutions worldwide are investing heavily to unravel multifaceted exosome biology and apply it for clinical benefit. Several biotech startups have been established solely with the vision of engineering exosome therapeutics. Their innovative work involves devising methods for large-scale exosome isolation, loading diverse molecular cargoes, surface engineering for targeting capabilities and establishing safety, pharmacokinetic and dosing benchmarks.
Academic centers globally are significantly participating in basic as well as preclinical exosome sciences, and in implementing industrial partnerships for product development. Large government funding is spurring exciting multi-institutional projects. International conferences focusing on exosome therapeutics witness tremendous participation with many new findings being presented each time. The literature base on their therapeutic use expands by thousands of publications annually. Leveraging this reinvigorated energy, the field seems well poised to see multiple exosome candidates advance into late-stage clinical development in the next 5 years. Such progress reflects the ever-growing commitment of stakeholders towards realizing the full promise of exosome-based medicines.
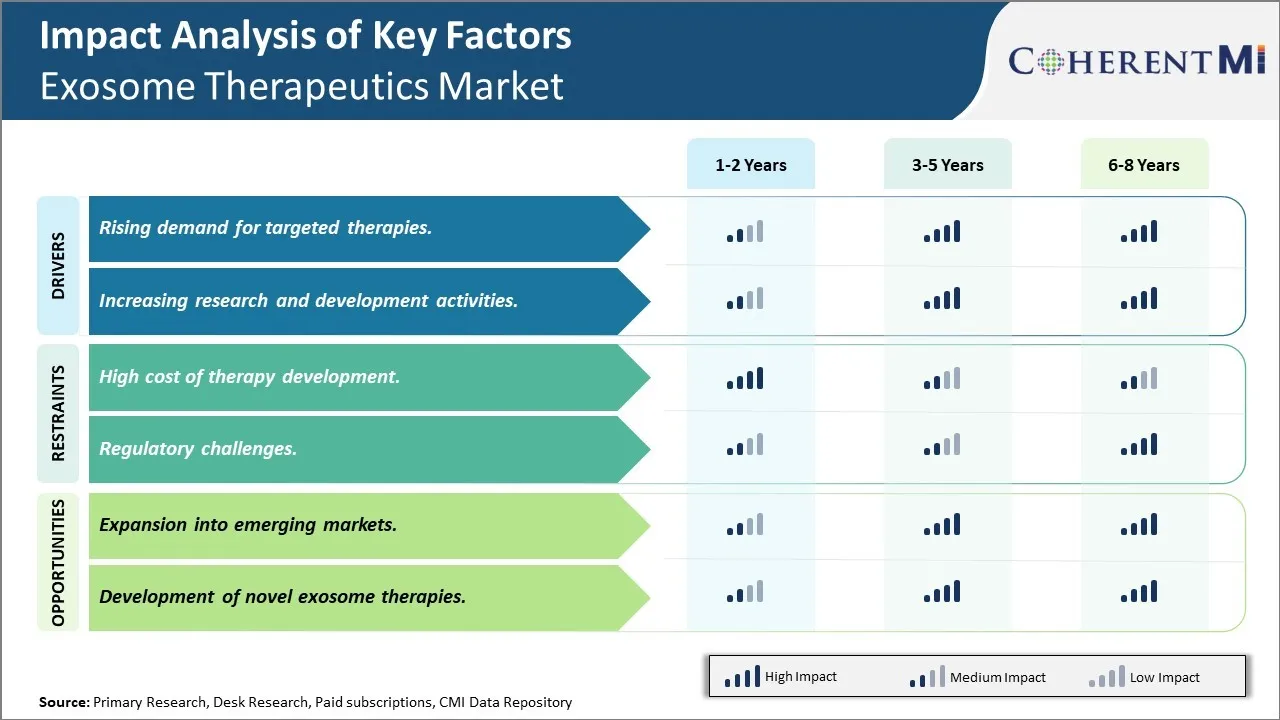
One of the major challenges currently being faced by players in the exosome therapeutics market is the extremely high cost associated with research and development of new therapies. Developing an exosome-based drug requires extensive laboratory research to first isolate exosomes from donor cells, optimize purification techniques, examine their cargo and functional properties, and engineer them for precise therapeutic applications. This is followed by rigorous pre-clinical testing on animal models to analyze treatment efficacy, safety, and assess biological interactions. If successful, multiple phases of clinical trials in human patients are then required to obtain regulatory approvals. Each stage takes years to complete and requires massive investments running into hundreds of millions of dollars. The financial risks are further amplified by the low probability of a candidate making it from the lab to the market. While the scientific premise is promising, high R&D costs pose significant barriers to entry for new players and limit investments towards innovative programs.
Market Opportunity - Expansion into emerging markets
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Exosome Therapeutics Market
One of the most effective strategies adopted by leading players has been forming strategic partnerships with pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions and biotech firms. For instance, in 2021 Exopharm formed a collaboration with CureDuchenne to develop exosome therapeutics for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. This allows companies to leverage each other's expertise and resources to advance their pipeline candidates.
Larger players have complemented their internal R&D through strategic acquisitions. For example, in 2019 Codiak BioSciences acquired specialized exosome engineering company NovoNutrients Inc. This boosted Codiak's capabilities in engineering exosomes for specific drug loading and tissue targeting applications. Such acquisitions strengthen technical expertise and product pipeline.
Segmental Analysis of Exosome Therapeutics Market
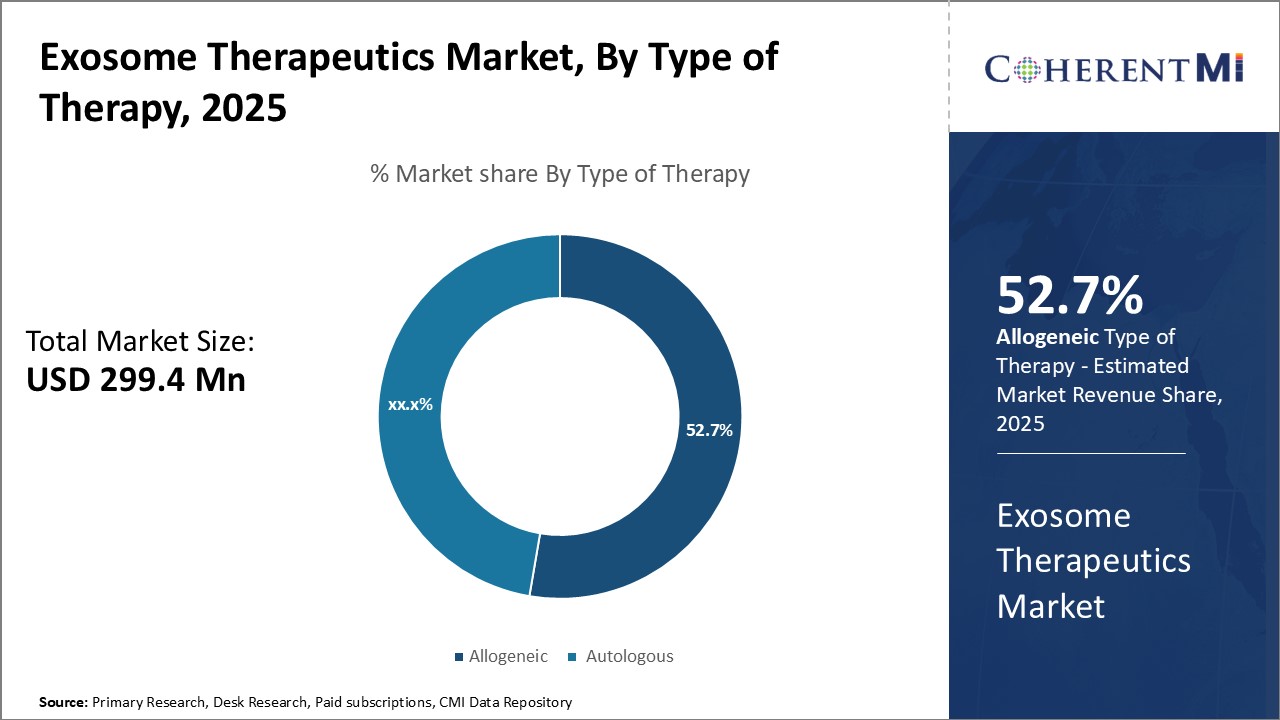 Insights, By Type of Therapy: Widespread therapeutic applications and promising clinical results of allogeneic therapy
Insights, By Type of Therapy: Widespread therapeutic applications and promising clinical results of allogeneic therapyIn terms of type of therapy, allogeneic sub-segment contributes the highest share of 52.7% in the market owing to their widespread therapeutic applications and promising clinical results. Allogeneic therapies utilize exosomes derived from healthy donor cells that can be mass produced and stockpiled. This allows them to be immediately available off-the-shelf for patients without requiring an individualized therapy generation process. Not having to wait for autologous exosome extraction and production provides a significant clinical advantage, especially for acute and rapidly progressing conditions.
Perhaps most importantly, early phase clinical trials have demonstrated the excellent safety profile of allogeneic exosome therapies. No signs of immunogenicity or graft-versus-host disease responses have been observed even without immunosuppression. This safety data combined with the off-the-shelf availability advantage has accelerated interest from big pharmaceutical companies and bolstered investment into large-scale production technologies. Further demonstration of therapeutic benefits would likely cement allogeneic exosomes as the dominant force in the exosome therapeutics landscape.
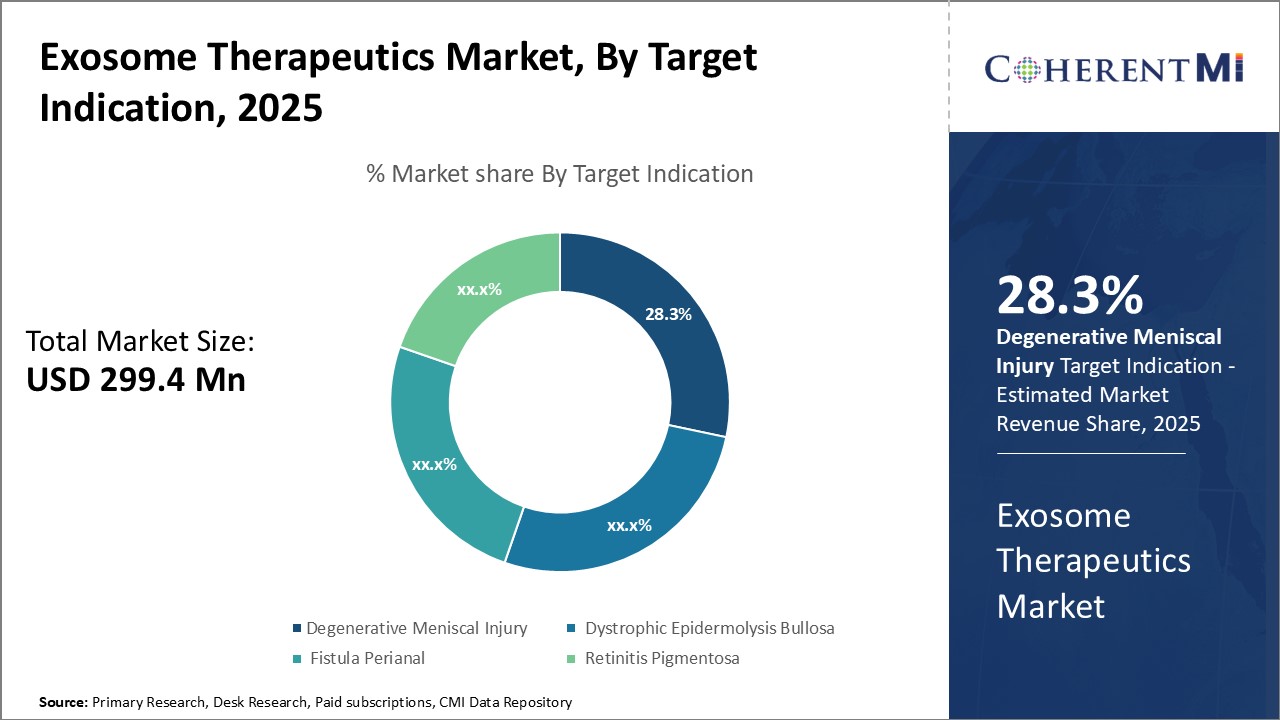
Among the indication segments in the exosome therapeutics market, degenerative meniscal injury sub-segment has emerged as the dominant target with a market share of 28.3% owing to the large population affected and limitations of current treatments. Meniscal tears are an extremely common sports injury, afflicting over 1 million people annually in the US alone. They also frequently occur alongside aging as cartilage degradation increases risk of tears during normal activity. However, surgical intervention like partial or total meniscectomy provides minimal symptom relief and accelerates the onset of osteoarthritis.
As the most widespread joint condition lacking effective long term treatments, degenerative meniscal injury represents low hanging fruit for exosome translation. Further demonstration of disease-modifying abilities could establish it as the flagship application that proves exosome therapeutic value. This makes it the clear leader currently among target segments within this innovative field.
Additional Insights of Exosome Therapeutics Market
- The antibody discovery market is poised for significant growth, driven by increasing reliance on CROs for outsourcing, advancements in antibody engineering, and the rising demand for targeted therapies. The integration of innovative technologies, such as transgenic animals and single-cell screening, is expected to enhance the efficiency and success rate of antibody discovery processes.
Competitive overview of Exosome Therapeutics Market
The major players operating in the exosome therapeutics market include Evox Therapeutics, ExoCoBio, ILIAS Biologics, Coya Therapeutics, Rion, SHIFTBIO, Curexsys, EV Therapeutics and Cellular Biomedicine Group.
Exosome Therapeutics Market Leaders
- Evox Therapeutics
- ExoCoBio
- ILIAS Biologics
- Coya Therapeutics
- Rion
Exosome Therapeutics Market - Competitive Rivalry

Exosome Therapeutics Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Exosome Therapeutics Market
- In August 2023, Evox Therapeutics collaborated with the Icahn School of Medicine to develop exosome-encapsulated AAV vectors for heart disease treatment.
- In June 2023, Sartorius extended a collaboration with RoosterBio for exosome-based therapies' downstream manufacturing.
- In March 2023, RoosterBio collaborated with Repligen to advance scalable exosome bioprocessing.
Exosome Therapeutics Market Segmentation
- By Type of Therapy
- Allogeneic
- Autologous
- By Target Indication
- Degenerative Meniscal Injury
- Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa
- Fistula Perianal
- Retinitis Pigmentosa

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the Exosome Therapeutics Market?
The Exosome Therapeutics Market is estimated to be valued at USD 299.4 in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 1961.1 Million by 2032.
What are the major factors driving the exosome therapeutics market growth?
The rising demand for targeted therapies and increasing research and development activities are the major factors driving the exosome therapeutics market.
Which is the leading type of therapy in the exosome therapeutics market?
The leading type of therapy segment is allogeneic.
Which are the major players operating in the Exosome Therapeutics Market?
Evox Therapeutics, ExoCoBio, ILIAS Biologics, Coya Therapeutics, Rion, SHIFTBIO, Curexsys, EV Therapeutics, and Cellular Biomedicine Group are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the exosome therapeutics market?
The CAGR of the exosome therapeutics market is projected to be 30.8% from 2025-2032.