Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) Market Size - Analysis
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR9.8%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 9.8% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Novartis AG, Pfizer Inc., Bayer AG, Roche Holding AG, Eli Lilly and Company and Among Others |
please let us know !
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) Market Trends
As the prevalence of cancer continues rising globally, patients and their families look for advanced treatment options that can effectively defeat their disease. GIST is no exception, with several cases diagnosed each year worldwide. Traditional chemotherapy and radiation have significant side effects and are not always successful. People affected by GIST greatly desire novel pharmaceuticals developed through cutting-edge research that can precisely target the cancer and eliminate it from the body with minimal toxicity.
The entry and success of pioneering GIST drugs have boosted hopes in the medical community as well as those suffering from the condition. Advancements in biopharmaceutical innovation directly enhance patient care, strengthening the demand for novel therapeutic options. Drug makers continue prioritizing GIST-centered R&D to develop next-generation solutions addressing unmet needs. This momentum plays a vital role in the gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) market’s positive trend.
Market Driver - Increased Research and Development in Oncology Drugs Targeting GIST
Market stakeholders are pumping substantial funds into GIST drug R&D programs annually based on promising indications from early trials. Multiple compounds at different stages target specific aberrations driving rapid tumor growth or inhibiting metastasis. Some work to enhance the body's natural defenses against the cancer or combine specialized mechanisms for stronger effect. Early results point to considerable potential to improve upon approved standards. This motivates intensified efforts to advance candidates up the drug development pipeline.
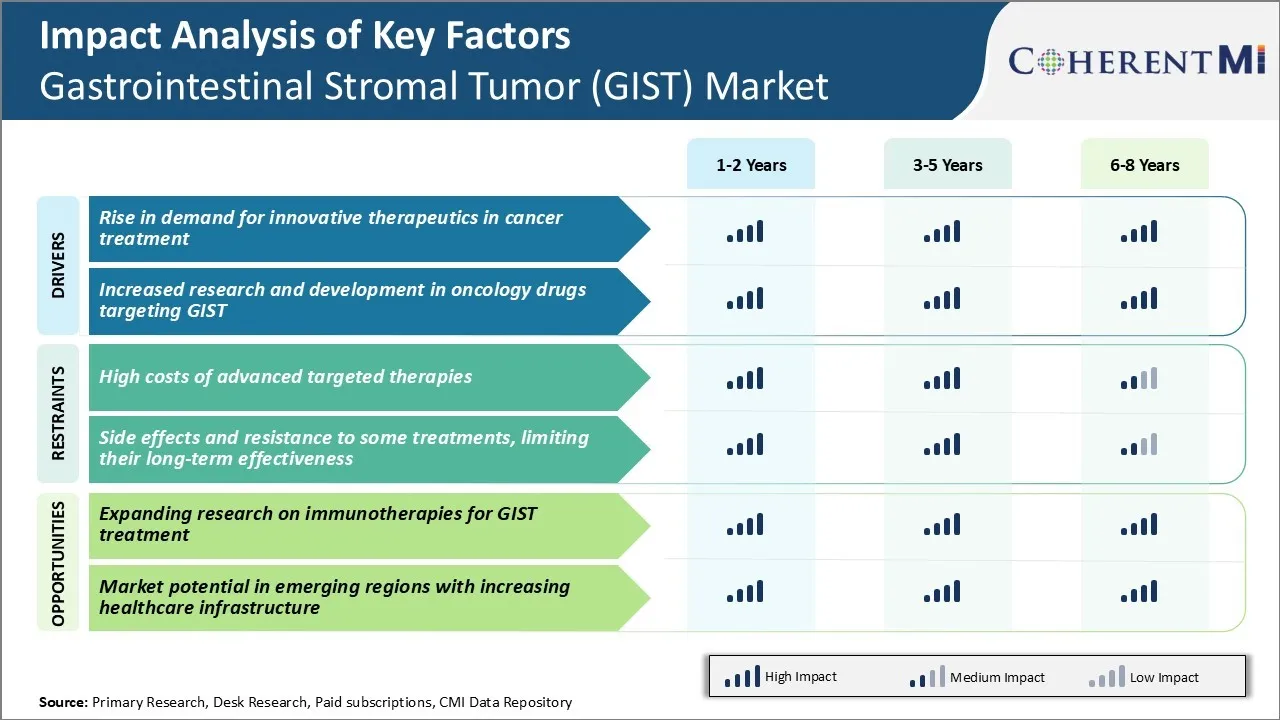
Market Challenge - High Costs of Advanced Targeted Therapies
However, they are also very expensive often costing over $100,000 per year of treatment. Due to the high costs, patient access to these life-saving medications remains a challenge particularly in developing countries with limited healthcare budgets. The high therapy costs also put significant financial burden on patients requiring them to pay high insurance premiums and co-pays. This financial toxicity associated with the treatments can negatively impact treatment adherence over time.
One significant opportunity in the GIST market lies in further expanding research on immunotherapies for GIST treatment. While targeted therapies have revolutionized GIST treatment, resistance to these drugs remains a challenge in the longer run. There is an urgent need to explore novel treatment approaches to combat drug-resistant GIST.
Positive results from ongoing studies can help establish immunotherapies as an important new treatment option. This will substantially expand the available armamentarium to effectively treat GIST at different stages of the disease. Increased research funding and support from government agencies can help accelerate development of immunotherapies. Their successful integration into clinical practice has the potential to transform long term outcomes for GIST patients worldwide.
Prescribers preferences of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) Market
GIST is typically treated through a step-wise approach based on the stage of disease. For localized resectable disease, surgery remains the standard first-line treatment with the goal of complete resection. For patients who are not surgical candidates or those with recurrent/metastatic disease, drug therapy is preferred.
For patients unsuitable or intolerant to both imatinib and sunitinib, the third-line regimen involves the use of regulatory approved regorafenib (Stivarga). Regorafenib inhibits multiple kinases involved in angiogenesis and oncogenesis and has shown survival benefits in refractory GIST patients. The dosage is typically 160mg taken orally once daily for 3 weeks on/1 week off treatment cycles.
Treatment Option Analysis of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) Market
GIST has four main stages - localized, locally advanced, metastatic/unresectable, and recurrent/progressive. For localized resectable GIST, surgical removal of the tumor (usually performed laparoscopically) is the primary treatment option.
For patients progressing on imatinib and sunitinib, regorafenib (Stivarga) is the standard third-line option. Regorafenib fights GIST by blocking several kinases involved in tumor growth and spread. Recent research found combining regorafenib with nintedanib provides a safe and effective fourth-line alternative for patients no longer responding to other targeted therapies.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) Market
One of the most important strategies adopted by players has been obtaining FDA approval and successfully launching new drugs to treat GIST. For example, Novartis gained FDA approval for Stivarga (regorafenib) in 2013 for metastatic GIST after failure of imatinib and sunitinib.
Focus on novel targeted therapies:
Bayer strengthened its oncology portfolio through the acquisition of BluePrint Medicines in 2020 for $1.5 billion. This added a pipeline of precision medicine programs including the investigational drug, pralsetinib, for the treatment of RET-altered solid tumors including GIST.
Lifecycle management of blockbusters:
Deciphera formed a collaboration with Zai Lab in 2020 to accelerate development and commercialization of rebastinib in Greater China. Such partnerships help companies access newer markets and patients more quickly.
Segmental Analysis of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) Market
-market-by-product.webp) Insights, By Product: Growth of Targeted Therapies with Marketed Drugs
Insights, By Product: Growth of Targeted Therapies with Marketed DrugsIn terms of product, marketed drugs are estimated to account for 65.5% share of the gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) market in 2025, owning to the availability of innovative targeted therapies. Significant research efforts over the past decade have led to development of targeted drugs with novel mechanisms of action that specifically inhibit cancer growth. Imatinib revolutionized GIST treatment by becoming the first approved targeted therapy. It demonstrated remarkable response rates and improved survival outcomes.
-market-by-drug-category.webp)
Insights, By Drug Category: Prevalence of Kinase Inhibition
Second generation multi-targeted TKIs like regorafenib and ripretinib offer additional benefits over imatinib. Their flexible dosing schedules and manageable toxicity profiles have improved patient outcomes and compliance. Continued research to discover novel kinase targets will likely see launch of newer TKIs in the future as well. Widespread clinical evidence validating benefits of kinase inhibition makes it the preferred treatment modality amongst medical professionals.
Insights, By Route of Administration: Convenience of Oral Administration
It allows convenient self-administration of drugs at home or alongside daily routines. This improves adherence and compliance to therapy. Oral drugs also offer freedom from hospital/clinic visits for infusion administration. Their ease of use promotes superior quality of life for GIST patients.
Additional Insights of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) Market
- Prevalence: GIST affects approximately 10-15 per million people annually worldwide.
- Mutation Breakdown: About 80% of GIST cases have KIT mutations, 10% have PDGFRA mutations, and the remaining 10% are wild-type or have other rare mutations.
- The integration of genomic testing in clinical practice has enabled more precise targeting of GIST mutations, improving treatment efficacy and patient survival rates.
- GIST remains a challenging malignancy to treat due to its resistance to some therapies, and the limited availability of targeted therapies, leading companies to focus on developing advanced treatments that can overcome these hurdles.
Competitive overview of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) Market
The major players operating in the gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) market include Novartis AG, Pfizer Inc., Bayer AG, Roche Holding AG, Eli Lilly and Company, Daiichi Sankyo, Astellas Pharma, Blueprint Medicines Corporation, Merck & Co., and Amgen Inc.
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) Market Leaders
- Novartis AG
- Pfizer Inc.
- Bayer AG
- Roche Holding AG
- Eli Lilly and Company
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) Market - Competitive Rivalry

Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) Market
- In September 2023, Daiichi Sankyo initiated Phase III clinical trials for a novel TKI aimed at overcoming resistance in GIST patients. Successful results could significantly impact the treatment landscape. Daiichi Sankyo has been actively involved in developing TKI-related therapies, particularly targeting resistance mechanisms in cancers such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with trials like HERTHENA-Lung01 and HERTHENA-Lung02, focusing on overcoming resistance to EGFR TKIs.
- In November 2022, Novartis announced the launch of a new Phase III clinical trial focusing on next-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors to treat advanced GIST, aiming to reduce resistance issues seen with previous therapies. Novartis has been actively involved in the development of various TKIs, including Scemblix® (asciminib), which has been studied in other types of cancers like chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). This drug targets resistance to prior TKIs and shows promising results, but no direct evidence was found for a GIST-specific trial from November 2022.
- In May 2020, Qinlock (ripretinib), a kinase inhibitor, was approved by the FDA for the treatment of advanced GIST after patients had already been treated with at least three other kinase inhibitors. This approval represented an important development in addressing resistance to previous treatments for metastatic GIST
- In April 2022, Roche Holding AG entered into a licensing agreement with Blueprint Medicines Corporation to co-develop a new GIST treatment. This partnership could accelerate drug availability in international markets. Roche and Blueprint Medicines have been collaborating on the development and commercialization of cancer drugs, particularly focusing on pralsetinib, which targets RET-altered cancers such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and thyroid cancers.
- In January 2020, Blueprint Medicines received FDA approval for avapritinib under the brand name Ayvakit for the treatment of GISTs with PDGFRA exon 18 mutations (including the D842V mutation), and the drug was already being used for certain Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) cases. In June 2023, Blueprint Medicines received FDA approval for the use of Ayvakit in treating indolent systemic mastocytosis (ISM).
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) Market Segmentation
- By Product
- Marketed Drugs
- Phase III Pipeline Drugs
- By Drug Category
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs)
- Chemotherapy
- Immunotherapy
- By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) market?
The gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.32 Billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 2.54 Billion by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) market?
The high costs of advanced targeted therapies, and the side effects and resistance to some treatments, which can limit their long-term effectiveness, are the major factors hampering the growth of the gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) market.
What are the major factors driving the gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) market growth?
The rise in demand for innovative therapeutics in cancer treatment and increased research and development in oncology drugs targeting GIST are the major factors driving the gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) market.
Which is the leading product in the gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) market?
The leading product segment is marketed drugs.
Which are the major players operating in the gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) market?
Novartis AG, Pfizer Inc., Bayer AG, Roche Holding AG, Eli Lilly and Company, Daiichi Sankyo, Astellas Pharma, Blueprint Medicines Corporation, Merck & Co., and Amgen Inc. are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) market?
The CAGR of the gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) market is projected to be 9.8% from 2025-2032.