Hereditary Amyloidosis Market Size - Analysis
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR12.00%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 12.00% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Inc., Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Akcea Therapeutics, Prothena Corporation and Among Others |
please let us know !
Hereditary Amyloidosis Market Trends
Improving diagnostic technologies have enabled physicians to more accurately diagnose cases of hereditary amyloidosis in recent years. Advances in genetic testing, imaging modalities and biochemical analysis have provided clinicians with minimally invasive and highly effective tools to confirm hereditary amyloidosis where previously it may have gone undiagnosed.
Armed with these improved testing options, clinicians are able to proactively screen at-risk relatives of known carriers. Large multi-generational cohort studies have also implemented population-level genetic screening programs to identify previously unknown mutation carriers. As a result, hereditary amyloidosis is being diagnosed far more frequently than in the past, even in early, presymptomatic stages of the disease.
After decades of limited therapeutic options for hereditary amyloidosis patients, breakthroughs in drug development are bringing real hope. Traditionally, treatments focused on managing symptoms and organ damage but lacked any effect on the underlying pathology. However, new biologic agents designed to specifically inhibit amyloid precursor protein production show exciting promise.
This breakthrough has energized both the pharmaceutical industry and research community, spurring widespread investment into further optimizing lead compounds and developing new molecular targets. As the field rapidly advances, forthcoming generations of RNAi and antisense drugs may provide even stronger, more durable responses. While significant work remains, these novel treatment strategies offer realistic hope that hereditary amyloidosis could transform from a bleak diagnosis to one with a promising future.
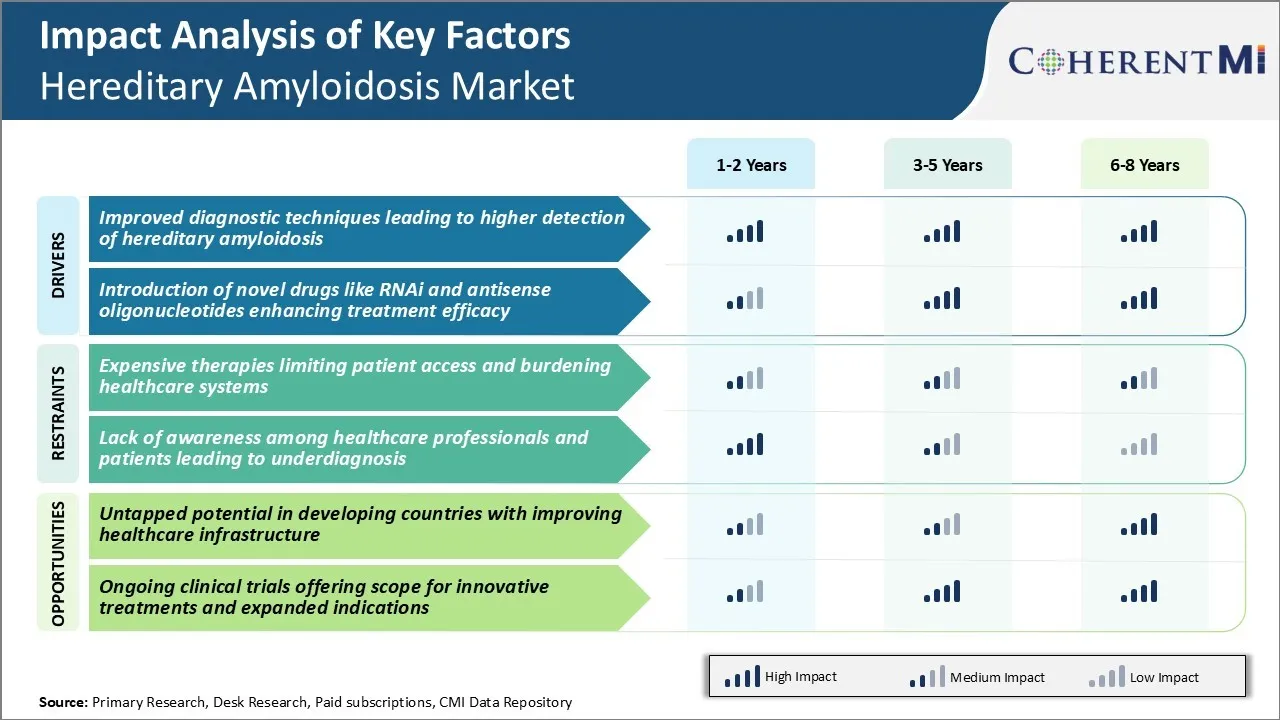
One of the major challenges being faced in the hereditary amyloidosis market is the high cost of available therapies. Developing effective treatments for this rare genetic condition requires extensive research and clinical trials. As a result, many of the approved drugs come with hefty price tags, often exceeding $100,000 per year. While these therapies have shown to significantly improve outcomes for patients, their pricing remains out of reach for many.
Insurance companies and governments struggle to bear the expense, leaving many patients with little or no coverage options. Pharmaceutical companies must work on developing more affordable treatment alternatives if broader patient access is to be achieved. Otherwise, amyloidosis will continue affecting lives and weighed heavily on overall healthcare spend.
Market Opportunity - Untapped Potential in Developing Countries with Improving Healthcare Infrastructure
A rising middle class is gaining greater access to private health insurance as well. As expertise in rare diseases increase and newly approved amyloidosis drugs become accessible in these regions, a tremendous unmet need is primed to be addressed.
Prescribers preferences of Hereditary Amyloidosis Market
Hereditary Amyloidosis is a rare and progressive disease characterized by abnormal protein deposits in tissues and organs. Treatment typically follows a staged approach based on disease severity and organ involvement.
Stage 3 indicates moderate organ dysfunction requiring additional treatment. At this line, immunomodulatory drugs like Melphalan (Alkeran) or Doxycycline are commonly used off-label. Due to safety risks, Melphalan is usually reserved for cardiac amyloidosis with specific eligibility. For resistant cases, stem cell transplants have shown some success in halting further progression by replacing affected cells.
Treatment Option Analysis of Hereditary Amyloidosis Market
As the disease advances, treatments aim to slow or halt further amyloid deposition. For stage 1 disease with mild to moderate kidney or liver impairment, the first-line treatment is oral tafamidis. Tafamidis is a transthyretin stabilizer that prevents transthyretin tetramers from dissociating into toxic monomers. This stops further amyloid formation and slows disease progression. Many patients experience prolonged stabilization or improvement in organ function on tafamidis.
In advanced stage 3 disease requiring organ transplants, stem cell transplants may offer the best chance of survival. A non-myeloablative stem cell transplant following chemo/radiation conditioning with melphalan provides the graft versus plasma cell effect. This can eliminate the pathogenic plasma cells and stabilize disease long-term in responsive patients. Aggressive treatment is warranted at this late stage to prevent post-transplant amyloid recurrence.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Hereditary Amyloidosis Market
Focus on developing novel therapies: Many big pharmaceutical companies have focused their resources on developing novel, targeted therapies to treat hereditary amyloidosis. For example, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals developed patisiran (Onpattro), the first-ever RNAi therapeutic approved by the FDA for hereditary ATTR amyloidosis in 2018. This novel approach specifically targets and silences mutant mRNA before production of problematic protein.
Focus on orphan drug designations: Most companies pursuing therapies for hereditary amyloidoses have sought orphan drug designation from FDA to provide valuable incentives like 7 years of market exclusivity upon approval. This lowers financial risks for additional clinical trials.
Segmental Analysis of Hereditary Amyloidosis Market
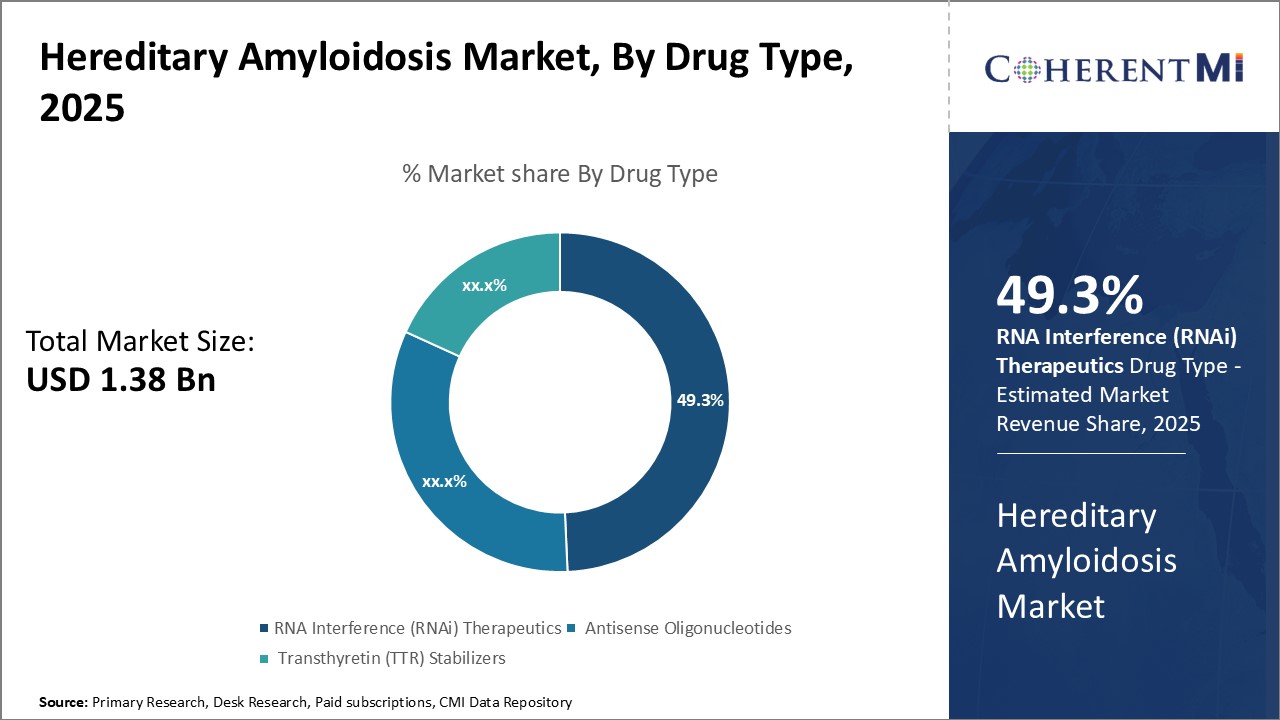 Insights, By Drug Type: Emergence of RNAi Therapy as a Promising Treatment Approach
Insights, By Drug Type: Emergence of RNAi Therapy as a Promising Treatment ApproachIn terms of drug type, RNA Interference (RNAi) therapeutics is expected to hold 49.3% share of the market in 2025, owning to its promising therapeutic potential. RNAi therapy has revolutionized the treatment landscapes of hereditary amyloidosis through targeted silencing of pathogenic genes. The introduction of RNAi drugs allows precise modulation of genes responsible for amyloid protein overproduction and aggregation.
The advent of optimized RNAi delivery systems also addresses previous limitations regarding stability, pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of RNAi molecules, further enhancing their therapeutic value. With continued development efforts, RNAi therapy is expected to play a major role in hereditary amyloidosis management and become the mainstream treatment in future.
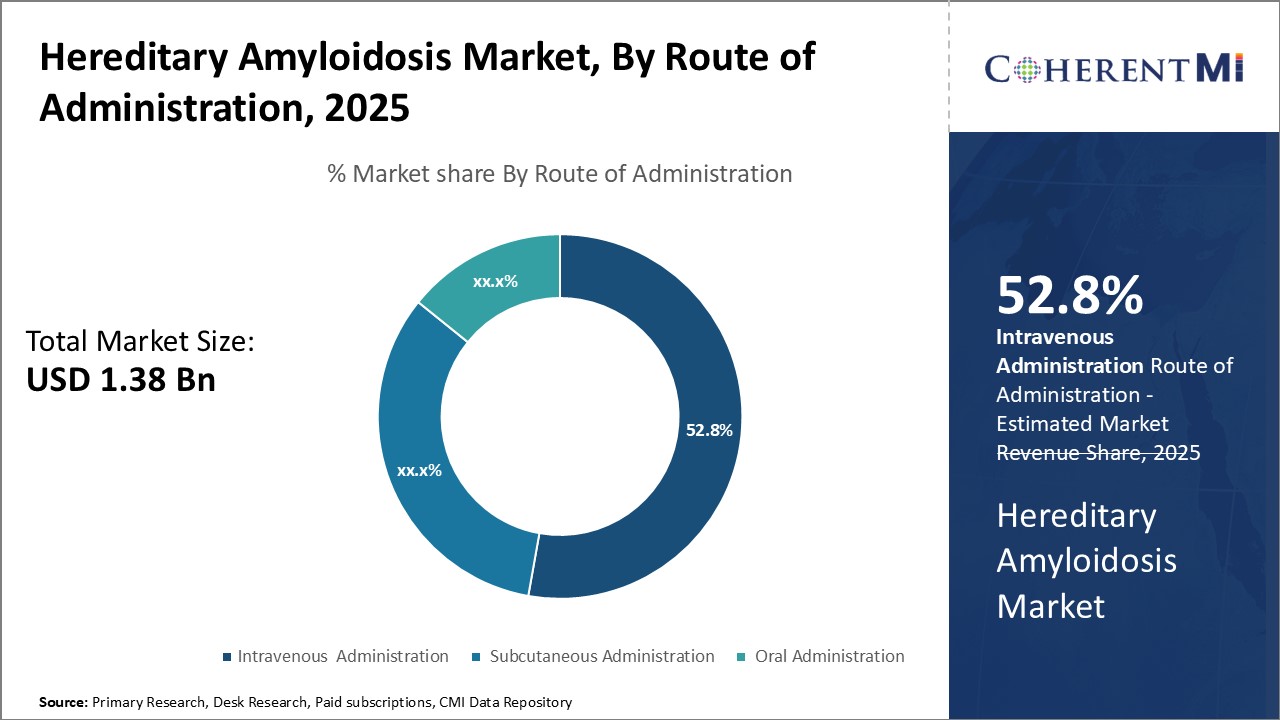
In terms of route of administration, intravenous administration segment is projected to account for 52.8% share of the market in 2025. Hereditary amyloidosis poses risk of life-threatening organ damage requiring immediate stabilization of disease condition. Intravenous administration allows rapid achievement of therapeutic drug concentrations in blood circulation and target sites compared to other routes.
Absence of complex dose titration Process and precise dosage regulation also make intravenous route preferred choice over oral and subcutaneous alternatives. Overall, intravenous administration serves as the mainstay of acute and active stage treatment of hereditary amyloidosis.
Insights, By Distribution Channel: Focus on Inpatient Management Drive Hospital Pharmacy Demand
Supervision of medication administration, dose titration, handling of adverse effects warrant dedicated pharmacy facilities and services provided most efficiently within hospital setups. Supervision of complex treatment regimens involving investigational drugs additionally rely on capabilities of hospital pharmacies.
Additional Insights of Hereditary Amyloidosis Market
- Disease Prevalence: Hereditary ATTR amyloidosis affects an estimated 50,000 people worldwide, but actual numbers may be higher due to underdiagnosis.
- Economic Burden: The high cost of treatment, which can exceed $450,000 annually per patient for some therapies, poses significant challenges for healthcare systems and patients.
- Patient Demographics: The condition predominantly affects individuals aged 30 to 70, with certain mutations more common in specific ethnic groups, such as the V30M mutation in Portugal, Sweden, and Japan.
- France has the highest diagnosed cases of hATTR in the EU5, while Germany has the lowest.
- Japan reported 648 diagnosed cases in 2020, with a focus on familial amyloid cardiomyopathy and polyneuropathy.
Competitive overview of Hereditary Amyloidosis Market
The major players operating in the hereditary amyloidosis market include Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Inc., Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Akcea Therapeutics, and Prothena Corporation.
Hereditary Amyloidosis Market Leaders
- Alnylam Pharmaceuticals
- Pfizer Inc.
- Ionis Pharmaceuticals
- Akcea Therapeutics
- Prothena Corporation
Hereditary Amyloidosis Market - Competitive Rivalry

Hereditary Amyloidosis Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Hereditary Amyloidosis Market
- In August 2023, BridgeBio Pharma announced the upcoming launch of Acoramidis for stabilizing transthyretin in Phase III clinical trials. The trial focused on Acoramidis, a transthyretin stabilizer, which is being tested for treating transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM). Key results from the study included an 81% survival rate for patients receiving Acoramidis, a relative reduction in cardiovascular mortality, and significant improvements in measures such as NT-proBNP levels and 6-minute walking distance.
- In August 2021, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals announced positive interim results from the Phase III HELIOS-A study for vutrisiran, a subcutaneous RNA interference (RNAi) therapeutic designed to treat hereditary transthyretin-mediated (hATTR) amyloidosis. The study showed promising outcomes, indicating that vutrisiran could be a beneficial treatment for patients with hATTR amyloidosis.
- In October 2020, Ionis Pharmaceuticals completed the full acquisition of Akcea Therapeutics, consolidating its pipeline of antisense therapies, including inotersen (Tegsedi). This merger aims to streamline operations, accelerate R&D efforts, and strengthen their position in the hereditary amyloidosis market. This acquisition consolidated Akcea’s antisense therapies pipeline, including inotersen (Tegsedi), aimed at treating hereditary amyloidosis.
- In May 2019, Pfizer Inc. received FDA approval for Vyndamax (tafamidis). Vyndamax, along with Vyndaqel (another formulation of tafamidis), is an oral transthyretin (TTR) stabilizer approved for the treatment of cardiomyopathy caused by transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis (ATTR-CM). This approval indeed expanded Pfizer's presence in the market and provided a critical treatment option for patients, with studies showing improved survival rates and reduced hospitalizations for heart failure.
Hereditary Amyloidosis Market Segmentation
- By Drug Type
- RNA Interference (RNAi) Therapeutics
- Antisense Oligonucleotides
- Transthyretin (TTR) Stabilizers
- By Route of Administration
- Intravenous Administration
- Subcutaneous Administration
- Oral Administration
- By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the hereditary amyloidosis market?
The hereditary amyloidosis market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.38 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 3.05 Bn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the hereditary amyloidosis market?
Expensive therapies limiting patient access and burdening healthcare systems and lack of awareness among healthcare professionals and patients leading to underdiagnosis are the major factors hampering the growth of the hereditary amyloidosis market.
What are the major factors driving the hereditary amyloidosis market growth?
The improved diagnostic techniques leading to higher detection of hereditary amyloidosis and introduction of novel drugs like RNAi and antisense oligonucleotides enhancing treatment efficacy are the major factors driving the hereditary amyloidosis market.
Which is the leading drug type in the hereditary amyloidosis market?
The leading drug type segment is RNA Interference (RNAi) therapeutics.
Which are the major players operating in the hereditary amyloidosis market?
Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Inc., Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Akcea Therapeutics, Prothena Corporation are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the hereditary amyloidosis market?
The CAGR of the hereditary amyloidosis market is projected to be 12.00% from 2025-2032.