

The plaque psoriasis market is estimated to be valued at USD 32.28 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 52.17 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.1% from 2025 to 2032. The plaque psoriasis market has been witnessing rising demand for biologics and biosimilars for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. Furthermore, expiry of patents of blockbuster biologics has led to market entry of biosimilars at more affordable prices than reference biologics, improving access to patients.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR7.1%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 7.1% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | AbbVie Inc., Novartis International AG, Johnson & Johnson (Janssen Pharmaceuticals), Eli Lilly and Company, Amgen Inc. and Among Others |
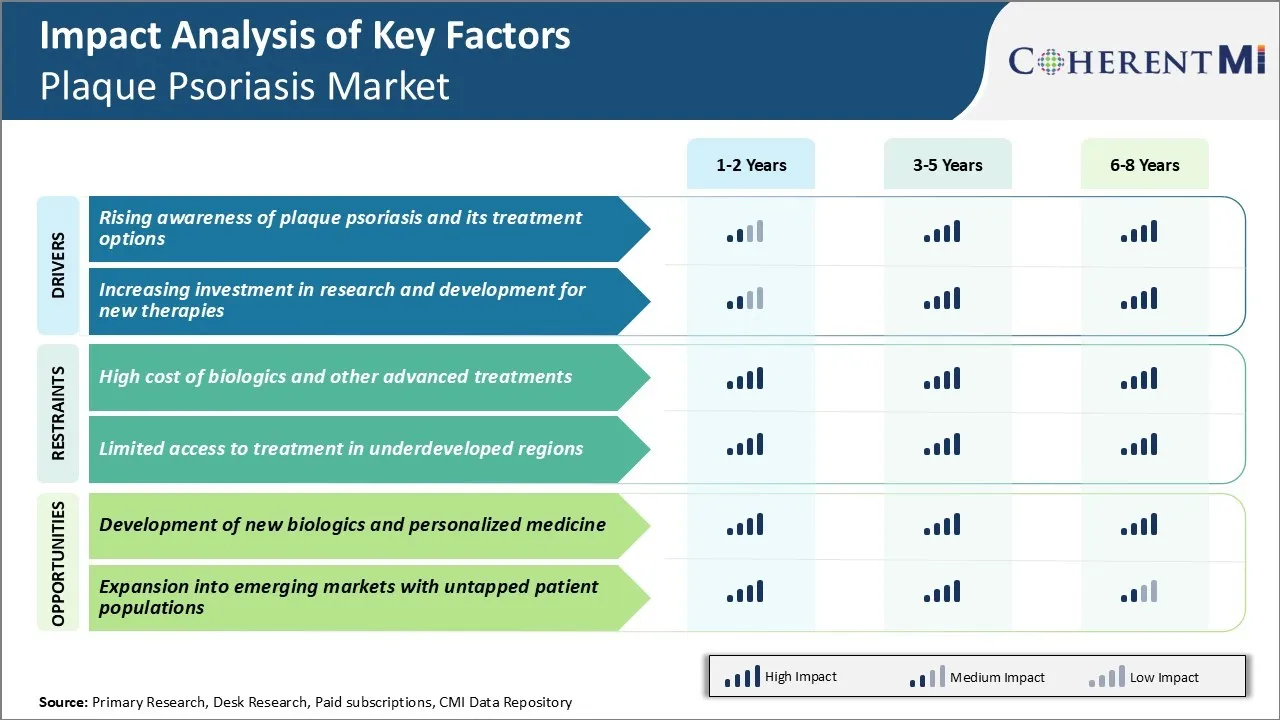
Market Driver - Rising Awareness of Plaque Psoriasis and its Treatment Options
As more light continues to shine on plaque psoriasis, patients are becoming increasingly aware of their condition and the avenues available for effective management. Recognition events like Psoriasis Awareness Day spread global attention to the fact that plaque psoriasis is much more than mere skin deep. Personal testimony by prominent public personalities battling the condition has also lifted the proverbial veil of secrecy.
With augmented recognition of plaque psoriasis being a life-long condition requiring continuous care, adherence to doctor prescribed treatments improves overall. The digital health revolution complements traditional awareness initiatives.
People explore web resources to fact check their symptoms, gain a richer understanding of pathology and stay abreast of latest therapeutic innovations. Online communities give individuals access to a supportive network sharing lived experiences. Telemedicine consultations further facilitate convenient participation in the decision-making process regarding care options.
Market Driver - Increasing Investment in Research and Development for New Therapies
Major biopharmaceutical players and startups alike recognize the commercial potential in a market crying out for novel solutions to plaque psoriasis management. Given prominent unmet needs persist despite existing treatment armamentarium, significant capital is being poured into the research and development pipeline.
Much of this investment targets advancing understanding of molecular pathways underlying chronic inflammation and aberrant skin cell turnover in plaque psoriasis. With a better grasp of disease pathogenesis, more targeted drug candidates can be designed.
Combination therapies marrying established drugs with newer entities also present an attractive avenue to enhance efficacy and tolerance profiles. Life cycle management of top selling biologics through additional formulations, convenient delivery methods and tailored therapeutic protocols aims at improving patient adherence and outcomes over the long term.
Bolstered by the success of breakthrough first-in-class approvals in recent history, venture capitalists display confidence in the viability and commercial feasibility of novel mechanisms for treatment. Notable acquisitions and large collaborations signal big pharma's affirmation of new drug pipelines being built at biotechs. Such deals promise accelerated development in the plaque psoriasis market.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High Cost of Biologics and Other Advanced Treatments
One of the major challenges plaguing the plaque psoriasis market is the high cost of biologics and advanced treatment options available for patients. Biologics such as anti-TNF inhibitors, IL inhibitors and other novel targets provide highly effective treatment options compared to traditional systemic therapies.
However, the development and production costs associated with biologics drives up the list prices and out-of-pocket costs for patients. The average annual cost of biologic therapy ranges anywhere between $30,000 to $100,000 depending on the drug.
Additionally, the required lifelong treatment with biologics also poses continued financial burden. This makes advanced therapies inaccessible for many patients and shifts them to conventional systemic drugs which are relatively less efficacious. The issues of affordability act as a barrier for patients to seek and adhere to optimal treatment regimens.
It also restricts the overall market growth potential for innovative biologics. Unless measures are taken to make these vital drugs more affordable, high treatment costs will continue to negatively impact both patients and the plaque psoriasis market.
Market Opportunity - Development of New Biologics and Personalized Medicine
One of the major opportunities for future growth in the market lies in development of new biologic compounds with novel mechanisms and personalized treatment approaches. Currently, the biologics in plaque psoriasis market is dominated by anti-TNF and anti-IL therapies.
However, newer biologics targeting additional pathways such as IL-17, IL-23 and IL-22 are emerging in the pipeline. These new molecular entities hold promise to address unmet needs of patients who are partial or non-responders to existing therapies.
At the same time, advancements are being made in the field of pharmacogenomics and predictive biomarkers to aid patient selection for optimal therapies. This shift towards personalized medicine will help maximize treatment effectiveness while minimizing trial-and-error based prescribing.
It will also improve real-world outcomes and patients' quality of life, thereby expanding the addressable scope in plaque psoriasis market over the long run. The next decade is expected to witness continuous approval of personalized medicine supported pipeline drugs, bolstering overall prospects for players.
Plaque psoriasis typically follows a step-care treatment approach based on disease severity and response to prior therapies. For mild disease, prescribers commonly recommend topical corticosteroids like clobetasol propionate (Temovate) or calcipotriene (Dovonex). If topicals are ineffective, photo(thermal)therapy may be introduced to induce remission.
For moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, prescribers often first opt for phototherapy - either narrowband ultraviolet B (NUVB) or psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA). Psoralen compounds like 8-methoxypsoralen (Oxsoralen) are administered prior to UVA exposure in PUVA therapy. When phototherapy proves inadequate or impractical, systemic medications are considered. At this stage, older oral treatments like methotrexate, cyclosporine, and acitretin may be prescribed.
For patients who do not respond or lose response to the above options, biologic disease-modifying therapies have become the standard of care. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors were the first biologics approved for psoriasis. Etanercept (Enbrel) and infliximab (Remicade) remain commonly prescribed options. Interleukin inhibitors targeting IL-17 or IL-23 pathways, such as secukinumab (Cosentyx), ixekizumab (Taltz), and guselkumab (Tremfya), have demonstrated high efficacy and are rapidly gaining share in the plaque psoriasis market, especially for moderate-severe disease.
Plaque psoriasis can range from mild to severe based on the extent of skin involvement and impact on quality of life. Treatment involves topical or oral systemic therapies based on severity and response to prior lines of treatment.
Mild disease typically involves less than 3% body surface area (BSA) and is initially managed with topical corticosteroids or vitamin D analogs alone or in combination. For those who fail or relapse with topicals, phototherapy is recommended. Narrowband UVB is preferred over broadband due to better safety profile.
Moderate to severe disease involves ≥3% BSA and warrants systemic therapies. First-line options include oral medications like methotrexate, cyclosporine, and retinoids. Among these, methotrexate is favored due to well-established efficacy and long-term safety data. However, monitoring is needed due to potential side effects like liver toxicity.
For patients who do not respond or lose response to first-line systemic therapies, biologics provide highly effective treatment options. TNF-α inhibitors like etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab are well-established choices, with adalimumab demonstrating best long-term clearance rates. Anti-IL drugs secukinumab and ixekizumab are preferred over biologics targeting other mechanisms due to superior efficacy data.
Biologics continue to dominate the plaque psoriasis market due to their high efficacy and safety profile. Companies like Janssen (Johnson & Johnson), AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Amgen, Novartis, and Pfizer have developed innovative biologic drugs that have revolutionized plaque psoriasis treatment. For example:
- In 2009, Janssen received approval for Stelara (ustekinumab), the first biologic treatment that targeted both IL-12 and IL-23 cytokines. Within a year, Stelaracaptured a sizable share in the plaque psoriasis market and became one of the top prescribed biologics due to its high efficacy and favorable safety profile.
- In 2014, Eli Lilly's Taltz (ixekizumab) was approved. Taltz is a monoclonal antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17A, a protein involved in inflammation. Taltz quickly gained acceptancedue to superior efficacy rates and convenient dosing over other IL-17 inhibitors like Cosentyx and Skyrizi. By 2018, Taltz sales reached $1 billion.
- More recently, in 2019 AbbVie’s Rinvoq (upadacitinib), an oral JAK inhibitor, was approved. Rinvoq represented the first approved oral treatment for plaque psoriasis in over 20 years. Its oral route of administration rather than injections gave it an edge over other biologics. Rinvoq captured a sizable share within its first year on the plaque psoriasis market.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
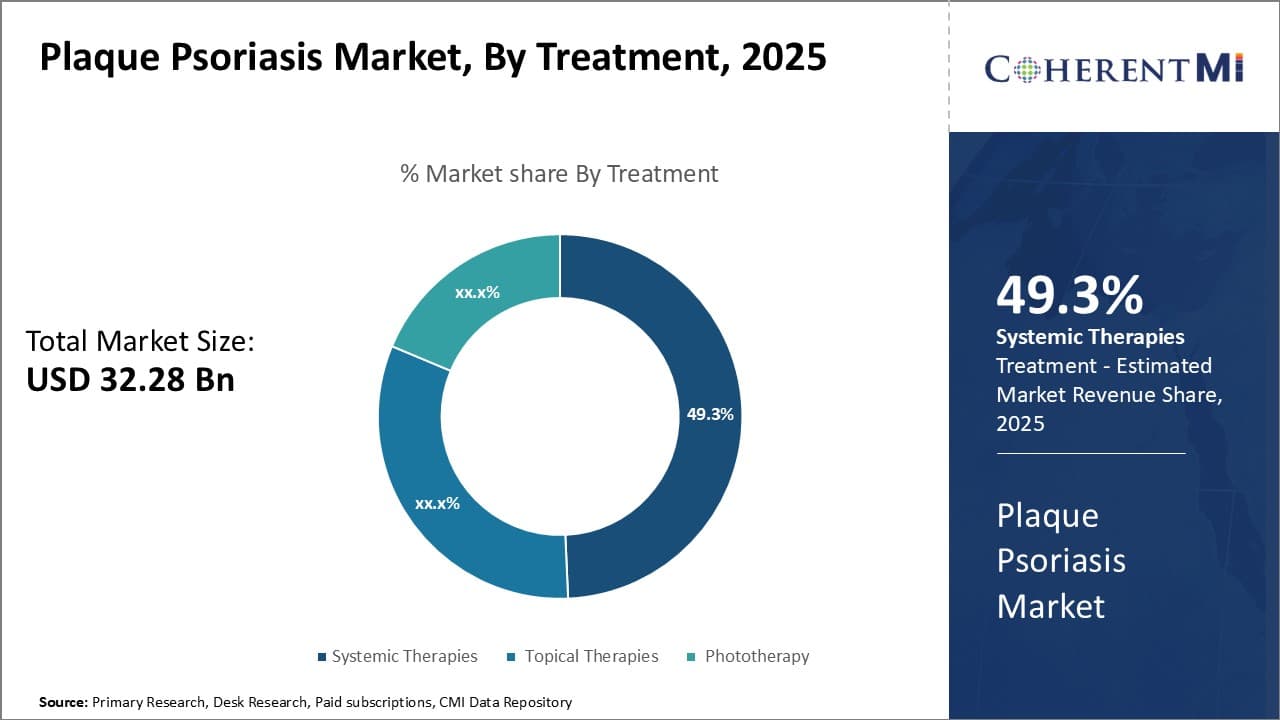
Insights, By Treatment: Accessibility drives adoption of Systemic Therapies
In terms of treatment, systemic therapies are expected to hold 49.3% share of the plaque psoriasis market in 2025. This is due to their accessibility and effectiveness in treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis symptoms. Systemic therapies provide patients suffering from moderate to severe plaque psoriasis an alternative treatment option that is able to tackle the root cause of their condition from within.
Traditional systemic agents such as methotrexate, acitretin and cyclosporine have been standard treatments for many years due to their widespread availability in generic forms, making them an affordable option for patients. More recently, the introduction of biologic therapies targeting cytokines like TNF inhibitors and IL inhibitors has expanded treatment choices further.
Although biologics are significantly more expensive than traditional systemic agents, their superior efficacy often justifies their cost for patients with more debilitating forms of plaque psoriasis that are unresponsive to other treatment lines. The accessibility of both traditional and biologic systemic treatment modalities, along with their effectiveness at managing even the most difficult cases of plaque psoriasis, drives the majority of share in the plaque psoriasis market towards systemic therapies within the overall treatment segment.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
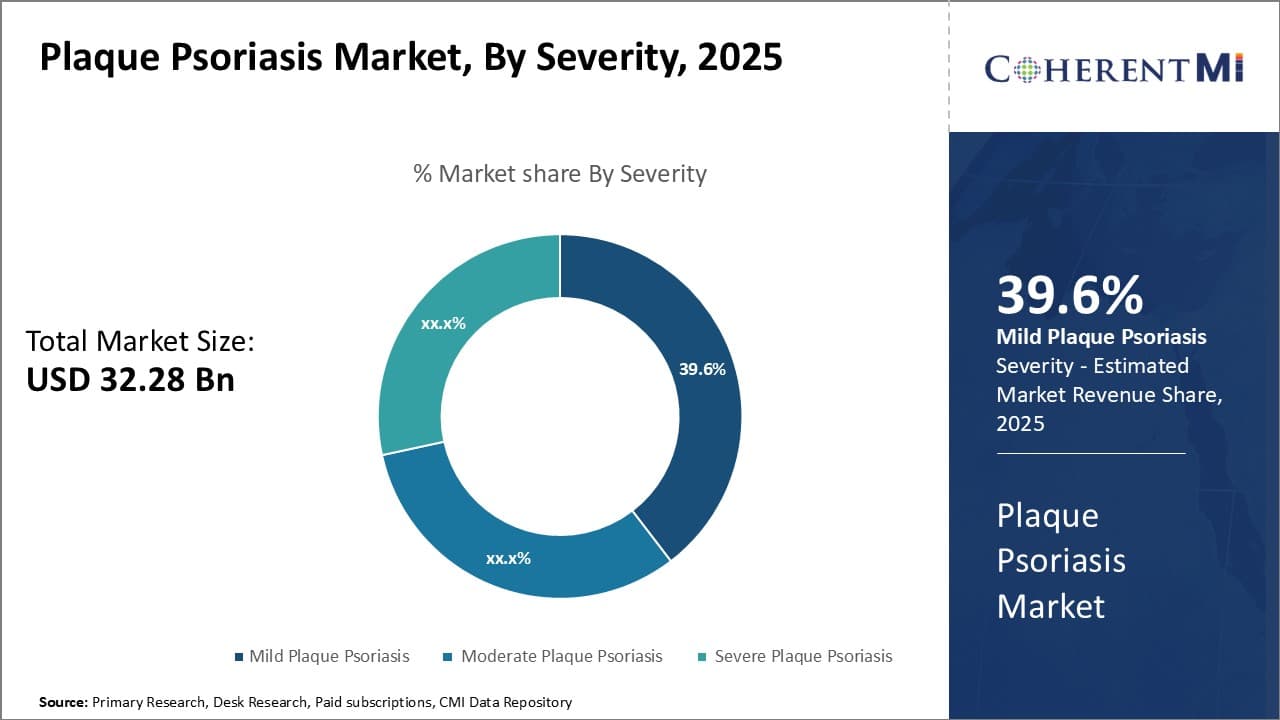
Insights, By Severity: Ease of Use Boosts Topical Therapies in Mild Plaque Psoriasis
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Severity: Ease of Use Boosts Topical Therapies in Mild Plaque Psoriasis
In terms of severity, mild plaque psoriasis is expected to hold 39.6% share of the plaque psoriasis market in 2025. This is driven by the ease of use associated with topical therapies for mild plaque psoriasis.
For patients with mild forms of plaque psoriasis affecting small body surface areas, topical therapies such as corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues and retinoids provide a simple treatment approach with minimal effort or time commitment required.
Creams and ointments can easily be applied in the home setting versus more complex administration routines associated with phototherapy or systemic oral and injectable medications. This convenience factor encourages treatment adherence and preference for topical therapies in mild cases.
Furthermore, topical corticosteroids are usually first-line due to their fast response times within one to two weeks of use. The non-invasive, low maintenance nature of topical therapies makes them ideal for patients whose plaque psoriasis symptoms are well-managed and not interfering significantly with daily life activities. Their ease of use compared to alternatives thus sustains topical therapies portion of the overall plaque psoriasis market.
Insights, By Distribution Channel: Expertise Drives Preference for Hospital Pharmacies
In terms of distribution channel, hospital pharmacies contribute the highest share of the plaque psoriasis market driven by expertise in specialty medications. For patients requiring complex biologic treatments or phototherapy with UV light therapy, hospital pharmacies provide easy access to specialized doctors, dermatologists and nursing staff who have extensive experience administering these therapies.
Biologic infusions and phototherapy sessions held in outpatient hospital facilities benefit from dedicated medical professionals, clean environments and established protocols to minimize safety and technical risks. This level of specialized expertise reassures patients and their doctors that the most technically demanding plaque psoriasis treatments can be managed reliably and effectively.
While retail pharmacies and online channels provide convenience, they lack the concentrated area of expertise found in hospital settings for intricate plaque psoriasis therapies. Therefore, hospital pharmacies remain the preferred distribution channel to obtain specialized plaque psoriasis treatments requiring oversight by medical experts. Their resources and staff competency drive plaque psoriasis market leadership in this distribution segment.
The major players operating in the plaque psoriasis market include AbbVie Inc., Novartis International AG, Johnson & Johnson (Janssen Pharmaceuticals), Eli Lilly and Company, Amgen Inc., Celgene Corporation (a Bristol Myers Squibb company), Pfizer Inc., UCB S.A., Merck & Co., Inc., Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Dermavant Sciences GmbH, IQVIA Biotech, Samsung Bioepis Co., Ltd, Durect Corporation, Astellas Pharma Inc., Biogen, Dow Pharmaceutical Sciences, Shire plc, Zalicus Inc., Santalis Pharmaceuticals Inc, Maruho Co Ltd., and AstraZeneca plc.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
Plaque Psoriasis Market is segmented By Treatment (Systemic Therapies, Topical Therapies, Photothera...
Plaque Psoriasis Market
How big is the plaque psoriasis market?
The plaque psoriasis market is estimated to be valued at USD 32.28 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 52.17 Bn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the plaque psoriasis market?
High cost of biologics and other advanced treatments and limited access to treatment in underdeveloped regions are the major factors hampering the growth of the plaque psoriasis market.
What are the major factors driving the plaque psoriasis market growth?
Rising awareness of plaque psoriasis and its treatment options and increasing investment in research and development for new therapies are the major factors driving the plaque psoriasis market.
Which is the leading treatment in the plaque psoriasis market?
The leading treatment segment is systemic therapies.
Which are the major players operating in the plaque psoriasis market?
AbbVie Inc., Novartis International AG, Johnson & Johnson (Janssen Pharmaceuticals), Eli Lilly and Company, Amgen Inc., Celgene Corporation (a Bristol Myers Squibb company), Pfizer Inc., UCB S.A., Merck & Co., Inc., Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Dermavant Sciences GmbH, IQVIA Biotech, Samsung Bioepis Co., Ltd, Durect Corporation, Astellas Pharma Inc., Biogen, Dow Pharmaceutical Sciences, Shire plc, Zalicus Inc., Santalis Pharmaceuticals Inc, Maruho Co Ltd, and AstraZeneca plc are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the plaque psoriasis market?
The CAGR of the plaque psoriasis market is projected to be 7.1% from 2025-2032.