Propionic Acidemia Therapeutic Market Size - Analysis
Market Size in USD Mn
CAGR7.8%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 7.8% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | HemoShear Therapeutics, LogicBio Therapeutics, Roche, Astellas Pharma, Moderna Therapeutics and Among Others |
please let us know !
Propionic Acidemia Therapeutic Market Trends
Gene therapy holds immense potential in treating various metabolic disorders including propionic acidemia by replacing the missing or defective genes. Recent breakthroughs in vector technology and gene delivery methods have enabled more targeted and reliable introduction of normal genes into the body's cells and tissues.
Some of the key research institutes evaluating gene therapy approaches for propionic acidemia include NIH Rare Diseases Clinical Research Network, University College London, Mount Sinai School of Medicine and Massachusetts General Hospital.
There is an increased emphasis on developing treatments for rare or orphan diseases. Regulatory agencies and governments across various countries are proactively supporting research on rare disorders through incentives such as tax credits, grant funding, fee waivers and market exclusivities. For instance, in the US, the Orphan Drug Act of 1983 aims to stimulate drug development for rare diseases by providing manufacturers with various benefits if the product is approved to treat a rare condition affecting less than 200,000 people.
There are also increased M&A deals involving small rare disease-focused biotechs which helps accelerate product pipelines. The rarity of individual rare disorders concentrates patient populations, making marketing and commercialization strategies more targeted and feasible. This industry evolution makes propionic acidemia an emerging therapeutic category attracting greater R&D investments.
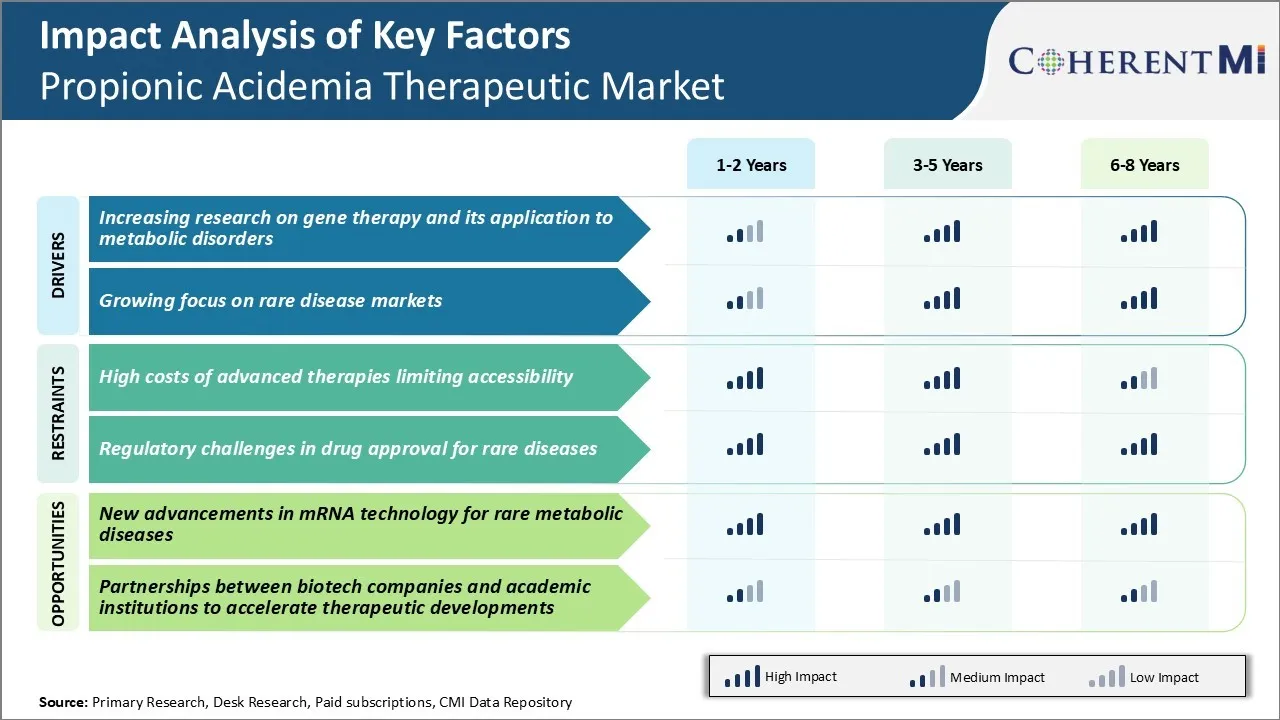
One of the major challenges facing the propionic acidemia therapeutic market is the high costs associated with advanced therapy options such as gene and cell therapies. These innovative treatment approaches have promising potential to effectively manage and even cure rare metabolic diseases like propionic acidemia.
Most national healthcare systems and private insurance providers have difficulty incorporating the costs of these new advanced treatments into their budgets. As a result, only a small subset of eligible patients who can afford the out-of-pocket costs or have sponsors willing to pay are able to access these potentially life-changing therapies.
One promising opportunity for propionic acidemia therapeutic market is the ongoing progress in mRNA technology. Researchers are exploring the application of messenger RNA as a new platform for developing gene therapies to treat rare metabolic disorders. Unlike traditional gene therapies that rely on viral vectors, mRNA therapeutics could offer advantages in safety, scalability of manufacturing, and possibly lower costs over the long term.
Advancements that result in safe, effective, and affordable mRNA therapies translatable to humans could open up a major new treatment option for propionic acidemia. Widespread application of mRNA technology holds potential to address one of the key current challenges facing market adoption of advanced therapies - high costs limiting accessibility. Successful development of mRNA gene replacements could re-shape the entire rare disease therapeutic landscape in the coming years.
Prescribers preferences of Propionic Acidemia Therapeutic Market
Propionic Acidemia is typically treated via a step-wise treatment approach consisting of multiple lines of therapy targeting different stages of the disease. For mild cases, prescribers typically start with nutritional interventions like restricting protein intake and supplementing with carnitine and glycine.
In more severe or chronic cases, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is considered. Prior to HSCT, prescribers aim to minimize toxic metabolite levels using the above medications. HSCT has shown promise in arresting further progression if performed early.
Treatment Option Analysis of Propionic Acidemia Therapeutic Market
Propionic Acidemia has four primary stages - Neonatal, Early Childhood, Late Childhood and Adulthood.
In early childhood, metabolic control is crucial to prevent further complications. A specialized low-protein diet with supplements to assist protein breakdown is initiated. Medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) oil provides an alternate energy source. Drugs like sodium benzoate and glycine help eliminate toxic byproducts.
In adulthood, the standard treatment comprises of dietary therapy with low protein foods supplemented by essential amino acids, carnitine, B12, glycine, MCT oil, sodium benzoate and sodium phenylbutyrate. While medications help control acute episodes, long-term complications involving heart, brain and muscles may arise needing multidisciplinary management. Liver and kidney transplant is considered in severe, treatment-resistant cases to cure the underlying defect.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Propionic Acidemia Therapeutic Market
Product Innovation: One of the most effective strategies adopted by players has been continuous product innovation. In 2017, Synlogic launched SYNB1618, a synthetic biotic designed to degrade propionate as a potential treatment for propionic acidemia. Clinical trials are currently underway. Earlier in 2013, Horizon Pharma launched BUPHENYL tablets, the first FDA approved drug to treat urea cycle disorders including propionic acidemia.
Acquisitions: Larger players have strengthened their portfolio through acquisitions of smaller biotechs. In 2019, Chiesi Farmaceutici acquired Orphan Technologies, acquiring rights to commercialize Orphan Technologies' product Carglumic acid for propionic acidemia in the EU. This expanded Chiesi's global presence.
Segmental Analysis of Propionic Acidemia Therapeutic Market
In terms of therapeutics, gene therapy is expected to hold 55.2% share of the market in 2024, owing to major advances in this field. Gene therapy offers the potential for a 'one-time' curative treatment by delivering therapeutic genes into target cells of patients to compensate for mutated genes that cause disease.
Additionally, new delivery methods allow for more targeted and efficient gene delivery compared to earlier techniques. As the technology matures, gene therapy is gaining recognition as a viable treatment option instead of standard of care enzyme replacement therapies that require frequent administrations.
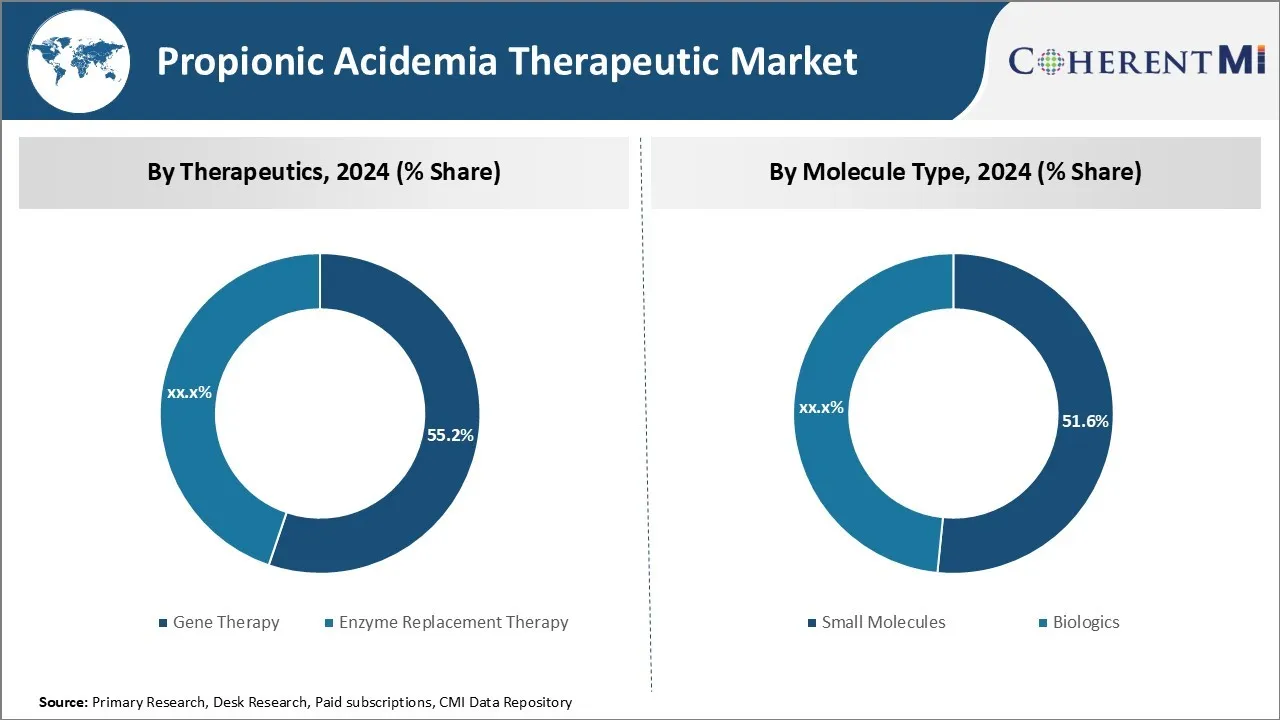
In terms of molecule type, small molecules are expected to hold 51.6% share of the market in 2024, due to the convenience they offer over biologics in administration. Small molecule therapies for propionic acidemia mainly aim to lower toxic metabolite levels or help bypass blocked metabolic pathways. They are easier to develop, manufacture, store and administer compared to biologics.
In terms of By Administration Route, the Oral route contributes the highest share due to the unparalleled ease and comfort it offers patients over other routes. Oral medications have clear advantages for long-term conditions like Propionic Acidemia, which require lifelong treatment. They are generally perceived as more natural and discreet by patients compared to alternatives involving needles or intravenous access. Additionally, oral drugs allow for self-administration at home without much training.
Additional Insights of Propionic Acidemia Therapeutic Market
Propionic acidemia affects approximately 1 in 100,000 people globally. Current treatments rely on strict dietary management and supplements, but gene therapy is expected to revolutionize the market by offering more comprehensive treatment options.
Competitive overview of Propionic Acidemia Therapeutic Market
The major players operating in the propionic acidemia therapeutic market include HemoShear Therapeutics, LogicBio Therapeutics, Roche, Astellas Pharma, Moderna Therapeutics, Homology Medicines, Inc., Abeona Therapeutics, Inc., and Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical Inc.
Propionic Acidemia Therapeutic Market Leaders
- HemoShear Therapeutics
- LogicBio Therapeutics
- Roche
- Astellas Pharma
- Moderna Therapeutics
Propionic Acidemia Therapeutic Market - Competitive Rivalry

Propionic Acidemia Therapeutic Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Propionic Acidemia Therapeutic Market
- In July 2024, HemoShear Therapeutics announced a breakthrough in gene therapy targeting Propionic Acidemia. The company’s research shows a potential 50% reduction in harmful metabolites, offering hope for long-term disease management.
- In October 2023, LogicBio Therapeutics completed its Phase I trial for a gene-editing treatment for Propionic Acidemia, marking a significant step toward precision medicine.
- mRNA-3927 is Moderna's investigational mRNA therapeutic for Propionic Acidemia (PA). It utilizes mRNA technology to encode for the alpha and beta subunits of the mitochondrial enzyme propionyl-CoA carboxylase (PCC). This enzyme is crucial for addressing the underlying genetic cause of Propionic Acidemia, where patients have mutations in the genes responsible for the production of this enzyme. Moderna's therapy aims to restore the enzyme's function, helping to reduce the accumulation of harmful metabolites.
- Gene therapy: Companies like Homology Medicines and Abeona Therapeutics are focusing on gene therapies to address genetic defects causing the disorder. Homology Medicines works on gene therapy and gene editing programs for conditions like PKU and Hunter syndrome, while Abeona Therapeutics focuses on gene therapies for lysosomal storage diseases and ophthalmic conditions.
Propionic Acidemia Therapeutic Market Segmentation
- By Therapeutics
- Gene Therapy
- Enzyme Replacement Therapy
- By Molecule Type
- Small Molecules
- Biologics
- By Administration Route
- Oral
- Intravenous

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the propionic acidemia therapeutic market?
The propionic acidemia therapeutic market is estimated to be valued at USD 600.6 Mn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 1016.6 Mn by 2031.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the propionic acidemia therapeutic market?
High costs of advanced therapies limiting accessibility and regulatory challenges in drug approval for rare diseases are the major factors hampering the growth of the propionic acidemia therapeutic market.
What are the major factors driving the propionic acidemia therapeutic market growth?
Increasing research on gene therapy and its application to metabolic disorders and growing focus on rare disease markets are the major factors driving the propionic acidemia therapeutic market.
Which are the leading therapeutics in the propionic acidemia therapeutic market?
The leading therapeutics segment is gene therapy.
Which are the major players operating in the propionic acidemia therapeutic market?
HemoShear Therapeutics, LogicBio Therapeutics, Roche, Astellas Pharma, Moderna Therapeutics, Homology Medicines, Inc., Abeona Therapeutics, Inc., and Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical Inc. are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the propionic acidemia therapeutic market?
The CAGR of the propionic acidemia therapeutic market is projected to be 7.8% from 2024-2031.