Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market Size - Analysis
The market is witnessing positive trends with strong product pipeline and launch of innovative drugs to treat pulmonary hypertension. Furthermore, the growing awareness about available treatment options and government support are supporting the adoption of pulmonary hypertension drugs in the market. However, high treatment cost and lack of disease-specific guidelines in some regions may hinder the market growth during the forecast period.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR7.3%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 7.3% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Tenax Therapeutics, Atgeno AB, Bayer, Bellerophon Therapeutics, United Therapeutics and Among Others |
please let us know !
Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market Trends
With increased awareness about symptoms and risk factors associated with pulmonary hypertension, a high number of people are getting themselves screened regularly. Pulmonary hypertension is usually difficult to diagnose at an early stage as symptoms are vague and non-specific. However, recent diagnostic advancements such as right heart catheterization and echocardiography have enabled accurate detection and classification of disease even at mild or moderate stages. This has significantly improved survival rates as patients can now seek treatment much before the condition progresses to later stages. Numerous non-profit organizations and advocacy groups are also educating general public and healthcare providers through various awareness programs. They educate people on recognising early warning signs of the disease and emphasise importance of timely medical advice. All these efforts have collectively contributed towards identifying more PH patients and allowing them to access life-prolonging therapies in a timely manner. As a result of early detection, the target population suitable for currently available treatment options has expanded. This acts as a major growth driver for pharmaceutical companies manufacturing approved drugs for pulmonary hypertension.
Market Driver - A Strong Pipeline with Novel Therapies That Target Multiple Pathways, Such as Vasodilators and Gene Therapies.
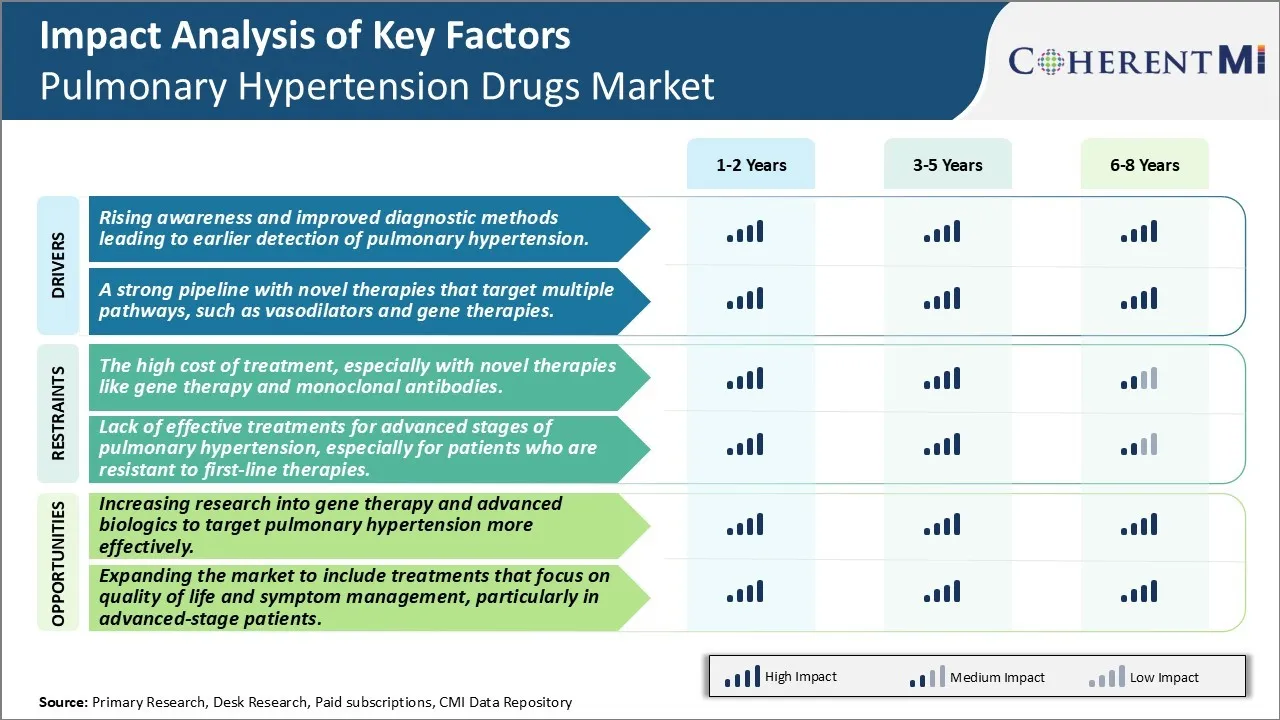
Market Challenge - The High Cost of Treatment, Especially with Novel Therapies Like Gene Therapy and Monoclonal Antibodies.
Increasing research into gene therapy and advanced biologics to target pulmonary hypertension more effectively offers promising opportunities for market growth. Scientists are exploring novel gene therapy approaches that could potentially cure pulmonary hypertension by correcting the underlying genetic defects. Several biotechs and pharmaceutical companies are actively conducting clinical trials of gene therapies delivered via viral vectors. At the same time, monoclonal antibodies and other biologic drugs are being developed that can better regulate pathways involved in pulmonary artery constriction and remodelling. If successful, such advanced modalities could revolutionise treatment by achieving superior efficacy than existing drugs with durability of response. Their ability to deliver long-lasting benefits in a single course of treatment also addresses the compliance challenges with daily oral regimens. As research progresses, newer biologics and gene therapies are expected to enter the market in the coming years, driving higher spending and expanding the pulmonary hypertension drugs market size significantly.
Prescribers preferences of Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market
Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) can be classified into five stages based on the mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP) and cardiac output. Initial treatment typically starts with Group 1 PH medications during Stages 1-3 when mPAP is 25-40 mmHg. Endothelin receptor antagonists (ERAs) such as bosentan (Tracleer) and ambrisentan (Letairis) are often first-line options due to favorable risk-benefit profiles. Phosphodiesterase type-5 inhibitors (PDE-5i) like sildenafil (Revatio) and tadalafil (Adcirca) are also commonly prescribed.
For patients in advanced Stages 4-5 with mPAP over 40 mmHg, prostanoids like epoprostenol (Flolan), treprostinil (Tyvaso), and iloprost (Ventavis) provide the most vasodilatory effect and hence, better survival benefits. However, due to their parenteral routes of administration and associated side effects, prostanoids are generally reserved for later lines of treatment.
Treatment Option Analysis of Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market
Pulmonary hypertension has four stages based on symptoms and hemodynamics. Stage I involves mild symptoms with a mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) of 25-30 mmHg at rest. Stage II shows moderate limitations with an mPAP of 31-35 mmHg.
For stage I, medications like Endothelin receptor antagonists (ERAs) such as ambrisentan (Letairis) or macitentan (Opsumit) are preferred. They work by blocking receptors that cause constriction of blood vessels in the lungs.
Stage III may require combining therapies like adding a phosphodiesterase type-5 inhibitor like tadalafil (Adcirca) to an ERA.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market
Drug Innovation Through R&D: Developing novel drugs has been a crucial strategy adopted by leading players to gain a competitive edge. For example, Actelion (now Janssen) launched Opsumit (macitentan) in 2013, the first oral endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA) approved for pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Opsumit was a major breakthrough as it offered improved efficacy and safety over existing ERAs. Its approval and commercial success helped Actelion strengthen its leadership position in the PAH market.
Targeted Acquisitions: Strategic acquisitions of smaller firms working on new drugs/technologies have reinforced product pipelines.
The above examples show that combinations of innovative R&D, prudent M&A activity, and exemplary commercialization have enabled companies to introduce multiple novel drugs and capture the majority market share in pulmonary hypertension over the past two decades.
Segmental Analysis of Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market
 Insights, By Stages, Phase-III is leading Due to Advancing Development Leads to Market Dominance in the Coming Years.
Insights, By Stages, Phase-III is leading Due to Advancing Development Leads to Market Dominance in the Coming Years.By Stages, Phase-III is expected to contribute the highest share 45.9% in 2025 owing to the extensive development undergone by drugs in this stage. Drugs in Phase-III have proven their efficacy and safety profile based on preliminary clinical trials involving larger human populations. Extensive testing allows manufacturers to identify and address any issues, refine dosage regimens, evaluate long-term effects and comparative effectiveness. This rigorous validation gives Phase-III drugs a stronger foundation for approval and commercial launch. They can rapidly attain widespread physician prescription and patient acceptance due to demonstrated clinical benefits and risk-mitigation.
Additionally, Phase-III studies allow sponsors to file for expedited approvals like Priority Review or Breakthrough Therapy Designation. This shortens review timelines and speeds market entry. It also positions Phase-III drugs as the standard of care, encouraging doctors to prefer them over early phase alternatives. First-mover advantage is cemented through loyal patient followings and doctor-patient familiarity. Therefore, Phase-III represents the pinnacle of clinical proof, enabling market-leading positioning, sales momentum and commercial sustainability in pulmonary hypertension management.
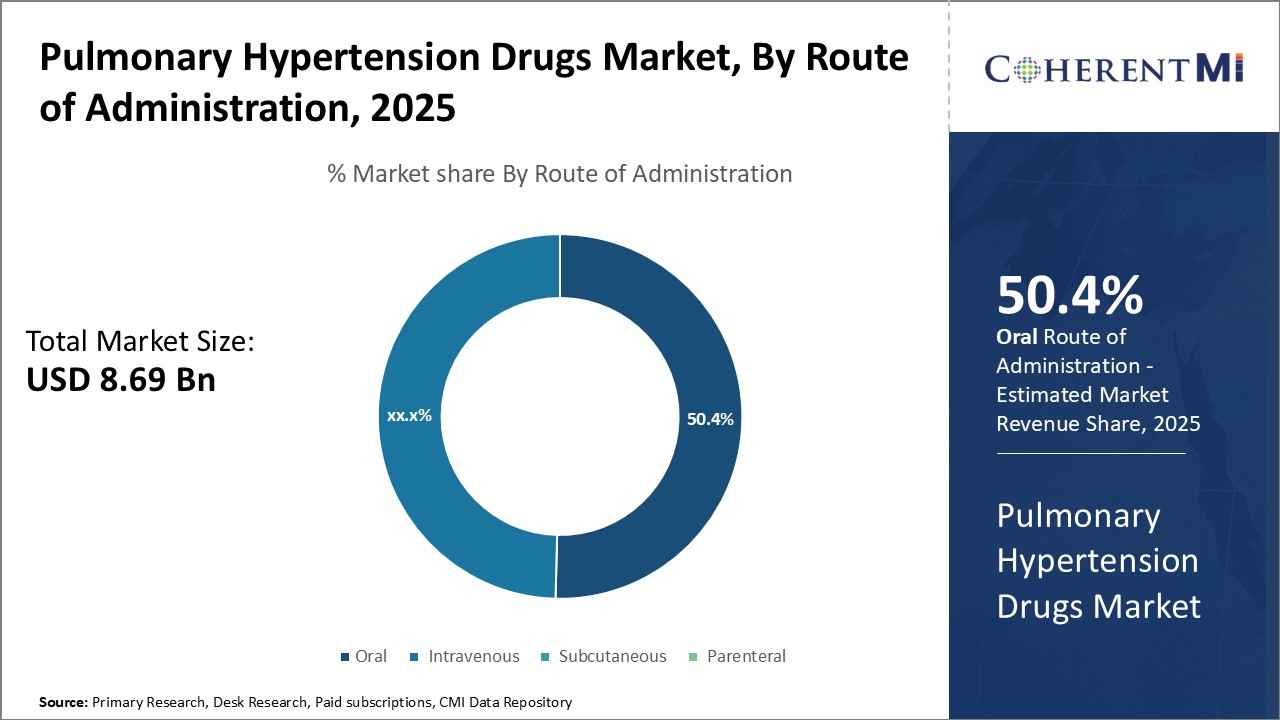
In terms of By Route of Administration, the oral route is expected to contribute the highest share 50.4% in 2025 due to unparalleled accessibility and comfort advantages over alternative pathways. Patients prefer oral medications as they are non-invasive and can be self-administered at home with minimal assistance. This ensures treatment adherence and compliance even in outpatient settings without physical monitoring.
Physicians also favor the oral route as it streamlines outpatient care without recurrent clinic/hospital visits or skilled nursing for administration. Apart from convenience, it reduces infection risks and vascular access issues associated with intravenous therapies. Oral drugs eliminate painful injections or indwelling catheters, boosting patient satisfaction and quality of life. Their widespread use decreases clinic overhead costs as well. Therefore, the ubiquitous, non-invasive nature of oral delivery translates directly into higher market preference and consistency in pulmonary hypertension management.
Insights, By Molecule Type, Versatility of Small Molecules Drives Widespread Adoption in the Forecast Period.
Small molecule drugs also have well-established structure-activity relationships facilitating systematic optimization of pharmacological properties. Extensive medicinal chemistry helps enhance target affinity, selectivity and potency while maintaining safety. As a result, small molecules can be designed to achieve diverse mechanisms of action - from vasodilation to antiproliferative effects. This multimodal capability addresses pulmonary hypertension more comprehensively than monoclonal or biologic alternatives with narrower MOAs.
Additional Insights of Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market
Pulmonary hypertension is a progressive and life-threatening condition characterized by increased blood pressure in the lungs. Despite advances in understanding the disease, current treatments remain limited, especially for advanced-stage patients. Novel therapies in the pipeline focus on addressing the underlying causes of pulmonary hypertension, such as improving vasodilation and targeting specific molecular pathways like soluble guanylate cyclase and nitric oxide signaling. Companies like Tenax Therapeutics, Bayer, and Atgeno AB are leading the charge with late-stage products that aim to improve patient outcomes by targeting multiple pathways simultaneously. With growing interest in gene therapy and small-molecule treatments, the pulmonary hypertension market is expected to see significant growth over the next decade as more therapies gain approval. The future of pulmonary hypertension treatment lies in a personalized approach that combines symptom management with disease-modifying therapies to improve long-term survival and quality of life for patients.
Competitive overview of Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market
The major players operating in the Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market include Tenax Therapeutics, Atgeno AB, Bayer, Bellerophon Therapeutics, United Therapeutics, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Acceleron Pharma, Altavant Sciences, Gossamer Bio, Actelion Ltd, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Steady Med Ltd, Eli Lilly and Company and Johnson & Johnson Services Inc.
Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market Leaders
- Tenax Therapeutics
- Atgeno AB
- Bayer
- Bellerophon Therapeutics
- United Therapeutics
Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market - Competitive Rivalry

Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market
- In August 2024, Tenax Therapeutics announced the progression of TNX-103 into Phase III trials for pulmonary hypertension, demonstrating significant improvement in exercise capacity and symptom management.
- In July 2023, Atgeno AB completed Phase II trials of PDNO, a first-of-its-kind intravenous drug utilizing nitric oxide to treat pulmonary hypertension, with promising results showing reduced pulmonary pressure.
Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market Segmentation
- By Stages
- Phase-III
- Phase-II
- Phase-I
- Preclinical
- Discovery
- By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
- Subcutaneous
- Parenteral
- By Molecule Type
- Small Molecules
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Peptides
- Gene Therapy

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How Big is the pulmonary hypertension drugs market?
The Global Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market is estimated to be valued at USD 8.69 bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 14.23 bn by 2032.
What will be the CAGR of the Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market?
The CAGR of the Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market is projected to be 7.12% from 2024 to 2031.
What are the major factors driving the Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market growth?
The rising awareness and improved diagnostic methods leading to earlier detection of pulmonary hypertension and a strong pipeline with novel therapies that target multiple pathways, such as vasodilators and gene therapies are the major factors driving the Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market?
The high cost of treatment, especially with novel therapies like gene therapy and monoclonal antibodies and lack of effective treatments for advanced stages of pulmonary hypertension, especially for patients who are resistant to first-line therapies are the major factor hampering the growth of the Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market.
Which is the leading stage in the Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market?
Phase-III is the leading stage segment.
Which are the major players operating in the Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs Market?
Tenax Therapeutics, Atgeno AB, Bayer, Bellerophon Therapeutics, United Therapeutics, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Acceleron Pharma, Altavant Sciences, Gossamer Bio, Actelion Ltd, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Steady Med Ltd, Eli Lilly and Company, Johnson & Johnson Services Inc are the major players.