Varicella Zoster HHV-3 Infections Market Size - Analysis
The global Varicella Zoster infections market is expected to experience positive growth trends over the next few years. There is an increasing awareness among people about the viral infection and availability of treatment options. Moreover, continuous investments by leading manufacturers for development of novel and improved vaccines and drugs for effective management of VZV infections will further drive the market growth.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR4.5%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 4.5% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Cangene Corporation, Novartis, GC Biopharma Corp, Pascoe Pharmazeutische Praeparate GmbH, SK Chemical Co. Ltd and Among Others |
please let us know !
Varicella Zoster HHV-3 Infections Market Trends
As more light has been shed on the Varicella Zoster virus and the diseases it can cause, patients and physicians alike are becoming increasingly knowledgeable. Whereas shingles was once seen as an inevitable albeit unpleasant aspect of aging, we now understand it as a neurological infection that can often be prevented or treated. Efforts over the past decade have focused on educating the public that VZV remains latent in human bodies long after childhood chickenpox, and reactivation is possible whenever immunity wanes.
A related benefit comes from growing recognition that postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) can sometimes plague shingles patients long-term. Publicity around relieved yet debilitating nerve pain has spurred those afflicted to try available antiviral medicines and vaccines. It has also sparked interest in novel long-acting therapies currently in development. As baby boomers age into higher risk demographics, it is anticipated their proactive approaches will sustain demand. Continued dialogue sustaining foresight of VZV infections seems poised to further diagnosis and management.
Market Driver - Development of Novel Therapeutic Approaches boosts the market growth.
Still other pipelines evaluate therapeutic vaccine revamps delivering antigen in novel ways to stimulate protective T cells. Long-term delivery systems like monoclonal antibodies also offer hope for preventing PHN onset when administered shortly after rash appearance. Nanoparticle formulations represent another pathway under study, with potential for sustained drug levels at infection sites. Cell-based therapies too are in preliminary stages, exploring everything from modified immune cells to killing virus-infected neurons.
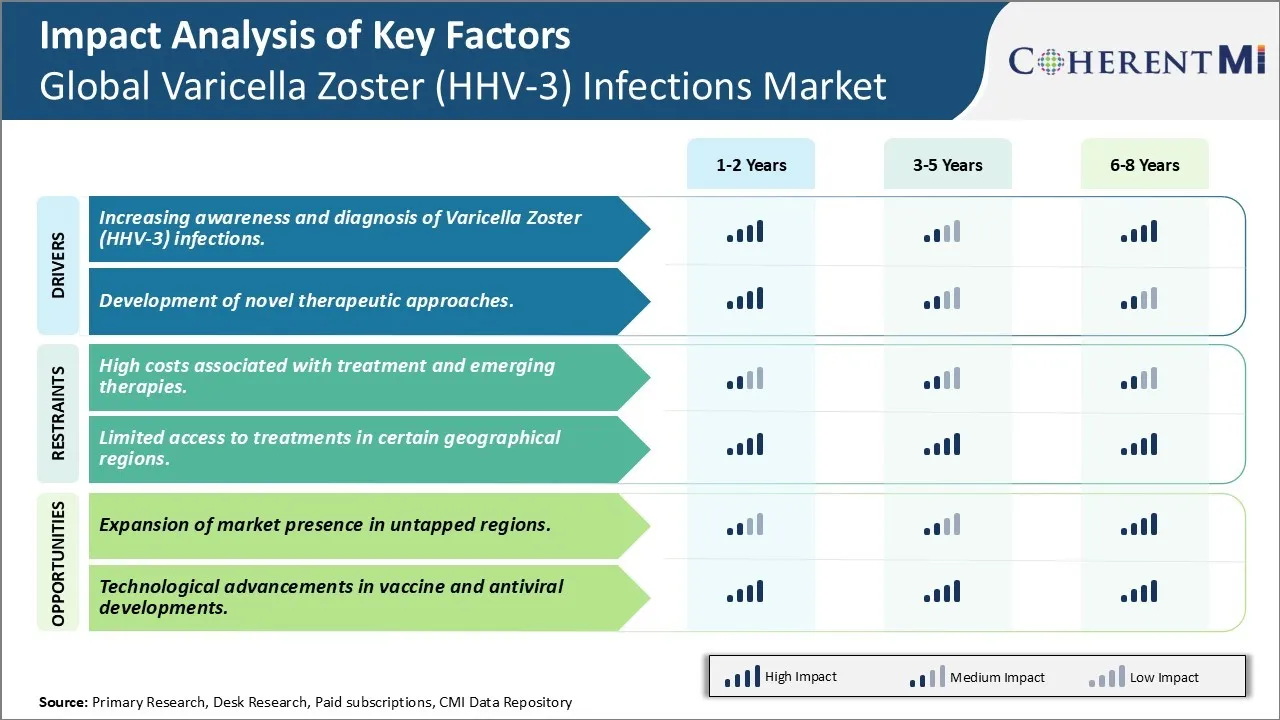
Market Challenge - High costs associated with treatment and emerging therapies.
One of the key opportunities for growth in the global varicella zoster infections market lies in the potential to expand presence and sales in currently underpenetrated or untapped geographic regions. While developed markets in North America and Western Europe currently account for a major share of the overall market, there still exists significant room for growth in other developing parts of the world with large patient pools. Regions such as Latin America, Asia Pacific and parts of Africa and the Middle East have been historically lower adopters of newer vaccines and antiviral drugs due to various access barriers. However, with improvements in economic conditions and healthcare infrastructure as well as local manufacturing opportunities, these emerging markets are expected to increase demands in the coming years. Additional investments into awareness and education campaigns coupled with collaborations with regional healthcare providers can help boost both diagnosis and treatment rates globally. With a co-ordinated targeted market expansion approach, companies operating in this space stand to gain considerably by tapping into the lucrative growth prospects across neglected regions worldwide.
Prescribers preferences of Varicella Zoster HHV-3 Infections Market
Varicella Zoster typically progresses through two main stages - acute varicella and herpes zoster. For acute varicella or chickenpox, antiviral medications such as oral acyclovir are prescribed as a first-line treatment to help reduce symptoms and duration of illness. Brand names include Zovirax and Sitavig.
During herpes zoster or shingles, antiviral drugs remain the mainstay of treatment. Oral antivirals like Famciclovir (Famvir) and Valacyclovir (Valtrex) are preferred first-line options initiated within 72 hours of rash onset. They work to speed up healing and decrease acute pain. For severe or complicated cases, Injectable antivirals like Acyclovir (Zovirax) are prescribed to attain higher plasma concentrations rapidly.
Treatment Option Analysis of Varicella Zoster HHV-3 Infections Market
Varicella zoster infections can be divided into three main stages - primary infection, latency and reactivation.
In older patients or those with weak immunity, reactivation can occur as herpes zoster or shingles. This stage often causes severe pain known as postherpetic neuralgia. Primary treatment involves antiviral drugs like acyclovir, valacyclovir or famciclovir, with valacyclovir being the treatment of choice due to its simple dosing regimen, high oral bio-availability and fewer drug interactions. For older patients or those with severe infections, intravenous antiviral drugs like foscarnet may be used. Capsaicin topical cream provides relief from postherpetic neuralgia. Vaccines like Zostavax reduce the chances of reactivation in older adults.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Varicella Zoster HHV-3 Infections Market
Product Innovation: One of the most successful strategies adopted by market leaders like Merck & Co. and GlaxoSmithKline has been continuous investment in R&D to develop novel and more effective vaccine formulations. For example, in 2017 Merck launched its recombinant zoster vaccine RZV, which has shown higher efficacy rates than the traditional Zostavax vaccine. RZV has since gained significant market share, accounting for over 50% of the zoster vaccine market by 2021.
Strategic Partnerships and Licensing: Collaboration helps companies commercialize products faster. In 2020, Merck signed agreements with Beijing Minhai Biotechnology to develop varicella vaccines in China. This allowed it access to the large and lucrative Chinese market sooner.
Geographic Expansion: Vaccine leaders pursued emerging markets and regional hubs aggressively. For example, its ventures in China helped GSK capture over 15% market share in that country by 2027, despite late entry.
Segmental Analysis of Varicella Zoster HHV-3 Infections Market
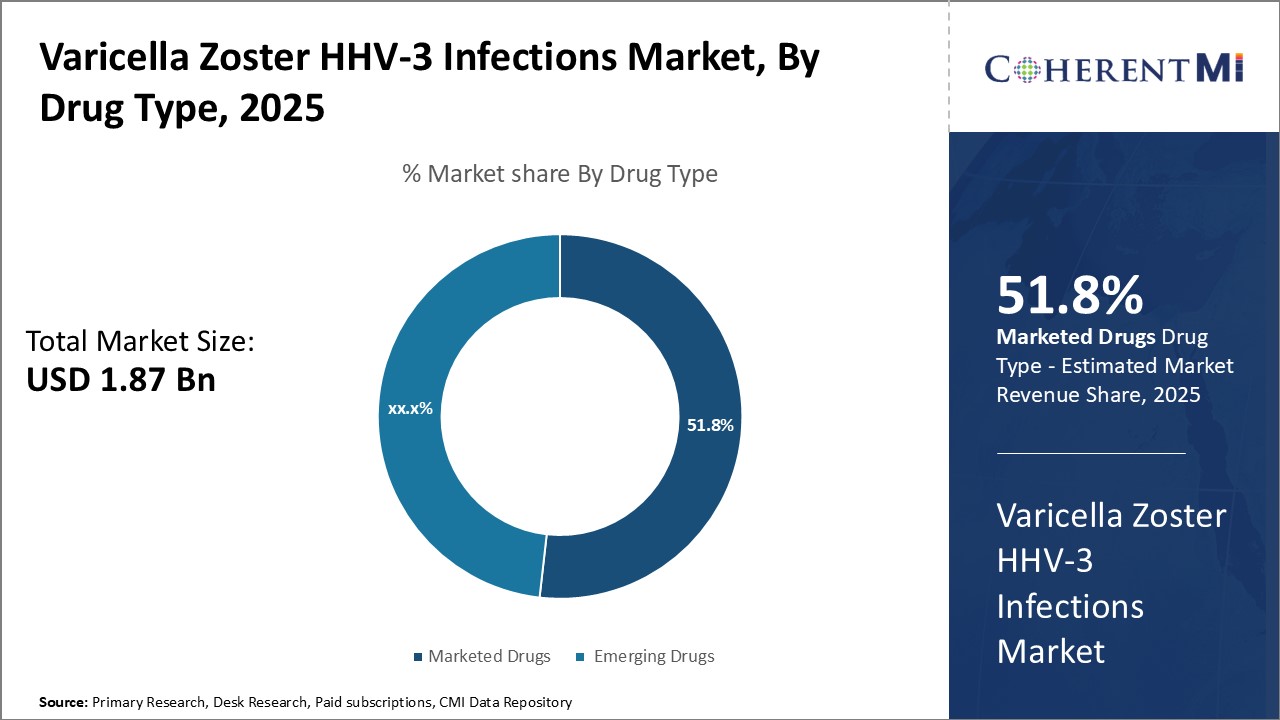 Insights, By Drug Type: Marketed drugs dominated due to established safety and efficacy
Insights, By Drug Type: Marketed drugs dominated due to established safety and efficacyThe Marketed Drugs segment currently dominates the global varicella zoster infections market due to the proven track record of medicines already approved and utilized. Drugs that have received regulatory approval like Zostavax and Shingrix have established efficacy through clinical trials as well as real-world usage over many years. Physicians are confident prescribing these treatments knowing the safety and effectiveness standards they were held to during development and subsequent pharmacovigilance.
The longevity of marketed drugs in the space provides physicians, patients, and payers with certainty regarding outcomes and cost. Treating physicians can determine appropriate patients likely to respond well based on clinical guidelines refined over prolonged use. For patients, it reduces uncertainty about embarking on a new treatment regimen. Insurance companies and healthcare systems appreciate predictable treatment pathways that fit into utilization management protocols. The established efficacy, safety, supply reliability and commercial experience collectively fuel the ongoing dominance of marketed varicella zoster medications.
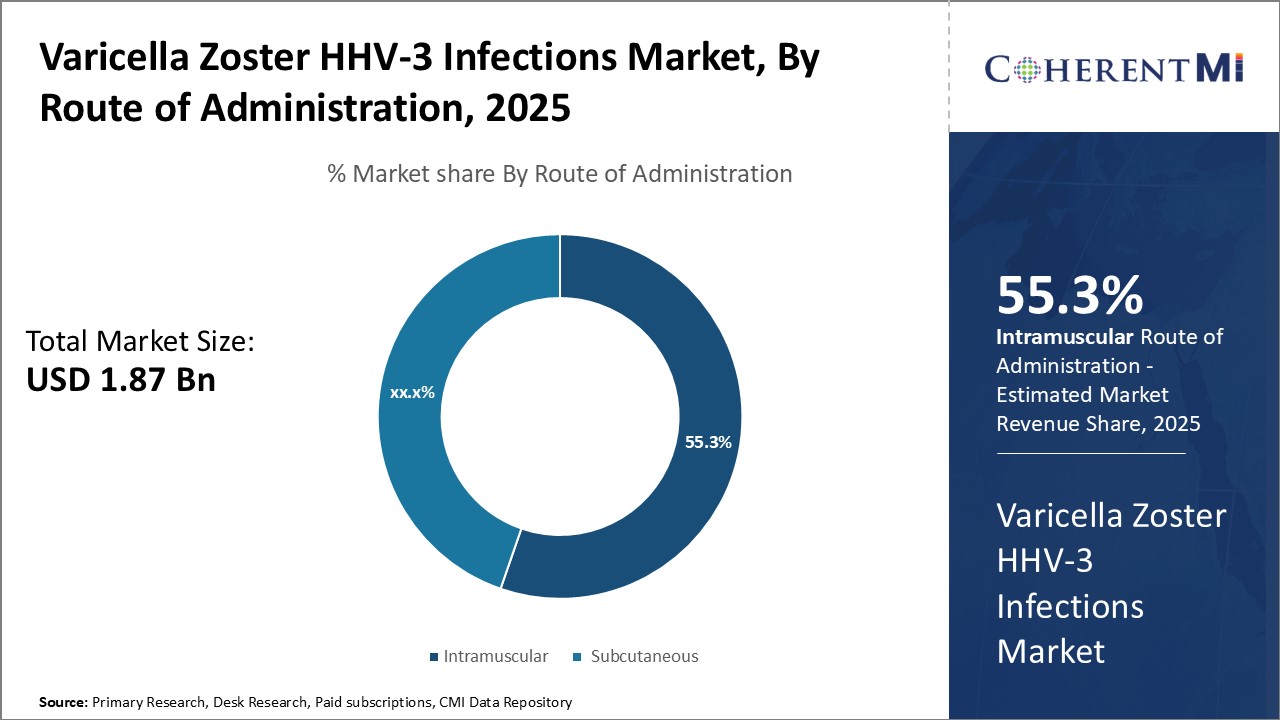
Within the route of administration segment for varicella zoster infections, intramuscular injections currently lead due to effectiveness delivering the medication systemically. Intramuscular injection of drugs like Zostavax and future replacements results in rapid absorption and widespread distribution of antiviral throughout the body. This ensures therapeutic levels reach affected nerves and eradicates any active infection. It also stimulates development of immunity to prevent future outbreaks.
Some individuals may prefer the one-time intramuscular injection approach versus ongoing oral therapy. This convenience factor increases patient acceptance and compliance with the prescribed treatment regimen. Without needing to remember daily pills, the patient experience supports intramuscular injections as a leading administration method. Overall, the effectiveness at delivering antiviral medication systemically makes intramuscular the preferred route utilized by the majority of varicella zoster patients.
Additional Insights of Varicella Zoster HHV-3 Infections Market
The Varicella Zoster (HHV-3) infections market is undergoing dynamic changes with rising awareness, incremental healthcare spending, and a growing number of drug developments targeting improved therapeutic outcomes. Emerging therapies are focused on addressing unmet medical needs, driven by innovative approaches such as self-replicating RNA vaccines and modRNA vaccines. Key market players are engaged in strategic initiatives, including clinical trials and market penetration efforts, which are expected to reshape the treatment landscape significantly by 2032.
Competitive overview of Varicella Zoster HHV-3 Infections Market
The major players operating in the Global Varicella Zoster (HHV-3) Infections Market include Cangene Corporation, Novartis, GC Biopharma Corp, Pascoe Pharmazeutische Praeparate GmbH, SK Chemical Co. Ltd, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Curevo Vaccine, GeneOne Life Science, SK Bioscience, GlaxoSmithKline, Moderna Inc, and BioNTech SE
Varicella Zoster HHV-3 Infections Market Leaders
- Cangene Corporation
- Novartis
- GC Biopharma Corp
- Pascoe Pharmazeutische Praeparate GmbH
- SK Chemical Co. Ltd
Varicella Zoster HHV-3 Infections Market - Competitive Rivalry

Varicella Zoster HHV-3 Infections Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Varicella Zoster HHV-3 Infections Market
- August 2023: Pfizer announced a phase 2 clinical trial for Shingrix to assess the safety, adverse reactions, and immune response of the Varicella Zoster Virus modRNA vaccine.
- May 2023: Immorna Biotherapeutics Inc. initiated a phase 1 clinical trial for JCXH-105, a self-replicating RNA vaccine to prevent Shingles, testing its safety and immune response.
Varicella Zoster HHV-3 Infections Market Segmentation
- By Drug Type
- Marketed Drugs
- Emerging Drugs
- By Route of Administration
- Intramuscular
- Subcutaneous

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How Big is the Varicella Zoster (HHV-3) Infections Market?
The Global Varicella Zoster (HHV-3) Infections Market was valued at USD 1.87 billion in 2025, and is expected to value at USD 2.54 billion by 2032.
What will be the CAGR of the Global Varicella Zoster (HHV-3) Infections Market?
The CAGR of the Global Varicella Zoster (HHV-3) Infections Market is projected to be 4.3% from 2024 to 2031.
What are the major factors driving the Global Varicella Zoster (HHV-3) Infections Market growth?
The increasing awareness and diagnosis of varicella zoster (hhv-3) infections. and development of novel therapeutic approaches are the major factor driving the Global Varicella Zoster (HHV-3) Infections Market.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the Global Varicella Zoster (HHV-3) Infections Market?
The high costs associated with treatment and emerging therapies. and limited access to treatments in certain geographical regions. are the major factor hampering the growth of the Global Varicella Zoster (HHV-3) Infections Market.
Which is the leading Drug Type in the Global Varicella Zoster (HHV-3) Infections Market?
Marketed drugs is the leading drug type segment.
Which are the major players operating in the Global Varicella Zoster (HHV-3) Infections Market?
Cangene Corporation, Novartis, GC Biopharma Corp, Pascoe Pharmazeutische Praeparate GmbH, SK Chemical Co. Ltd, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer are the major players.