

The acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) market is estimated to be valued at USD 151.2 Mn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 340.6 Mn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.3% from 2025 to 2032. The market is expected to showcase significant growth during the forecast period due to the rising diagnosis of ASMD and growing access to enzyme replacement therapies.
Market Size in USD Mn
CAGR12.3%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 12.3% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Sanofi, Orphazyme, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Actelion Pharmaceuticals and Among Others |
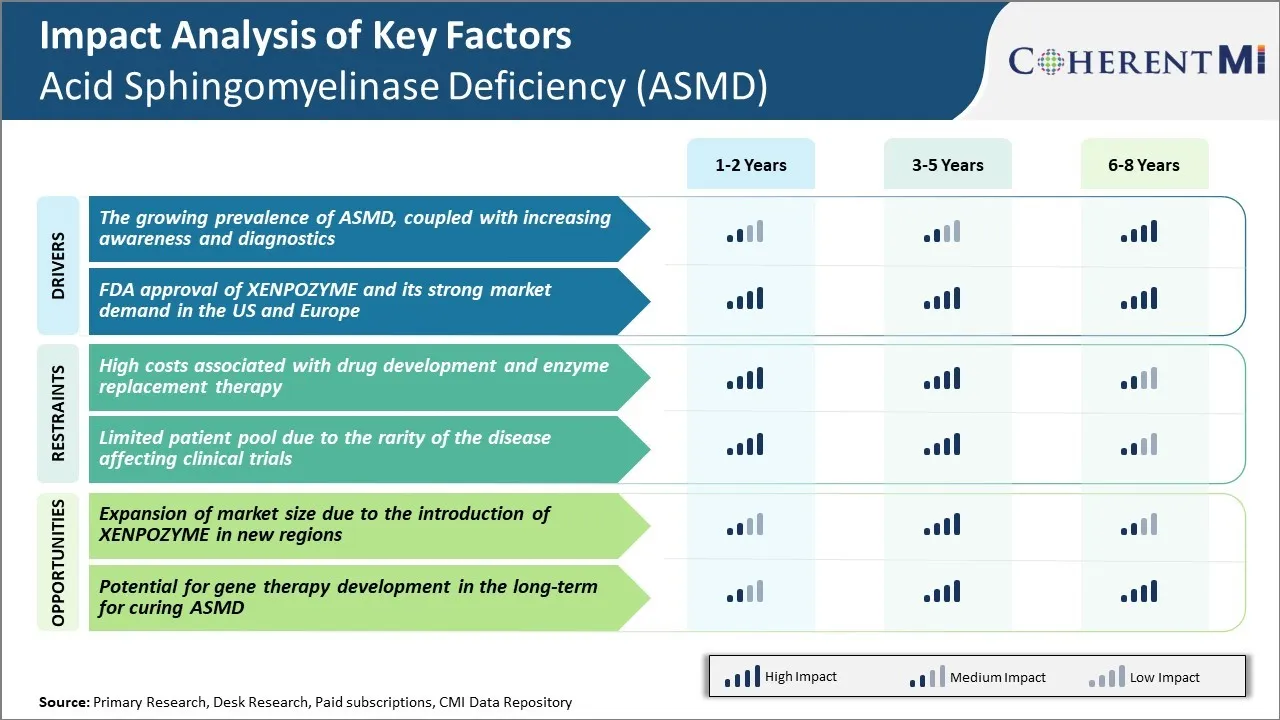
Market Driver - Growing Prevalence of ASMD, Coupled with Increasing Awareness and Diagnostics
ASMD is an extremely rare lysosomal storage disease caused by mutations in the SMPD1 gene which result in a deficiency of the acid sphingomyelinase enzyme. This genetic defect prevents the normal breakdown of sphingomyelin, a fatty substance found in membranes of cells, causing it to accumulate to harmful levels over time.
Historically, ASMD was considered one of the rarest lysosomal diseases with estimates of only around 50 to 150 known patients worldwide. However, new research indicates the actual prevalence may be higher than previously believed as improved diagnostics allow for more cases to be accurately identified. Additionally, it is now recognized that the condition exists in both a severe infantile form and a milder late-onset form.
As the true prevalence of ASMD comes into better focus, efforts are ongoing to raise awareness about the condition among the medical community and public. Patient advocacy groups play an important role in educating about signs, symptoms and available testing options. Diagnosis traditionally relied on invasive bone marrow biopsy but new dry blood spot tests allow for more convenient newborn screening and diagnosis of late-onset patients. Increased overall awareness combined with easier diagnostic pathways is facilitating the identification and confirmation of more ASMD cases worldwide.
Market Driver - FDA Approval of XENPOZYME and its Strong Market Demand in the US and Europe
Another key driver within the ASMD treatment market is the FDA's recent approval of XENPOZYME, the first ever drug specifically indicated for this rare genetic disorder. Developed by Genzyme, a Sanofi company, XENPOZYME received accelerated approval in January 2022 based on data demonstrating its ability to reduce sphingomyelin accumulation in cells. It is a recombinant human acid sphingomyelinase enzyme replacement therapy administered weekly as an IV infusion or injection intended to replace the deficient or missing enzyme.
XENPOZYME represents the first ever disease-modifying treatment option for ASMD which was previously managed solely through symptomatic care. Clinicians recognize it has the potential to meaningfully impact the often-devastating multisystem complications of this progressive condition. Initial real-world experience supports the positive efficacy and safety demonstrated in clinical trials.
Market research focusing on both patient and physician surveys indicates XENPOZYME will likely become the standard of care treatment for ASMD worldwide. Overall, the availability of this groundbreaking targeted therapy is anticipated to be a major growth driver, increasing diagnosis rates and fueling the overall acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) market value in the coming years.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High Costs Associated with Drug Development and Enzyme Replacement Therapy
The acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) market faces significant challenges due to the high costs associated with drug development and enzyme replacement therapy for this rare disease. Developing drugs to treat such a rare condition requires extensive research and clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy in small patient populations. This drug development process is very expensive and risky for pharmaceutical companies to undertake.
Additionally, the approved enzyme replacement therapy called Cerdelga is priced at over $300,000 per year, making it too costly for many healthcare systems and patients. The small patient numbers mean the overall size of acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) market is limited, providing little revenue potential for pharmaceutical companies to recoup their drug development investments.
High production costs are also incurred for enzyme replacement therapies due to their complex biologic nature. These significant financial challenges may discourage further research into new treatment options and limit patient access to existing therapies for ASMD.
Market Opportunity - Expansion of Market Size due to the Introduction of XENPOZYME in New Regions
The approval and commercialization of the new ASMD drug XENPOZYME represents a major opportunity to expand the market size for this condition. XENPOZYME, developed by Xenetic Biosciences, has demonstrated safety and efficacy in clinical trials.
With regulatory approval, the company is planning to launch XENPOZYME in the key markets of the United States, Europe and Japan in 2023. This will provide ASMD patients in these new regions with an important additional treatment option. The introduction of XENPOZYME also has the potential to significantly grow the overall acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) market.
As XENPOZYME gains uptake among eligible patients, it could start to offset some of the market currently held by Cerdelga. This market expansion would help improve the return on investment for companies developing therapies for this rare disease population.
Acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) is a rarelysosomal storage disorder where the lysosomal enzyme acid sphingomyelinase is deficient or absent. Prescribers follow a step-wise treatment approach depending on the stage and severity of the disease.
For mild to moderate cases without organ involvement, patients are initially managed through supportive care and symptom management. These include analgesics, antibiotics, physical/occupational therapy etc.
As the condition progresses, enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) becomes the standard first-line treatment. For infantile neuroaxonal ASMD, Cerliponase alfa (Brineura) is prescribed as intrathecal ERT via infusion every other week. This helps degrade sphingomyelin accumulation in the central nervous system, slowing neurological decline.
For non-neurologic forms, prescribers prefer substrate reduction therapy (SRT) using drugs like Miglustat (Zavesca). It works by inhibiting glucosylceramide synthase, thus reducing substrate levels. Brands like Zavesca help delay disease progression in patients without neurological symptoms.
In severe later-stage disease, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation may be considered. However, given the rarity of disease and limited long-term outcome data, prescribers are cautious in recommending this invasive procedure. Cost of treatment also influences preferences, with ERT being preferred over SRT due to proven efficacy in neurologic forms.
In early or mild stages, supportive management is provided to address individual symptoms as they arise. Physical, occupational and speech therapies may be recommended. Antibiotics are given to prevent infections.
For more moderate to severe cases, enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) is the standard first-line treatment. The only FDA-approved ERT drug is Alexion's Strensiq (alglucosidase alfa), a recombinant human acid sphingomyelinase enzyme administered via intravenous infusion every 2 weeks. Strensiq reduces sphingomyelin accumulation in cells and ameliorates disease manifestations. It is most effective when started in early childhood to prevent organ damage progression.
For patients who are not candidates for or do not respond to ERT, a bone marrow transplant may be considered. This aims to replace the defective gene through donor stem cells. While carrying risks, it provides a permanent correction if successful.
Other emerging treatments under investigation include gene therapy using viruses to deliver functional copies of the acid sphingomyelinase gene. If proven safe and effective, this could be a one-time curative option. Overall, treatment largely focuses on managing symptoms early, with ERT as the standard first-line approach due to its effectiveness in slowing disease progression.
Early market entry with first FDA approved treatment: In 2017, Alexion Pharmaceuticals gained first-mover advantage by obtaining FDA approval for Kanuma (sebelipase alfa), the first and only approved treatment for ASMD. This early market entry allowed Alexion to dominate the market in the crucial initial years by providing the only approved treatment option to patients. Kanuma quickly became the standard of care and generated over $100 million in annual sales.
Aggressive commercialization and expansion of treatment access: Alexion invested heavily in commercializing Kanuma globally. It has obtained regulatory approvals in over 25 countries worldwide. The company has worked closely with patient advocacy groups to educate physicians and expand diagnosis rates. It also provides broad patient support programs to help navigate insurance and access challenges. These efforts have helped grow Kanuma revenues from $35 million in 2018 to over $150 million in 2021, establishing it as the clear market leader.
Commitment to ongoing R&D of new treatments: To maintain its leadership position, Alexion is investing in clinical trials of an experimental intravenous formulation of sebelipase alfa that may offer more convenient dosing. It is also supporting academic research into novel gene therapies and other treatment modalities for ASMD.
-market-by-therapy.webp&w=3840&q=75) To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Therapy: XENPOZYME Consumes Huge Market Share Owing to its Clinical Efficacy and Targeted Mode of Action
XENPOZYME is an enzyme replacement therapy developed specifically for Acid Sphingomyelinase Deficiency (ASMD), a rare and life-threatening genetic disorder. It works by replenishing deficient or defective acid sphingomyelinase enzyme levels in patients, thereby addressing the underlying cause of ASMD.
In clinical trials, XENPOZYME has demonstrated significant reductions in sphingomyelin accumulation in major organ systems afflicted by ASMD such as the liver, spleen and lungs. It has also showed improvements in lung function parameters in treated patients.
XENPOZYME's targeted approach at restoring acid sphingomyelinase activity makes it a more effective treatment Option for ASMD compared to other non-specific supportive therapies. Its effectiveness at improving organ function and symptoms has helped establish it as the standard of care for ASMD patients. Additional benefits like convenient routes of administration further enhance treatment adherence for patients.
Strong clinical value offered by XENPOZYME to manage the debilitating effects of ASMD has enabled it to dominate the Acid Sphingomyelinase Deficiency treatment market space and capture the highest market share compared to other emerging therapy segments.
The major players operating in the acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) Market include Sanofi, Orphazyme, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and Actelion Pharmaceuticals.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Acid Sphingomyelinase Deficiency (ASMD) Market is segmented By Therapy (XENPOZYME (olipudase alfa), ...
Acid Sphingomyelinase Deficiency (ASMD) Market
How big is the acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) market?
The acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) market is estimated to be valued at USD 151.2 Mn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 340.6 Mn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) market?
The high costs associated with drug development and enzyme replacement therapy and limited patient pool due to the rarity of the disease affecting clinical trials are the major factors hampering the growth of the acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) market.
What are the major factors driving the acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) market growth?
The growing prevalence of ASMD, coupled with increasing awareness and diagnostics and FDA approval of XENPOZYME and its strong market demand in the US and Europe are the major factors driving the acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) market.
Which is the leading therapy in the acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) market?
The leading therapy segment is XENPOZYME (olipudase alfa).
Which are the major players operating in the acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) Market?
Sanofi, Orphazyme, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and Actelion Pharmaceuticals are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) market?
The CAGR of the acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) market is projected to be 12.3% from 2025-2032.