X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market is Segmented By Therapeutics (Oral Medications, Injectable Medications, Gene Therapies), By End Users (Hospitals, Spe....
X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market Size - Analysis
The X-linked hypophosphatemia market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.5 Bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2.8 Bn by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.4% from 2024 to 2031.
The market is expected to witness positive growth during the forecast period. The increasing government support and rising product approvals is anticipated to drive the market. Additionally, rising investments by key players for the development of novel and advanced treatment options is further expected to provide opportunities for growth. However, stringent regulations for approval of new treatments may hamper market growth to some extent.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR9.4%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 9.4% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Kirin, Ascendis Pharma, Pfizer, Chiesi Farmaceutici and Among Others |
please let us know !
X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market Trends
Market Driver - Increasing prevalence of X-linked hypophosphatemia globally
One of the major factors driving the growth of the X-linked Hypophosphatemia market is the increasing prevalence of the condition worldwide. X-linked Hypophosphatemia is a genetic disorder characterized by abnormally low levels of phosphorus in the blood and bones. The exact prevalence of XLH is unknown, however estimates suggest it affects approximately 1 in 20,000 individuals globally. Some studies have found a higher prevalence in certain populations such as 1 in 12,000 live male births in Denmark.
While the cause of XLH is genetic in nature, linked to mutations on chromosome X, environmental and lifestyle factors are believed to play a role in increasing the risks as well. With changing dietary patterns, more sedentary lifestyles and urbanization on the rise across both developing and developed countries, risks of metabolic conditions like XLH have been escalating. Additionally, advanced screening and diagnostic capabilities have enabled more cases to be detected now than ever before. Growing health awareness combined with better access to healthcare in many developing nations is also contributing to the improved reporting of XLH cases worldwide.
All of these factors indicate the patient pool for XLH is expanding rapidly. As a result, demand for effective treatment options and management of the condition is surging. Traditional therapies like phosphate and vitamin D supplements have been the mainstay of XLH treatment but newer biologic therapies targeting the underlying cause are gaining popularity. Their ability to more comprehensively address symptoms and long term complications of XLH makes them an attractive proposition for both patients and physicians alike, driving higher adoption and uptake. The growing prevalence and identification of more XLH cases presents a sizable opportunity for drugs and therapies in this market.
Market Driver - Advances in gene therapy technologies
Another key growth driver for the X-linked hypophosphatemia market has been the significant advances in gene therapy technologies in recent years. Gene therapy involves replacing, manipulating or supplementing nonfunctional genes in a patient's cells and tissues to treat or cure genetic disorders. For XLH, which arises due to mutations in the PHEX gene located on the X chromosome, gene therapy holds promising potential.
Over the past decade, there have been major breakthroughs in the development of various gene therapy delivery systems like viral vectors, non-viral gene transfer methods and gene editing tools like CRISPR that have enabled more targeted and effective genetic manipulation. Clinical trials on various monogenic diseases have proven gene therapies can provide long term therapeutic benefits with a single dose treatment versus the need for repeated drug administration in traditional therapies. This makes them highly appealing to patients coping with a lifelong condition like XLH.
Encouraged by these successes, efforts to develop gene therapies for XLH have intensified. Currently several companies have preclinical programs investigating the use of AAV vectors, lentiviral vectors and oligonucleotide approaches to replace the defective PHEX gene or compensate for its absence. With gene therapy now considered one of the most innovative areas in medicine, greater funding is also flowing into accelerating the research work. If clinical success can be achieved, it could potentially revolutionize XLH management by addressing the root cause in a onetime cure rather than symptom suppression as seen with current options. This promising avenue has become a major driver catapulting the XLH therapeutics field forward.
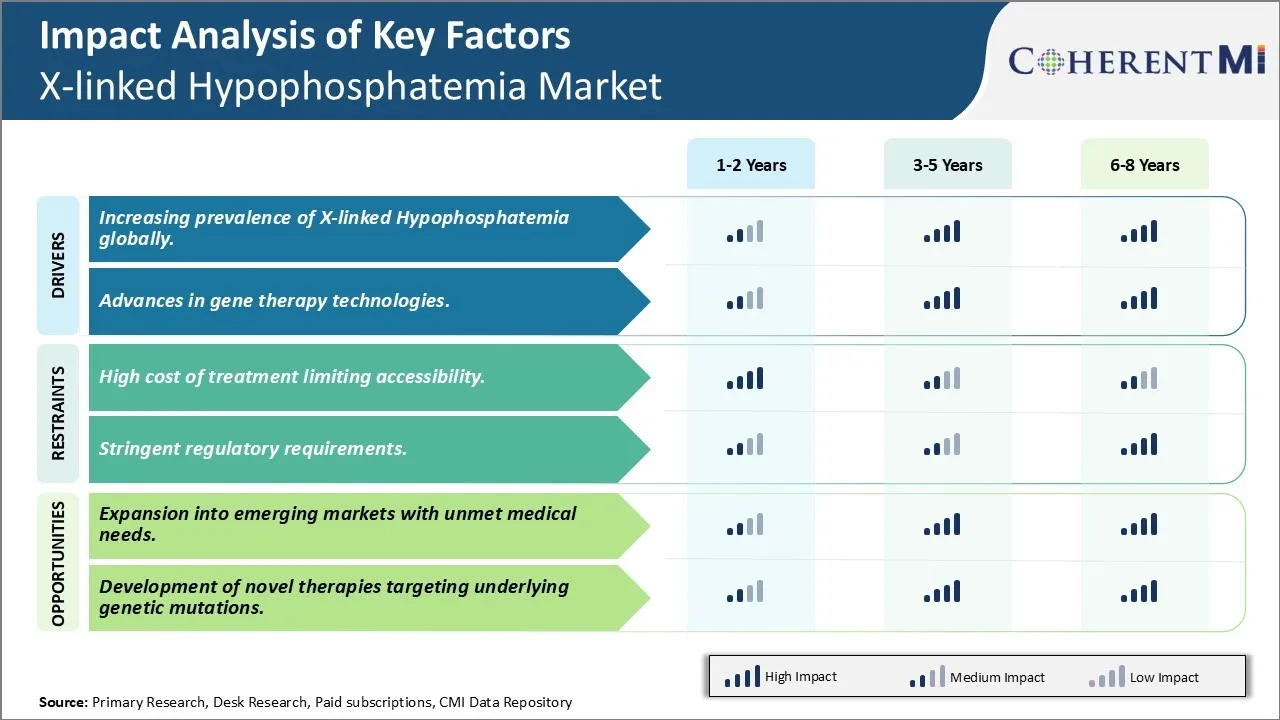
Market Challenge - High cost of treatment limiting accessibility
One of the major challenges faced by the X-linked Hypophosphatemia market is the high cost of treatment which severely limits accessibility to a large patient population. Treatment of XLH involves lifelong medication with expensive phosphate and vitamin D supplements which places a heavy financial burden on patients. The average annual cost of treatment in Western countries ranges between $5,000 to $10,000 per patient. This high cost is a major barrier for many patients, especially those located in less developed regions or without adequate health insurance. Many patients struggle to afford regular prescribed doses or are forced to ration their medication. This leads to suboptimal treatment outcomes and worsening of symptoms over time. The high costs also discourage pharmaceutical companies from investing in new drug development for this rare disease. Unless new policies are introduced to curb treatment expenses or provide subsidies, accessibility will remain extremely limited for a large number of underprivileged XLH patients globally.
Market Opportunity: Expansion into emerging markets with unmet medical needs
One key opportunity for players in the XLH market is the potential for expansion into emerging economies which have large patient populations with significant unmet medical needs. Many Asian and Latin American countries have a high prevalence of XLH due to genetic factors but lack proper diagnosis rates and access to treatment. This represents a large untapped market base. Pharmaceutical companies could look at obtaining regulatory approvals and establishing supply chains and distribution networks in these regions. Partnering with local healthcare providers and patient advocacy groups would help in screening, identification and enrollment of patients. Introducing more affordable generic formulations tailored for these markets also provides an opportunity to expand accessibility. With rising incomes and awareness, demand is expected to grow rapidly over the coming years. Companies addressing the treatment gap in emerging nations stand to benefit significantly from first-mover advantage in these expanding XLH markets of the future.
Prescribers preferences of X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market
X-linked hypophosphatemia is typically treated via a stepwise approach based on the stage and severity of symptoms. In mild early-stage disease, diet and lifestyle modifications may be sufficient to manage phosphate levels. For more significant symptoms, prescription medication becomes necessary. The first-line treatment is usually an oral phosphate supplement to increase phosphate levels in the blood. If this is not effective, combination therapy with a vitamin D analog such as calcitriol may be prescribed.
For patients who do not respond adequately, other options under investigation include bisphosphonates or calcimimetics. Later-stage disease with skeletal deformities or short stature may also involve surgery in some cases. Physical therapy can further support treatment goals. Prescribers consider efficacy, safety, cost and patient convenience in deciding the optimal therapeutic approach.
Treatment Option Analysis of X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market
X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) is typically treated based on disease severity and stage. For mild cases, the first-line treatment is oral phosphate supplementation and active vitamin D therapy. Common phosphate supplements used include PhosLo and PhosPhoSol which provide the recommended daily intake amount. Vitamin D therapies help regulate phosphorus levels and include calcitriol (Rocaltrol) and alphacalcidol (Calcichew).
For moderate to severe cases, the same first-line treatments are used but at higher doses under close medical supervision. Additionally, newer combination drug therapies may be prescribed such as Burosumab (Crysvita). Burosumab is a fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) blocking antibody that targets the underlying cause of excess FGF23 production in XLH patients. It works synergistically with phosphate and vitamin D supplements to more effectively maintain normal phosphorus levels.
Surgical options such as corrective osteotomies may be considered for bowing deformities of the lower extremities in older children and adults. However, drug therapies are now preferred first due to less invasive nature and ability to address systemic effects beyond just musculoskeletal symptoms. Regular monitoring through laboratory tests and physical exams allows doctors to properly titrate treatments based on the individual's response and disease progression over time. A multidisciplinary care team helps maximize Treatment outcomes at each stage of XLH.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market
Launching new and improved treatment options has been a very effective strategy for companies in this market. For example, in 2017, Kyowa Hakko Kirin launched the powder version of the only approved drug for XLH, Burosumab (Crysvita). This new formulation solved issues associated with stability and storage of the drug. It received positive nod from regulatory authorities and physicians, aiding strong uptake. Such product innovations help companies expand their market share by addressing unmet needs.
Acquiring emerging firms developing promising drug candidates has enabled large players to strengthen their product pipelines. For instance, in 2019, Ultragenyx acquired Arcturus Therapeutics, gaining its mRNA-based XLH therapy. This addition boosted Ultragenyx's XLH program. Earlier acquisitions, like Kyowa Hakko Kirin buying Relypsa in 2016 for its Phase 3 asset Burosumab, helped these companies dominate the market. Acquisitions are a key non-organic growth strategy in this specialized space.
Launching drugs in new international markets where they receive orphan drug designation and pricing benefits has paid off well. For example, Kyowa Kirin expanded Crysvita's availability from Japan, US to EU in 2019. This enabled it to tap into the sizeable European patient pool and boosted product sales manifold. Other players like Ultragenyx are also pursuing regulatory approvals in multiple regions for long term growth.
Segmental Analysis of X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market
Insights, By Therapeutics: Convenience and effectiveness of oral medications
In terms of therapeutics, oral medications sub-segment contributes the highest share of 445.6% in the X-linked hypophosphatemia market owing to their convenience and effectiveness. Being available in the form of tablets and capsules, oral medications offer patients an easy to use and pain-free treatment option for managing their hypophosphatemia symptoms. The avoidance of frequent hospital visits for intravenous administration of drugs significantly improves patient compliance with oral medications.
Most oral medications are administered once or twice daily which fits well into patients' daily routines. This drives preference over injectable drugs requiring administration several times a week under medical supervision. The long-term control achieved through consistent intake of oral drugs also outweighs the short-term symptomatic relief offered by injectables. Moreover, lack of infections risks and discomfort associated with injections makes oral drugs a safer bet for long-term hypophosphatemia management.
Overall, the non-invasive nature and flexible dosing of oral medications have enabled them to gain higher patient acceptance compared to other drug types. This has solidified oral medications' dominance in the X-linked Hypophosphatemia therapeutic segment over time.

Insights, By End Users: Hospitals are the primary access point for hypophosphatemia care
Among the various end-users, hospitals account for the largest share of 52.2% in the X-linked hypophosphatemia market. This can be attributed to their central role in initial diagnosis and ongoing management of the disorder. As hypophosphatemia symptoms often require specialized tests and multidisciplinary care, hospitals serve as the preferred access points for most patients.
Their advanced diagnostic facilities enable confirmation of X-linked hypophosphatemia through genetic testing and imaging studies. Moreover, adverse drug reactions or deteriorating medical condition can be promptly addressed in the hospital setting. For pediatric patients in particular, hospitals provide a comprehensive and coordinated team approach involving pediatricians, orthopedic surgeons, endocrinologists and other specialists.
The availability of inpatient and outpatient treatment options also allow for closer monitoring during critical phases. Hospitals have the infrastructure and resources to regularly evaluate treatment responses, especially during periods when medications may need adjustments or replacements. Over time, as patients' health stabilizes, care can be transitioned to specialty clinics or home-based settings. However, most patients continue relying on hospitals for periodic follow-ups or management of complications and co-morbidities. This cements hospitals' prominence in the overall hypophosphatemia treatment landscape.
Additional Insights of X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market
- The X-linked Hypophosphatemia market is poised for significant growth over the coming years, driven by advancements in gene therapy and increasing disease prevalence. The current treatment landscape includes a mix of traditional therapies and innovative approaches, with a focus on improving patient quality of life.
Competitive overview of X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market
The major players operating in the X-linked hypophosphatemia market include Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Kirin, Ascendis Pharma, Pfizer, Chiesi Farmaceutici, Radius Health, and Novo Nordisk.
X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market Leaders
- Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical
- Kyowa Kirin
- Ascendis Pharma
- Pfizer
- Chiesi Farmaceutici
X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market - Competitive Rivalry

X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market
- In March 2024, Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical announced the expansion of its gene therapy pipeline with the acquisition of a new technology platform that is expected to enhance the treatment of X-linked Hypophosphatemia. This strategic move is anticipated to strengthen the company’s market position and drive future growth.
- In July 2023, Kyowa Kirin successfully completed Phase III clinical trials for a new oral formulation, showing significant improvement in patient outcomes. The company plans to file for regulatory approval in early 2024.
X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market Segmentation
- By Therapeutics
- Oral Medications
- Injectable Medications
- Gene Therapies
- By End Users
- Hospitals
- Specialty Clinics
- Homecare Settings

Would you like to explore the option of buyingindividual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the X-linked hypophosphatemia market?
The high cost of treatment limiting accessibility and stringent regulatory requirements are the major factors hampering the growth of the X-linked hypophosphatemia market.
What are the major factors driving the X-linked hypophosphatemia market growth?
The increasing prevalence of x-linked hypophosphatemia globally and advances in gene therapy technologies are the major factors driving the X-linked hypophosphatemia market.
Which are the leading therapeutics in the X-linked hypophosphatemia market?
The leading therapeutics segment is oral medications.
Which are the major players operating in the X-linked hypophosphatemia market?
Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Kirin, Ascendis Pharma, Pfizer, Chiesi Farmaceutici, Radius Health, and Novo Nordisk are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the X-linked hypophosphatemia market?
The CAGR of the X-linked hypophosphatemia market is projected to be 9.4% from 2024-2031.