

The acute pancreatitis market is estimated to be valued at USD 547.1 Mn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 754.6 Mn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.7% from 2025 to 2032. The increasing incidence of gallstone diseases and alcohol consumption are major factors leading to the rise in number of acute pancreatitis cases. Acute pancreatitis poses a substantial disease burden worldwide with high rates of hospitalization and mortality.
Market Size in USD Mn
CAGR4.7%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 4.7% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Novartis AG, Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline, AbbVie Inc. and Among Others |
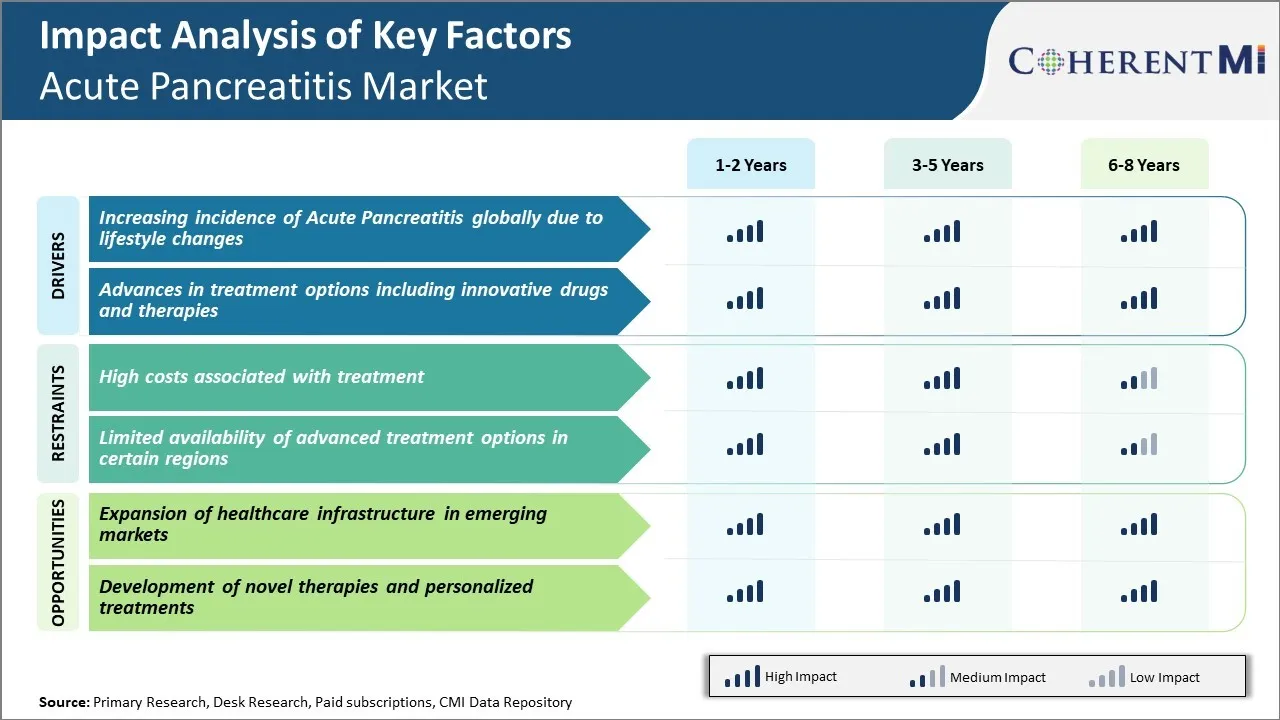
Market Driver - Lifestyle Changes Fueling Rise in Acute Pancreatitis Cases
The global incidence of acute pancreatitis has been rising steadily over the past few decades. A key factor behind this rise has been the widespread lifestyle changes that more and more people are adopting. Unhealthy eating habits, physical inactivity, excessive alcohol consumption and smoking are some of the major lifestyle aspects that are considered significant risk factors for developing acute pancreatitis.
Excessive alcohol intake has likewise become very common, especially among younger demographic groups. Binge drinking is almost seen as casual socializing by many. But medical research has clearly shown that heavy sporadic or regular alcohol consumption can easily trigger acute pancreatitis attacks. Similarly, the number of smokers worldwide also continues to be alarmingly high despite anti-tobacco campaigns. Cigarette smoking is a well-established risk factor that has been implicated in many cases of acute pancreatitis.
All of the above lifestyle habits that promote weight gain, metabolic disorders and put additional strain on digestive organs have led to a surge in the occurrence of acute pancreatitis. Unless concerted efforts are made to promote healthier lifestyle changes on a mass scale, instances of acute pancreatitis stemming from an inappropriate modern lifestyle will keep growing over the coming years.
Market Driver - Advances in Treatment Options for Acute Pancreatitis
One of the key areas where substantial advancements have occurred is in drug development for treating the underlying causes and modulating the disease process. Several clinical trials over the past decade have evaluated different medications that can help reduce pancreatic inflammation and accelerate recovery. A few promising drug classes under investigation include enzyme inhibitors, anti-oxidants, anti-inflammatory agents and certain immunomodulators. If proven safe and effective, these newer drug formulations will enhance clinicians' armamentarium to deal with acute pancreatitis cases.
At the same time, minimally invasive surgical techniques and interventional endoscopic options are also gaining ground. Procedures like endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) enable diagnosing and addressing conditions like gallstones which frequently underlie pancreatitis attacks. Similarly, procedures to place drainage stents in problematic pancreatic ducts are boosting management of complications. The integration of advanced imaging methods and image-guided precision has further augmented such interventional approaches.
Overall, continual refinements in the therapy paradigms backed by a stream of innovative medications and technologies bode well for improving patient outcomes and quality of life in acute pancreatitis. This progress is anticipated to strengthen the commercial outlook of this industry as it fosters higher demand for better-tolerated and more effective therapeutics over the conventional standard of care.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High Costs Associated with Treatment
One of the major challenges faced by the acute pancreatitis market is the high costs associated with treatment. Acute pancreatitis requires hospitalization and intensive medical care. The treatment involves extensive monitoring along with administration of intravenous fluids and pain medications. In severe cases, surgical intervention may also be required which further increases the overall costs.
Due to the complex nature of the disease, the treatment costs per patient are considerably high. As per estimates, the average total costs per patient range between $15,000 to $30,000 in the United States depending on the severity level. This places a huge financial burden on patients and their families. Moreover, the in-patient hospital stays associated with acute pancreatitis are substantially long which puts additional cost pressures on the already over-burdened healthcare systems across regions.
With rising incidence rates of acute pancreatitis, the spending on treatment is projected to grow significantly. However, the limitations in healthcare budgets and reimbursement challenges pose constraints in addressing the rising disease burden. This acts as a major market challenge that needs to be tackled for ensuring accessible and affordable care.
Market Opportunity - Expansion of Healthcare Infrastructure in Emerging Markets
One of the key opportunities for the acute pancreatitis market is the expansion of healthcare infrastructure in emerging markets. There is growing investments towards building healthcare facilities and improving access to advanced treatment options in developing countries.
This includes setting up of new hospitals, expansion of medical infrastructure in rural areas, and increasing healthcare spending per person by various governments. As a result of these developments, more patients are now able to seek timely treatment for acute pancreatitis even in remote locations.
Additionally, improved diagnostic capabilities are enabling early detection and management of the disease. This factor is positively impacting the market growth in emerging nations. With further planned investments towards strengthening healthcare systems, emerging markets are expected to provide significant expansion prospects for players in the acute pancreatitis market over the coming years. Companies can gain a competitive edge by focusing on these high potential regions and catering to the rising medical needs.
Acute pancreatitis has three defined stages - mild, moderate and severe. Initial treatment for mild cases primarily involves pain management with analgesics like intravenous opiates. Oral intake is restricted and IV hydration started. As the condition subsides, patients are progressed to oral fluid and diet intake.
Moderate cases see the addition of antimicrobials to prevent infection. Aminoglycosides such as amikacin and third-generation cephalosporins like ceftriaxone are commonly prescribed. Nutritional support with IV feeding is also initiated.
Severe cases involve management of complications which dictate therapy. For infected necrosis, broad-spectrum antibiotics covering enteric flora like meropenem and metronidazole are preferred. Sterile necrosis may require interventions like percutaneous drainage. Respiratory failure necessitates ventilator support. Hemodynamic instability leads to vasopressor use, for example norepinephrine and dopamine.
Prescribers consider disease severity, individual risk factors, comorbidities, local antimicrobial resistance patterns and hospital protocols when choosing a treatment regimen. Cost is another factor, especially for expensive biologics. Off-label use of drugs like becaplermin and nesiritide show promise but require more evidence before widespread adoption. Multi-disciplinary input from gastroenterologists, surgeons and intensivists further helps guide optimal management.
Acute pancreatitis has three main stages - mild, moderate, and severe. Mild cases involve minimal inflammation that can be treated supportively with bowel rest, IV fluids, and pain medication. The goal is to correct dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
For moderate cases with greater inflammation or organ dysfunction, additional treatment steps may be needed. Antibiotics are sometimes used preventively as pancreatic necrosis can increase infection risk. The most commonly used antibiotics are mersolyl or imipenem/cilastatin which provide broad coverage against gut and pancreatic bacteria.
In severe acute pancreatitis, aggressive treatment is required to prevent multi-organ failure which can be life-threatening. In addition to IV fluids, pain control, and possibly antibiotics, other interventions may include indomethacin suppositories to reduce pancreatic inflammation or somatostatin/octreotide IV to reduce exocrine pancreatic secretions. For necrotizing pancreatitis, minimally-invasive techniques like percutaneous or endoscopic drainage of infected fluid collections are preferable to surgery when possible due to lower risks.
Nutritional support via nasojejunal tube feeding with a semi-elemental formula is especially important in moderate and severe cases to prevent malnutrition, promote healing, and reduce costs from long hospital stays. Overall treatment involves a multidisciplinary approach along a continuum of care that progresses based on the severity and complications of each individual case.
Focus on developing novel drug formulations: Developing novel drug formulations to treat acute pancreatitis is a key strategy adopted by players. In 2018, Twist Bioscience partnered with AbbVie to develop novel monoclonal antibodies for treating acute pancreatitis. Phase 1 clinical trials showed promising results with no adverse effects. This novel formulation improved outcome and reduced hospital stay for patients.
Acquisitions and partnerships for pipeline expansion: Companies have acquired or partnered with other players to expand their product pipeline. In 2020, Nestle Health Science acquired Anumana, a biotech company focused on developing AI solutions for pancreas disorders including acute pancreatitis. This gave Nestle access to Anumana's pipeline drugs and AI technology to predict flare-ups, a major win.
Geographic expansion: Players have focused on expanding into profitable emerging markets like Asia Pacific and Latin America which are expected to be high growth regions for acute pancreatitis treatment. In 2019, AbbVie expanded into China by launching Creon, a pancreatic enzyme replacement drug for treating pancreatitis. Within a year, it captured over 15% of the Chinese market, demonstrating the potential.
Differentiated offerings: Companies providing differentiated treatment options like minimally invasive procedures have seen strong growth. In 2017, Boston Scientific launched SpyGlass Direct Visualization System allowing examination of the pancreatic duct through the mouth, reducing pain and recovery time for patients. It captured 60% of the emerging pancreas self-cleaning device market.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
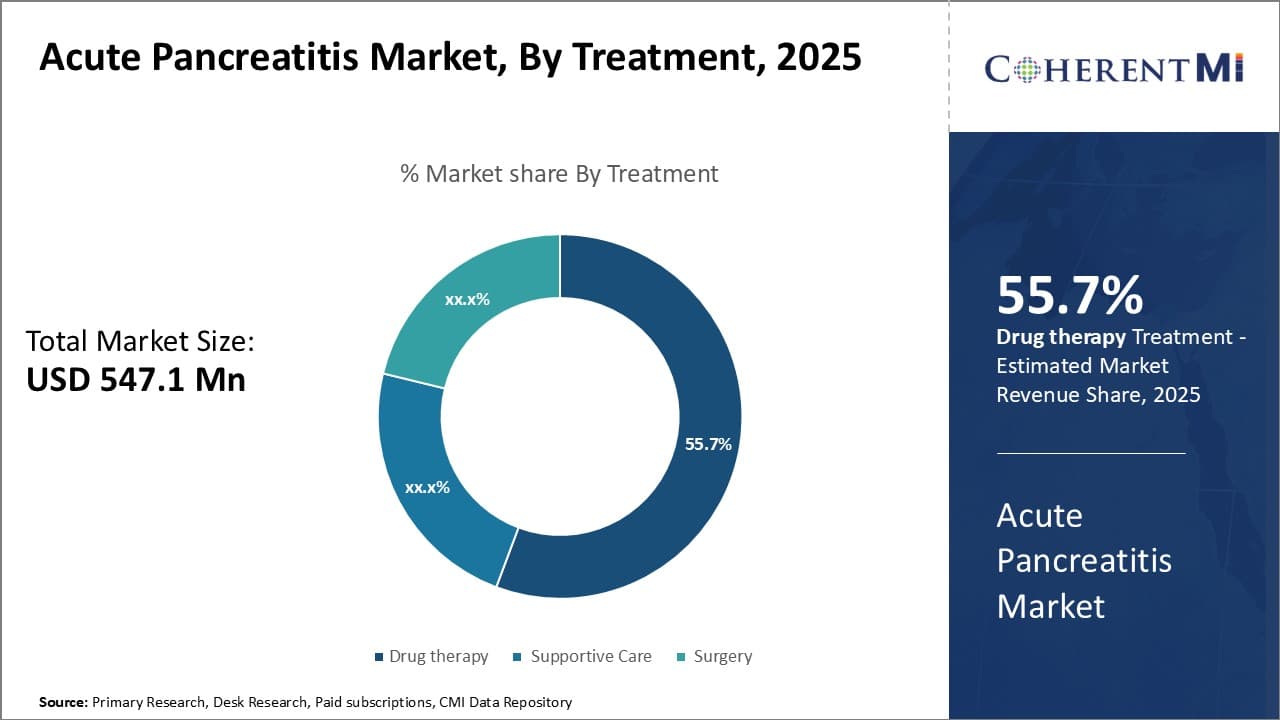
Insights, By Treatment: Aggressive Drug Development Drives Drug Therapy segment growth
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Treatment: Aggressive Drug Development Drives Drug Therapy segment growth
In terms of treatment, drug therapy contributes the highest share of the market owning to aggressive research and development of new drugs by major pharmaceutical companies. Drug therapy remains the primary treatment approach for acute pancreatitis to manage pain and inflammation. Existing drug classes like proteasome inhibitors, antisecretory agents, and pancreatic enzyme replacements have shown some efficacy but come with side effects and other challenges. This has prompted pharmaceutical firms to invest heavily in developing novel drug entities.
Many candidate drugs are currently in clinical trials, with several in late phase testing. Some of the most promising drug classes under investigation include trypsin inhibitors, antioxidant drugs, anti-inflammatory agents, and gene therapy applications. Trypsin inhibitors work by blocking activation of enzymes like trypsinogen that cause pancreatic auto-digestion during pancreatitis attacks.
On the gene therapy front, researchers are exploring using modified viruses to deliver genetic material into pancreatic cells to block specific inflammatory pathways and reduce trypsin activity. Gene therapy could potentially revolutionize pancreatitis treatment if proven safe and effective. Overall, the large development pipelines and success potential of these novel drug candidates is a primary driver keeping the drug therapy segment at the forefront of available treatment options for acute pancreatitis.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
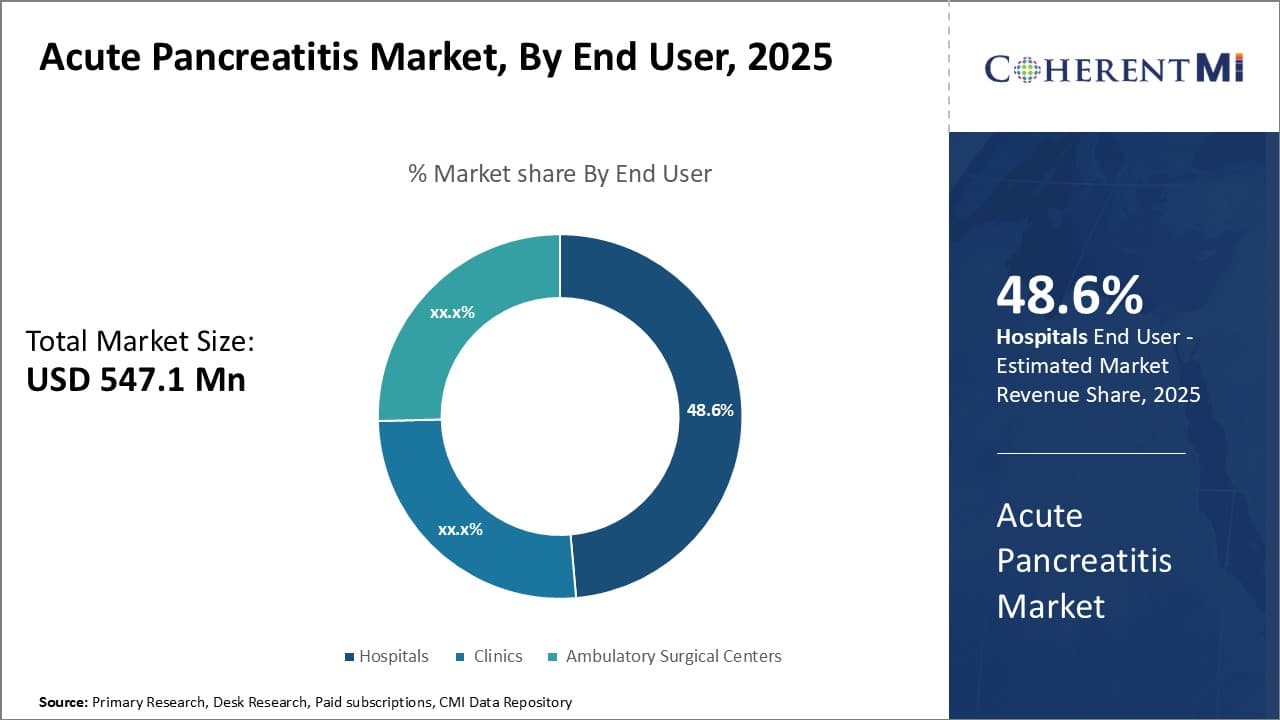
Insights, By End User: Healthcare Infrastructure Drives Hospital Segment Share
In terms of end user, hospitals contribute the highest share of the market owing to well-established healthcare infrastructure in most countries. Acute pancreatitis often requires in-patient care, intensive monitoring, and availability of specialists. It can cause complications affecting other organ systems that may need multi-disciplinary management. Hospitals are best suited to provide such complex care and perform invasive procedures if surgery is needed. Most nations have policies and insurance models that encourage treatment of acute medical conditions in hospitals over alternatives settings.
Developed countries in particular have comprehensive hospital networks with advanced facilities, equipment, and staffing levels to handle even severe pancreatitis cases. Presence of dedicated pancreatology departments, intensive care units, and high-end diagnostic technologies in major hospitals attract serious pancreatitis cases. Nursing and paramedical staff in hospitals also receive specialized training to closely monitor patients and recognize deterioration in condition. Inpatient hospital stay allows for proper fluid/electrolyte management, administration of medications by intravenous route if needed, and prompt intervention or surgery in emergencies. The concentration of healthcare resources in hospitals makes them the priority choice for acute pancreatitis care, sustaining their large market share in this segment.
Insights, By Cause: High Disease Burden Drives Gallstone-induced Pancreatitis
In terms of cause, gallstones account for the highest share as they represent the most common trigger of acute pancreatitis attacks. Gallstones form when bile contained in the gallbladder crystallizes into hard, pebble-like deposits. During an attack, one such gallstone may accidentally block the common bile duct and cause a backup of enzymes into the pancreas. This auto-digestion initiates a destructive inflammatory response leading to acute pancreatitis.
Gallstones predominantly develop due to lifestyle and dietary factors that promote cholesterol crystallization like obesity, high calorie diets, and physical inactivity. Unfortunately, such risk factors have been rising significantly worldwide. The growing global prevalence of obesity, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes has seen gallstone incidence spike across many nations over the past few decades.
Countries undergoing nutrition transition have witnessed some of the steepest increases in gallstone formation. As gallstone disease burden mounts, so does the number of pancreatitis attacks induced by obstructing gallstones. Unless lifestyle patterns change drastically, gallstones will likely maintain their position as a dominant cause of acute pancreatitis well into the foreseeable future. The swelling patient population with gallstones ensures steady demand for this segment.
The major players operating in the Acute Pancreatitis Market include Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Novartis AG, Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline, and AbbVie Inc.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
Acute Pancreatitis Market is segmented By Treatment (Drug therapy, Supportive Care, Surgery), By End...
Acute Pancreatitis Market
How big is the acute pancreatitis market?
The acute pancreatitis market is estimated to be valued at USD 547.1 Mn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 754.6 Mn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the acute pancreatitis market?
The high costs associated with treatment and limited availability of advanced treatment options in certain regions are the major factors hampering the growth of the acute pancreatitis market.
What are the major factors driving the acute pancreatitis market growth?
The increasing incidence of acute pancreatitis globally due to lifestyle changes and advances in treatment options including innovative drugs and therapies are the major factors driving the acute pancreatitis market.
Which is the leading treatment in the acute pancreatitis market?
The leading treatment segment is drug therapy.
Which are the major players operating in the acute pancreatitis market?
Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Novartis AG, Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline, and AbbVie Inc. are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the acute pancreatitis market?
The CAGR of the acute pancreatitis market is projected to be 4.7% from 2025-2032.