Cannabis Use Disorder Market Trends
Market Driver - Increasing Awareness and Diagnosis of Cannabis Addiction
With growing social acceptance of cannabis usage, what has also increased remarkably is public awareness about potential harms of substance abuse and addiction. Only in recent years, extensive scientific studies and their reporting in mainstream media has educated general population about diagnosable cannabis use disorder and how it can negatively impact one's personal and professional life if not addressed properly.
Now people are more informed that using cannabis every day or almost daily to cope with stress, sleeplessness or for entertainment carries risk of psychological as well as physical reliance on the substance. Concepts like cannabis withdrawal syndrome and cannabis addiction are no more foreign terms.
Additionally, mental health professionals are more trained today to identify underlying cannabis use issues during routine assessment of patients reporting mood, anxiety or other psychiatric disorders. All this growing recognition has encouraged many individuals with problematic cannabis consumption patterns to openly seek clinical help rather than considering it a casual habit.
Some are even referred to treatment programs by their colleges, family or friends who notice adverse impacts.
This lifting of the veil of ignorance around risks of cannabis is driving up identification of people affected by cannabis use disorder.
Market Driver - Ongoing Advancements in Cannabinoid Receptor-targeting Therapies
Neuroscientists have deepened their understanding of endocannabinoid system in humans and how activation of cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 influences myriad physiological and cognitive functions. Despite complex interactions, it is clear now that sustained cannabis exposure induces neuroplastic changes in these endogenous cannabinoid pathways leading to tolerance and withdrawal symptoms.
Meanwhile natural and synthetic cannabinoids are also being experimented as replacement therapy during treatment induction phase. The substitution approach aims to gradually wean patient off heavy cannabis use by providing regulated alternative until their endocannabinoid tone stabilizes. Aside, medication assisted options such as nabiximols, a balanced mixture of THC and CBD is showing effectiveness as an adjuvant for therapy in cases of relapse prevention and as an add-on to behavioural counseling modules.
Such innovative approaches bring hope that just like for other substance dependence disorders, cannabis addiction management will transition from wholly psychosocial to combined pharmacological solutions supported by continuously expanding repository of clinical trials and research data.
All these encouraging advances at the frontier of cannabinoid pharmacology lift spirits of individuals seeking long-lasting recovery and thereby fuel the momentum in cannabis use disorder therapeutics sector.
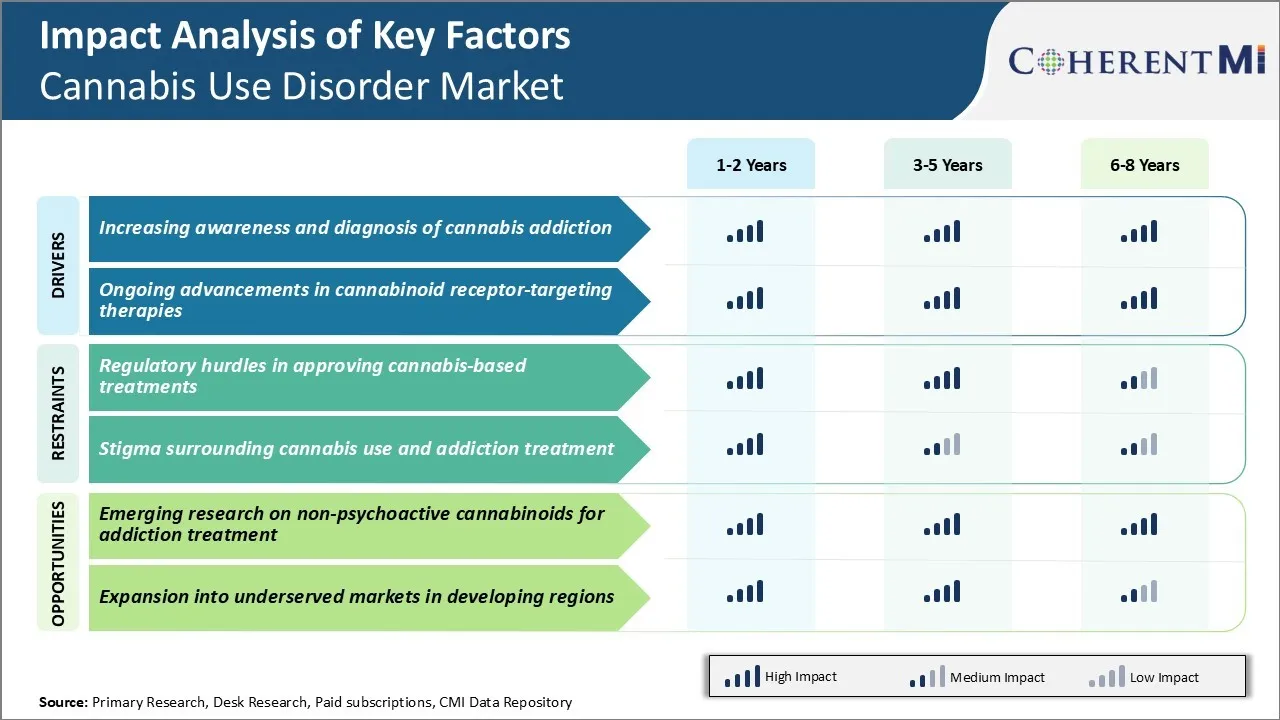
Market Challenge - Regulatory Hurdles in Approving Cannabis-based Treatments
There are significant regulatory hurdles facing the development and approval of cannabis-based treatments for cannabis use disorder. Cannabis remains a Schedule I substance according to the United States Drug Enforcement Administration, meaning it is considered to have no accepted medical use. This classification creates immense difficulty for researchers seeking to study potential medical applications of cannabis.
Extensive clinical trials are required to demonstrate a treatment's safety and efficacy to a rigorous standard before it can be approved, but strict regulations and the Schedule I status of cannabis make research extraordinarily challenging.
Researchers must contend with onerous registration processes, security and monitoring requirements, import and export restrictions, and limited funding options due to cannabis's legal status. These factors collectively slow the pace of research and increase its costs considerably.
If and when medical cannabis treatments are brought forward for regulatory approval, agencies may view them with more skepticism compared to other substances due to the ongoing conflict between scientific evidence and legal classification of cannabis. Resolving this conflict is critical to helping the cannabis use disorder market reach its full potential.
Market Opportunity - Emerging Research on Non-Psychoactive Cannabinoids for Addiction Treatment
There is a significant opportunity for the cannabis use disorder market from emerging research on non-psychoactive cannabinoids and their applications. In particular, cannabidiol (CBD) is being extensively studied for its therapeutic potential without psychoactive side effects. CBD does not directly activate the cannabinoid receptors that are responsible for marijuana's psychoactivity.
Several studies have found CBD may help reduce cravings and relapse rates in individuals with cannabis use disorder by its calming and anti-anxiety effects. CBD is also being studied for its ability to mitigate some of the adverse cognitive and psychiatric effects of THC, the primary psychoactive compound in marijuana. If CBD or other non-psychoactive cannabinoids are proven effective and approved to treat cannabis addiction, it could open up a substantial market. These treatments may be more widely acceptable than therapies utilizing psychoactive cannabis extracts.
The low abuse potential further increases accessibility and commercial viability. Continued preclinical and clinical research focused on isolating therapeutic compounds in cannabis holds great promise to expand options for those struggling with cannabis use disorder.