Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) Treatment Market Size - Analysis
The Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) treatment market is estimated to be valued at USD 16.36 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 28.2.40 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2% from 2025 to 2032.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR8.2%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 8.2% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Taizhou Mabtech Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Celldex Therapeutics, Allakos, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline and Among Others |
please let us know !
Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) Treatment Market Trends
Chronic idiopathic urticaria, also known as chronic spontaneous urticaria, is a common condition characterized by itchy hives or wheals on the skin that last for more than six weeks. While the exact cause remains unknown in many cases, its prevalence has been increasing over the past couple of decades around the world. Many factors such as environmental triggers, stressful lifestyle, and food allergies are considered to play a role in the development of CIU symptoms. With more people getting affected by this distressing condition, the demand for effective CIU treatment options has surged significantly.
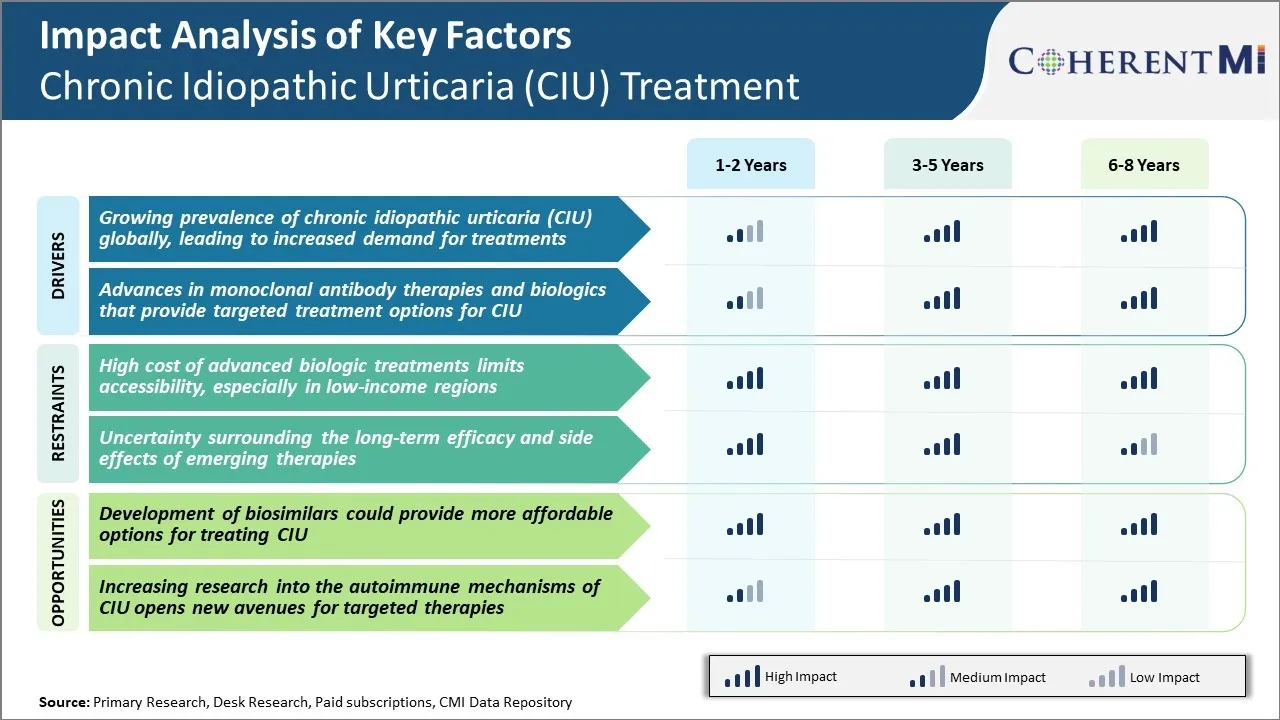
Researchers have been vigorously working on developing novel treatment approaches for refractory chronic idiopathic urticaria that does not adequately respond to conventional second-generation antihistamines. This has led to significant advances in monoclonal antibody therapies and biologic agents that precisely target the underlying disease mechanisms.
More recently, faricipimab and ligelizumab, both targeting immune system signals involved in CIU, entered late-stage clinical evaluation. Their promising efficacy and safety profile observed so far indicates these treatments could emerge as major game changers for managing difficult to control CIU cases.
Market Challenge - High Cost of Advanced Biologic Treatments Limits Accessibility
While they may prove cost-effective by reducing the need for other health services in responders, their high acquisition cost puts them out of reach for many healthcare systems and individual patients in low and middle-income countries. Even in developed markets, the out-of-pocket costs after insurance reimbursement can be prohibitively high for some patients. This price barrier limits access to the most effective therapies especially for underprivileged populations in developing or resource-limited regions.
The emergence of biosimilars referencing leading biologic therapies for CIU offers a potential opportunity to address their high treatment costs and expand access to patients worldwide. Biosimilars which have demonstrated comparable quality, safety and efficacy to their reference products but are marketed at a discounted price, could capture a sizable portion of the market once patent protection for innovator drugs begins to expire.
Wider availability of affordable near-biosimilar or biosimilar equivalents of biologics could enable physicians to optimize treatment for many more CIU patients, especially those in price-sensitive regions where cost had been a barrier to care.
Prescribers preferences of Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) Treatment Market
Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) is typically treated through a step-wise approach over multiple lines of therapy depending on disease severity and patient response. For mild cases in the initial stages, antihistamines such as cetirizine (Zyrtec) or loratadine (Claritin) are prescribed as first-line treatment. However, 20-50% of patients do not achieve adequate disease control with first-generation antihistamines alone.
Cost of treatment is an important factor influencing prescriber decisions, especially considering the chronic nature of CIU. While generic antihistamines offer good cost-effectiveness as first-line options, biologics like omalizumab entail a higher expense. Overall, treatment approaches are customized based on each patient's disease severity, budget constraints as well as their response to prior therapeutic regimens.
Treatment Option Analysis of Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) Treatment Market
CIU is characterized by the recurrent appearance of hives or wheals for more than six weeks. Treatment is focused on reducing symptoms and includes various options depending on the stage and severity of disease.
For such patients, second line options include levocetirizine and desloratadine - newer generation antihistamines that are more potent. They provide better relief either as monotherapy or in combinations. Omalizumab, a monoclonal antibody, is also used in cases where antihistamines fail. It inhibits immunoglobulin E and is effective in approximately 65% of patients.
Montelukast, a leukotriene receptor antagonist, has shown promise in multiple studies, either alone or in combination with antihistamines. As a third line option, it provides additional relief mechanisms for refractory urticaria.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) Treatment Market
Focus on newer product innovation and development: Players have increasingly focused on developing newer and more effective products to treat CIU. For example, in 2017, Novartis obtained FDA approval for Cinqair (reslizumab), the first FDA-approved biologic for the treatment of CIU. Cinqair introduced a new treatment mechanism targeting immunoglobulin E.
Expand geographic footprint: Key players have focused on expanding their commercial footprint, especially in high-growth markets like Asia Pacific and Latin America. For instance, between 2015-2019, GSK partnered with several distributors to launch its antihistamine Zyrtec (cetirizine) across multiple Asian and Latin American countries for CIU treatment. This helped drive significant sales growth.
Segmental Analysis of Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) Treatment Market
-treatment-market-by-route-of-administration.webp) Insights, By Route of Administration: Convenience and Safety Drive Subcutaneous Adoption
Insights, By Route of Administration: Convenience and Safety Drive Subcutaneous AdoptionIn terms of route of administration, subcutaneous contributes the highest share of the market owning to its convenience and safety profile. Subcutaneous injections can be easily self-administered at home without the need for specialized medical facilities or healthcare professionals. This ease of administration increases patient compliance to the prescribed treatment regimen. Furthermore, subcutaneous injections carry a lower risk of infection compared to intravenous methods as there is no direct contact with the bloodstream. The subcutaneous tissue also has more space to absorb drug molecules gradually as compared to intramuscular injections, thus reducing the chance of overdose or adverse reactions. Overall, the non-invasive nature and safety of subcutaneous injections have made it the preferred route for chronic conditions like CIU that require long-term management.
-treatment-market-by-molecule-type.webp)
In terms of molecule type, monoclonal antibody contributes the highest share of the market due to their high specificity and precision. Monoclonal antibodies are artificially synthesized in the laboratory to target a single epitope or antigen on the pathogen cell. This specificity allows them to neutralize the intended cell very effectively with minimal off-target interactions.
In terms of product type, mono contributes the highest share of the market owing to the benefits of simplicity. Most patients prefer standalone drug treatments rather than complex multi-drug combinations due to lower pill burden, fewer drug interactions, and simpler dosing schedules. Mono therapies are also more cost-effective for payers compared to fixed-dose combinations.
Additional Insights of Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) Treatment Market
- The prevalence of CIU is increasing, affecting around 0.5% to 1% of the population globally. However, there remains a significant unmet need for treatments, particularly in severe cases resistant to standard therapies.
- Several drugs are in the Phase II or III stages of clinical trials, indicating a dynamic development landscape for CIU.
Competitive overview of Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) Treatment Market
The major players operating in the Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) Treatment Market include Taizhou Mabtech Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Celldex Therapeutics, Allakos, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, UCB Pharma, and Teva Pharmaceuticals.
Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) Treatment Market Leaders
- Taizhou Mabtech Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.
- Celldex Therapeutics
- Allakos
- Novartis
- GlaxoSmithKline
Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) Treatment Market - Competitive Rivalry

Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) Treatment Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) Treatment Market
- In July 2024, Taizhou Mabtech Pharmaceutical announced that it is conducting a Phase III clinical trial for CMAB007, a biosimilar of omalizumab. This study compares efficacy, immunogenicity, and safety in CIU patients. The development aims to address unmet needs in the chronic urticaria space.
- In May 2024, Celldex Therapeutics announced that Celldex’s Barzolvolimab (CDX-0159) in Phase III targets the KIT receptor to prevent allergic reactions, offering hope for severe CIU cases. Its positive impact in early trials shows potential to reshape CIU treatment.
Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) Treatment Market Segmentation
- By Route of Administration
- Subcutaneous
- Intravenous
- Oral
- By Molecule Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Small Molecule
- Recombinant Fusion Proteins
- By Product Type
- Mono
- Combination
- By Development Phase
- Phase I
- Phase II
- Phase III

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) treatment market?
The Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) treatment market is estimated to be valued at USD 16.36 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 28.40 Bn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) treatment market?
The high cost of advanced biologic treatments limits accessibility, especially in low-income regions and uncertainty surrounding the long-term efficacy and side effects of emerging therapies are the major factors hampering the growth of the Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) treatment market.
What are the major factors driving the Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) treatment market growth?
The growing prevalence of chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU) globally, leading to increased demand for treatments and advances in monoclonal antibody therapies and biologics that provide targeted treatment options for ciu are the major factors driving the Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) treatment market.
Which is the leading route of administration in the Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) treatment market?
The leading route of administration segment is subcutaneous.
Which are the major players operating in the Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) treatment market?
Taizhou Mabtech Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Celldex Therapeutics, Allakos, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, UCB Pharma, Teva Pharmaceuticals are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) treatment market?
The CAGR of the Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) treatment market is projected to be 8.2% from 2025-2032.