

The chronic spontaneous urticaria market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.66 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 5.49 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.9% from 2025 to 2032. The increasing prevalence of chronic spontaneous urticaria and growing awareness about its treatment options are contributing to the growth of this market.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR10.9%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 10.9% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Roche, Novartis, Sanofi/Regeneron, AstraZeneca, Amgen and Among Others |
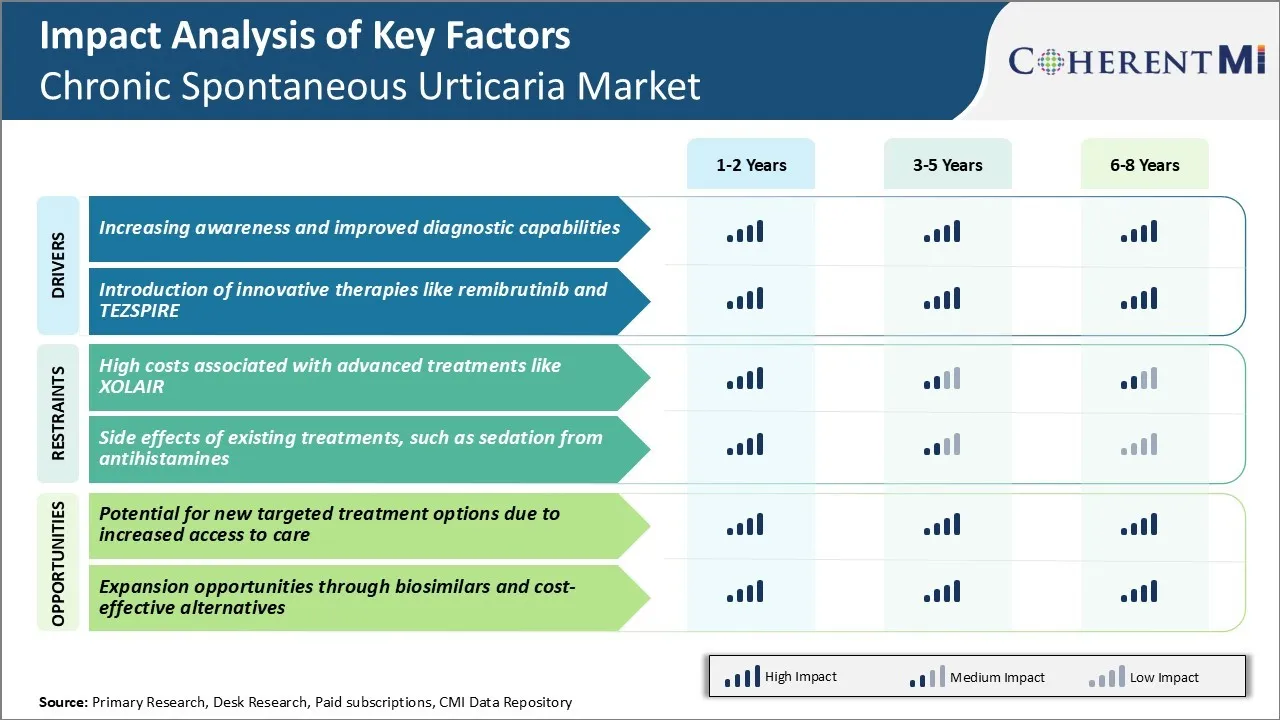
Market Driver - Increasing Awareness and Improved Diagnostic Capabilities
Over the past decade, patient advocacy groups and medical associations have launched numerous campaigns aimed at educating both medical professionals and the general public. Doctors are now much more vigilant in evaluating patients presenting with hives and angioedema, investigating for potential underlying triggers and making an accurate diagnosis.
Symptom diaries, skin testing, and laboratory assays have markedly enhanced clinicians' ability to distinguish chronic spontaneous urticaria from other similar conditions. This has allowed patients to receive targeted treatment instead of merely trialing various antihistamines.
The accessibility of health information on the internet has empowered individuals to learn more about their condition and advocate for proper evaluation. Online communities provide peer support that helps normalize the experience and boosts morale. Partnerships between advocacy organizations and pharmaceutical companies have sponsored educational initiatives in hospitals, clinics, and universities to spread understanding among medical professionals.
As awareness spreads and diagnostic prowess improves, more cases are brought to light, appropriately characterized, and plugged into treatment algorithms. This growing visibility and validation of chronic spontaneous urticaria as a significant disease state is strengthening the basis for the chronic spontaneous urticaria market of associated drugs and services.
Market Driver - Introduction of Innovative Therapies Like Remibrutinib and TEZSPIRE
The development of novel treatment modalities beyond traditional antihistamines represents great promise for advancing chronic spontaneous urticaria management. Early phase trials demonstrated Remibrutinib's potential to induce rapid and sustained response in patients unresponsive to antihistamines alone. Its targeted mechanism of action holds hope for improved symptom control with fewer side effects than immunosuppressants like cyclosporine.
Similarly, the recently FDA approved TEZSPIRE offers the first approved biologic option for chronic spontaneous urticaria. As a monoclonal antibody inhibiting the interleukin-31 receptor, it works to block itching signaling at its source rather than simply tamp down downstream symptoms.
Entry of these novel drugs in the chronic spontaneous urticaria market represents an inflection point, going beyond symptom palliation to target specific pathogenic mechanisms. Their varied mechanisms of action stand to significantly expand the therapeutic arsenal and benefit a broader portion of the chronic spontaneous urticaria population. By directly addressing underlying disease drivers, remibrutinib and TEZSPIRE are changing standards of care and improving quality of life for those previously uncontrolled on traditional approaches alone. Their innovative profiles will surely help invigorate the pharmaceutical segment of this therapeutic space.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High Costs Associated with Advanced Treatments like XOLAIR
One of the key challenges facing the chronic spontaneous urticaria market is the high costs associated with advanced treatment options like XOLAIR. XOLAIR is a monoclonal antibody injection approved for the treatment of chronic idiopathic urticaria. However, each 300mg injection carries a wholesale acquisition cost of over $2000.
As a biologic drug, it requires injection or infusion administered by a health professional, making each treatment session more expensive compared to oral therapies. The effectiveness of XOLAIR does alleviate symptoms for many refractory patients who fail standard oral treatments. Yet the high price per injection creates barriers for broader access and reimbursement challenges.
With urticaria being primarily managed in an outpatient setting, the costs burden often falls on patients themselves via high co-payments or being uninsured. The high list prices of newer biologics threaten the sustainability of healthcare systems and patients' adherence to therapy due to cost-related concerns. This cost challenge remains a key consideration for physicians determining appropriate treatment escalation pathways as well as for market growth potential of these new urticaria therapeutics.
Market Opportunity - Potential for New Targeted Treatment Options Due to Increased Access to Care
One opportunity for the chronic spontaneous urticaria market lies in the potential for new targeted treatment options due to increased access to care. As healthcare systems evolve to improve overall primary care access via initiatives lowering barriers like telehealth and community clinics, it expands the total addressable market for new urticaria drugs.
With a better economic climate enabling greater employment and insurance coverage post-pandemic, more urticaria patients may be able to obtain an accurate diagnosis and treatment guidance from an allergist rather than remaining untreated or under-treated by primary care physicians unfamiliar with urticaria management guidelines. This creates a situation where pharmaceutical companies focused on precision or personalized urticaria treatments have a viable pathway to reach more eligible patients.
Treatments targeting specific immunologic triggers or biomarkers of disease severity have potential to deliver superior outcomes than existing one-size-fits-all therapies. If such new options demonstrate clear cost-effectiveness through shorter time to remission or decreased rescue medication use, they could overcome many reimbursement obstacles faced by high-cost drugs today.
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria (CSU) typically follows a step-wise treatment approach based on disease severity and symptom control. For mild symptoms, prescribers often recommend first-generation antihistamines like cetirizine (Zyrtec) or loratadine (Claritin). These are preferred initially due to their safety and cost-effectiveness.
If symptoms are not adequately managed, prescribers may advance treatment to second-generation antihistamines. Bilastine (Xyzal) and levocetirizine (Xyzal) are highly prescribed at this stage for their strong affinity to H1-receptors. Prescribers also consider fexofenadine (Allegra) as it provides 24-hour relief from itching and hives.
For moderate-severe CSU, prescribers rely on omalizumab (Xolair), a monoclonal antibody that targets immunoglobulin E. Given as a monthly subcutaneous injection, omalizumab is highly effective but also the most expensive treatment option. It is typically reserved for cases where other interventions fail to control symptoms.
When symptoms remain uncontrolled despite above interventions, cyclosporine (Sandimmune) may be prescribed off-label. As a calcineurin inhibitor, cyclosporine suppresses the immune system and provides relief. However, long-term side effects require close monitoring by prescribers.
Cost of treatment significantly influences prescribers' preferences at each line. Safety profiles and ease of administration also impact their choices. Patient feedback often aids prescribers in assessing response and adjusting future therapy accordingly.
CSU can be classified into different stages based on disease severity and duration of symptoms. Mild CSU is characterized by hives less than 4 times per week and minimal itching/swelling. However, moderate-severe CSU causes hives more frequently along with noticeable discomfort.
First-line treatment for mild CSU involves the use of second-generation H1 antihistamines such as cetirizine or loratadine. These are preferred initially due to their mild side effect profile and low cost. For moderate-severe CSU, higher potency H1 antihistamines like fexofenadine, levocetirizine or desloratadine are recommended either as monotherapy or in combination with H2 antihistamines like ranitidine.
If hives are not adequately controlled after 2-4 weeks of first-line options, then omalizumab (Xolair) - a monoclonal antibody, becomes the preferred add-on therapy. It selectively binds to immunoglobulin E to curb the allergic response causing hives. Omalizumab leads to a rapid response within 4-8 weeks with fewer side effects than corticosteroids.
For frequent flares even with omalizumab, cyclosporine (Immunosopres) - a calcineurin inhibitor, is recommended for short term use (up to 6 months) to improve quality of life while minimizing steroid exposure. It works by suppressing T-cell activation and reducing hives within 4 weeks. Close monitoring is required due to potential nephrotoxicity.
Focus on developing innovative drug formulations:
Many top players like Xolair (Novartis/Genentech) and Nucala (GlaxoSmithKline) have focused on developing innovative biologics and monoclonal antibodies to treat chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU). Xolair was the first FDA approved medication specifically for CSU in 2014. It saw great success as it provided significant symptom relief for many patients who did not respond to antihistamines alone. Its approval validated monoclonal antibodies as an important therapeutic approach for CSU.
Pursue comprehensive clinical trial programs:
Companies dedicate large resources towards establishing the safety and efficacy of their drug candidates through multi-regional clinical trials covering diverse patient groups. For example, the phase 3 clinical program for Nucala enrolled over 800 patients across several countries. This helped address key questions from regulatory agencies and provided a robust data package for approval and reimbursement decisions.
Build extensive patient support programs:
Players partner with patient advocacy groups to run awareness campaigns and establish dedicated support services like patient assistance programs, nursing support, and co-pay assistance. Xolair's parent company Genentech runs a comprehensive support program called "XolairComplete" which helps patients navigate insurance approvals and affords treatment.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
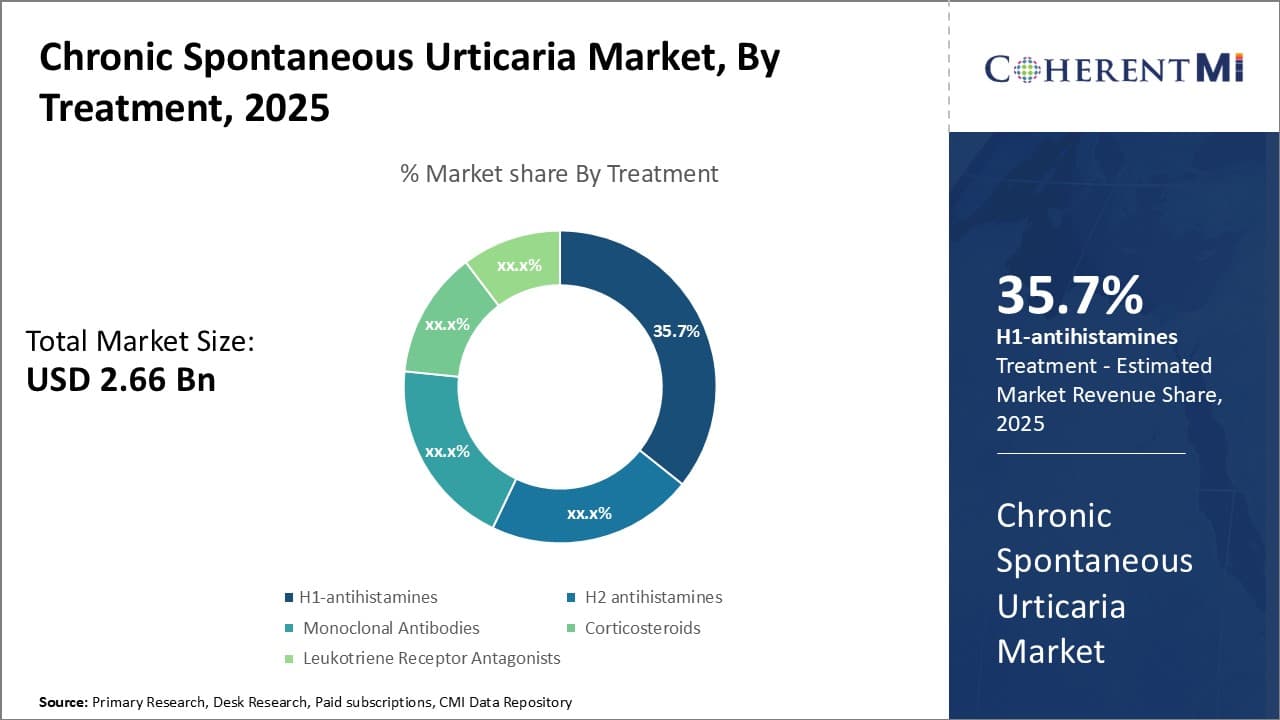
Insights, By Treatment: H1-antihistamines Drive Treatment Segment Leadership Due to Strong Efficacy and Safety Profile
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Treatment: H1-antihistamines Drive Treatment Segment Leadership Due to Strong Efficacy and Safety Profile
Within the chronic spontaneous urticaria treatment segment, H1-antihistamines is likely to hold 35.7% market share in 2025, owing to their demonstrable efficacy and favorable safety profile. As the first-line pharmacological intervention for chronic hives, H1-antihistamines effectively suppress histamine release and interrupt its binding to H1 receptors, rapidly relieving itching and hives. Numerous clinical trials have established H1-antihistamines as a safe and effective initial treatment option for even severe urticaria cases.
Compared to other treatment types, H1-antihistamines also offer a gentler side effect profile. Adverse reactions tend to be mild, including sleepiness and dry mouth. More serious potential side effects seen with some other treatments, such as infection from immunosuppression or cardiovascular risks, are largely avoided. This favorable risk-benefit ratio encourages treatment adherence and allows H1-antihistamines to be prescribed long-term for chronic urticaria patients whose symptoms remain uncontrolled on alternative therapies.
The availability of both prescription and OTC H1-antihistamine options further enhances accessibility and consistency of care. Patients can choose from a variety of formulations based on individual symptom severity, convenience needs, insurance coverage, and cost preference. This treatment flexibility, combined with H1-antihistamines' proven efficacy record and established safety, has made them the standard first-line monotherapy approach worldwide for chronic hives. Generic availability now provides low-cost maintenance choices, solidifying H1-antihistamines' dominant share of this treatment segment.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
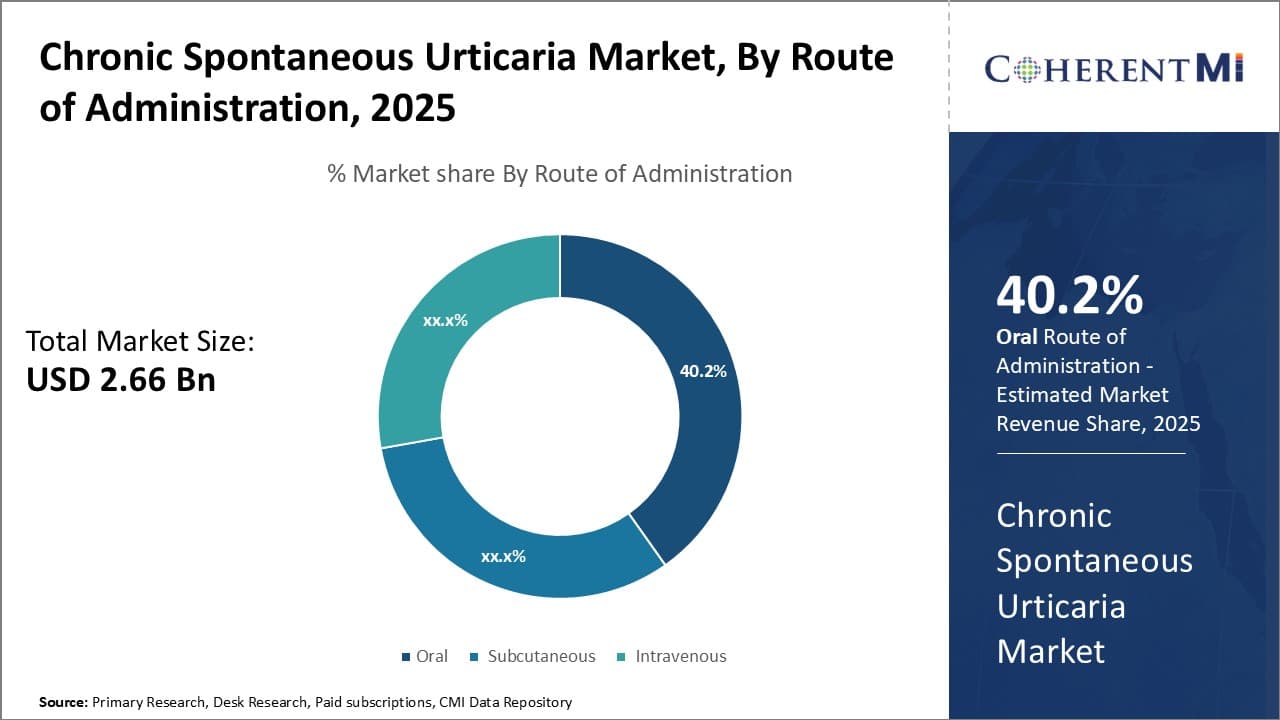
Insights, By Route of Administration: Oral Administration Drives Highest Share Due to Convenience and Compliance
Within the route of administration segment, oral administration is estimated to account for 40.2% share of the chronic spontaneous urticaria market in 2025, due to its inherent convenience and ability to support medication compliance. Compared to subcutaneous injections or intravenous infusions requiring clinical administration, oral dosing allows for self-care at home. This provides patients greater independence, spontaneous symptom control through on-demand dosing, and around-the-clock availability of relief without disrupting daily lives or work schedules.
Consistent oral intake is also easier for most patients, encouraging proper long-term treatment adherence vital for chronic urticaria management. Accurate self-dosing is simpler with oral pills or liquids versus injections patients may find difficult to self-administer or fearful of using improperly. Additionally, oral treatment avoids injection-site reactions, pain, needle phobias, and other issues that can hamper preference and compliance with subcutaneous or intravenous alternatives.
For healthcare systems, oral administration provides vastly increased convenience through widespread pharmacy access versus reliance on clinical infusion centers. This decreases administrative burdens and costs to providers, payers, and the overall healthcare sector.
It also allows coordinated long-term follow-up primarily through primary care physicians rather than specialists. Taking treatment orally on a consistent schedule is ultimately the most simple and compatible approach for the majority of chronic urticaria patients and their stakeholders.
The major players operating in the chronic spontaneous urticaria market include Roche, Novartis, Sanofi/Regeneron, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Taiho Pharmaceutical, and other smaller players.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria Market is segmented By Treatment (H1-antihistamines, H2 antihistamines...
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria Market
How big is the chronic spontaneous urticaria market?
The chronic spontaneous urticaria market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.66 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 5.49 Bn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the chronic spontaneous urticaria market?
High costs associated with advanced treatments like Xolair and side effects of existing treatments, such as sedation from antihistamines are the major factors hampering the growth of the chronic spontaneous urticaria market.
What are the major factors driving the chronic spontaneous urticaria market growth?
The increasing awareness, improved diagnostic capabilities, and introduction of innovative therapies like Remibrutinib and Tezspire are the major factors driving the chronic spontaneous urticaria market.
Which is the leading treatment in the chronic spontaneous urticaria market?
The leading treatment segment is H1-antihistamines.
Which are the major players operating in the chronic spontaneous urticaria market?
Roche, Novartis, Sanofi/Regeneron, AstraZeneca, Amgen, and Taiho Pharmaceutical are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the chronic spontaneous urticaria market?
The CAGR of the chronic spontaneous urticaria market is projected to be 10.9% from 2025-2032.