

The diabetic peripheral neuropathy market is estimated to be valued at USD 5.10 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 9.88 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.9% from 2025 to 2032. The market is primarily driven by the rising global prevalence of diabetes and growing geriatric population worldwide who are at a higher risk of developing diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN).
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR9.9%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 9.9% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Helixmith, Aptinyx, WinSanTor, Inc., Regenacy Pharmaceuticals, Grünenthal GmbH and Among Others |
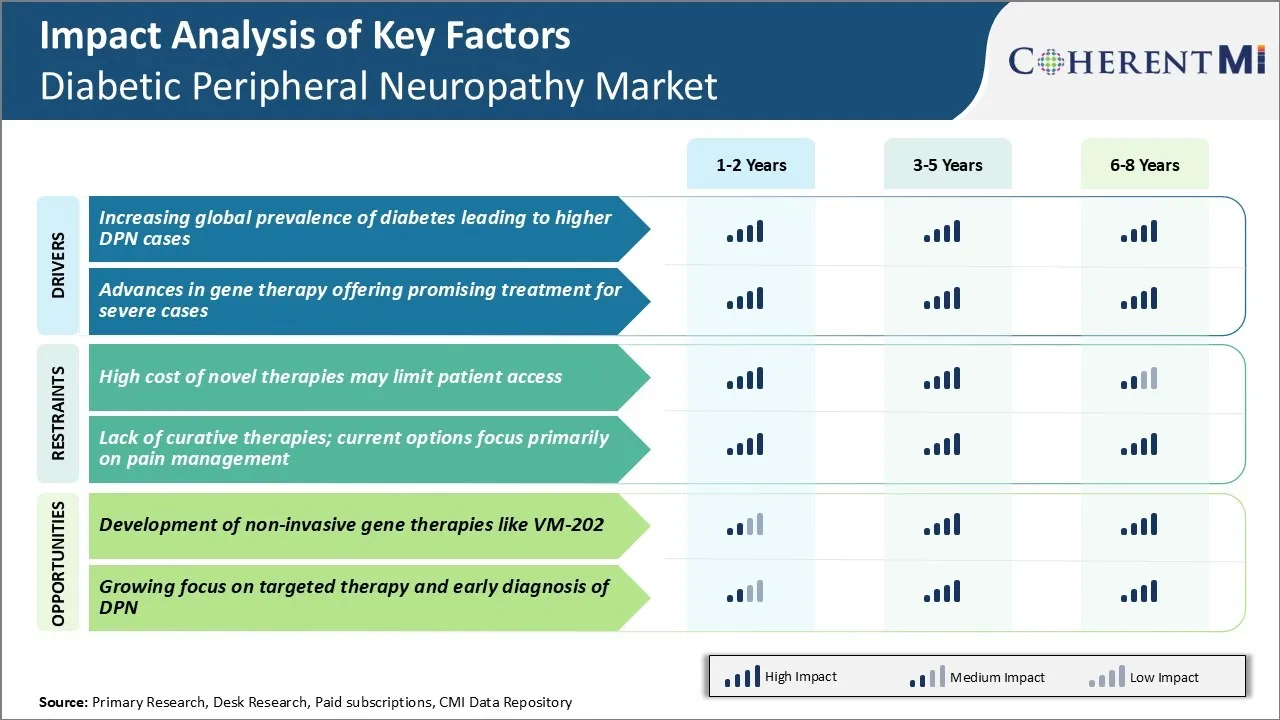
Market Driver - Increasing Global Prevalence of Diabetes Leading to Higher DPN Cases
With over 420 million people suffering from diabetes across the globe currently according to recent estimates from WHO, the prevalence has increased manifolds over the past few decades. Further, this number is projected to escalate to around 630 million by 2045 if decisive measures are not taken to curtail the diabetes burden. Alarmed by this stark projection, public health officials and researchers are sparing no effort to spread awareness and promote diabetes self-management.
However, diabetes remains a largely underdiagnosed and underreported condition in vast swathes of emerging economies where healthcare infrastructure and accessibility are inadequate. As more and more people develop diabetes owing to the interplay of various macro factors, an increasing number of them are destined to experience diabetic neuropathy symptoms over the course of their disease progression. This is evident from studies reporting rising DPN prevalence ranging from about 8% to 13% among diagnosed diabetics.
The healthcare costs associated with managing DPN and its multi-systemic complications have become a huge economic burden globally. With an aging global population further heightening the diabetes risk, it is evident more investment and medical innovation is direly needed to prevent nerve damages in diabetes patients for alleviating their burden.
Market Driver - Advances in Gene Therapy Offering Promising Treatment for Severe Cases
Gene therapy has emerged as one of the most fascinating avenues that hold enormous promise for revolutionizing the treatment paradigm of currently incurable conditions including treatment-resistant DPN cases. In the last decade or so, scientists have gained deeper understanding of the molecular pathways contributing to nerve cell degeneration and symptoms in DPN through extensive research. This has helped identify new targets that can be modulated using gene therapy vectors to stop or slow down the neurodegenerative process.
Some of the cutting-edge technologies being explored actively are gene knockdown approaches using antisense oligonucleotides or RNA interference techniques to inhibit overexpression of pain-causing genes involved in neuropathic pain mechanism. Viral vectors like AAV and lentivirus are being evaluated as carriers to deliver corrective genes or factors like neurotrophic proteins that promote neuron survival and function. Initial safety and efficacy results from animal studies look highly encouraging. Several novel gene candidates as therapeutics are under active preclinical screening.
While it may take many years for comprehensive evaluation and potential approvals, gene therapy field holds tremendous scope for breakthroughs. Success stories could revolutionize the healthcare paradigm for severe, chronic forms of DPN in the future.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High Cost of Novel Therapies May Limit Patient Access
The development of novel therapies that can potentially modify the course of diabetic peripheral neuropathy has increased treatment options for patients.
However, these new treatment approaches such as non-opioid analgesic therapies, gene therapies and stem cell therapies often come with a high price tag. As per our analysis, the cost of some of the newly approved and late-stage pipeline drugs ranges anywhere between $10,000 to $50,000 per patient, per year of treatment.
While these therapies have demonstrated benefits in improving neuropathy symptoms and slowing progression in clinical trials, their high cost can be a significant barrier for widespread adoption. Most private and public drug plans have strict restrictions on coverage for such expensive therapies.
Only patients with very severe symptoms who have failed other standard of care options are likely to be approved for coverage. This limited access means majority of the patients suffering from diabetic peripheral neuropathy will remain reliant on generic medications like gabapentin and duloxetine that are effective for symptomatic relief but do no modify disease progression. The high cost of novel drugs thus remains one of the key challenges hampering effective management of the disease over the long run.
Market Opportunity – Development of Non-Invasive Gene Therapies like VM-202 Offers Promising Opportunity
One of the areas offering high potential for future growth in the diabetic peripheral neuropathy market is the development of non-invasive gene therapies. VM-202, an investigational topical gene therapy undergoing late-stage clinical trials, presents an attractive opportunity as a potential non-invasive treatment option. If approved, VM-202 will be the first non-systemic gene therapy for diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
As per preliminary clinical results, a single application of VM-202 has provided pain relief for 6 months or longer in a majority of patients. Its non-invasive delivery method through permeation of plasmid DNA into skin cells makes it safer than repetitive administration of viral vectors required for other gene therapies.
Being an outpatient treatment administered by the patient, VM-202 also promises to be more cost effective than monthly infusion therapies. Its unique mechanism of action targeting small fiber neuropathy also provides hope as a disease modifying therapy. With a favorable safety profile thus far and strong unmet need, VM-202 has potential to penetrate a significant share of the diabetic peripheral neuropathy market upon approval.
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is typically treated via a step-wise approach based on the stage and severity of symptoms. For early/mild DPN with only pain symptoms, prescribers commonly start with over-the-counter oral medications like acetaminophen or topical agents like lidocaine 5% patches.
If symptoms progress, the first-line treatment is often oral antidepressants/anticonvulsants due to their analgesic effects. Commonly prescribed options include duloxetine (Cymbalta), pregabalin (Lyrica), and gabapentin. These are generally well-tolerated and provide pain relief for many patients.
For those with more significant pain or inadequate response to first-line treatments, prescribers may try topical lidocaine creams or consider stronger medications like opioids. Tapentadol extended release (Nucynta ER) is an option that provides both pain relief with fewer side effects than alternatives like oxycodone or morphine sulfate.
In advanced DPN with loss of sensation and functional impairment, prescribers have limited medication options and tend to focus on neurological assessments, specialty referrals, assistive devices, and physical or occupational therapy. Overall, treatment decisions are guided by balancing efficacy, safety, tolerability, and costs - especially considering many DPN patients have diabetes and other comorbidities. Patient preferences also play an important role.
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) can broadly be divided into three stages based on symptoms - mild, moderate and severe.
In the mild stage, patients may experience numbness, tingling or pain in the feet and legs. First line treatments typically include pregabalin (Lyrica) and duloxetine (Cymbalta). These oral medications target gabapentin and serotonin-norepinephrine receptors respectively to reduce pain sensations. Pregabalin is preferred initially due to its proven efficacy and safety profile.
As symptoms progress to moderate pain, burning or poor balance, second line options include gabapentin enacarbil (Horizant) - an approved prodrug of gabapentin with better absorption. Tramadol (Ultram) - an opioid pain reliever and SNRI may also be used. For those unresponsive, topical lidocaine patches (Lidoderm) are applied to feet for localized relief.
In severe cases with foot ulcers or risk of amputation, strong opioids like oxycodone (OxyContin) along with tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) like nortriptyline and analgesics are tried. As a last resort, spinal cord stimulators or surgical sympathectomy may be considered to disrupt pain signals. Control of blood sugar levels and physical/occupational therapy continue to be mainstay alongside pharmacological management at all stages of DPN.
R&D Investments and New Product Launches: Companies have significantly invested in R&D to develop innovative and effective treatment options for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. For example, Pfizer invested over $8 billion in R&D in 2021 to develop new drugs and therapies. In 2022, it launched Qulipta, a once-daily oral calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist (galcanezumab-gnlm) indicated for the preventive treatment of migraine in adults.
Targeted Marketing and Awareness Campaigns: Players run targeted digital and multimedia campaigns to create awareness about diabetic peripheral neuropathy and new treatment options. For example, Eli Lilly runs the "Step Together" campaign featuring patient testimonials on managing diabetes and nerve pain. It has significantly improved Lilly's brand awareness among patients and physicians. Between 2020-22, Lilly saw a 20% increase in sales of Cymbalta, a number one prescribed drug for diabetic nerve pain.
Strategic Partnerships and Licensing Deals: Companies partner and sign licensing deals with biotechs to gain access to new pipeline candidates and technologies. For example, in 2022 Pfizer partnered with Anthropic to accelerate AI research for conditions like diabetic neuropathies. They aim to develop digital biomarkers to improve diagnosis and outcomes. Such deals allow big pharma to strengthen portfolios without significant in-house investments.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
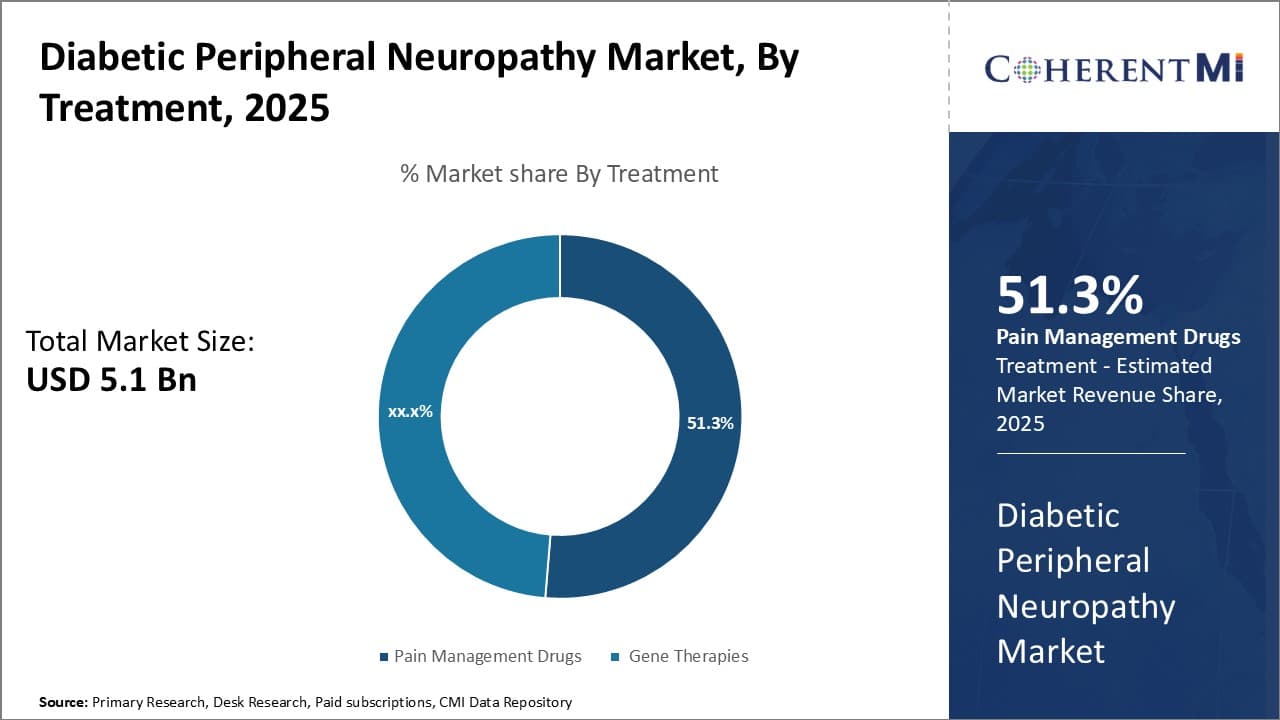
Insights, By Treatment: >Pain Management Drugs (e.g., Opioids, Anticonvulsants) - Relieving Pain Through Effective Treatment
In terms of treatment, pain management drugs (e.g., opioids, anticonvulsants) is expected to hold 51.3% share of the diabetic peripheral neuropathy market in 2025, owning to their proven effectiveness in relieving the chronic pain experienced by many neuropathy patients. Neuropathy causes pain by sensitizing the nerves, making them more susceptible to pain signals.
Opioids and anticonvulsants are often first-line treatments as they act on the central nervous system to reduce pain perception. Opioids work by bonding to opioid receptors in the brain, spinal cord and nervous system to inhibit transmission of pain signals. Commonly prescribed opioids include hydrocodone, oxycodone and tramadol. Their analgesic effects make them a mainstay for managing diabetic neuropathy pain.
Anticonvulsants’ mechanisms of action are similar, blocking sodium channels or enhancing inhibitory neurotransmitters like GABA in the central nervous system. Pregabalin and gabapentin are frequently prescribed anticonvulsants that provide relief for many patients through these actions. Their proven safety and efficacy profiles have gained physician and patient acceptance, driving the segment's growth through high prescription rates.
However, concerns around risks of addiction and tolerance with long-term opioid use may spur interest in alternative options over time.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
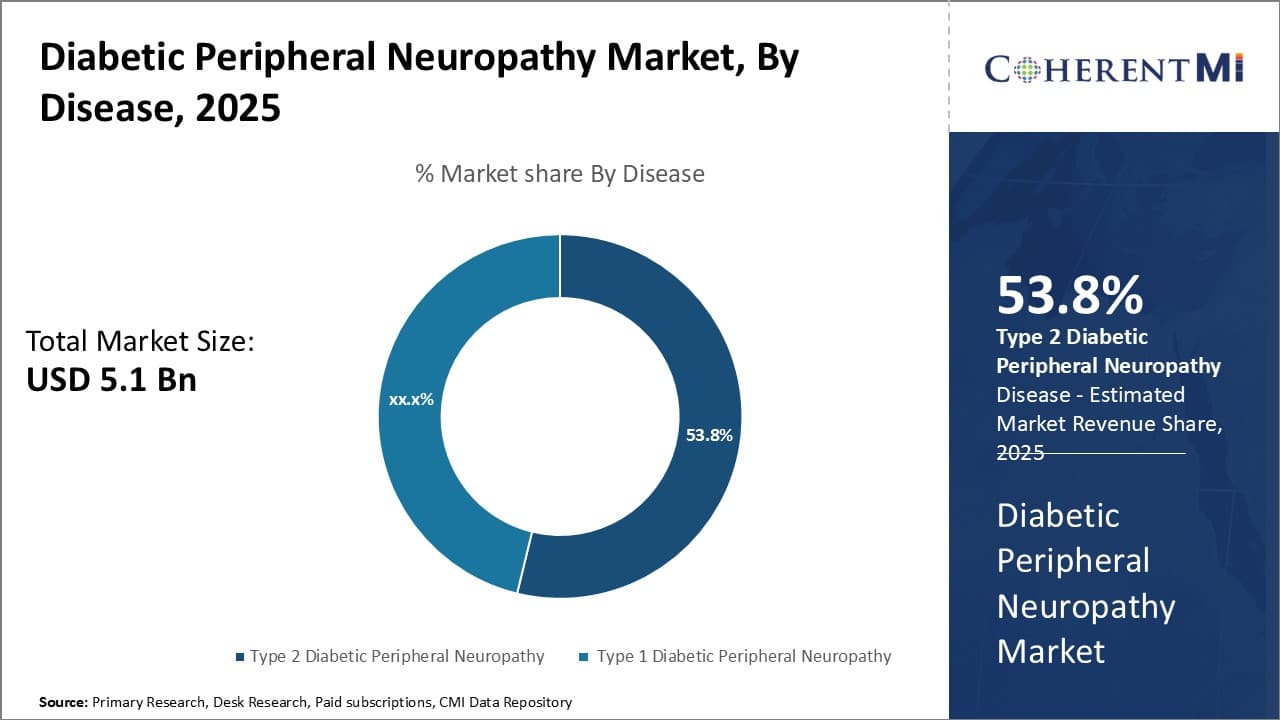
Insights, By Disease: Focus on Type 2 Patients
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Disease: Focus on Type 2 Patients
In terms of disease, type 2 diabetic peripheral neuropathy is projected to hold 53.8% share of the diabetic peripheral neuropathy market in 2025. This is primarily due to the much larger prevalence of type 2 diabetes compared to type 1. Approximately 90-95% of diabetes cases globally are classified as type 2. As neuropathy is a long-term complication that often emerges years after initial diagnosis, the sheer numbers of those living with type 2 means many will go on to develop the condition.
Genetic and lifestyle factors like obesity that raise type 2 risk also contribute to susceptibility for neuropathy. Improved survival of type 2 patients on newer diabetes drugs may see rising neuropathy cases as well. The metabolic abnormalities characteristic of type 2 diabetes, such as high blood glucose, blood fat and blood pressure levels, promote neuropathy through prolonged exposure of nerves to these harmful conditions.
Clinicians prioritize management of type 2 diabetes and related risk factors to prevent or slow neuropathy onset and progression in these high-risk patients.
Insights, By Therapy: Managing Mood and Pain Together
In terms of therapy, antidepressants (e.g., SSRIs, SNRIs) contributes the highest share of the market. While primarily used to treat depression, certain antidepressants are also effective analgesics for neuropathic pain. They work through inhibition of serotonin and/or norepinephrine reuptake in the central nervous system. This dual action makes them valuable where mood disorders commonly co-occur with neuropathy.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like duloxetine and venlafaxine are first-line options owing to evidence from clinical trials of their efficacy against painful diabetic neuropathy symptoms. As many patients live with both negative emotional impacts and physical suffering from their condition, combining pain relief with mood improvement through one medication enhances adherence and quality of life.
Neuropathy pain itself can induce feelings of depression, so antidepressants provide a two-pronged approach. This holistic therapy strategy drives growth in the segment by empowering better patient outcomes and experiences.
The major players operating in the diabetic peripheral neuropathy market include Helixmith, Aptinyx, WinSanTor, Inc., Regenacy Pharmaceuticals, Grünenthal GmbH, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Reata Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, and Glenmark Pharmaceuticals.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Market is segmented By Treatment (Pain Management Drugs, Gene Therapi...
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Market
How big is the diabetic peripheral neuropathy market?
The diabetic peripheral neuropathy market is estimated to be valued at USD 5.10 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 9.88 Bn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the diabetic peripheral neuropathy market?
High cost of novel therapies may limit patient access and lack of curative therapies; current options focus primarily on pain management are the major factors hampering the growth of the diabetic peripheral neuropathy market.
What are the major factors driving the diabetic peripheral neuropathy market growth?
Increasing global prevalence of diabetes leading to higher DPN cases and advances in gene therapy offering promising treatment for severe cases are the major factors driving the diabetic peripheral neuropathy market.
Which is the leading treatment in the diabetic peripheral neuropathy market?
The leading treatment segment is pain management drugs (e.g., opioids, anticonvulsants).
Which are the major players operating in the diabetic peripheral neuropathy market?
Helixmith, Aptinyx, WinSanTor, Inc., Regenacy Pharmaceuticals, Grünenthal GmbH, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Reata Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, and Glenmark Pharmaceuticals are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the diabetic peripheral neuropathy market?
The CAGR of the diabetic peripheral neuropathy market is projected to be 9.9% from 2025-2032.