

The Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.48 Billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 2.18 Billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% from 2025 to 2032. The market is driven by increasing aging population who are at high risk of EBV infection and rising awareness about early EBV detection.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR5.7%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 5.7% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Atara Biotherapeutics, Inc., Pierre Fabre, Viracta Therapeutics, AlloVir, Nana-val and Among Others |
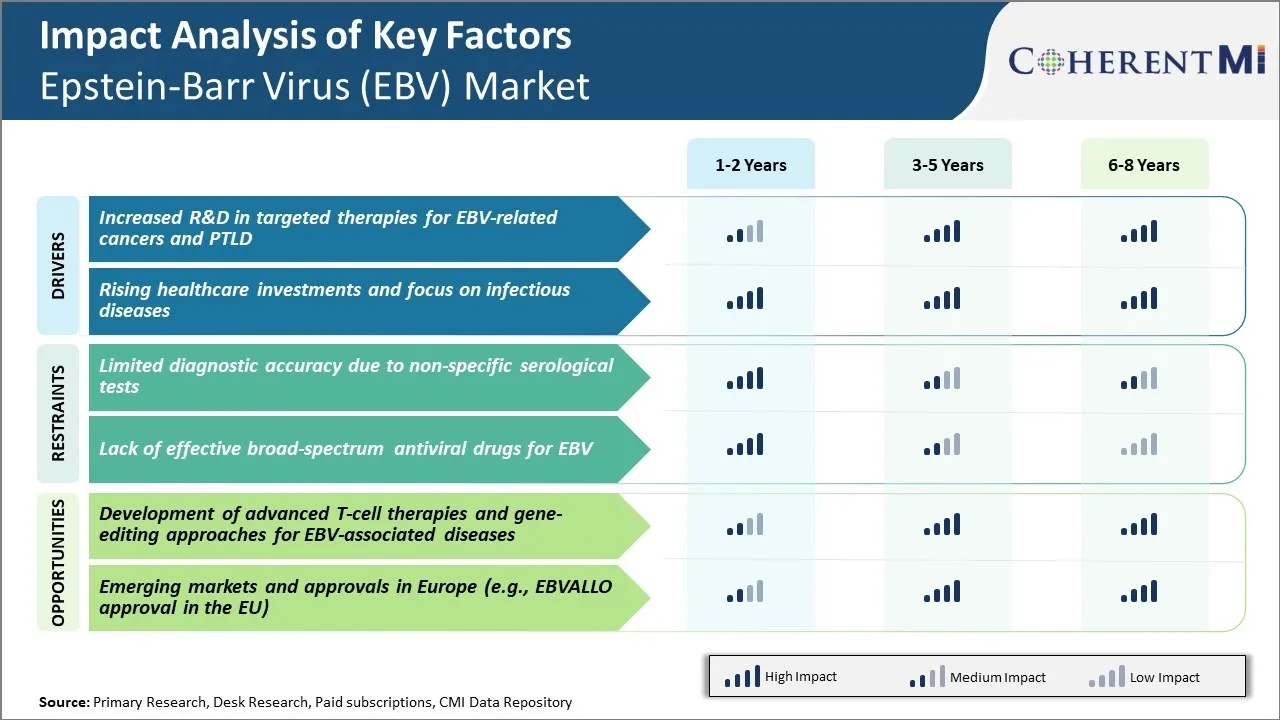
Market Driver - Increased R&D in Targeted Therapies for EBV-related Cancers and PTLD
There has been significant rise in research activities focused on developing novel targeted therapies for EBV associated cancers as well as Post Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder (PTLD). EBV is known to cause several malignancies like Burkitt's lymphoma, Nasopharyngeal carcinoma and gastric carcinoma. However, current treatment options are limited and most of the therapies lack targeted approach. With advancement in understanding of viral pathogenesis and host immune responses, potential molecular targets have been identified in recent years.
This has accelerated research on developing drugs against these targets and some of the candidates are already in clinical trials. For example, adoptive T-cell therapy is being evaluated in phase 1/2 trials. The approach involves collecting and modifying patient's T-cells to recognize viral or tumor antigens and reinfusing back to boost immune response. Some of the clinical studies have reported promising efficacy with no significant toxicities.
Overall, substantial research inputs are being made globally to translate these candidate therapies into approvals. With expectations of good clinical benefits and fewer side effects than currently available treatments, they would improve the management of EBV-associated cancers. This factor is projected to significantly drive future growth in the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market.
Market Driver - Rising Healthcare Investments and Focus on Infectious Diseases
There is increasing priority given to strengthening healthcare systems and preparedness against infectious diseases worldwide. Global collaborative efforts have helped pool resources towards delivery of effective prevention, diagnosis and treatment programs. International agencies like WHO have played a critical role in coordinating control strategies and aid distribution for priority pathogens. At the same time, governments across developing and developed nations have been raising investments towards expansion of healthcare infrastructure and provision of universal coverage to populations.
In view of the current pandemic situation, it is understandable that authorities want to plug gaps and blind spots that could threaten their defense against future pathogens. This translates to greater policy level attention, monitoring systems as well as health financing directed towards prevalent viruses like EBV. Diagnostic technologies, treatment guidelines, research networks are being strengthened around EBV which generates opportunities. Multilateral development assistance and public-private initiatives signify commitment to fight infectious agents and tackle issues of inequities in access to healthcare. Industry stands to aid such priorities through provision of vaccines, tests, medications, and technology partnerships.
In conclusion, the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market is poised to benefit from conducive healthcare climate brought about by rising investments dedicated to fighting infectious diseases of global health importance. This driver will play a supporting role in growth projections over medium to long term timelines.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - Limited Diagnostic Accuracy due to Non-specific Serological Tests
One of the key challenges in the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market is the limited diagnostic accuracy due to the use of non-specific serological tests. EBV causes infectious mononucleosis and is associated with several types of cancer. However, currently available diagnostic tests possess certain limitations.
The commonly used serological tests detect antibodies produced against EBV antigens, but these antigens are also present in other herpes viruses. Therefore, the serological tests cannot conclusively establish a causal association between EBV and a disease. The presence of antibodies only indicates past exposure to the virus but not necessarily an active infection. This affects the ability to accurately diagnose EBV-related conditions.
Moreover, seroconversion patterns are complex and not all infected individuals will develop antibodies. As a result, serological techniques alone fail to discriminate between acute, past and asymptomatic infections. This diagnostic uncertainty poses challenges for physicians in guiding treatment decisions and assessing disease prognosis.
It also impacts epidemiological research on EBV and associated diseases. There is an urgent need for development of newer diagnostic approaches with higher sensitivity and specificity for unequivocal detection of EBV.
Market Opportunity: Development of Advanced T-cell Therapies and Gene-editing Approaches
One of the major opportunities in the EBV market lies in the development of advanced T-cell therapies and gene-editing approaches for the treatment of EBV-associated diseases. EBV establishes a lifelong latent infection by evading immune surveillance from T-cells. Recent advances in cellular immunotherapy have enabled engineering of virus-specific T-cells to treat EBV-driven malignancies. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies are being investigated that are genetically modified to target EBV antigens like LMP1 and LMP2.
Concurrently, gene-editing technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9 allow precise modifications to T-cells that can enhance their ability to recognize and destroy virally infected cells. These novel strategies have shown promise in preclinical and early clinical studies. Their adoption could revolutionize the management of cancer and other complications caused by chronic EBV infection.
It is anticipated that over the coming years, significant investments will be made in refining T-cell and gene therapy approaches, thereby addressing a major unmet need and presenting sizable commercial opportunities in the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market.
EBV is generally a self-limiting infection, however management involves supportive care and symptom monitoring at the initial acute infectious mononucleosis stage. Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen are recommended to reduce fever and throat pain. As symptoms ease in 4-6 weeks, no further treatment is needed for most patients.
However, for a small percentage who develop complications, prescribers may opt for different lines of therapy. For cases with severe complications like hepatitis or encephalitis, a first-line antiviral like valacyclovir (Valtrex) is often prescribed. Its ability to inhibit viral DNA polymerase makes it effective against EBV. For patients unresponsive to antivirals or those with prolonged fatigue, prescribers may try corticosteroids like prednisone next.
In rare cases of EBV-driven cancers like Hodgkin's lymphoma, chemotherapy takes precedence. Combination therapies using doxorubicin (Adriamycin), bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (ABVD) are common. For post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder caused by uncontrolled EBV infection, reducing immunosuppression may be attempted initially before considering rituximab (Rituxan).
Overall disease severity, complications, responsiveness to previous treatment and potential drug interactions also influence prescribers' selection between brand and generic options at different stages.
There is no cure for EBV infection, but treatment is available to manage symptoms. For acute or primary EBV infection, treatment focuses on relieving symptoms through rest, fluids, and medication for fever/pain. As the infection clears in 2-4 weeks, no specific anti-viral drugs are usually needed.
For mononucleosis symptoms that persist beyond 6 months, antiviral drugs may be tried. Acyclovir is a nucleoside analogue drug that stops the virus from replicating. It is taken orally 5 times a day for 7-10 days and can reduce symptoms like fatigue. Valacyclovir has similar effects to acyclovir but as a once-daily dose, improving compliance.
For cases where EBV has led to complications like hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), intensive chemotherapy with drugs like etoposide, corticosteroids and cyclosporine A may be administered. This multi-agent immunosuppressive regimen aims to stop the overactive immune response causing HLH.
In immunocompromised patients, prolonged high EBV DNA levels can lead to post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD). Treatment involves reducing immunosuppression and using rituximab, a monoclonal antibody targeting B cells where EBV resides. For non-responsive PTLD, chemotherapy with drugs like doxorubicin, gemcitabine, and vinorelbine may be used.
Stem cell transplant may be considered for severe, unresponsive cases. This potentially cures by replacing the immune system and allowing it to clear the EBV infection. Close monitoring is needed long-term to watch for PTLD.
Collaborations and partnerships: Players have formed important collaborations to boost drug development and market reach. In 2015, MacroGenics partnered with Incyte to develop MGD013, an investigational combination monoclonal antibody therapy for EBV-positive cancers. If approved, this will provide an important treatment option. Such partnerships allow companies to pool resources and expertise to accelerate development of innovative drugs.
Acquisitions of smaller biotechs: Established players have acquired smaller biotechs working on EBV to enhance their portfolio. For example, GSK acquired Tesaro in 2019 for $5.1 billion primarily to gain control of Zejula, an ovarian cancer drug but also Tesaro's early stage EBV vaccine program. This strengthened GSK's oncology pipeline. Such acquisitions help large pharma expand in therapeutic areas like EBV.
Focus on emerging markets: As EBV impact is higher in developing nations, companies are targeting these markets. In 2013, Chimerix launched Bridgit, a fast-track registration trial of brincidofovir for EBV in China and other Asian markets. This allowed them first-mover advantage in high growth regions. Emerging regions in the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market present major opportunities and targeting them early improves market share.
-market-by-disease.webp&w=3840&q=75) To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Disease: Increasing Cancer Rates Drive EBV-Associated Cancer Segment
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Disease: Increasing Cancer Rates Drive EBV-Associated Cancer Segment
In terms of disease, EBV-associated Cancers contributes the highest share of the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market owning to increasing incidence and prevalence of various cancers associated with EBV infection. EBV is known to cause several types of cancers including Hodgkin's lymphoma, Burkitt's lymphoma, and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. The risk of developing these EBV-related cancers is rising globally due to factors such as aging population, lifestyle changes, and environmental exposures. Hodgkin's lymphoma for example affects over 3,000 new patients per year in the United States, with the incidence peaking between ages 15-40 years.
Similarly, nasopharyngeal carcinoma is highly prevalent in Southeast Asia and parts of Africa due to both genetic and environmental risk factors. The growing cancer burden caused by EBV makes screening and management of EBV-associated cancers central to the virus detection market. Development of more sensitive diagnostic techniques and targeted treatment options have also boosted demand within this segment of the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market.
-market-by-diagnostic-methods.webp&w=3840&q=75) To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Diagnostic Methods: Serological Methods Dominate Due to Ease of Testing
In terms of diagnostic methods, serological methods contribute the highest share of the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market owing to its ease of testing and widespread availability. Serological tests such as ELISA and immunofluorescence assays are the standard frontline investigations for detecting EBV infection. They allow fast and inexpensive and detection of EBV IgM and IgG antibodies in blood samples, aiding diagnoses of acute infectious mononucleosis and ruling out past EBV exposure.
The non-invasive nature and low turnaround times of serological testing have ensured its popularity among clinicians for screening high-risk patients and epidemiological studies. Advancements including automated platforms have further increased throughput while lowering costs. Combined with the chronic and recurrent nature of EBV, serological testing provides a reliable yet low-cost means of monitoring EBV-associated disorders long-term.
Insights, By Treatment Option: Antiviral Drugs Dominate Treatment Segment Due to Lack of Preventive Vaccines
In terms of treatment options, antiviral agents contribute the highest share of the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market owing to lack of preventive vaccines for EBV infection and associated diseases. Despite being common, infecting over 90% of adults worldwide, no vaccine is available to protect against EBV infection. This is because the virus establishes lifelong latent infection, hiding from the immune system within B-cells making conventional vaccination approaches challenging. As a result, treatment focuses on attenuating symptoms during the acute or reactivation phases using antiviral drugs.
While no antivirals are specifically approved for EBV, some nucleoside analogues are repurposed. Ganciclovir and acyclovir help suppress viral replication and reduce shedding during active infection and inflammation. In the absence of a cure, antivirals provide the main recourse for managing clinical manifestations of EBV and related malignancies such as post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Their widespread prescription has maximized this segment share.
The major players operating in the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Market include Atara Biotherapeutics, Inc., Pierre Fabre, Viracta Therapeutics, AlloVir and Nanatinostat in combination with valganciclovir (Nana-val).
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Market is segmented By Disease (EBV-Associated Cancers (Hodgkin\'s lymphoma...
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Market
How big is the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market?
The Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.48 Billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 2.18 Billion by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market?
The limited diagnostic accuracy due to non-specific serological tests and lack of effective broad-spectrum antiviral drugs for EBV are the major factors hampering the growth of the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market.
What are the major factors driving the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market growth?
The increased R&D in targeted therapies for EBV-related cancers and PTLD and rising healthcare investments and focus on infectious diseases are the major factor driving the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market.
Which is the leading disease in the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market?
The leading disease segment is EBV-Associated cancers.
Which are the major players operating in the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market?
Atara Biotherapeutics, Inc., Pierre Fabre, Viracta Therapeutics, AlloVir, and Nana-val are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) market?
The CAGR of the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Market is projected to be 5.7% from 2025-2032.