Gestational Diabetes Market Trends
Market Driver - Rising Obesity Rates and Advanced Maternal Age
As more women are waiting until later in life to have children, advanced maternal age has also been linked to a higher risk of gestational diabetes. As women age, their bodies' ability to produce and respond to insulin can decline over time. When pregnancy hormones alter everything from metabolism to blood circulation, an older woman may face greater challenges keeping her blood sugar stable.
Some research has indicated the risk increases somewhat linearly after age 25. With so many health organizations now recognizing obesity as a global epidemic, and birthrates for women in their 30s and 40s on the rise in many Western nations, this combination of factors has served to drive up the number of gestational diabetes cases seen each year.
More overweight or obese women of advancing maternal age means a growing population at higher risk entering pregnancy. Until nations are more successful at stemming obesity rates across all demographics, and social norms around family planning change again, these trends will continue contributing significantly to the increased disease burden of gestational diabetes.
Market Driver - Development of Advanced Diagnostic Tools and Insulin Delivery Systems
As medical science advances our understanding of diabetes and develops new technologies, providers have gained improved ability to both screen for and safely manage cases of gestational diabetes. Standardized oral glucose tolerance tests can more uniformly identify at-risk patients. Continuous glucose monitors also give clinicians highly granular readouts of an expectant mother's constant fluctuations in blood sugar levels over days or weeks.
These enhanced detection capacities have naturally resulted in higher reported instance of the disease as more mild or short-lived cases are picked up. Insulin pumps, pens, and other user-friendly delivery mechanisms as well have emboldened doctors' willingness and ability to actively treat the condition when necessary.
The improved medical surveillance and management options provided by new diagnostic devices and therapeutic regimens not only benefit patient outcomes but have elevated recognition of the full prevalence of gestational diabetes within populations. In being better able to identify and accommodate more cases, the advanced care technologies now available have unavoidably contributed to higher reported rates and incidence statistics of this condition.
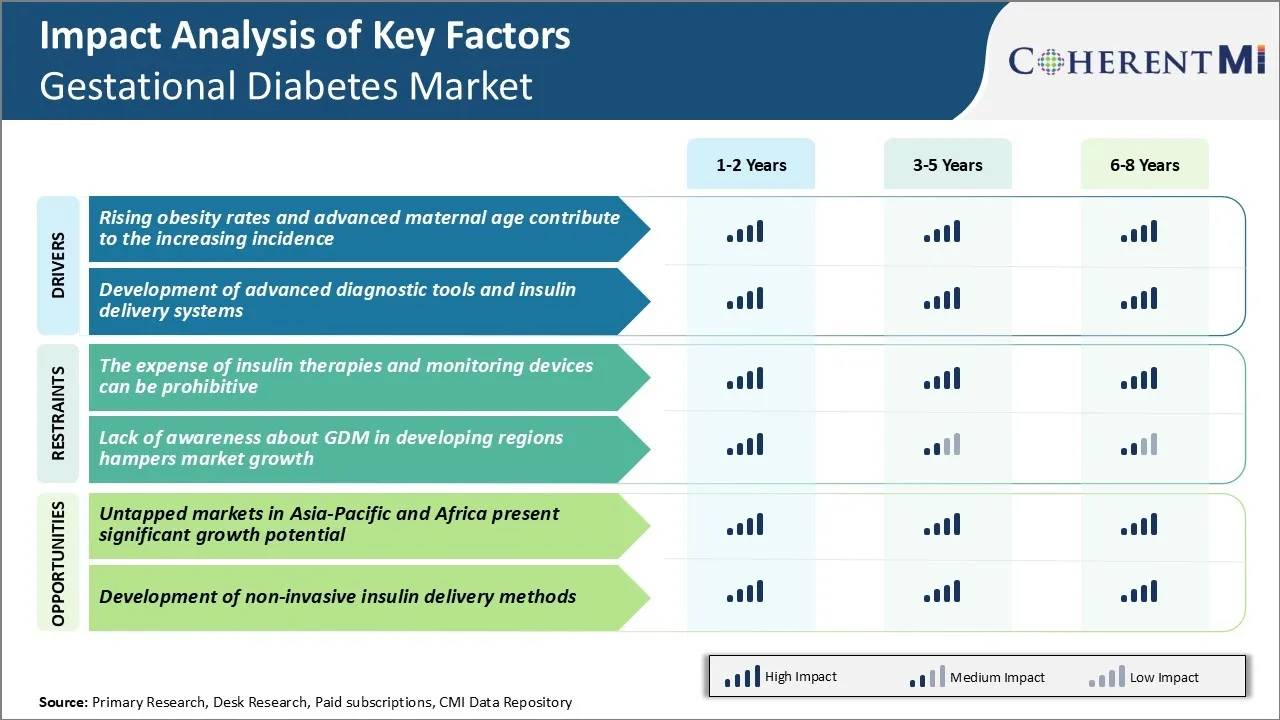
Market Challenge - The Expense of Insulin Therapies and Monitoring Devices
One of the major challenges facing the gestational diabetes market is the expense of insulin therapies and continuous glucose monitoring devices. Treating gestational diabetes often requires intensive insulin treatment which can be an economic burden for many patients. Not only is insulin itself expensive, patients may need to test their blood glucose levels several times a day. This requires buying test strips and lancets on a regular basis.
For those choosing to use continuous glucose monitors, the upfront costs can be several hundred dollars and many insurance plans do not fully cover these devices. The out-of-pocket costs of managing this condition throughout pregnancy can rapidly add up and act as a barrier to effective treatment. This represents a challenge for healthcare providers and device manufacturers aiming to improve diagnosis and treatment rates.
High treatment expenses may also impact adherence if patients cannot consistently afford the supplies needed. Addressing the costs associated with insulin and monitoring technologies is important to expand access and help more women receive the care they need.
Market Opportunity - Untapped Markets in Asia-Pacific and Africa Present Significant Growth Potential
One of the major opportunities in the gestational diabetes market is the potential for growth in under-screened and underserved regions such as Asia-Pacific and Africa. Rates of gestational diabetes are increasing globally due to rising obesity levels and older maternal ages.
However, screening and diagnosis rates remain relatively low in many developing nations where risk factors are prevalent. This represents an untapped market for device manufacturers and service providers. As awareness increases and screening protocols improve in these regions, the number of cases identified is projected to rise significantly in the coming years.
With a combined population of over 4 billion people, Asia-Pacific and Africa have the capacity to drive huge gains in the gestational diabetes market. By introducing more affordable solutions and innovative care models, companies operating in these regions have an opportunity to reach massive numbers of undiagnosed women and help establish standards of treatment. This growth potential presents a valuable opportunity for stakeholders to expand their customer bases and drive future revenue growth.