Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis Market Size - Analysis
The giant papillary conjunctivitis market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.29 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 2.17 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.7% from 2025 to 2032. The market is expected to witness positive growth over the forecast period due to rising incidences of digital eye strain due to extensive use of digital devices. Additionally, increasing awareness about various eye diseases and their treatment options among consumers is further expected to support the market growth.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR7.7%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 7.7% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Allergan plc, Alcon Laboratories, Inc., Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Inc., Bausch & Lomb Incorporated, CooperVision, Inc., Allergan plc and Among Others |
please let us know !
Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis Market Trends
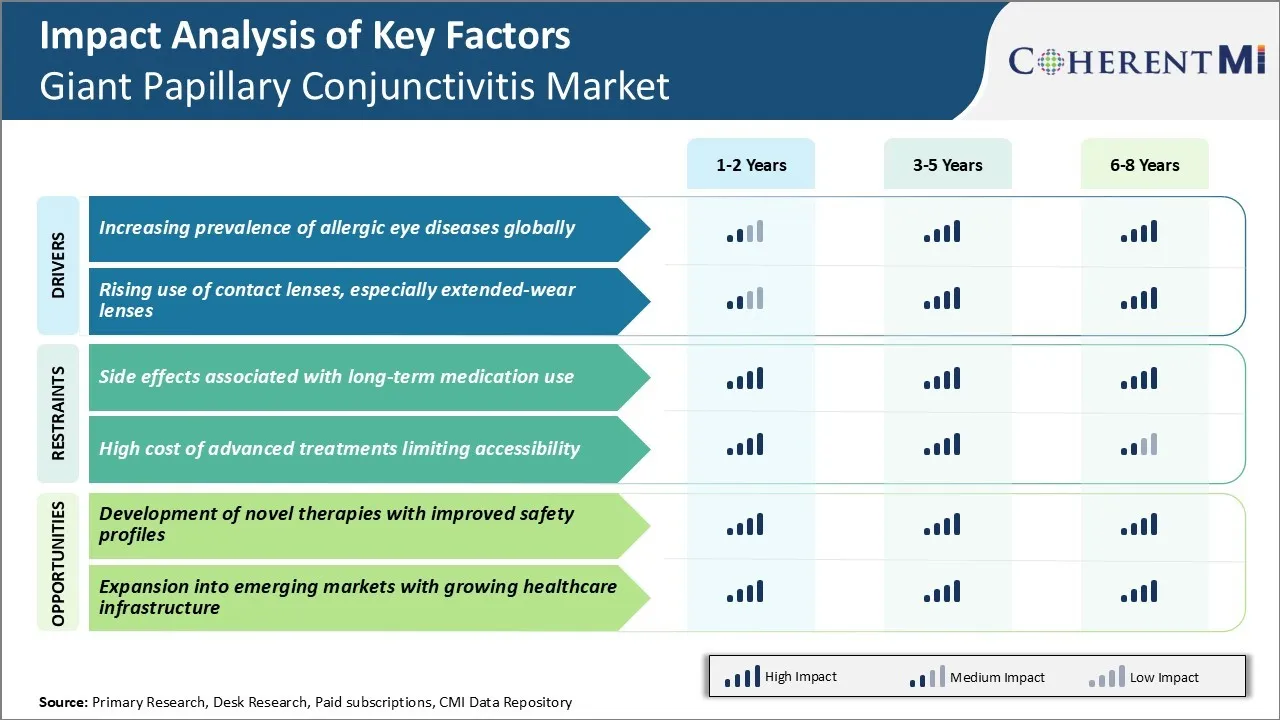
Market Driver - Increasing Prevalence of Allergic Eye Diseases Globally
The global burden of allergic eye diseases has been rising steadily over the past few decades. It is estimated that over 30% of the world’s population suffers from some form of allergic conjunctivitis currently. Rates are even higher in developed nations where people spend more time indoors under artificial lighting and air conditioning away from natural ventilation and seasonal changes.
The most common form of allergic eye disease linked to giant papillary conjunctivitis (GPC) is vernal keratoconjunctivitis (VKC). Data from various global eye health surveys shows that almost 10% of children and young adults now suffer from VKC compared to just 2-3% some 20 years back.
Warm and humid regions close to the equator have borne the maximum brunt of rising VKC prevalence over the past few decades due to genetic predisposition in the population coupled with increased environmental allergens. Indoor air pollution from biomass cooking fuels is an important contributor in developing countries.
Affordability of healthcare has also improved in emerging markets enabling more people to seek treatment for allergic eye conditions like GPC.
Market Driver - Rising Use of Contact Lenses, Especially Extended-Wear Lenses
The global contact lenses market has grown exponentially in the past few decades driven by rising disposable incomes, growing fashion consciousness and improving vision correction technologies. An estimated 145 million people worldwide now wear contact lenses on a regular basis for vision correction or cosmetic purposes up from less than 50 million in the 1990s. The advent of innovative materials, designs and care solutions have made extended and continuous wear options safer leading to their wider adoption globally.
However, increased usage has also resulted in higher incidences of lens related complications like corneal neovascularization, keratitis and giant papillary conjunctivitis. Long term lens wear disrupts the normal tear film and blinking mechanisms of the eye enabling deposition of proteins and allergens on the lens surface. This acts as an irritant and inflammatory trigger for the condition over time. Failure to practice proper lens hygiene and care further raises the risk. Younger generations are also opting for colored and cosmetic lenses often on an extended wear basis for occupational or lifestyle reasons without realizing the risks. Unless addressed properly, this rising trend will continue keep demand for GPC treatment options robust in the foreseeable future.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - Side Effects Associated with Long-Term Medication Use
One of the major challenges faced by the giant papillary conjunctivitis market is the side effects associated with long-term use of medications prescribed for the condition. Currently available drugs such as topical antibiotics, antihistamines and mast cell stabilizers are effective at controlling symptoms in the short term.
However, their prolonged usage can lead to problems like drug resistance, soreness or redness in the eyes. Patients often find it difficult to adhere to the treatment regimen due to undesirable effects of medicines. This reduces treatment effectiveness and compliance over time. The risk of side effects rises with increasing duration of pharmaceutical therapy.
Managing chronic cases requires lifelong use of medication which further increases the vulnerability to drug-related complications. The issue of side effects poses a significant barrier to market growth as it impacts treatment outcomes negatively. Pharmaceutical companies need to focus on developing safer therapies to address this challenge.
Market Opportunities - Development of Novel Therapies with Improved Safety Profiles
The giant papillary conjunctivitis market represents major opportunities for players focused on developing novel therapies with enhanced safety and tolerability profiles. There is considerable scope for therapies that can achieve clinical efficacy comparable to current medicines but with lower risk of adverse reactions on prolonged use.
Companies can tap into market potential by investing in research on new drug delivery technologies, mechanisms of action and formulations. One avenue is exploring targeted drug delivery to eyes using innovative mechanisms like modified-release systems, nanoparticle-based carriers and intraocular implants. This can help minimize unwanted systemic exposure and maintain therapeutic drug levels at site of action.
Development of topical treatments combining multiple active ingredients can also address unmet needs by providing polypharmacy benefits with a favorable risk-benefit balance. Overall, the need for improved treatment options presents a lucrative opportunity for players advancing therapies with safer long-term usage profiles.
Prescribers preferences of Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis Market
Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis (GPC) is a chronic allergic inflammatory eye condition affecting the conjunctiva. Prescribers typically follow a step-wise treatment approach based on severity andstage of GPC.
For mild cases, over-the-counter artificial tears like EyeDrops and Refresh Tears are usually prescribed to reduce irritation and inflammation. Prescribers may also recommend eyelid hygiene and warmth compresses.
In moderate cases, topical mast cell stabilizers like Cromolyn sodium 4% ophthalmic solution (Crolom) and lodoxamide 0.1% ophthalmic solution (Alomide) are generally prescribed. These are often prescribed 1-2 times daily along with artificial tears.
For severe persistent cases, topical antihistamines such as olopatadine 0.1% ophthalmic solution (Patanol) and epinastine 0.05% ophthalmic solution (Elestat) are prescribed along with mast cell stabilizers. Prescribers may also consider topical steroids like loteprednol etabonate 0.5% ophthalmic suspension (Lotemax) for short term use to reduce inflammation.
Surgical options like tarsorrhaphy or conjunctival resection may be considered for cases that do not respond to medical management. Prescriber preference is also influenced by factors like patient compliance, insurance coverage, and drug side effect profiles in the chronic management of GPC.
Treatment Option Analysis of Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis Market
GPC has three main stages - mild, moderate, and severe - based on symptoms.
In mild GPC, the predominant symptoms are irritation, mild itching, and small papillae on the palpebral conjunctiva. Topical mast cell stabilizers like cromolyn sodium 4% are generally recommended initially to reduce inflammation.
As the disease progresses to moderate GPC, papillae enlargement and conjunctival hyperemia increase. Topical steroids like loteprednol etabonate 0.5% or fluorometholone acetate 0.1% are prescribed, either as monotherapy or in combination with mast cell stabilizers, to reduce inflammation more effectively. Artificial tear supplements are also used to relieve dryness and irritation.
In severe GPC, large papillae cause significant irritation, foreign body sensation, and mucus discharge. In these cases, topical steroids are insufficient, and doxycycline 100mg twice daily orally works better to reduce papillae size and inhibit collagenase activity. Switching to smaller contact lenses also provides relief.
Contact lens discontinuation is recommended for short term in very severe cases, after which multifocal rigid gas permeable contact lenses can be tried instead of soft lenses to avoid recurrence. Surgery is rarely required and reserved for refractory cases not responding to maximum medical management. This staged approach aims to balance symptom relief with least intervention.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis Market
Product Innovation: Continuous innovation in product offerings has been a core strategy for major players. For example, in 2018, Allergan launched OZURDEX® (dexamethasone intravitreal implant), a biodegradable sustained-release implant for the treatment of giant papillary conjunctivitis. This was the first FDA-approved biodegradable product for this indication. With minimized side effects compared to eye drops, it gained significant market share.
Targeted Marketing: Players focus marketing and awareness initiatives towards eye care professionals who can influence treatment. Allergan conducted extensive education programs for doctors on proper diagnosis and management of giant papillary conjunctivitis using OZURDEX. This helped create brand loyalty and preference among practitioners.
Leveraging Digital Channels: Online patient support communities and resources are leveraged. Novartis provides information on diagnosis, treatment options and lifestyle tips for managing symptoms on its GIANT trial website. This improves patient engagement and establishes the company as an industry leader.
Partnerships: Companies partner with optometrist and ophthalmologist associations for knowledge sharing and consensus building around best practices. For example, Eyevance's sponsorship of American Optometric Association conferences helped introduce its line of eye drops to a large pool of eye doctors.
Segmental Analysis of Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis Market
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
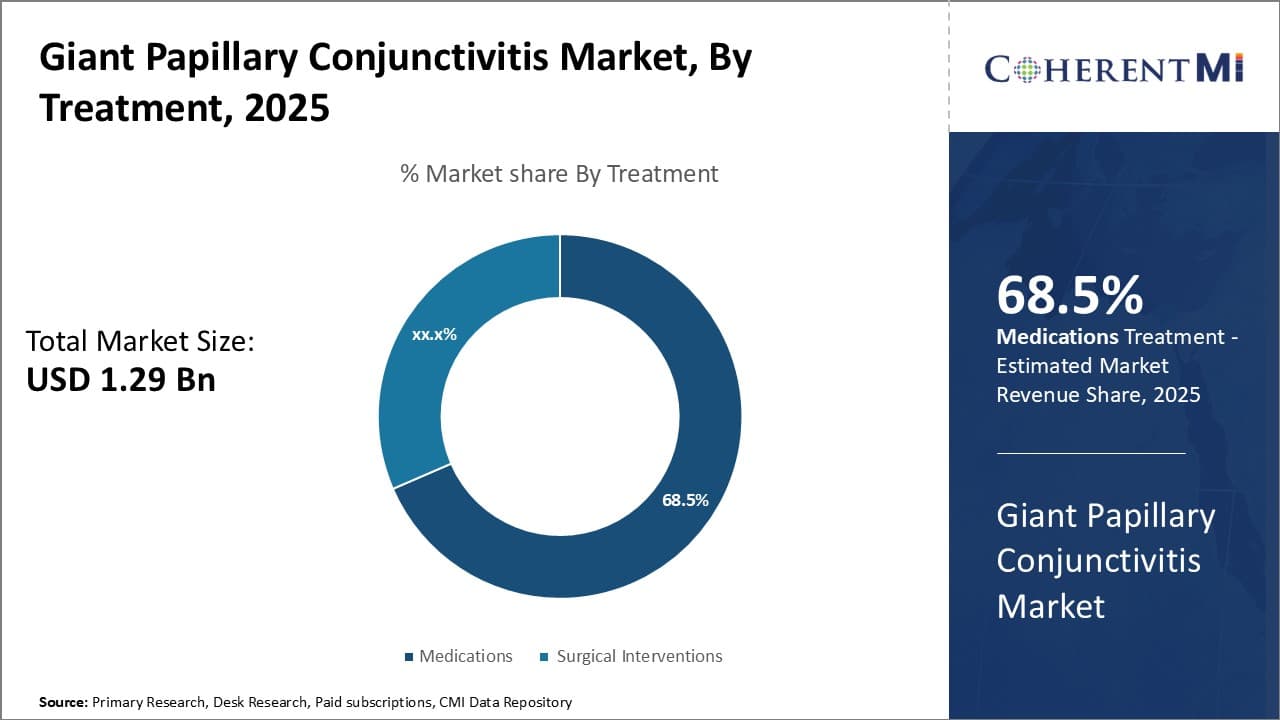
Insights, By Treatment: Ease of Administration Drives Higher Adoption of Medications
In terms of treatment, medications are estimated to contribute 68.5% revenue share of the market in 2025, owning to the ease of administration compared to other options. Medications provide a convenient way for patients suffering from giant papillary conjunctivitis to manage their symptoms without complex surgical procedures or frequent visits to the hospital.
Within medications, antihistamines are widely used as they help reduce allergic inflammation and relieve itching, redness, and swelling effectively. Additionally, mast cell stabilizers that inhibit the release of inflammatory mediators from mast cells are also popular choices.
Furthermore, NSAIDs and corticosteroids are effective at reducing inflammation and relieving associated pain. The non-invasive nature of drops, ointments, and pills make medications the most preferable first-line treatment option, leading to higher consumption compared to surgical interventions or other options.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
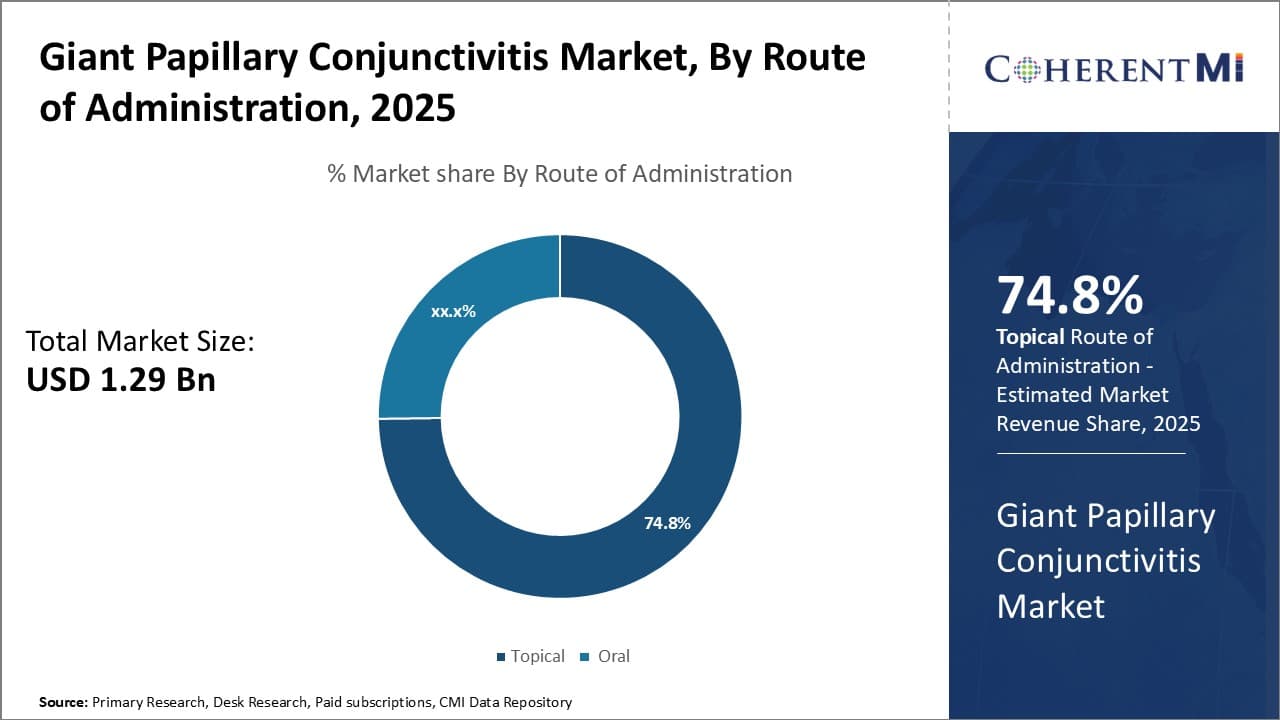
Insights, By Route of Administration: Convenience and Compliance Drives Preference for Topical Administration
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Route of Administration: Convenience and Compliance Drives Preference for Topical Administration
In terms of route of administration, topical administration is projected hold 74.8% share of the market in 2025, owing to the convenience it offers compared to oral administration. Eye drops and ointments allow for direct application of the medication to the affected site, maximizing the drug concentration in the conjunctiva for better treatment outcomes. This localized delivery also helps minimize possible systemic side effects associated with oral drugs.
Furthermore, topical forms do not require strict administration timings, increasing patient compliance in sticking to the dosage schedule. With easy once or twice a day application, topical routes have emerged as the most user-friendly way to administer medications for giant papillary conjunctivitis.
Insights, By Distribution Channel: Higher Access and Expertise Drives Higher Adoption Through Hospital Pharmacies
In terms of distribution channel, hospital pharmacies contribute the highest share of the market owing to greater access to medications and medical expertise. As Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis often requires prescription-only medications, patients tend to first consult ophthalmologists at hospitals.
Hospital pharmacies can offer a wider range of medications suited for varied disease severities. They also have better inventory management and no stock-out issues. Patients are comfortably able to access medications and medical advice under one roof.
Furthermore, through regular follow-ups patients gain better knowledge about their condition and treatment protocol from experts, driving continued purchases of medications from the same hospital pharmacies. This consolidated care helps hospitals pharmacies achieve the highest sales in this market.
Additional Insights of Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis Market
- Prevalence Rate: GPC affects approximately 10% of all contact lens wearers.
- Patient Demographics: Higher incidence observed in individuals aged 15-35 years due to higher contact lens usage.
- The shift towards daily disposable lenses is reducing the incidence of GPC among contact lens users.
- Increased funding in ophthalmology research is leading to better understanding and management of GPC.
Competitive overview of Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis Market
The major players operating in the giant papillary conjunctivitis market include Alcon Laboratories, Inc., Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Inc., Bausch & Lomb Incorporated, CooperVision, Inc., and Allergan plc.
Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis Market Leaders
- Allergan plc
- Alcon Laboratories, Inc.
- Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Inc.
- Bausch & Lomb Incorporated
- CooperVision, Inc.
- Allergan plc
Recent Developments in Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis Market
- In June 2021, Alcon Laboratories introduced a new antihistamine eye drop that provides longer relief for GPC symptoms, enhancing patient compliance and comfort. Alcon has introduced several products in recent years, such as Systane Zaditor and Pataday, which are antihistamine eye drops offering up to 12 hours of relief from allergy-related itching, targeting common allergens like pollen and pet dander. These products are designed to improve patient comfort and compliance.
- In April 2021, Johnson & Johnson Vision Care launched daily disposable contact lenses designed to reduce protein deposits, thereby lowering the risk of developing GPC. Johnson & Johnson Vision has been actively innovating within the contact lens space, including the introduction of lenses with advanced features such as those designed for presbyopia and lenses that incorporate antihistamines for treating ocular allergies.
Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis Market Segmentation
- By Treatment
- Medications
- Antihistamines
- Mast Cell Stabilizers
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- Corticosteroids
- Surgical Interventions
- Removal of papillae
- Conjunctival surgeries
- Medications
- By Route of Administration
- Topical
- Eye drops
- Ointments
- Oral
- Topical
- By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Nikhilesh Ravindra Patel is a Senior Consultant with over 8 years of consulting experience. He excels in market estimations, market insights, and identifying trends and opportunities. His deep understanding of the market dynamics and ability to pinpoint growth areas make him an invaluable asset in guiding clients toward informed business decisions. He plays a instrumental role in providing market intelligence, business intelligence, and competitive intelligence services through the reports.
