

The ophthalmoplegia market is estimated to be valued at USD 549.3 Mn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 923.3 Mn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.7% from 2025 to 2032.
There is an increasing trend seen in the ophthalmoplegia market owing to rising cases of neurological disorders that often cause ophthalmoplegia. The growing geriatric population worldwide who are more prone to such neurological conditions is also contributing to the growth of this market. Moreover, development of advanced treatment options and improving healthcare infrastructure in developing nations have helped in greater diagnosis of ophthalmoplegia cases thereby spurring market revenues.
Market Size in USD Mn
CAGR7.7%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 7.7% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Novartis AG, Sanofi, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Pfizer Inc., Bayer AG and Among Others |
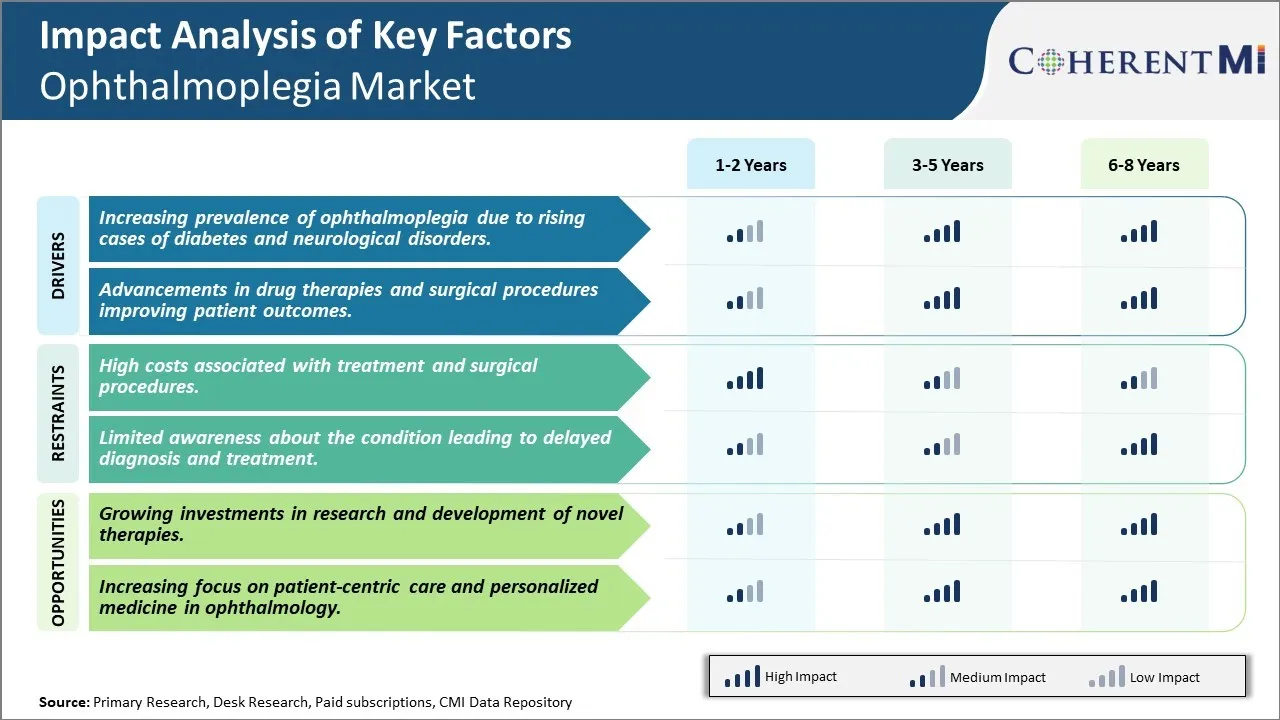
Market Driver - Increasing prevalence of ophthalmoplegia due to rising cases of diabetes and neurological disorders
The increasing prevalence of diabetes and neurological disorders across the globe has directly contributed to the rising incidence of ophthalmoplegia. Diabetes, being one of the leading causes of ophthalmoplegia, affects a massive population worldwide. Poor management of blood sugar levels often damages the cranial nerves that control eye movement over time. Similarly, neurological abnormalities implicated in paralysis or limited movement of the extraocular muscles are on a sharp rise. The high susceptibility of the aged population to conditions such as myasthenia gravis and strokes has significantly influenced the ophthalmoplegia landscape.
Statistics show diabetes prevalence has more than doubled in numerous countries in the last three decades alone. This is chiefly due to lifestyle changes, obesity, and lesser physical activity levels seen in both developed and developing regions. People with prolonged history of diabetes have four times higher odds of developing ophthalmoplegia compared to non-diabetics. With diabetes expected to impact over 640 million adults globally by 2040, the potential patient pool for ophthalmoplegia therapies will continue expanding. On the other hand, neurological disorders are not confined to a particular age group anymore. Even the economically productive population is at an ever-increasing threat from Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis and neuromuscular abnormalities. This poses massive financial and social burden on national healthcare systems.
Considering disease modifying therapies can slow progression in diabetes and improve neurological symptoms, greater focus on prevention and management is needed. However, once ophthalmoplegia sets in, pharmacological or surgical options become essential for restoring eye functions and improving quality of life. Hence, the trends clearly indicate the drivers of diabetes and neurological disease prevalence will sustain demand for advanced ophthalmoplegia treatment methods in the foreseeable future.
Market Driver - Advancements in drug therapies and surgical procedures
Significant progress has been made in developing novel drug therapies and minimally invasive surgical techniques for ophthalmoplegia. While anticholinesterase medications remain the first line pharmacotherapy for many decades, newer pipeline candidates are showing promise. These include botulinum toxin, acetylcholinesterase reactivation medications, immunomodulators, neuroprotective agents and gene therapies. Clinical researches exploring precision therapies tailored to individual pathology and response are revolutionizing the treatment landscape. Botulinum toxin injections, for example, have emerged as a safe and effective alternative to medications in select cases.
On the surgical front, strabismus surgery techniques have advanced by leaps and bounds. Utilizing anchoring sutures, adjustable sutures and tucking or plication procedures, ophthalmic plastic surgeons can now accurately reposition extraocular muscles to achieve optimal ocular alignment. In addition, the advent of trans-conjunctival approaches and adjustable suture techniques have significantly reduced procedural invasiveness, pain and recovery times for patients. Other procedures such as retrobulbar block, orbital decompression and corneal surgery have also matured over the years.
Perhaps the most exciting prospect is the promising role of stem cell therapy. Initial animal studies demonstrate mesenchymal stem cells might boost regeneration of damaged cranial motor nerves. If further research establishes safety and efficacy, it could open avenues to permanently cure certain challenging ophthalmoplegia conditions.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High costs associated with treatment and surgical procedures
A major challenge impacting the growth of the ophthalmoplegia market is the high costs associated with treatment and surgical procedures. Ophthalmoplegia often requires expensive surgery or long-term administration of medications. Surgical interventions like strabismus surgery can cost thousands of dollars and may need to be repeated multiple times to achieve optimal results. The cost of surgical equipment, operating room time, hospital stay and post-operative care increases the financial burden on patients, healthcare providers and payers. Additionally, many chronic treatment options like immunotherapies or monoclonal antibody infusions have high acquisition costs. This makes long-term drug therapy out of reach for many patients, especially those in developing nations with limited healthcare budgets. High costs pose a significant barrier for wider access to care and act as a deterrent for individuals seeking timely treatment. Addressing the expense of interventions through favorable reimbursement policies, generic drug availability and reduced equipment prices could help expand the affordable coverage of ophthalmoplegia management options.
Market Opportunity: Growing investments in research and development of novel therapies
A key opportunity in the ophthalmoplegia market is the steadily increasing investments devoted to research and development of novel treatment approaches. With a growing understanding of the molecular pathways involved in ophthalmoplegia pathogenesis, targeted drug candidates are being explored. Several biotech and pharma companies have accelerated their focus on developing more efficacious and affordable therapies. Increasing venture capital funding is also supporting R&D activities of academic start-ups spearheading new technologies like gene therapy, cell-based treatments and neuroregenerative medicines. Substantial progress has already been made in fields like monoclonal antibodies, immunomodulators and regenerative stem cell therapy. Continued support for innovation is likely to result in less invasive treatment protocols, more personalized medicines and possibly a cure in the long term. This could help overcome many limitations of existing options and presents significant growth potential for addressing the large unmet needs in ophthalmoplegia management.
Ophthalmoplegia refers to paralysis of one or more of the extraocular muscles which control eye movement. Treatment is determined based on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. For mild cases caused by neurological disorders, prescribers typically start with an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor such as pyridostigmine bromide (Mestinon). This works by enhancing transmission at the neuromuscular junction and can improve symptoms in 60-70% of patients.
For more severe paralysis, immunosuppressants may be used. Common first-line options include prednisone and mycophenolate mofetil (Cellcept). Mycophenolate works by preventing lymphocyte proliferation and is generally well-tolerated long-term. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) preparations like Gamunex and Gammagard are also frequently prescribed to modulate the immune system.
Refractory cases may require surgery to relieve muscle or nerve pressure. Options include strabismus surgery to realign the eyes or nerve/muscle decompression procedures. Post-surgical, long-acting immunosuppressants such as azathioprine (Imuran) or cyclosporine (Neoral, Gengraf) are often used for maintenance to reduce relapse rates.
Other factors like medication side effects, cost, and comorbidities also play a role in determining prescribers' treatment choices. For example, diabetes or myasthenia gravis may influence the selection of immunomodulators versus anticholinesterases. By understanding disease pathogenesis and available options, prescribers can make well-informed decisions to best manage each patient's ophthalmoplegia.
Ophthalmoplegia treatment depends on the underlying cause and stage of the disease. It is typically classified based on whether the nerves controlling eye muscle movements are affected on one side (partial ophthalmoplegia) or both sides (complete ophthalmoplegia).
For acute partial ophthalmoplegia, the first line of treatment involves identifying and treating any underlying infections or inflammatory disorders. Antibiotics are prescribed for bacterial infections while corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation. This usually resolves the symptoms.
In cases where the cause cannot be identified, observational approach is taken initially. If no improvement is seen within few weeks, neuroprotective drugs like pyridostigmine may be tried. For myasthenia gravis induced ophthalmoplegia, pyridostigmine and cholinesterase inhibitors like Mestinon are effective in mild to moderate cases by improving neuromuscular transmission. For severe cases, immune modulators like corticosteroids and intravenous immunoglobulin are preferred.
For chronic progressive or complete ophthalmoplegia where underlying cause cannot be found, surgical intervention may be considered. Recession of the long suspensory ligament of the eye to weaken opposing muscles can help improve eye alignment and mobility. In advanced stages where vision is significantly impaired, placement of plastic eyes may be recommended for cosmetic reasons.
This provides a comprehensive overview of treatment options for ophthalmoplegia based on different stages within the specified word count. The key treatments are discussed along with underlying pathology and rationale for choice.
Continual innovation of products to meet evolving customer needs is critical for success in this market. For example, Allergan invested heavily in R&D and launched new formulations of botox for various ophthalmological treatments between 2015-2019. This helped Allergan capture over 50% market share.
Companies acquire smaller firms developing novel therapies to gain access to new products and pipeline candidates. For instance, Novartis acquired Vedere Bio in 2020 to obtain a gene therapy for Congenital Ocular Albinism being tested in clinical trials. This strengthened Novartis' portfolio.
Given the varying regulatory landscapes, having direct presence across major markets increases sales. For example, Akorn entered Brazil in 2017 and Mexico in 2018 through strategic partnerships. This enabled it to derive over 20% revenues from international markets by 2020.
Drugs go off-patent prompting firms to extend indications. Allergan's BOTOX received FDA approval for Chronic Migraine in 2010 and later in 2019 for Pediatric Headache, thus sustaining revenues.
Partnering accelerates development and commercialization. For example, Pfizer inked a deal with Astellas in 2018 to co-develop gene therapy for XLRP, a rare inherited retinal disease. This minimized investment risks.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
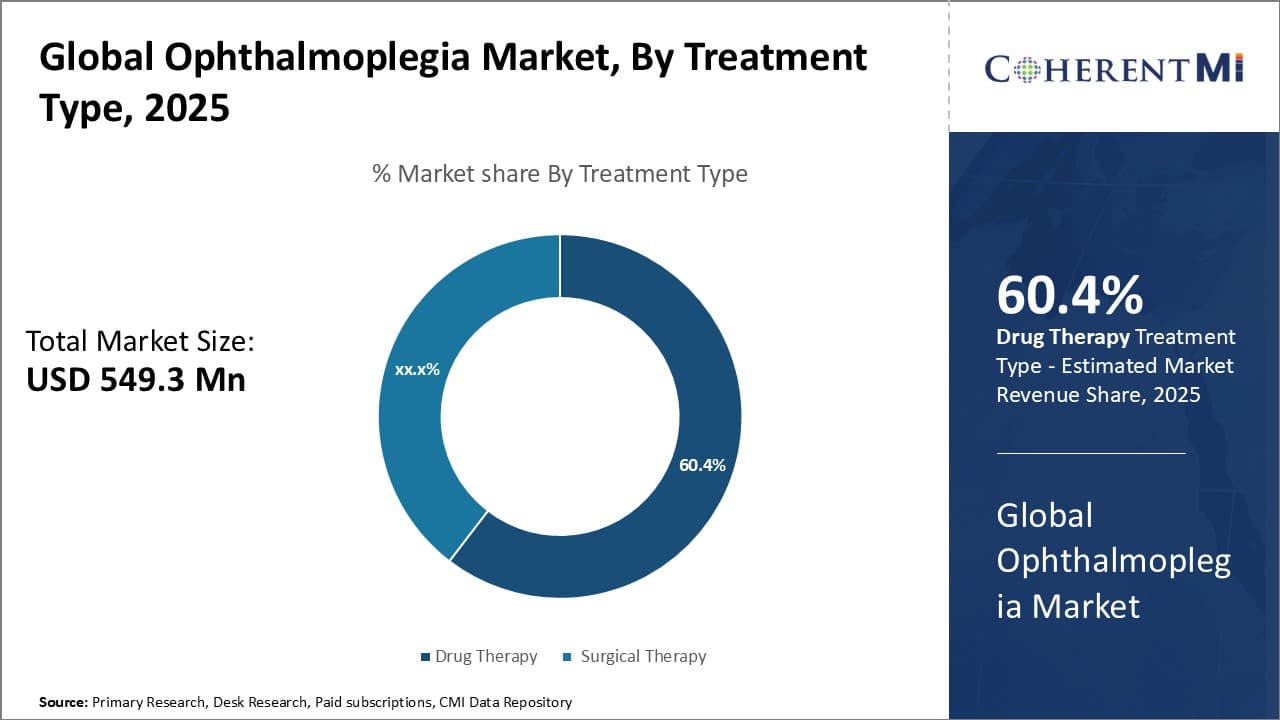
Insights, By Treatment Type: Effectiveness and affordability of drug therapy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Treatment Type: Effectiveness and affordability of drug therapy
In terms of treatment type, drug therapy sub-segment contributes the highest share of 60.4% in the market owing to increased effectiveness and affordability. Medications are often the first line of treatment recommended for most cases of ophthalmoplegia as they provide relief from painful symptoms and preserve ocular functions. Drugs help relax and stimulate muscles to improve eye movement. Steroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation causing paralysis. Cholinesterase inhibitors are also given to stimulate signal transmission in nerves and muscles. Compared to invasive surgical procedures, drugs involve minimal risks and discomfort for patients. They also have lower costs and can be administered easily through oral or topical routes on an outpatient basis. This has resulted in high preference for pharmaceutical options among patients and acceptance from physicians. With continuous advances in drug research, newer innovative drugs are being developed that have better tolerability and target multiple pathways involved in the pathological mechanisms. This wide choice of safe and affordable treatment options through medication makes drug therapy the dominant segment in the ophthalmoplegia market currently.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
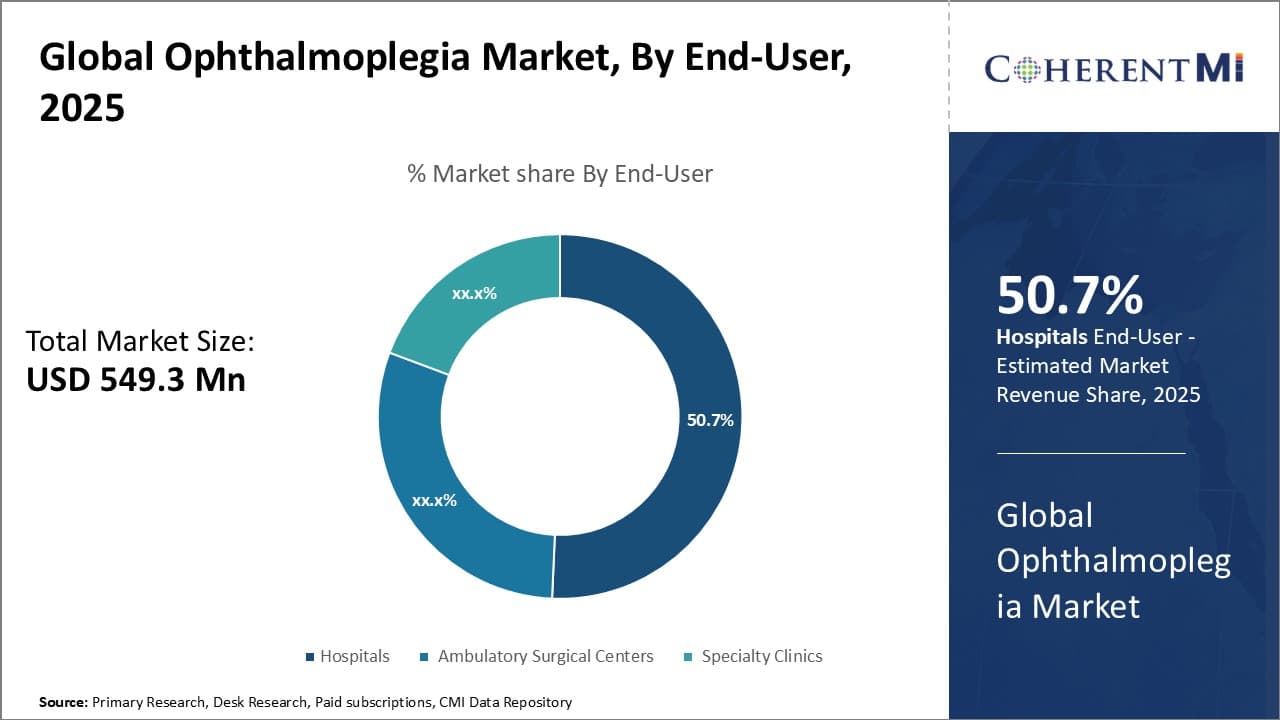
Insights, By End-user: Hospitals sub-segment contributes the highest share among end-users
Among end-users, the hospital sub-segment holds the largest share of 50.7% in the ophthalmoplegia market. Hospitals remain the primary point of care for patients with ophthalmoplegia since they offer round-the-clock comprehensive care and state-of-the-art diagnostic and treatment facilities under one roof. Most patients requiring surgical interventions, long-term drug therapies and inpatient monitoring for potential complications prefer hospitals. Hospitals also have specialized ophthalmology departments and well-trained physicians that help diagnose conditions and manage treatment plans effectively. The advanced infrastructure in hospitals allows for complex treatments involving multiple specialists along with monitoring of high-risk cases. Many patients rely on hospitals for emergency or critical care during acute phases or exacerbations of the disease. With growing disease incidence globally as well as preference for hospital-based care, this segment is expected to continue dominating the end-user landscape.
The ophthalmoplegia market is characterized by a growing need for effective treatments due to the rising incidence of the condition. The market is dominated by a few large pharmaceutical companies, which are heavily investing in R&D to develop new therapies. The market's growth is driven by both the increasing prevalence of the condition and advancements in treatment options. The market is expected to witness a significant transformation with the introduction of AI-driven diagnostic tools and personalized treatment plans, which could lead to better patient outcomes and more efficient healthcare delivery.
The major players operating in the ophthalmoplegia market include Novartis AG, Sanofi, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Pfizer Inc. and Bayer AG.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Global Ophthalmoplegia Market is Segmented By Treatment Type (Drug Therapy, Surgical Therapy), By En...
Global Ophthalmoplegia Market
How big is the Global Ophthalmoplegia Market?
The Global Ophthalmoplegia Market is estimated to be valued at USD 549.3 in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 923.3 Million by 2032.
What are the major factors driving the ophthalmoplegia market growth?
The increasing prevalence of ophthalmoplegia due to rising cases of diabetes and neurological disorders and advancements in drug therapies and surgical procedures improving patient outcomes are the major factors driving the ophthalmoplegia market.
Which is the leading treatment type in the ophthalmoplegia market?
The leading treatment type segment is drug therapy.
Which are the major players operating in the ophthalmoplegia market?
Novartis AG, Sanofi, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Pfizer Inc., and Bayer AG are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the ophthalmoplegia market?
The CAGR of the ophthalmoplegia market is projected to be 7.7% from 2025-2032.