Group B Streptococcus GBS Diagnosis Market Size - Analysis
The group B streptococcus (GBS) diagnosis market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.67 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 2.45 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.6% from 2025 to 2032. Rapid advancements in screening technologies and growing awareness about GBS infections during pregnancy are expected to drive the group B streptococcus (GBS) diagnosis market during the forecast period.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR5.6%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 5.6% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Pfizer Inc., Novartis AG, Merck & Co., Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Sanofi and Among Others |
please let us know !
Group B Streptococcus GBS Diagnosis Market Trends
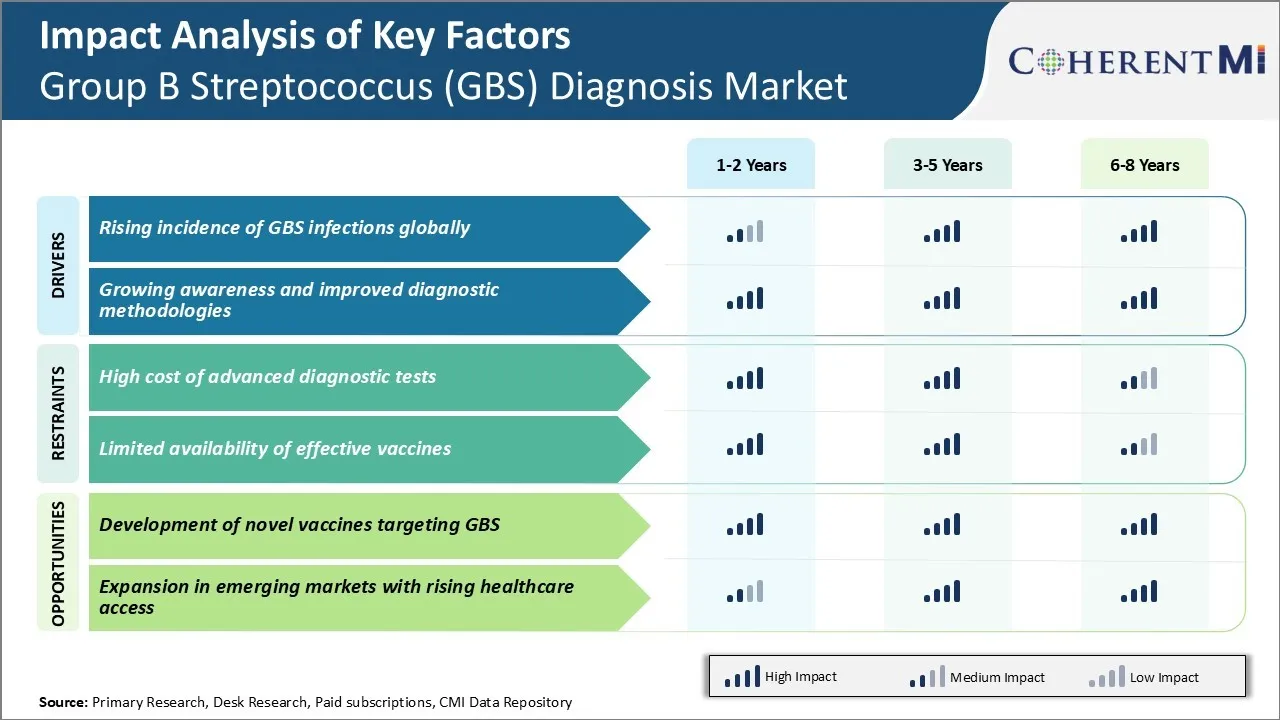
Market Driver - Rising Incidence of GBS Infections Globally
Rising incidence of GBS infections across the world has significantly contributed to the growth of the GBS diagnosis market. GBS is one of the leading causes of life-threatening infections like sepsis and meningitis in newborns. Even years after declining rates of invasive GBS disease in developed countries, certain regions continue to observe an increasing trend in early-onset and late-onset GBS infections among infants.
According to recent estimates by public health officials, nearly 50,000 babies are infected with GBS globally every year, resulting in over 20,000 deaths. The death toll has remained consistently high even with improved protocols for screening and treating pregnant women. Developing nations in Asia Pacific and Africa have some of the highest reported case-fatality rates for GBS infections in newborns.
The heightened risk has compelled governments and healthcare agencies to implement more effective prevention strategies. This involves near universal screening of pregnant women between 35 to 37 weeks of gestation through rapid diagnostic tests. Timely identification of carriers followed by peri-partum antibiotic prophylaxis has proven highly successful in slashing transmission rates. However, resource constraints continue to hamper screening efforts, especially in low and middle-income countries with high disease prevalence. This has amplified the demand for cost-effective and rapid point-of-care diagnostic tests.
Market Driver - Growing Awareness and Improved Diagnostic Methodologies
The growing awareness about GBS infections and their health impact has positively contributed towards market growth by encouraging timely screening and diagnosis. Earlier, GBS was not considered a major threat and diagnosis often happened late when complications had set in.
Technological advancements have played a key role here by providing faster and reliable diagnostic options. Traditional diagnostic tests like bacterial culturing could take 2-3 days to confirm if a woman is GBS carrier or not. The long turnaround severely limited the ability to provide timely antibiotic prophylaxis. However, newer rapid molecular techniques like polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and enzyme immunoassays can now detect GBS from vaginal/rectal swabs within hours instead of days. This has expanded point-of-care testing capabilities, boosting case detection even in remote locations.
Moreover, newer platforms are being developed to overcome existing limitations like complex sample-to-answer workflows and requirement of specialized equipment and training. Simple lateral flow immunoassays are emerging as promising alternatives for near-patient or home-use rapid testing. A POC test with self-collection capabilities would be highly desirable in resource-limited areas. Such user-friendly innovations are anticipated to improve screening compliance and access to prompt diagnosis substantially.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High Cost of Advanced Diagnostic Tests
One of the major challenges currently faced by the Group B Streptococcus (GBS) diagnosis market is the high cost of advanced diagnostic tests. Gold standard diagnostic methods like PCR and culture-based diagnostic tests require specialized equipment and reagents which make these tests quite expensive for routine use.
While PCR tests can detect GBS with high accuracy, the significant costs involved limits their widespread adoption, especially in developing nations where resources are limited. This high-cost poses affordability issues and prevents universal screening of pregnant women for GBS colonization.
Additionally, advanced GBS tests can only be performed at specialized laboratories which hinders accessibility in remote areas. The expensive nature of these tests also reduces repeat testing which is crucial for timely intrapartum antibioprotic prophylaxis of infected mothers. Unless low-cost alternatives are developed, the financial barriers will continue hampering efforts to curb GBS infections through large-scale screening programs.
Market Opportunity - Development of Novel Vaccines Targeting GBS
One major opportunity for stakeholders in the GBS diagnosis market lies in the development of novel vaccines targeting GBS. Currently available diagnostic tests only allow detection of active GBS colonization or infection but provide no protection against future occurrences. This has fueled the demand for preventive vaccines which could eliminate the need for repeated screening and diagnosis.
Considerable research efforts are ongoing to design cost-effective GBS vaccines offering cross-serotype protection. Successful development of such vaccines would curb the incidence of GBS disease globally and eliminate the need for extensive diagnostic testing over time.
It may also open lucrative revenue streams for vaccine manufacturers. This presents a multi-billion-dollar commercial opportunity for players to capitalize on the preventive approach of vaccination. Novel GBS vaccines also have the potential to significantly reduce healthcare costs associated with treatment and long-term management of GBS infections.
Prescribers preferences of Group B Streptococcus GBS Diagnosis Market
GBS is typically treated through a combination of antibiotics during pregnancy and delivery to prevent newborn infection. For asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy, prescribers commonly recommend a first-line oral regimen of penicillin or amoxicillin. If the patient is allergic to penicillin, cephalexin (Ceporex) may be prescribed instead.
For pregnant women experiencing chorioamnionitis or premature pre-term rupture of membranes, intravenous agents are preferred due to increased risk of infection. Common choices include penicillin G (Crystapen), ampicillin (Oxoid), or cefazolin (Cefazolin Kabi). If maternal risks warrant, second-line options like clindamycin (Dalacin) or vancomycin (Vancocin) are also considered.
During delivery for GBS-positive mothers, first-line prophylaxis typically involves intravenous administration of penicillin G or ampicillin shortly before delivery. For those with severe penicillin allergies, vancomycin is the standard alternative. Following an uncomplicated vaginal delivery, newborns are monitored for signs of early-onset GBS disease and treated promptly, if necessary, usually with ampicillin (Oxoid).
Key factors influencinging prescribers' preferences include efficacy, safety, cost, ease of use, and alignment with treatment guidelines from medical organizations like the CDC. Individual patient characteristics like co-morbidities, risk factors and allergies are also carefully evaluated.
Treatment Option Analysis of Group B Streptococcus GBS Diagnosis Market
For colonization during pregnancy, intravenous penicillin G is the standard preventive treatment during labor to reduce risk of early-onset GBS disease in the newborn. A single dose is administered at least 4 hours before delivery. For patients with allergies to penicillin, cefazolin or clindamycin are alternatives.
For early-onset GBS disease in newborns under 7 days old, initial treatment depends on the infant's clinical condition. Mild to moderate cases may be treated with intravenous ampicillin plus gentamicin for at least 5 days. For severe infections or treatment failure, vancomycin is added to cover for possible resistant organisms.
Late-onset GBS disease in infants 7 days to 3 months old is usually treated as outpatient with oral amoxicillin for a total course of 10-14 days. Hospitalization is required for infants unable to take oral medications or those with more serious symptoms. Intravenous ampicillin or penicillin remain first line, with ceftriaxone or cefotaxime as alternatives for those with penicillin allergies.
Adult GBS disease treatment involves intravenous penicillin or ceftriaxone for 10-14 days. For penicillin-allergic patients, vancomycin is recommended due to lower resistance profiles. Source control through drainage of abscesses is also important.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Group B Streptococcus GBS Diagnosis Market
Product Innovation - One of the most successful strategies adopted by market leaders has been continuous investment and focus on product innovation. For example, in 2016, bioMérieux launched a new rapid molecular test called Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT) called BIOFIRE GBS which provided results within an hour instead of 2-3 days for conventional culture tests.
Acquisitions - Key players have grown both organically and inorganically via strategic acquisitions. For instance, in 2017, Roche acquired company Alere to gain access to its point-of-care molecular diagnostics platform including Alere q which had a GBS test.
Geographic Expansion - Leading companies have expanded into emerging markets which are expected to witness highest growth. Thermo Fisher entered into agreements with distributors in Latin America and Asia Pacific in 2018 to market its GBS diagnostic assays and expand footprint outside U.S. and Europe. This pre-emptive strategy aided revenue growth in high potential regions.
Leveraging Digital Platforms - Companies are also partnering with digital health platforms to enhance customer experience and drive higher test volumes. In 2020, Binx Health partnered with digital clinic PlushCare to integrate its IO rapid test onto PlushCare's telehealth platform, allowing physicians to easily order the test and receive results remotely.
Segmental Analysis of Group B Streptococcus GBS Diagnosis Market
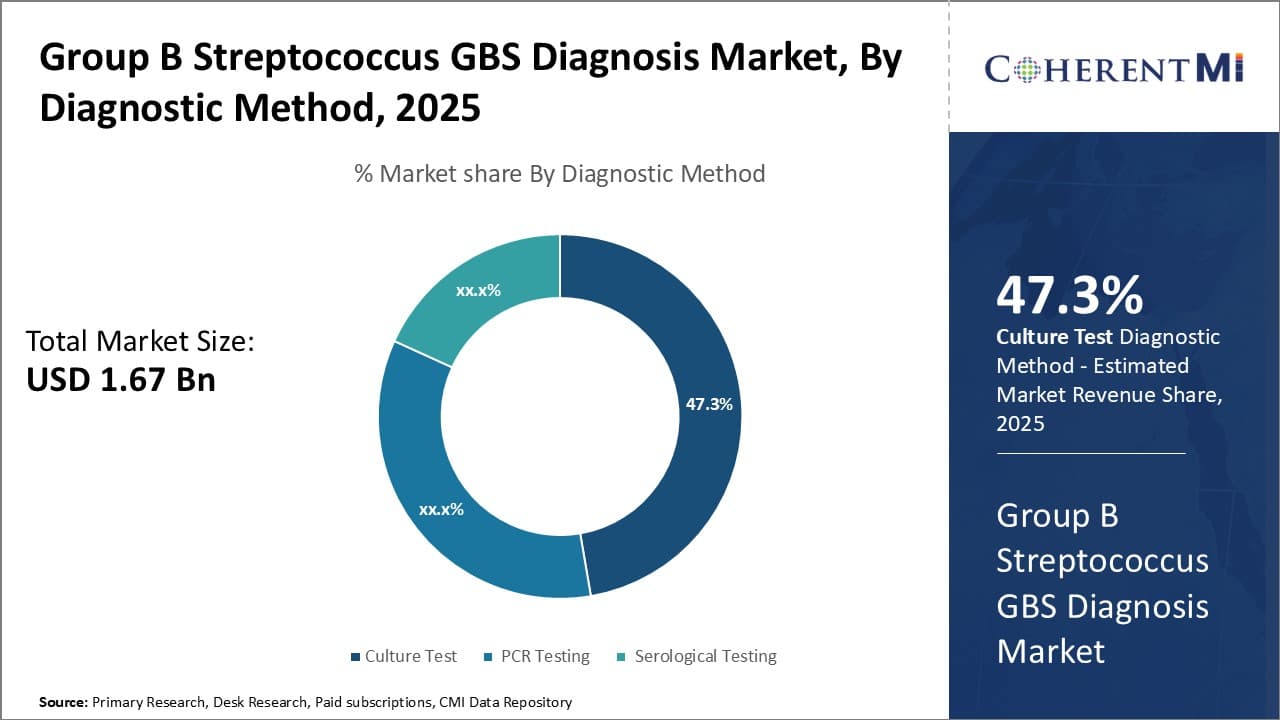 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy Insights, By Diagnostic Method: Convenience and Familiarity Drive Culture Test Adoption
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy Insights, By Diagnostic Method: Convenience and Familiarity Drive Culture Test Adoption
In terms of diagnostic method, culture test contributes the highest share of the group B streptococcus (GBS) diagnosis market owing to its convenience and familiarity among healthcare providers. Culture tests have long been the standard diagnostic method for identifying GBS as they provide definitive results through bacteria isolation and identification. While newer molecular techniques like PCR offer improved accuracy and turnaround time, culture remains a reliable option that is easy to perform with widely available equipment found in most clinical microbiology laboratories.
Culture tests do not require specialized equipment or highly trained personnel compared to molecular methods. Basic microbiology skills are sufficient to plant, incubate, read and report out culture results. This ease of use makes culture a very accessible option for laboratories of all sizes.
In addition, healthcare professionals are very comfortable interpreting culture results after years of experience. This predictability provides reassurance for clinicians making critical treatment decisions. While newer methods may offer advantages, most providers prefer sticking with culture's simplicity and track record they can depend on rather than transitioning to unfamiliar techniques. The extensive familiarity among the medical community serves as a major factor driving ongoing preference and market share for GBS culture testing.
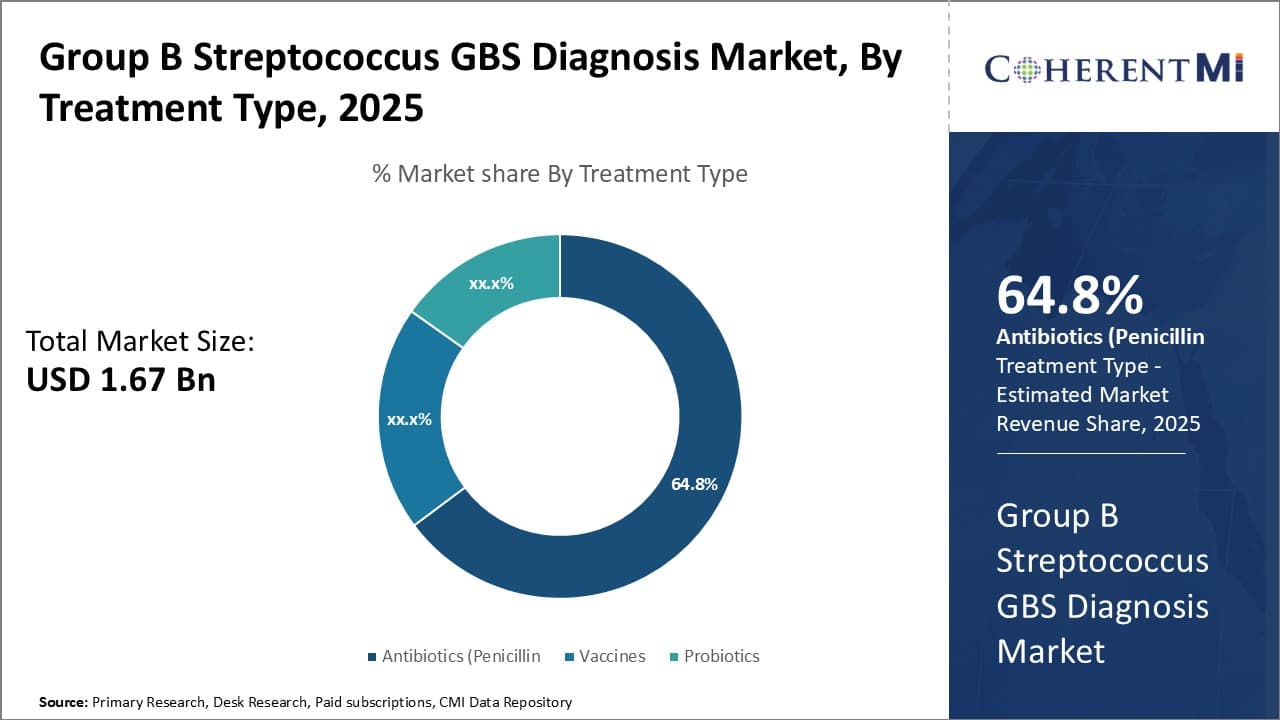 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Treatment Type: Effective Treatment Drives Antibiotic Dominance
In terms of treatment type, antibiotics contributes the highest share of the group B streptococcus (GBS) diagnosis market due to its proven effectiveness in treating GBS infections. Once a patient is diagnosed with GBS through testing, the standard and recommended treatment involves a course of intravenous antibiotics during delivery. Penicillin has long been considered the first-line antibiotic therapy owing to its reliability against GBS bacteria.
When a pregnant woman tests positive for GBS, penicillin or ampicillin treatment during labor and delivery can reduce the newborn GBS infection risk by more than 80%. No other treatment modalities have demonstrated such impressive efficacy outcomes against this potentially devastating pathogen. The ability of antibiotics to reliably cure GBS infections and prevent mortality gives clinicians and patients high confidence in them as the go-to management option.
While alternative approaches like probiotics and vaccines show promise, they have not achieved the same proven success as antibiotics in clinical studies and real-world use. In the coming future, physicians will likely continue relying on them as the gold standard for GBS treatment and prophylaxis in both mother and newborn. Their superior efficacy directly translates to the antibiotic segment's market dominance in the GBS diagnosis space.
Insights, By End User: Testing Convenience Drives Hospital Segment Leadership
As the traditional healthcare setting for labor and delivery, hospitals are able to offer a comprehensive one-stop solution for expectant mothers. They have obstetrics departments and staff equipped to perform GBS screening, deliver babies, and administer IV antibiotics if needed - all under one roof.
The convenience of this integrated care model means lower logistical hurdles for patients. They do not need to coordinate between multiple provider offices or labs to get tested and treated. Everything occurs seamlessly within the hospital. This streamlined process helps reduce delays, improve care coordination, and give peace of mind that GBS issues will be properly managed during delivery. It also means hospitals themselves face less operational complexity in handling these time-sensitive cases.
Additionally, hospitals have the infrastructure, expertise and economies of scale to maintain advanced on-site clinical labs and 24/7 staffing. This allows for continuous GBS testing capabilities without needing to outsource work. It also enables rapid turnaround when test results are most critical during labor. The convenient one-stop integrated testing and treatment environment hospitals provide is unparalleled compared to alternatives like physician offices or reference labs. Their unique care model plays a major role in driving their market leadership as the top GBS diagnosis end user.
Additional Insights of Group B Streptococcus GBS Diagnosis Market
- The prevalence of GBS in pregnant women is estimated to be around 15-25%, with a significant risk of transmission to newborns during childbirth.
- Antibiotic prophylaxis during labor has been shown to reduce the risk of neonatal GBS infections by over 80%.
Competitive overview of Group B Streptococcus GBS Diagnosis Market
The major players operating in the Group B Streptococcus (GBS) Diagnosis Market include Pfizer Inc., Novartis AG, Merck & Co., Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Sanofi, Abbott Laboratories, and Johnson & Johnson.
Group B Streptococcus GBS Diagnosis Market Leaders
- Pfizer Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- GlaxoSmithKline plc
- Sanofi
Recent Developments in Group B Streptococcus GBS Diagnosis Market
- In April 2024, Pfizer announced the launch of a clinical trial for a new GBS vaccine aimed at pregnant women to prevent neonatal GBS infections, showing promise in early safety assessments. This investigational vaccine aims to protect newborns from severe conditions like sepsis, pneumonia, and meningitis. The Phase 2 study, ongoing in the U.S., U.K., and South Africa, evaluates the safety and immunogenicity of GBS6 in pregnant women and their infants.
- In September 2023, Novartis published findings from a study demonstrating the effectiveness of a new rapid PCR test for GBS, significantly reducing diagnostic time in clinical settings.
Group B Streptococcus GBS Diagnosis Market Segmentation
- By Diagnostic Method
- Culture Test
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) Testing
- Serological Testing
- By Treatment Type
- Antibiotics
- Penicillin
- Ampicillin
- Vaccines
- Probiotics
- Antibiotics
- By End User
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Diagnostic Laboratories
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Komal Dighe is a Management Consultant with over 8 years of experience in market research and consulting. She excels in managing and delivering high-quality insights and solutions in Health-tech Consulting reports. Her expertise encompasses conducting both primary and secondary research, effectively addressing client requirements, and excelling in market estimation and forecast. Her comprehensive approach ensures that clients receive thorough and accurate analyses, enabling them to make informed decisions and capitalize on market opportunities.
