Hypercholesterolemia Market Size - Analysis
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR4.6%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 4.6% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Amgen Inc., Pfizer Inc., Roche Holding AG, Novartis International AG, Sanofi S.A. and Among Others |
please let us know !
Hypercholesterolemia Market Trends
As people become more educated and aware about their health and medical conditions, there has been a notable rise in awareness of hypercholesterolemia in recent years. Individuals are taking a more proactive approach towards managing cardiovascular risk factors and getting their cholesterol levels checked on a regular basis.
The healthcare industry too has stepped up efforts to routinely check cholesterol levels, especially in high-risk populations. Various diagnostic guidelines now recommend measuring lipid profiles periodically for all adults as part of regular health checkups.
Continuous research and development efforts from drug manufacturers have led to the approval of several new lipid-lowering drug classes and agents with superior efficacy and tolerability profiles.
PCSK9 inhibitors opened new possibilities for treating patient groups that were previously difficult to manage such as those with genetic conditions predisposing very high cholesterol. They can be effective alternatives for statin intolerant patients and provide additional options to consider before starting last-resort therapies like lomitapide.
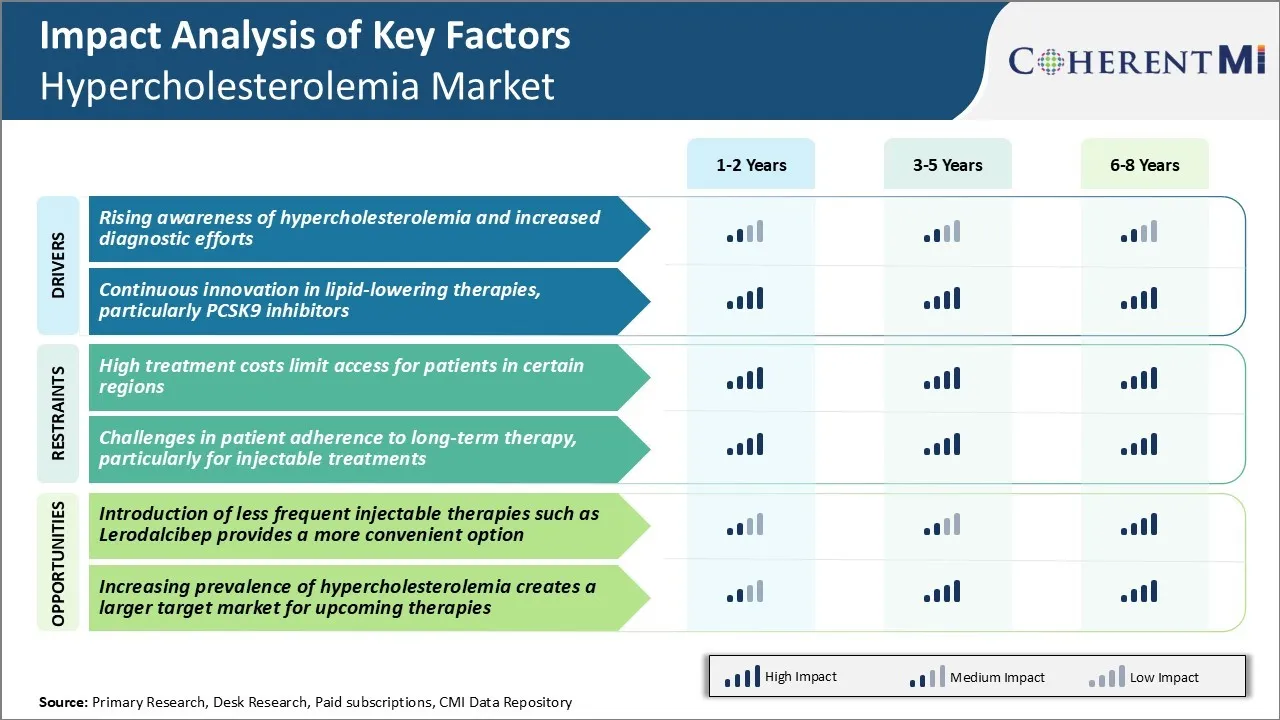
Market Challenge - High Treatment Costs Limit Access for Patients in Certain Regions
Current PCSK9 inhibitor therapies require bi-weekly or monthly injections which can be an inconvenience leading to non-compliance over the long term. A therapy that could be administered once every 6 months can make treatment more compatible with patient lifestyles and busy schedules. This can help improve adherence to lipid-lowering regimens. The potential for half-yearly dosing with Lerodalcibep addresses one of the key limitations of existing PCSK9 inhibitors. If proven effective in ongoing late-stage trials, it may capture a portion of the hypercholesterolemia market currently satisfied with oral drugs alone as well as attract those patients who find frequent injections impractical. This opens up new opportunities for growth and also helps maximize patient and population health outcomes through better management of high cholesterol levels over the long-run.
Prescribers preferences of Hypercholesterolemia Market
Hypercholesterolemia treatment follows guidelines that recommend starting lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise for all patients. Prescribers typically consider drug therapy for those with LDL-C levels above 100 mg/dL or 130 mg/dL for those with risk factors.
When lifestyle changes and statin/statin plus ezetimibe therapy do not control LDL-C sufficiently, prescribers consider switching to more potent PCSK9 inhibitors. Alirocumab (Praluent) and evolocumab (Repatha), administered via autoinjector, can reduce LDL-C by 60% on average either as monotherapy or when added to other lipid lowering therapies.
Treatment Option Analysis of Hypercholesterolemia Market
Hypercholesterolemia has various stages of disease progression. Initial stage or mild hypercholesterolemia is characterized by LDL cholesterol levels between 130-159 mg/dL. Lifestyle modifications focused on diet and exercise are recommended as first line of treatment.
Severe hypercholesterolemia with LDL greater than 190 mg/dL needs aggressive therapeutic intervention. Maximally tolerant statin doses may not suffice. Addition of Ezetimibe, a cholesterol absorption inhibitor, to ongoing statin therapy forms an attractive dual lipid lowering approach. The Ezetimibe+Atorvastatin combined formulation (Eg. Ezetrol) delivers consistent LDL reductions of 55-65%, making it the mainstay of treatment at this stage.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Hypercholesterolemia Market
One of the major strategies adopted was developing PCSK9 inhibitors which target PCSK9 - a protein that reduces the liver's ability to remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. In 2015, Amgen launched Repatha (evolocumab) becoming the first PCSK9 inhibitor approved by the FDA for treatment of Hypercholesterolemia. Clinical trials showed Repatha reduced LDL cholesterol by 60% on average when added to statin therapy. This novel mechanism of action and superior efficacy levels compared to statins helped Amgen capture a significant market share.
Players are also focusing on oral alternatives to injections. In 2019, Esperion Therapeutics gained FDA approval for Nexcelom (bempedoic acid) - the first non-statin, oral therapy for Hypercholesterolemia. Nexcelom works by inhibiting ATP-citrate lyase and reduces cholesterol production in the liver. The convenience of an oral therapy gave Esperion an edge over injectables.
Segmental Analysis of Hypercholesterolemia Market
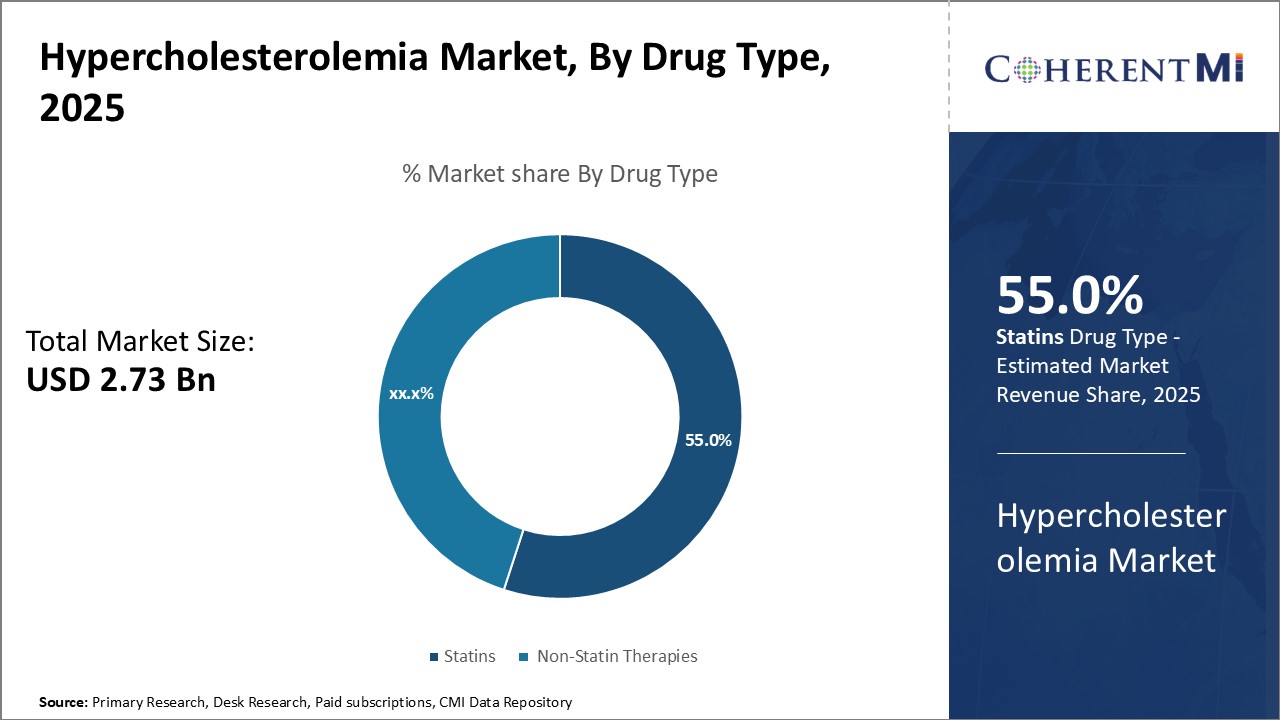
Insights, By Drug Type: Cost-effectiveness drives Statins dominance
Due to their generic status, statins offer good value for money compared to expensive branded non-statin therapies or injectable PCSK9 inhibitors. This cost advantage, coupled with the extensive clinical evidence demonstrating statins' benefits, has made them the therapy of choice for the majority of patients with high cholesterol. Their widespread use across all healthcare settings, from hospitals to retail pharmacies, has enabled statins to dominate the hypercholesterolemia drug market by attributable share.
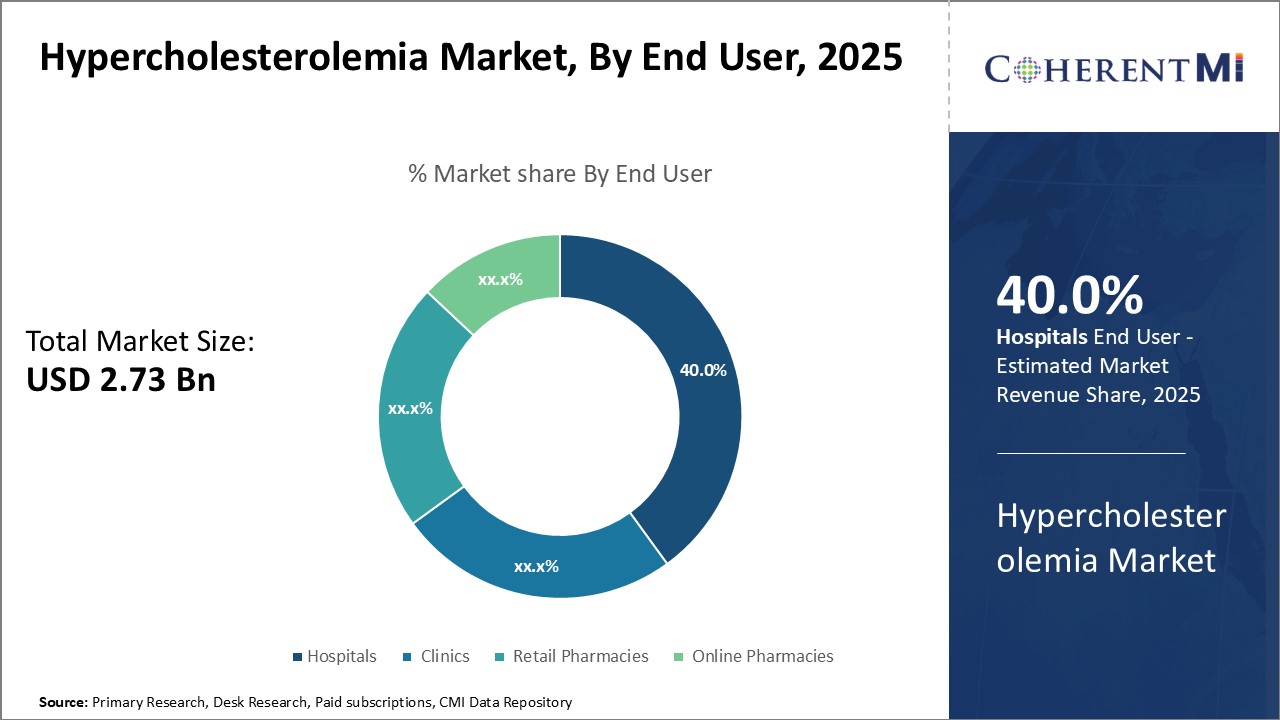 Insights, By End User: Convenience Drives Hospitals Prominence
Insights, By End User: Convenience Drives Hospitals Prominence
The institution-based care provides seamless access to cardiologists, dieticians as well as laboratory tests needed to accurately diagnose and manage high cholesterol. It also addresses challenges faced by certain patients like the elderly or those from rural areas in regularly visiting standalone clinics or pharmacies. The "one-stop-shop" convenience of comprehensive care, from diagnostics to long-term drug management, appeals to a significant customer segment.
In terms of distribution channel, online sales contribute the highest share driven by the perception of security it offers customers. People buying medicines for health conditions like hypercholesterolemia are wary of privacy and safety when purchasing online.
Furthermore, e-pharmacies leverage technologies like artificial intelligence to offer personalized suggestions, chatbot assistance and contextual rewards for loyal customers. These experiences have made online channels the most appealing distribution avenue, thereby contributing their fastest growing share.
Additional Insights of Hypercholesterolemia Market
- Prevalence Rates: Approximately 40% of the adult population globally is affected by hypercholesterolemia, highlighting the substantial market potential for cholesterol-lowering therapies.
- In the US, around 31.7% of adults have high levels of LDL-C, doubling their risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- 0% of adults have elevated LDL cholesterol, with prevalence increasing with age (48.4% in adults aged 65–74 years).
- Regional Growth: Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the hypercholesterolemia market due to rising disposable incomes and improved healthcare infrastructure.
- Treatment Adoption: Statins currently hold the largest market share, accounting for 60% of the total market, driven by their proven efficacy and widespread acceptance.
Competitive overview of Hypercholesterolemia Market
The major players operating in the hypercholesterolemia market include Amgen Inc., Pfizer Inc., Roche Holding AG, Novartis International AG, and Sanofi S.A.
Hypercholesterolemia Market Leaders
- Amgen Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Roche Holding AG
- Novartis International AG
- Sanofi S.A.
Hypercholesterolemia Market - Competitive Rivalry

Hypercholesterolemia Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Hypercholesterolemia Market
- In August 2024, Pfizer Inc. entered a strategic partnership with a biotech firm to develop next-generation statins, focusing on enhanced efficacy and patient compliance. Pfizer has been involved in various strategic collaborations aimed at advancing cardiovascular treatments. One such partnership, established in August 2024 with Quotient Therapeutics, focuses on developing treatments for cardiovascular and renal diseases, though it is not explicitly tied to statins. This partnership is part of Pfizer's broader initiative to leverage biotechnological innovations through collaborations.
- In April 2024, Amgen Inc. launched a new PCSK9 inhibitor, aiming to provide more effective cholesterol management with reduced side effects, potentially capturing a larger market share. Amgen remains a significant player in the PCSK9 inhibitor market, primarily with its well-established product Repatha (evolocumab), which has been a game-changer in cholesterol management. Repatha has been clinically proven to significantly lower LDL cholesterol and reduce cardiovascular risks. Amgen continues to explore innovations in this field.
- In October 2023, Roche Holding AG received FDA approval for its latest non-statin therapy, which offers improved lipid-lowering capabilities, expanding its therapeutic portfolio.
- In December 2021, the FDA approved LEQVIO (inclisiran), developed by Novartis. LEQVIO is a biannual injection that helps reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels, particularly for adults with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH). This treatment is significant because it is the first small interfering RNA (siRNA) therapy approved for this purpose, offering sustained LDL-C reduction with only two doses per year after an initial dose and one at three months. This regimen provides a more convenient option for patients who struggle with adherence to more frequent cholesterol-lowering treatments, like statins.
- In February 2020, Esperion Therapeutics launched two new cholesterol-lowering medications: NEXLETOL (bempedoic acid) and NEXLIZET (a combination of bempedoic acid and ezetimibe). Both drugs were approved by the FDA as adjuncts to diet and maximally tolerated statin therapy for adults with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) who require further reduction in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C).
Hypercholesterolemia Market Segmentation
- By Drug Type
- Statins
- Atorvastatin
- Simvastatin
- Non-Statin Therapies
- Ezetimibe
- PCSK9 Inhibitors
- By End User
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
- By Distribution Channel
- Online Sales
- Offline Sales
- Direct Sales

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the hypercholesterolemia market?
The hypercholesterolemia market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.73 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 3.74 Bn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the hypercholesterolemia market?
The high treatment costs limit access for patients in certain regions and challenges in patient adherence to long-term therapy, particularly for injectable treatments, are the major factors hampering the growth of the hypercholesterolemia market.
What are the major factors driving the hypercholesterolemia market growth?
Rising awareness of hypercholesterolemia and increased diagnostic efforts and continuous innovation in lipid-lowering therapies, particularly PCSK9 inhibitors are the major factors driving the hypercholesterolemia market.
Which is the leading drug type in the hypercholesterolemia market?
The leading drug type segment is statins.
Which are the major players operating in the hypercholesterolemia market?
Amgen Inc., Pfizer Inc., Roche Holding AG, Novartis International AG, and Sanofi S.A. are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the hypercholesterolemia market?
The CAGR of the hypercholesterolemia market is projected to be 4.6% from 2025-2032.