

The hypophosphatasia treatment market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.94 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 4.25 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% from 2025 to 2032. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment coupled with rising prevalence of hypophosphatasia are major factors driving the market growth.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR5.4%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 5.4% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | AstraZeneca (Alexion Pharmaceuticals), AM Pharma, PuREC, Novartis AG, Pfizer and Among Others |
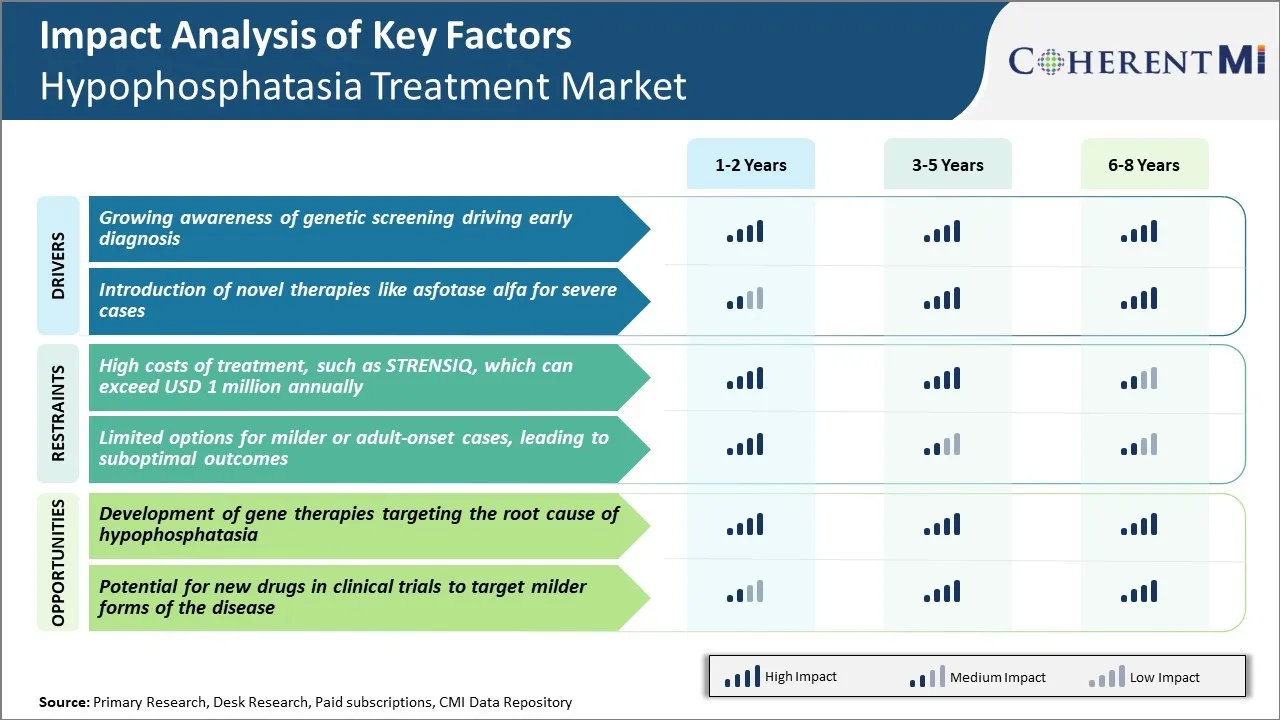
Market Driver - Growing Awareness of Genetic Screening Driving Early Diagnosis
Genetic testing serves as an important tool for families who have a history of hypophosphatasia in their blood relatives. By identifying the gene mutations associated with the disease, at-risk family members can be diagnosed promptly. Carrier screening is also being widely used for expecting parents to determine the risk of having an affected child. This is playing a major role in facilitating early interventions that can help curb the progression of the condition and reduce complications in pediatric patients. With advancing genomic technologies, genetic testing has become more affordable and accessible to a larger population globally.
To spread more awareness, patient advocacy groups are also arranging educational programs and seminars for healthcare experts as well as the general public. The objective is to highlight the importance of genetic screening so that the diagnosis rate can be improved.
More physicians are now routinely including hypophosphatasia in their differential diagnoses, especially for unexplained fractures or skeletal abnormalities in children. This is resulting in prompt referrals for genetic testing and shortening the time lag between symptom onset and treatment initiation. As more patients are diagnosed at younger ages, it also allows them to benefit fully from upcoming treatment advances.
Market Driver - Introduction of Novel Therapies like Asfotase Alfa for Severe Cases
A major breakthrough for patients with severe hypophosphatasia has been the development of asfotase alfa, the first-ever enzyme replacement therapy to receive global regulatory approvals for this condition. Asfotase alfa aims to supplement the missing alkaline phosphatase enzyme to address the underlying pathophysiology of the disease. With subcutaneous administration available from infancy onwards, it offers a personalized treatment approach with convenient dosing.
In clinical trials, asfotase alfa has demonstrated promising results in improving rickets, preventing fractures, promoting skeletal mineralization and overall growth. It has been shown to significantly elevate serum alkaline phosphatase levels as well as other markers of disease severity. With continued therapy, patients are able to achieve developmental motor milestones without requiring walking aids and perform daily activities independently.
The approval and availability of the first-ever treatment has revitalized hopes within the patient and medical communities. It means that severe cases which were earlier deemed untreatable or fatal can now look forward to a normal life expectancy with permanent correction of the low alkaline phosphatase levels. This offers caregivers and families reassurance like never before. More children will now get diagnosed to benefit from this therapy, as its approval has disseminated more knowledge about this rare disease globally.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High Costs of Treatment, such as STRENSIQ, which can Exceed USD 1 Million Annually
While hypophosphatasia is a rare disease, current treatment options come with exorbitantly high costs that present a significant challenge to wider adoption and access. The only medication approved for pediatric-onset hypophosphatasia, STRENSIQ (asfotase alfa) - developed by Alexion Pharmaceuticals - requires administration through frequent and lifelong injectable doses.
Alexion charges over $300,000 per year for treatment with STRENSIQ, and total lifetime costs per patient can easily exceed $1 million according to some estimates. This high economic burden places treatment out of reach for many patients and healthcare systems globally. The rarity of hypophosphatasia also means the potential customer base for any pharmaceutical company is limited, reducing commercial incentives to invest in researching and developing more affordable therapies.
Addressing the challenge of high costs will be crucial to improving quality of life for more patients living with hypophosphatasia worldwide.
Market Opportunity: Development of Gene Therapies
A promising area ripe with opportunities is the development of gene therapies targeting the root cause of hypophosphatasia by replacing the defective ALPL gene. Gene therapies hold potential to alter the disease course through a single or limited administration, circumventing the need for lifelong injectable regimens like STRENSIQ. This represents an opportunity to significantly reduce long-term costs of management by transforming hypophosphatasia into a potentially one-time treatable condition. Several biotechs have launched research programs pursuing gene therapy approaches for hypophosphatasia including Asklepios BioPharmaceutical and Aruvant Sciences.
If proven safe and effective through clinical trials, FDA approval of gene therapies could expand treatment access by offering more affordable options compared to enzyme replacement therapies. This presents a major opportunity for pharmaceutical companies to demonstrate transformative value and earn significant first-mover advantages in the hypophosphatasia treatment market with high unmet needs.
Hypophosphatasia is a rare hereditary metabolic bone disease with varying severity based on the stage of presentation. For infants, the acute form presents within the first 6 months of life with life-threatening complications. Prescribers commonly initiate treatment with the orphan drug asfotase alfa (STRENSIQ), administered via daily subcutaneous injections. For children and adults with the juvenile and adult forms, they typically start on bisphosphonate therapies like alendronate (Fosamax) which helps increase bone mineralization.
As the disease progresses, if patients do not respond adequately to bisphosphonates, prescribers may switch to asfotase alfa to further improve skeletal mineralization and symptoms. According to many rheumatologists and endocrinologists, asfotase alfa has shown greatest efficacy in management of moderate to severe cases since it treats the underlying enzyme deficiency. Though well-tolerated, its high list price and lifelong treatment duration are significant prescribing considerations.
Other factors influencing drug choice include a patient's symptoms, severity of complications and genomic testing results. Vitamin D, calcium, and physical therapy supplements may be prescribed alongside medications. Overall, prescribers seek options that can halt disease progression, improve quality of life and in critical infant cases, help infants survive. Their preferences are dynamically tailored based on individual patients' disease stage and treatment response over time.
Product Innovation: One of the most common strategies adopted by leading players is continuous innovation in products to meet unmet needs. For example, Kyowa Kirin launched the world's first gene therapy for hypophosphatasia named Evkeeza in 2020. This represented a major breakthrough as it is a more effective treatment than existing options. Evkeeza received FDA approval based on positive results from a Phase 3 trial that showed improved survival and motor development in children with the condition.
Partnerships & Collaborations: Companies often collaborate with smaller biotechs to gain access to new therapies and accelerate drug development. For instance, Ultragenyx partnered with Kyowa Kirin in 2019 to co-develop and commercialize Evkeeza outside of Japan and Korea. Such partnerships enable companies to share resources and risks, bringing novel treatments to patients faster. This collaboration strategy has been successful as it led to the approval and launch of Evkeeza worldwide.
Acquisitions: Large pharmas acquire smaller firms developing promising drug candidates to enhance their product pipelines. For example, Alexion acquired Achillion Pharmaceuticals in 2020 primarily to gain access to early-stage oral supplement treatment for hypophosphatasia. This allows Alexion to expand its portfolio and capabilities in this market. Such strategic acquisitions position companies favorably to capture future sales.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
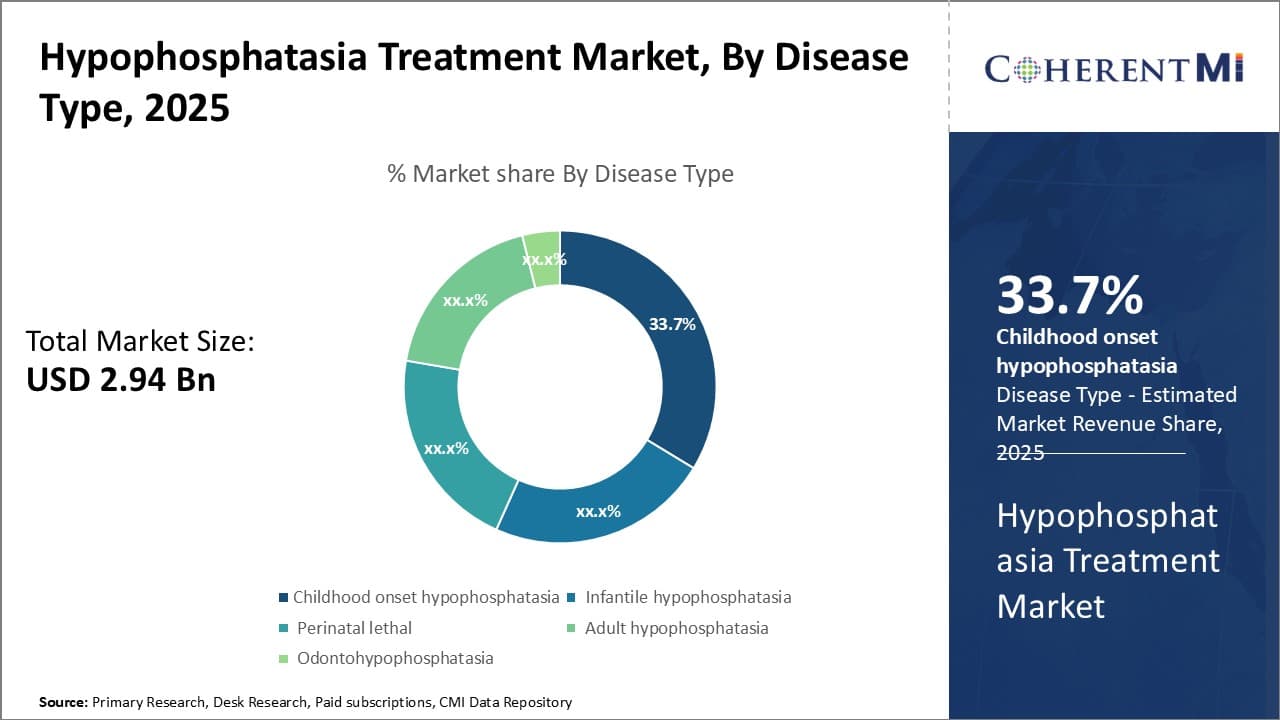
Insights, By Disease Type: Early Onset and High Prevalence Rate of Childhood Onset Hypophosphatasia Impacts Market Trends
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Disease Type: Early Onset and High Prevalence Rate of Childhood Onset Hypophosphatasia Impacts Market Trends
Childhood onset hypophosphatasia contributes the largest share in the hypophosphatasia treatment market in terms of disease type segment. This is primarily due to its early onset during childhood, between ages 6 months to 6 years. Symptoms of childhood onset hypophosphatasia usually become apparent during this period and include skeletal abnormalities, weak or brittle bones, shorter stature and defective tooth development.
The disease prevalence is also relatively high for childhood onset hypophosphatasia compared to other types. It is estimated that around 1 in 100,000 newborns are diagnosed with this form annually. The inherited genetic variant that causes deficient alkaline phosphatase enzyme activity has a higher frequency of occurrence. Combined with non-lethal nature compared to infantile type, this drives greater number of diagnoses and need for lifelong treatment.
Furthermore, being a childhood condition, it requires long term management and monitoring by pediatricians and orthopedic specialists. This regular interaction with healthcare providers increases awareness and screening. Any signs of deterioration in bone health or development are promptly identified and addressed. Early intervention plays a vital role in preventing complications and improving clinical outcomes for patients.
Overall, the early onset, lifelong nature and high disease prevalence of childhood onset hypophosphatasia contribute significantly to its leading market share growth potential in the segment.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
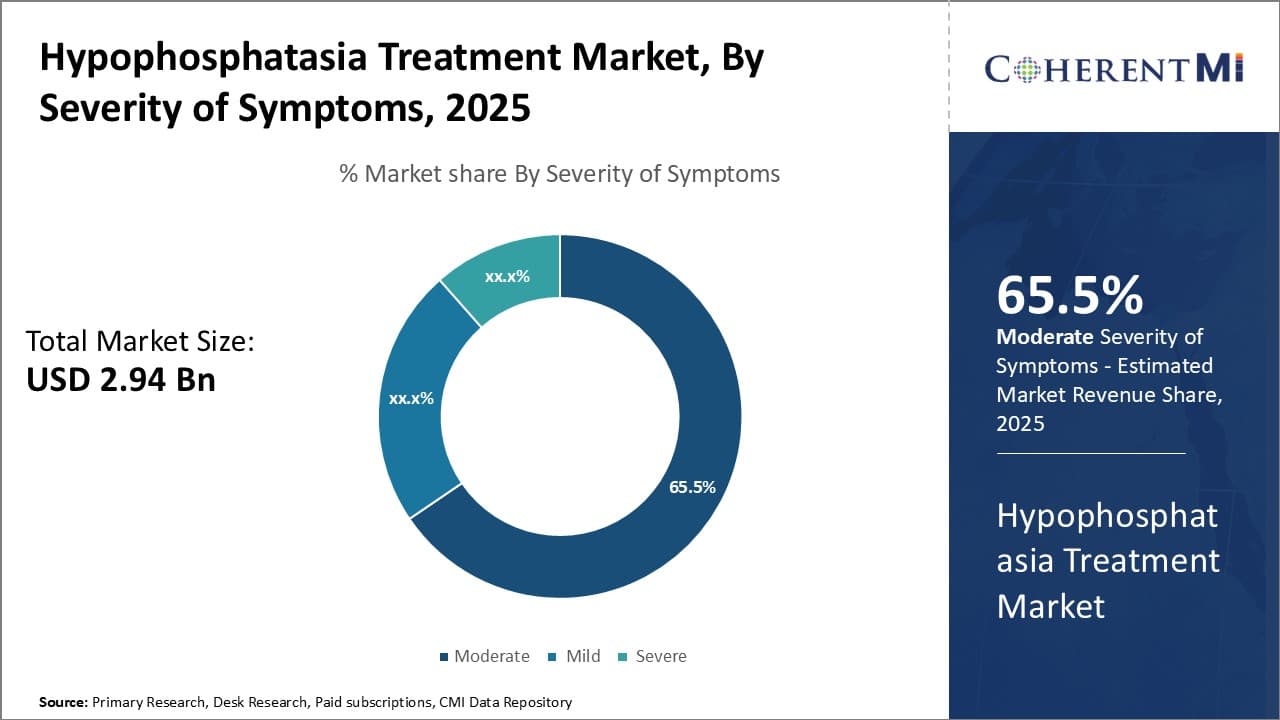
Insights, By Severity of Symptoms: Moderate Hypophosphatasia Continues to Have a Wider Patient Pool
Within the hypophosphatasia treatment market based on severity of symptoms, the moderate segment captures the dominant share. This is primarily attributed to the larger pool of patients that fall within the moderate category. Moderate hypophosphatasia affects individuals with mild to intermediate levels of symptoms that impact mobility and quality of life.
Compared to severe presentations where symptoms are debilitating, a moderate form has a slower progression. This allows for a wider diagnosis window where treatment can be initiated before complete disability occurs.
As symptoms emerge gradually, patients and doctors are more likely to recognize the condition early and start management. Early intervention plays an important role in modifying disease course and outcomes for moderate hypophosphatasia patients.
In addition, a moderate disease state is more conducive to long term treatment compliance compared to severe or mild forms. Patients are motivated to adhere to lifelong therapy to prevent worsening and maintain acceptable functionality. This supports sustained usage of hypophosphatasia drugs and nutritional supplements. The slow but steady symptom progression also means regular monitoring and adjustments can be made to therapy over time.
Overall, the prevalence of moderate hypophosphatasia cases coupled with opportunities for early detection and treatment drive its leadership position compared to other severity categories. Close healthcare supervision and medication compliance further contribute to its high market dominance potential.
The major players operating in the hypophosphatasia treatment market include AstraZeneca (Alexion Pharmaceuticals), AM Pharma, PuREC, Novartis AG and Pfizer.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
Hypophosphatasia Treatment Market is segmented By Disease Type (Childhood onset hypophosphatasia, In...
Hypophosphatasia Treatment Market
How big is the hypophosphatasia treatment market?
The hypophosphatasia treatment market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.94 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 4.25 Bn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the hypophosphatasia treatment market?
The high costs of treatment, such as STRENSIQ, which can exceed USD 1 million annually and limited options for milder or adult-onset cases, leading to suboptimal outcomes are the major factor hampering the growth of the Hypophosphatasia Treatment Market.
What are the major factors driving the hypophosphatasia treatment market growth?
The growing awareness of genetic screening driving early diagnosis and introduction of novel therapies like asfotase alfa for severe cases are the major factor driving the hypophosphatasia treatment market.
Which is the leading disease type in the hypophosphatasia treatment market?
The leading disease type segment is childhood onset hypophosphatasia.
Which are the major players operating in the hypophosphatasia treatment market?
AstraZeneca (Alexion Pharmaceuticals), AM Pharma, PuREC, Novartis AG, and Pfizer are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the hypophosphatasia treatment market?
The CAGR of the hypophosphatasia treatment market is projected to be 5.4% from 2025-2032.