

The intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.10 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 1.90 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.1% from 2025 to 2032. The intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market is experiencing positive growth owing to rising prevalence of liver cancer worldwide. Many biopharmaceutical companies are heavily investing in clinical trials to evaluate new drugs for improved patient outcomes. Recent approval of targeted therapy drugs has provided promising treatment options.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR8.1%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 8.1% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Bayer AG, Incyte Corporation, Novartis AG, AstraZeneca, Taiho Pharmaceutical and Among Others |
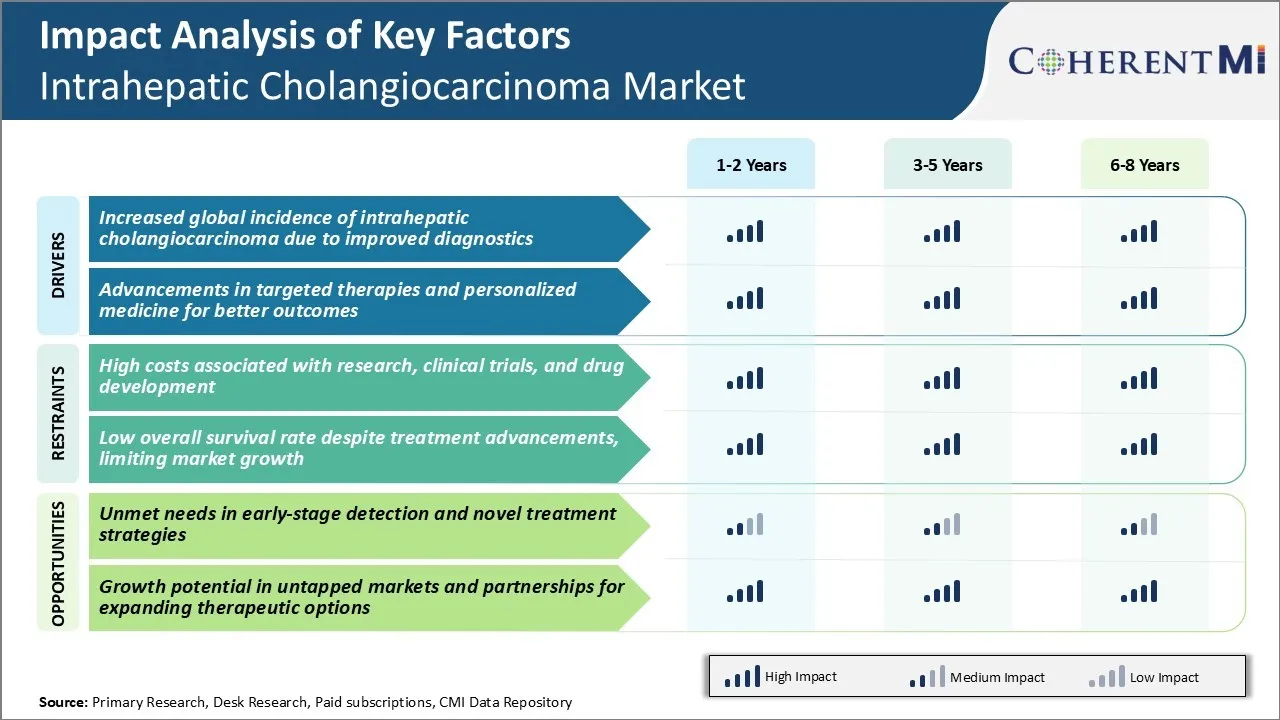
Market Driver - Increased Global Incidence of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma due to Improved Diagnostics
With advancements in medical imaging technologies and diagnostic tools, more cases of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) are being identified globally. Factors such as rising awareness among medical professionals, wider availability of diagnostic modalities and growing emphasis on early diagnosis have played a pivotal role in identifying previously under-diagnosed ICC cases across different regions.
Multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have become standard first-line tools for evaluation of biliary abnormalities. Compared to older generation scanners, current MDCT and MRI systems provide high resolution images that allow clear distinction between ICC and other liver lesions.
Equally important has been the refinement of biochemical markers and tumor markers that signal the presence of ICC. For instance, serum levels of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA 19-9) are routinely measured due to its high specificity for cholangiocarcinoma.
Widespread adoption of these improved diagnostic methods by healthcare facilities globally has inevitably led to discovery of previously undetected ICC cases. This is evidenced by registries showing rising incidence rates of ICC over the past two decades across different world regions. Improved diagnostics are hence considered a key driver for the growth of the overall intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market.
Market Driver - Advancements in Targeted Therapies and Personalized Medicine for Better Outcomes
Significant progress has been made in understanding the molecular mechanisms and genetic alterations underlying intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC). Novel targeted agents are in various stages of development and evaluation, bringing hope for improving clinical outcomes which have historically been very poor with conventional chemotherapy.
For example, abnormalities in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway are present in approximately 50% of ICC cases. Several EGFR inhibitors have exhibited anti-tumor activity against EGFR-driven ICC in early clinical trials. Other frequently altered molecular pathways in ICC like the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and the fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) pathways are also being therapeutically targeted.
The ongoing biomarker-driven clinical evaluations of these molecularly targeted agents aim to establish molecular profiling as a standard of care for determining best targeted treatment options based on each patient's tumor genetics.
As targeted therapies demonstrate promising results and molecular diagnostics become more widespread, personalized medicine looks poised to play an increasingly important role in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma care pathways. This represents a ray of hope for the disease and is anticipated to drive higher demand for newer targeted agents and related services.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High Costs Associated with Research, Clinical Trials, and Drug Development
One of the major challenges faced by players in the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market is the extremely high costs involved in research, clinical trials, and drug development. Cancer research and drug development is an expensive process, and developing therapies for rare cancers like intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma poses even greater financial challenges due to the relatively small patient population and market size.
Developing a new cancer drug and conducting the requisite clinical trials to prove its safety and efficacy before receiving regulatory approval often costs hundreds of millions, and sometimes even over a billion dollars. With limited private funding available for orphan diseases, pharmaceutical companies are hesitant to invest extensively in areas like ICC where the potential returns may not justify the high costs.
Additionally, clinical trials for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma drugs often require multi-center studies across countries due to the low incidence of cases in individual locations, further driving up costs. The financial challenges disincentivize extensive R&D into new treatment strategies for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Market Opportunity - Unmet Needs in Early-stage Detection and Novel Treatment Strategies
One of the key opportunities in the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market lies in addressing the large unmet needs that exist in early detection and treatment of the disease. Currently, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma often goes undetected until it has reached an advanced stage due to non-specific symptoms and a lack of adequate screening and diagnostic tools. By the time the cancer is diagnosed, the five-year survival rate drastically drops to less than 10%.
The development of novel biomarkers and imaging modalities that enable earlier and more accurate detection of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomahas significant potential to improve patient outcomes and quality of life by allowing for prompt treatment intervention. There also exists a major need for additional therapeutic innovations beyond the current standard of care, such as immune-targeted therapies and molecularly-driven targeted therapies.
Promising treatment strategies continue to emerge from ongoing clinical research, representing opportunities for companies to develop first- or best-in-class therapies addressing key molecular drivers and pathways of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma tumor growth. Novel drugs demonstrating clear efficacy over existing options could achieve commercial success in the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market.
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is typically treated with chemotherapy, either alone or along with other therapies such as surgery or radiation, depending on the stage of cancer. For early-stage intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (Stage I/II), surgery to remove the tumor is the primary treatment option. For more advanced stages (III/IV) where the cancer has spread, chemotherapy is preferred.
The first-line chemotherapy regimen commonly prescribed includes gemcitabine and cisplatin. Brand names for these drugs include Gemzar and Platinol, respectively. Recent clinical trials have shown that combining gemcitabine and cisplatin provides a modest increase in median overall survival compared to gemcitabine alone. For patients who progress on or are intolerant to the gemcitabine/cisplatin combination, second-line treatments often involve single-agent chemotherapy options like gemcitabine, capecitabine (Xeloda), or oxaliplatin (Eloxatin).
For advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomathat is no longer responding to platinum-based chemotherapy agents, newer targeted therapies and immunotherapy drugs are beginning to play a role. For example, clinical data supports using the FGFR inhibitor Pemazyre (pemigatinib) for FGF/FGFR marker-positive, advanced/metastatic intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomaafter prior chemotherapy. The PD-1 inhibitor Keytruda (pembrolizumab) is also approved as a subsequent therapy for microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) can be categorized into early, locally advanced, and metastatic stages.
For early stage localized intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, surgical resection offers the best chance of cure if the tumor can be completely removed. The surgery may involve removing the part of the liver containing the tumor (partial hepatectomy) or the entire liver (liver transplant).
For patients who cannot undergo surgery, ablation techniques like radiofrequency ablation can be considered.
For locally advanced but unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, chemotherapy combined with radiation therapy (chemoradiation) is the standard first-line treatment. Gemcitabine plus cisplatin is the preferred chemotherapy regimen for this stage. It has shown favorable results with a median overall survival of 11.7 months in phase III clinical trials.
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is also gaining acceptance for precise localized treatment with fewer side effects compared to traditional radiation.
For metastatic intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, first-line treatment involves chemotherapy like gemcitabine plus cisplatin.
Second-line options after progression include regorafenib tablets and capecitabine. Regorafenib was the first drug to show a survival benefit in second-line setting with a median overall survival of 10.6 months compared to 7.8 months for placebo in clinical trials. Capecitabine helps control symptoms and delays disease progression in some patients.
Product Innovation: One of the most effective strategies adopted by major players like Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte Corporation, and Aslan Pharmaceuticals has been continuous investment and focus on product innovation. For example, in 2018 Bristol-Myers Squibb received FDA approval for Opdivo (nivolumab) for previously treated advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Acquisitions & Partnerships: Players have strategically acquired or partnered with biotech companies developing promising drug candidates to gain access to new pipeline assets and technologies. For example, in 2019 Incyte partnered with Epizyme to develop and commercialize epithelioid sarcoma drug tazemetostat. Similarly, Aslan Pharmaceuticals partnered with CSL for global development of ASLAN004, a novel monoclonal antibody for biliary tract cancer.
Clinical Trial Excellence: Well-designed and efficiently conducted clinical trials have helped establish certain drugs as standards of care. For example, between 2016-18 Roche/Genentech published results from the phase 3 clinical trial of atezolizumab showing improvements in overall survival for previously treated patients.
Aggressive Commercialization: Players generate significant revenues through rapid commercialization approvals and strong sales operations. For example, in the U.S. Bristol-Myers Squibb launched Opdivo for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma within 4 months of FDA approval, quickly establishing it in the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market. A coordinated commercial strategy amplified its revenues from the drug.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
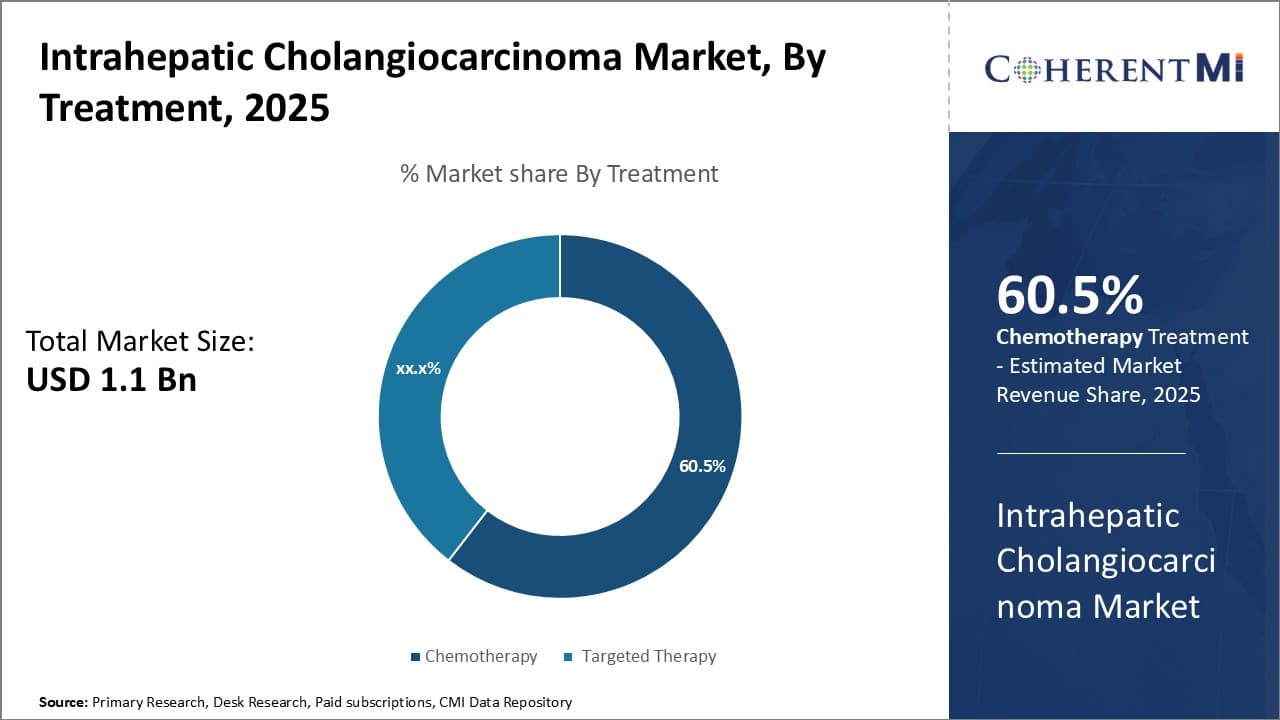
Insights, By Treatment: Dominance of Chemotherapy in Treating Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
In terms of treatment, chemotherapy is projected to hold 60.5% share of the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market in 2025, owning to its ability to target fast-growing or quickly dividing cancer cells throughout the body. Chemotherapy works by interfering with cancer cell division and inhibiting tumor growth. As intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is usually diagnosed at an advanced stage, chemotherapy serves as an important first-line treatment approach to reduce tumor burden before surgery is considered.
The availability of various chemotherapeutic drug regimens allows oncologists to tailor treatment based on individual patient's disease characteristics and tolerability. Gemcitabine-based combinations remain a standard treatment and have shown improved outcomes compared to gemcitabine alone.
However, side effects of chemotherapy such as nausea, fatigue, and suppressed immunity continue to challenge patient compliance. Ongoing research on improving treatment efficacy while reducing toxicity can further solidify the lead position of chemotherapy in managing this cancer type.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
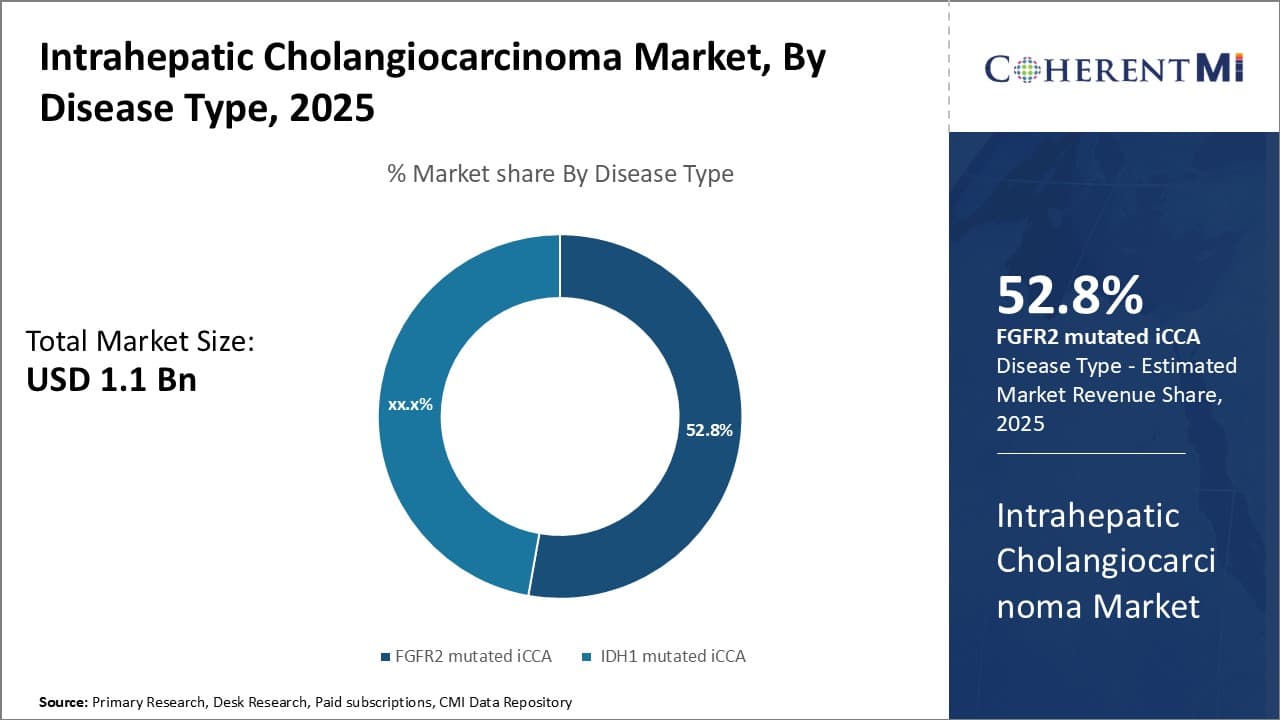
Insights, By Disease Type: The Rise of FGFR2 Mutated iCCA as the Major Subtype
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Disease Type: The Rise of FGFR2 Mutated iCCA as the Major Subtype
In terms of Disease Type, FGFR2 mutated iCCA is expected to account for 52.8% share of the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market in 2025, owing to its high prevalence over other subtypes such as IDH1 mutated iCCA. Recent genomic studies have found that around 15-30% of iCCA cases carry a genetic mutation in FGFR2, with the mutation selectively activating the FGFR2 signaling pathway involved in cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis. This subtype has been associated with poor prognosis and limited treatment options.
However, emerging targeted therapies blocking the FGFR2 pathway hold promise to fill this unmet need. Pharmaceutical companies have accelerated development of FGFR inhibitors relevant to FGFR2 mutated iCCA based on its significant representation as the largest subgroup within the iCCA patient population. A better understanding of the underlying biology driving FGFR2 dependent tumors allows for tailored treatment approaches to improve clinical outcomes.
Insights, By Route of Administration: Oral Administration Dominates Route of Administration in iCCA
In terms of route of administration, oral route contributes the highest share of the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market owing to advantages over intravenous and subcutaneous options. Patients prefer oral medication due to ease of self-administration at home without need for frequent hospital visits. This removes the infrastructure needs and medical supervision associated with intravenous therapy. While oral bioavailability is a concern for some drugs, formulation advances continue to enhance absorption.
Moreover, oral drugs prevent uncomfortable sensations from injection and lower risk of blood-borne infections compared to subcutaneous route. Healthcare providers also find oral treatment more cost-effective and convenient for long-term use. Thus, the simplicity, safety and increased accessibility afforded by oral administration make it the favored choice amongst route options for managing intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
The major players operating in the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market include Bayer AG, Incyte Corporation, Novartis AG, AstraZeneca, Taiho Pharmaceutical, TransThera Biosciences, J-Pharma Co., Ltd., Nuvectis Pharma, Inc., Zymeworks, and Agios Pharmaceuticals.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Market is segmented By Treatment (Chemotherapy, Targeted Therapy), B...
Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Market
How big is the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market?
The intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.10 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 1.90 billion by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market?
High costs associated with research, clinical trials, and drug development, and low overall survival rate despite treatment advancements are the major factors hampering the growth of the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market.
What are the major factors driving the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market growth?
Increased global incidence of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma due to improved diagnostics and advancements in targeted therapies and personalized medicine for better outcomes are the major factors driving the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market.
Which is the leading treatment in the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market?
The leading treatment segment is chemotherapy.
Which are the major players operating in the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market?
Bayer AG, Incyte Corporation, Novartis AG, AstraZeneca, Taiho Pharmaceutical, TransThera Biosciences, J-Pharma Co., Ltd., Nuvectis Pharma, Inc., Zymeworks, and Agios Pharmaceuticals are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market?
The CAGR of the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma market is projected to be 8.1% from 2025-2032.