Microbiome Therapeutics Whitespace Analysis Market Trends
Market Driver - Advancement in microbiome-related technologies
With each passing year, our understanding of the human microbiome and the intricate role it plays in health and disease is expanding greatly due to monumental advancements in microbiome-related technologies. Technologies like next generation sequencing have enabled researchers to characterization the composition of microbial communities in the human body at an unprecedented scale and resolution. This has led to valuable insights into how changes in the microbiome are linked to several disorders. Additionally, advances in bioinformatics and computational techniques are helping researchers analyze massive microbiome datasets and identify subtle changes and patterns that can potentially serve as biomarkers.
New sampling and culturing techniques are also allowing researchers to capture a more complete view of the microbes colonizing different body sites. Microfluidic devices and microfabrication methods are enhancing our ability to study microbial interactions ex-vivo. Such technological capabilities are fueling exploration of novel mechanisms through which the microbiome influences multiple physiological processes. They are demonstrating the immense clinical potential of modulating gut microbes to promote human health. The elucidation of specific microbiome-derived metabolites, molecules and pathways involved in microbiome-host communication is opening up exciting opportunities for development of precision microbiome-based therapies.
Platforms for microbiome engineering through targeted introductions or enhancements of beneficial bacteria are also progressing steadily. Proof-of-concept studies illustrate the feasibility of microbiota transplantation approaches to restore microbial diversity. Advances in synthetic and systems biology are bringing us closer to design of "next-generation" probiotics with enhanced stability and defined mechanisms of action. Continuous technological breakthroughs in areas like microbiome analysis, modeling, engineering and therapeutics delivery are strengthening the scientific foundations for microbiome-based applications. They hold tremendous promise to transform the diagnosis, monitoring and treatment of numerous chronic as well as complex disorders in the future.
Growing awareness of gut-brain axis
In recent years, there is an significant increase in public and scientific recognition of the existence of a bidirectional communication pathway between the gut and the brain, commonly referred as the gut-brain axis. Extensive research has demonstrated that gut microbiota plays a crucial role in modulating this gut-brain signaling and thereby influences brain functions as well as multiple aspects of behavior, mood and cognition. Although still an emerging field of research, studies have implicated gut microbiota in regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity, production of neuroactive substances like serotonin, GABA and dopamine as well as development and function of the central nervous system.
Simultaneously, mass media coverage of research elucidating links between alterations in gut microbiota and psychiatric conditions like autism, depression, anxiety and Alzheimer's disease has resonated strongly with the general population. Several best-selling books, magazine articles and documentaries aimed at public audiences have drawn attention to the potential clinical applications of modulating gut bacteria to treat brain-related dysfunctions. Personalized nutrition companies marketing microbiome-based products have also successfully leveraged consumer interest in the gut-brain axis concept. Retail availability of non-regulated probiotic supplements claiming benefits such as relief from stress or mental clarity underline the commercialization of this field.
The growing awareness among both healthcare practitioners and the public at large regarding the far-reaching implications of the gut-brain communication pathway is an important factor driving further R&D in microbiome-based diagnostics and therapeutics. It is contributing to higher patient engagement for clinical studies evaluating microbiota-targeted therapies for neurological and neuropsychiatric conditions. Overall, the substantial publicity surrounding the concept of gut-brain axis in mainstream press over the past few years has spurred expectations regarding development of meaningful microbiome-based interventions for central nervous system health.
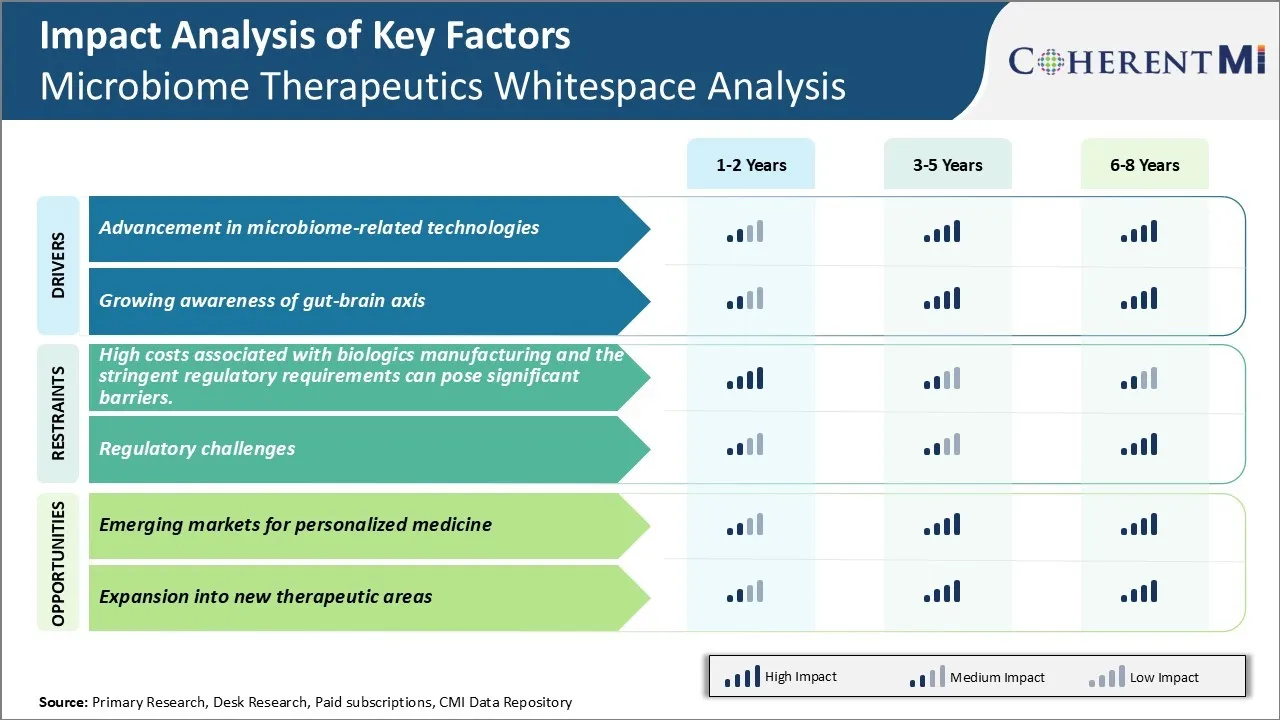
Challenge: High costs associated with biologics manufacturing and stringent regulatory requirements
For microbiome therapeutics to reach its true potential as an innovative medical technology, significant challenges around the high costs of biologics manufacturing and stringent regulatory requirements must be addressed. Developing live biotherapeutic products that are tailored to an individual's microbiome is an intricate process that involves culturing specific microbial strains under tightly controlled conditions. This custom manufacturing approach results in high production expenses that are exacerbated by costly good manufacturing practices (GMP) compliance. Additional expenses arise from extensive preclinical and clinical testing that is mandated by regulatory agencies given that these products contain live organisms. Meeting all regulatory expectations can prolong development timelines and raise the financial investment required to bring a microbiome therapeutic to market. These interlinked challenges of high manufacturing costs and rigorous regulatory oversight threaten the commercial viability of personalized microbiome medicines if they translate to prohibitively high drug prices. Concerted efforts are needed from stakeholders across industry, science and policy to drive innovations that reduce production expenses and create clearer, less risk-averse pathways to approval.
Opportunity: Emerging markets for personalized medicine
The nascent field of microbiome therapeutics is positioned to drive significant advancements in the promising area of personalized medicine. By giving clinicians the ability to precisely characterize an individual's gut microbial composition and then design targeted microbiome-modulating interventions, this area opens up opportunities to move away from a "one-size-fits-all" approach to treatment. Microbiome profiling technologies continue to mature, enhancing opportunities to identify microbiome signatures associated with various human diseases. In turn, this improves the chances of developing microbiome diagnostic tests and personalized microbiome medicines. Whereas current drug development has largely pursued population-level solutions, microbiome therapies provide a pathway for truly individualized treatments tailored for a patient's distinct genetic and microbiome profiles. As scientific validation and clinical studies accumulate demonstrating the efficacy of microbiome interventions, emerging opportunities exist for first-mover companies to establish their technologies and expertise in supporting personalized care approaches. The future potential market appears sizable as microbiome-based personalized medicines begin making inroads against major global health issues.