

The nasopharyngeal cancer market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.62 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 2.74 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2025 to 2032. The nasopharyngeal cancer market is expected to witness steady growth over the forecast period. This can be attributed to the increasing prevalence of nasopharyngeal cancer worldwide and growing awareness about the disease.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR7.8%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 7.8% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Novartis, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, Coherus BioSciences and Among Others |
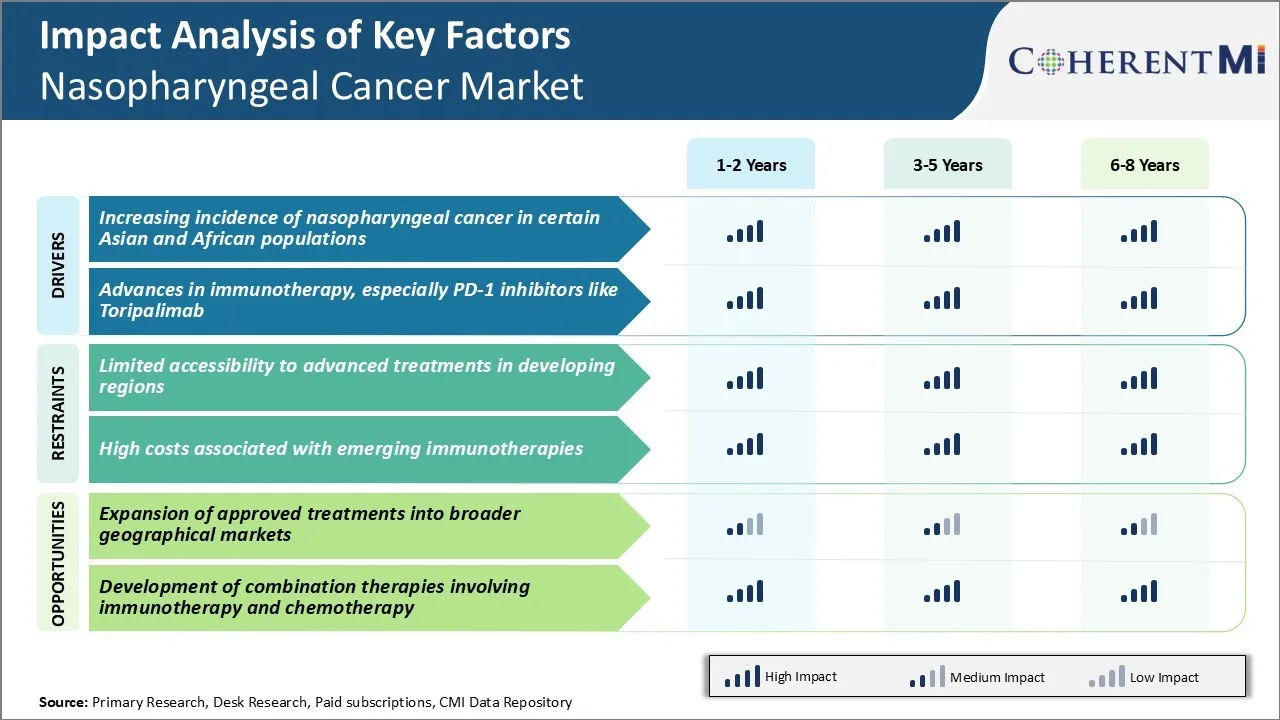
Market Driver - Increasing Incidence of Nasopharyngeal Cancer in Certain Asian and African Populations
The incidence of nasopharyngeal cancer has been on the rise particularly in certain parts of Asia and Africa. The highest incidence rates globally are witnessed in Southern China, where nasopharyngeal cancer affects around 20-50 individuals per 100,000 population. The autonomous region of Guangdong has one of the highest rates globally with over 30 cases per 100,000 individuals.
Other high-risk areas include Southeast Asia, parts of the Mediterranean, Middle East, and North Africa. Genetic studies have revealed that certain human leukocyte antigen (HLA) haplotypes predispose to higher cancer risks. Exposure to carcinogenic factors like preserved foods and smoke also raise risks, especially in traditionally preserved dietary practices.
The persistence of environmental risks coupled with genetic predispositions have ensured that nasopharyngeal cancer rates remain stubbornly high in these populations. While lifestyle changes and reduced environmental exposures have led to partial declines over time, the disease burden still severe. For instance, over 80% of new nasopharyngeal cancer cases in China occur in the southern provinces. Early detection also continues to pose a challenge given the location of the disease. All these factors have kept the number of new patients rising each year, further fueling the nasopharyngeal cancer market for diagnosis and treatment solutions.
Market Driver - Advances in Immunotherapy, Especially PD-1 Inhibitors Like Toripalimab
Immunotherapy has significantly advanced the treatment landscape for nasopharyngeal cancer in recent times. Checkpoint inhibitors targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 pathways have shown promising results. Drugs like toripalimab that block the PD-1 receptor have gained attention due to favorable clinical trial outcomes. In a phase 2 study, toripalimab monotherapy produced an objective response rate of 36% in recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal cancer. It also demonstrated a durable response exceeding 16 months in some patients.
Based on these results, toripalimab received approval in China in 2021 as the first PD-1 inhibitor globally for recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal cancer with no suitable chemotherapy options. The success of toripalimab has intensified research on other checkpoint modulators too. Drugs targeting complementary pathways like LAG-3 and TIGIT are under testing. Combining agents addressing different brakes is an attractive strategy to enhance responses.
Early results prove encouraging in boosting response rates and durations over single agents alone. These advances will facilitate customized immunotherapy selections and sequence options to optimize treatment for different patient situations. The field is still evolving at a rapid pace, bringing novel treatment options to strengthen patient management.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - Limitations to Accessibility of Advanced Treatments in Developing Regions
One of the key challenges facing the nasopharyngeal cancer market is the limited accessibility to advanced treatments in developing regions. Nasopharyngeal cancer incidence rates are highest in parts of Asia such as Southern China, Southeast Asia, and North Africa.
However, many developing countries in these regions still have limited access to modern treatment modalities such as intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and targeted therapy drugs. IMRT is now considered the standard of care for nasopharyngeal cancer, as it allows for higher and more precise radiation doses to be delivered to the tumor while minimizing damage to surrounding normal tissues.
However, IMRT requires sophisticated radiation equipment that may not be widely available or affordable for many hospitals in developing parts of Asia and Africa. Similarly, targeted therapies such as cetuximab that have improved treatment outcomes in endemic regions when combined with IMRT are often not registered or reimbursed.
The high cost of such treatments presents a significant barrier to access for patients in the public healthcare systems of these low and middle-income countries. This limited availability of advanced treatments threatens to further widen disparities in survival outcomes for nasopharyngeal cancer patients based on their country of residence and economic status.
Market Opportunity - Expansion of Approved Treatments into Broader Geographical Markets
One major opportunity for the nasopharyngeal cancer market is the potential expansion of approved treatments into broader geographical markets. As discussed earlier, incidence rates of nasopharyngeal cancer exhibit strong regional variations with the highest rates concentrated in Asia and parts of Africa.
However, many currently available therapies are only approved and reimbursed in limited major markets like the United States and Europe. There is scope to pursue broader international registrations and reimbursement approvals for therapies such as IMRT and targeted drugs in regions that account for a large burden of nasopharyngeal cancer cases but limited treatment access.
For instance, major pharmaceutical players can explore obtaining regulatory approvals and building partnerships to market and distribute drugs in high incidence Asian countries. Similarly, equipment vendors may seek to expand the availability of IMRT technologies in developing Asian and African markets through technology transfers and customized financing schemes. Such initiatives can help address an important unmet need and also open up potentially significant incremental revenues for companies.
Nasopharyngeal cancer treatment often starts with chemotherapy and radiation therapy for localized stage I-II disease. Prescribers commonly prefer a platinum-based chemotherapy regimen such as cisplatin (Platinol) either alone or combined with 5-FU (Adrucil). Radiation therapy typically comprises intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) delivered as daily fractions to the head and neck region.
For more advanced stage III-IVB cancers, multi-agent chemotherapy prior to concurrent chemoradiation is the standard first-line treatment. The preferred regimen involves cisplatin with a taxane such as docetaxel (Taxotere) or paclitaxel (Paclitaxel, Abraxane). This is followed by cisplatin-based chemoradiation. Some prescribers also recommend adding targeting agents like cetuximab (Erbitux) or nivolumab (Opdivo) to address higher relapse risks.
Upon relapse or metastasis, single-agent chemotherapy is commonly used. Prescribers favored options include carboplatin (Paraplatin), gemcitabine (Gemzar), or paclitaxel. For palliative care, prescribers may choose a less toxic regimen like fluorouracil. Additionally, prescribers consider factors like performance status, organ involvement, line of treatment and prior therapies when selecting the appropriate regimen. Overall regimen tolerability and toxicity profiles also play an important role in prescribers' decisions.
Nasopharyngeal cancer is staged from stage I to stage IV based on tumor size and spread. Stage I involves a small tumor only in the nasopharynx, while stage IV means the cancer has spread widely.
For Stage I-II disease, the primary treatment is radiation therapy, which can be either external beam radiation or brachytherapy (internal radiation). Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) is commonly used to better target the tumor and spare surrounding healthy tissues. Chemotherapy may be added for larger Stage II tumors.
For Stage III-IVA disease, the standard of care is concurrent chemotherapy and IMRT. Platinum-based drugs like cisplatin or carboplatin are generally given weekly with radiation. This more aggressive chemoradiation approach helps control both the primary tumor and any nearby lymph node involvement.
For recurrent or persistent locally-advanced disease after chemoradiation, Salvage surgery may provide a chance of cure if the recurrence is localized. Otherwise, palliative chemotherapy is used with cytotoxic drugs such as taxanes, gemcitabine or 5-fluorouracil either alone or in combinations.
For metastatic Stage IVB disease, platinum-based palliative chemotherapy remains the mainstay of treatment to alleviate symptoms and prolong survival. Combinations including paclitaxel, gemcitabine or 5-fluorouracil are commonly used.
Focus on innovations in diagnosis and treatment:
One of the main strategies adopted by leading players like Sanofi, Merck & Co., and Bristol-Myers Squibb has been focusing on R&D to develop more effective and targeted therapies for nasopharyngeal cancer. For example, in 2020, Merck & Co. received FDA approval for KEYTRUDA (pembrolizumab) for the treatment of recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Expand into emerging markets:
As the prevalence of nasopharyngeal cancer is higher in certain Asian countries, players like Sanofi have focused on expanding their presence and access to therapies in emerging markets like China and Southeast Asian nations. For example, in 2015, Sanofi partnered with a Chinese company to commercialize Taxotere for NPC in China.
Strategic M&A activities:
Companies have also pursued strategic mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their oncology portfolios and pipelines. For instance, in 2019, Bristol-Myers Squibb acquired Celgene Corporation for $74 billion, gaining access to the blockbuster drug Revlimid and a strong early-stage NPC drug candidate liso-cel. Such deals enable players to quickly boost their capabilities and offerings in oncology, including for nasopharyngeal cancer.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
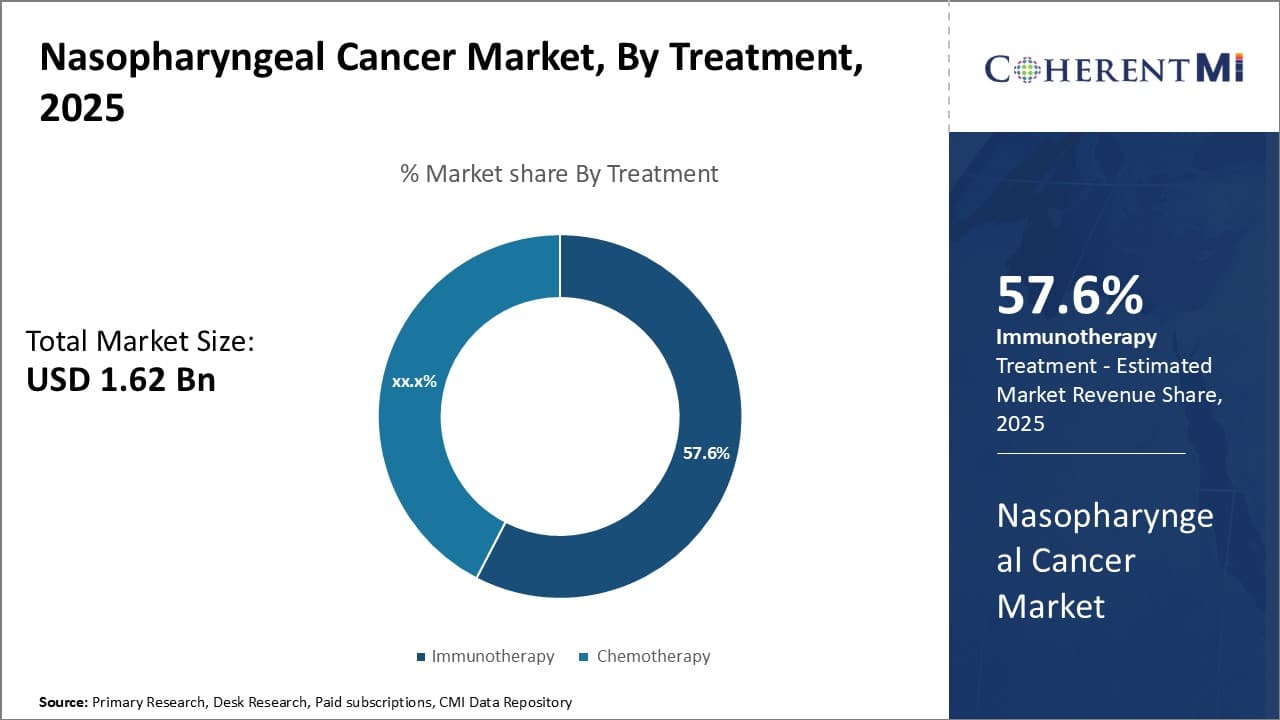
Insights, By Treatment: Advances in Immunotherapy Drive its Dominance in Treatment
In terms of treatment, immunotherapy is expected to account for 57.6% share of the nasopharyngeal cancer market in 2025, owning to significant advances being made in the area. Immunotherapy involves harnessing the body's own immune system to fight cancer and has emerged as a promising treatment option for nasopharyngeal cancer in recent years. Several immunotherapies are being explored that aim to release the brakes on immune responses against tumors.
Checkpoint inhibitors that target molecules like PD-1 and PD-L1 have shown success in clinical trials at improving survival. Drugs like Toripalimab have gained regulatory approvals in some markets for recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal cancer based on phase 3 trial results demonstrating superior response rates over chemotherapy.
The non-toxic nature and durability of responses provided by immunotherapies make them an attractive option for patients. They also allow combinations with other therapies like chemotherapy and radiation for improved outcomes. Research continues on combinations as well as newer immuno-oncology targets and modalities. Cell therapies utilizing engineered T cells directed at tumor-associated antigens show promise.
As understanding of tumor microenvironments and immune evasion mechanisms deepens, more biomarkers and combination regimens are being explored to make immunotherapy more effective. Its superior efficacy and safety profile compared to chemotherapy have driven increased adoption in treatment of nasopharyngeal cancer. Widespread approvals and reimbursements are further catalyzing the growth of immunotherapy segment.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
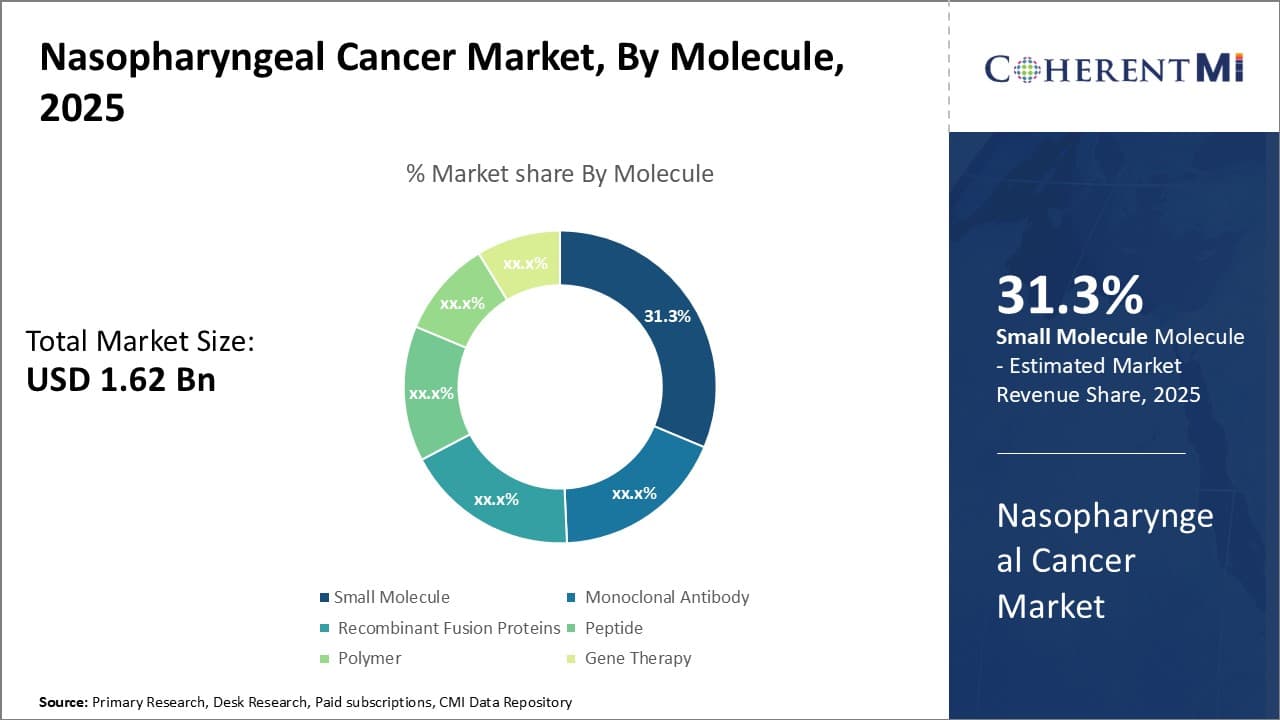
Insights, By Molecule: Small Molecules Lead Drug Pipeline Segment
In terms of molecule, small molecules is projected to hold 31.3% share of the nasopharyngeal cancer market in 2025. Several advantages make small molecule drugs popular in oncology. They have well-defined chemical properties and are usually administered orally, enabling outpatient use and improved convenience. Being low molecular weight, they also show good tissue penetration and oral bioavailability. Their discrete structures allow targeted modulation of specific proteins and receptor sites in cellular pathways to achieve anticancer effects.
Compared to biologics, small molecules also have lower production costs and greater manufacturing scalability. Several small molecule inhibitors developed by major pharmaceutical companies are in late-stage trials for nasopharyngeal cancer. These target critical nodes in growth signaling and cell cycle regulation altered in the disease, such as EGFR, MAPK, CDK, PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Hedgehog pathways. Their well-studied mechanism of actions and structurally optimized leads provide confidence in achieving proof-of-concept.
If successful, these oral targeted therapies can replace injectable options and chemotherapy as first-line or maintenance regimens. Their competitive advantages over biologics in cost and development timeframe is stimulating increased R&D on small molecule anti-cancer drugs.
Insights, By Drug Pipeline: Monoclonal Antibodies Take Lead in Pipeline
In terms of drug pipeline, monoclonal antibodies contribute the highest share owing to their exquisite target specificity and clinical success. They are engineered versions of immune system proteins that can identify tumor antigens and recruit immune effector cells for a coordinated attack.
Monoclonal antibodies have revolutionized cancer treatment over the last decade with blockbuster drugs against diverse cancers. In nasopharyngeal cancer, they are being evaluated alone as well as combined with chemotherapy or immunotherapies.
Drugs like Nivolumab, Pembrolizumab and Camrelizumab that block immune checkpoint molecules PD-1 and PD-L1 have shown promise. Phase 3 trials on Camrelizumab led to its approval in China based on improved progression-free survival. Others in development target proteins vital for tumor growth and spread like VEGF (Bevacizumab) or immune modulators like 4-1BB. Their ability to tag multiple types of tumor cells for destruction drives durable remissions.
Progress in recombinant DNA technology, humanization and conjugation with payloads further enhance efficacy. Sustained focus on biomarkers to identify patients most likely to respond increases potential of monoclonal antibodies to transform treatment landscape in nasopharyngeal cancer.
The major players operating in the nasopharyngeal cancer market include Novartis, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, Coherus BioSciences, SystImmune, Takeda, Ascentage Pharma, I-Mab Biopharma, Innovent Biologics, Alphamab Oncology, Merck & Co., Inc., and GlaxoSmithKline.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Nasopharyngeal Cancer Market is segmented By Treatment (Immunotherapy, Chemotherapy), By Molecule (S...
Nasopharyngeal Cancer Market
How big is the nasopharyngeal cancer market?
The nasopharyngeal cancer market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.62 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 2.74 Bn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the nasopharyngeal cancer market?
Limited accessibility to advanced treatments in developing regions and high costs associated with emerging immunotherapies are the major factors hampering the growth of the nasopharyngeal cancer market.
What are the major factors driving the nasopharyngeal cancer market growth?
Increasing incidence of nasopharyngeal cancer in certain Asian and African populations and advances in immunotherapy, especially pd-1 inhibitors like Toripalimab are the major factors driving the nasopharyngeal cancer market.
Which is the leading treatment in the nasopharyngeal cancer market?
The leading treatment segment is immunotherapy.
Which are the major players operating in the nasopharyngeal cancer market?
Novartis, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, Coherus BioSciences, SystImmune, Takeda, Ascentage Pharma, I-Mab Biopharma, Innovent Biologics, Alphamab Oncology, Merck & Co., Inc., and GlaxoSmithKline are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the nasopharyngeal cancer market?
The CAGR of the nasopharyngeal cancer market is projected to be 7.8% from 2025-2032.