

The neuroendocrine prostate cancer market is estimated to be valued at USD 1034.5 Mn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 1694.1 Mn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% from 2025 to 2032. The increasing prevalence of prostate cancer globally is expected to drive the demand for effective treatment options.
Market Size in USD Mn
CAGR7.3%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 7.3% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Amgen, BioXcel Therapeutics, Oric Pharmaceuticals, Xencor, Astellas Pharma/Medivation and Among Others |
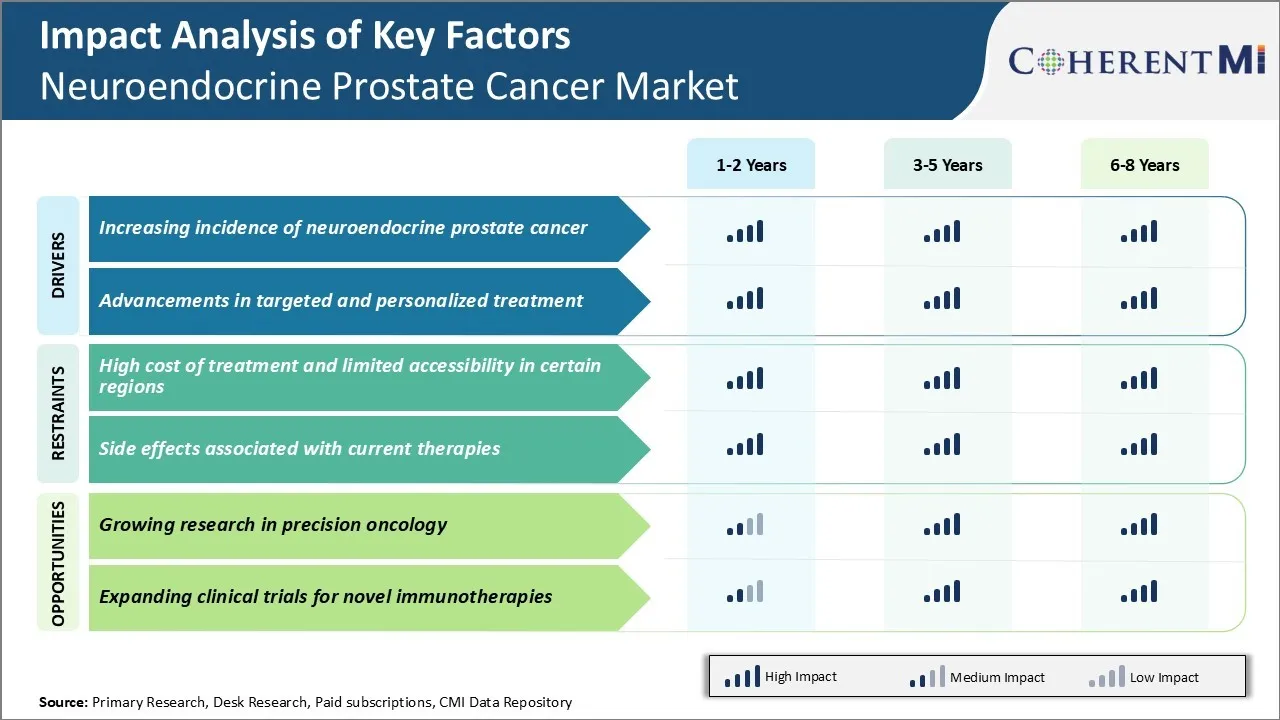
Market Driver - Increasing Incidence of Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer
Cases of neuroendocrine prostate cancer have shown a steady rise in recent years. This rare and aggressive form of prostate cancer is becoming more prevalent majorly due to increasing risk factors in modern lifestyles. Current estimates show that around 5-10% of metastatic prostate cancers progress to this neuroendocrine stage. This is attributed to changes in cellular machinery as a result of androgen deprivation therapy.
Prolonged use of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) has proven to drive this progression for many patients, especially those with multiple comorbidities and chronic illnesses. Lifestyle elements including obesity, lack of physical activity, certain genetic mutations and family history also increase susceptibility. Advanced age is a predominant contributor as well, considering more than 60% prostate cancers are diagnosed in men aged 65 or older.
Developing nations are witnessing faster aging of the male population compared to developed economies over the last couple of decades. Additionally, improved diagnostics and surveillance methods have enabled earlier detection of neuroendocrine traits in many patients previously deemed responsive to standard hormone therapy.
Market Driver - Advancements in Targeted and Personalized Treatment
Major pharmaceutical companies and biotech startups have shown intense focus on developing effective treatment alternatives for neuroendocrine prostate cancer in the recent past. The unmet need in this area opened opportunities for research in precision oncology and biomarker-driven approaches.
Comprehending the molecular underpinnings of the disease better has enabled design of targeted treatment regimens. Several ongoing studies evaluate addition of immune checkpoint inhibitors, PARP inhibitors and angiogenesis inhibitors to standard chemotherapy backbones in select patient groups.
Research involving tumor sequencing, liquid biopsies and biomarker profiling helps recognize prognostic and predictive markers to guide personalized strategies. Some patients may respond well to agents inhibiting AR signaling via novel mechanisms or targeting neuroendocrine differentiated cells specifically.
A few clinical studies even explore multikinase inhibitors, BET inhibitors, and HDAC inhibitors for their activity against neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Further trials evaluate safety and efficacy of vaccine therapies designed to trigger anti-tumor immune responses. Such advancements promise better outcomes through right treatment for the right patient at the right time. This is certainly stimulating increased demand for advanced diagnostic tests and companion therapeutics in the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High Cost of Treatment and Limited Accessibility in Certain Regions
One of the major challenges faced in the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market is the high cost of treatment options available. Neuroendocrine prostate cancer is an aggressive form of prostate cancer with limited treatment alternatives. The primary treatment available is chemotherapy which is often very expensive.
Additionally, many novel targeted therapeutics and immunotherapies that are used for other cancer types are still under clinical trials for neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Even if these new therapies receive regulatory approval, their initial costs will be high given the small patient pool that can afford such treatments.
The out-of-pocket costs for patients not adequately covered by insurance can be prohibitive. Thereby, high cost significantly limits accessibility of effective therapies especially in underdeveloped and developing regions in the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market. With most patients being elderly, affordability of treatment continues to be a major barrier to tackling this lethal form of prostate cancer.
Market Opportunity - Growing Research in Precision Oncology
Rising focus on precision oncology approaches for neuroendocrine prostate cancer presents a major opportunity in neuroendocrine prostate cancer market. Academia and pharmaceutical companies have increased research efforts to better understand the molecular alterations and immune profiles of neuroendocrine prostate cancer.
Several clinical studies are underway to develop biomarkers to predict response as well as identify new drug targets. This growing research has the potential to accelerate development of innovative targeted therapies and immunotherapies. Recent advances in gene sequencing and analysis tools also allow for more precise stratification of patients for clinical trials.
Increased understanding of disease biology through robust biomarkers may help design effective combination regimens. This focus on precision approaches could transform treatment landscape in the coming years with the promise of improved outcomes for select patient subgroups.
Neuroendocrine prostate cancer is an aggressive variant with limited treatment options. For early-stage disease, physicians typically prescribe ADT such as Lupron or Zoladex to suppress testosterone levels. However, most patients eventually progress to castration-resistant NEPC (CR-NEPC).
For patients with CR-NEPC, chemotherapy is the standard first-line treatment. Popular options include Taxotere (docetaxel) administered with prednisone or Jevtana (cabazitaxel) with prednisone. Both have shown to extend survival by 2-3 months compared to mitoxantrone and prednisone. Relevant factors influencing prescribers include the patient's comorbidities, organ function, and performance status.
For those who progress on first-line chemo, physicians may consider newer second-line treatments if the patient's health allows. Targeted radiation drug Lutetium-177-PSMA-617 has demonstrated response in some CR-NEPC patients. Immunotherapies like Opdivo (nivolumab) and Keytruda (pembrolizumab) have also helped a minority, though responses are often short-lived. Enrollment in clinical trials is another option investigated prescribers recommend to eligible patients seeking newer alternatives.
The report provides a comprehensive yet detailed overview of treatment preferences at different NEPC stages with examples of specific medications. Context on factors influencing prescriber decisions is also included.
Neuroendocrine prostate cancer can be classified into small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (SCNC) and large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNC) based on histological features. Treatment options vary depending on the stage of disease.
For localized SCNC or LCNC, patients may undergo surgery to remove the prostate (radical prostatectomy) along with chemotherapy and/or radiation. Drugs like carboplatin and etoposide are commonly used in the identical drug combination as for small cell lung cancer. This involves a platinum-based chemotherapy drug along with an antibiotic chemotherapy drug.
For locally advanced or metastatic NEPC, chemotherapy is the primary treatment option. The standard first-line regimen is carboplatin-etoposide. Some clinicians also add docetaxel, a chemotherapy drug, to improve efficacy. Second-line options include taxanes like cabazitaxel or docetaxel. Newer therapies involving PARP inhibitors like olaparib or immunotherapy with PD-1 inhibitors like pembrolizumab are being studied in clinical trials.
The choice of treatment depends on disease extent, performance status, organ function, prior treatments received, and patient preferences. While chemotherapy aims to prolong survival, novel agents targeting NEPC tumor biology hold promise to improve outcomes through more selective targeting of the disease. Close monitoring is needed due to the aggressiveness of NEPC and likelihood of developing resistance to treatments.
Focus on R&D for new treatment options: Players like Pfizer and Novartis have invested heavily in R&D to develop new targeted therapies for neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC). Pfizer's investments led to the approval of Xtandi (enzalutamide) in 2017, which became the first FDA-approved treatment for metastatic NEPC. Xtandi helped delay disease progression by several months compared to chemotherapy. Novartis is currently evaluating several pipeline candidates like LXS196, an inhibitor of IGF-1R/IR pathways that drive NEPC growth.
Partnerships and collaborations: Companies in the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market often partner to leverage each other's strengths and expedite drug development. For example, in 2018, Novartis partnered with Trigger Pharma to develop TRG-1901, a PI3K inhibitor, for NEPC. In 2021, LegoChem Biosciences partnered with IPSEN to develop LCB71, an antagonist of N-glycan biosynthesis, for NEPC. Such partnerships help mitigate risks and costs associated with late-stage R&D.
Acquisitions to gain early access to pipelines: Some players make strategic acquisitions to expand their oncology portfolios. For example, in 2021, Pfizer acquired Trillium Therapeutics, giving it access to innovative pipeline assets like TTI-621, a SIRPaFc fusion protein in Phase 1 for relapsed/refractory hematologic malignancies including NEPC. This strengthened Pfizer's leadership in prostate cancer therapies.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
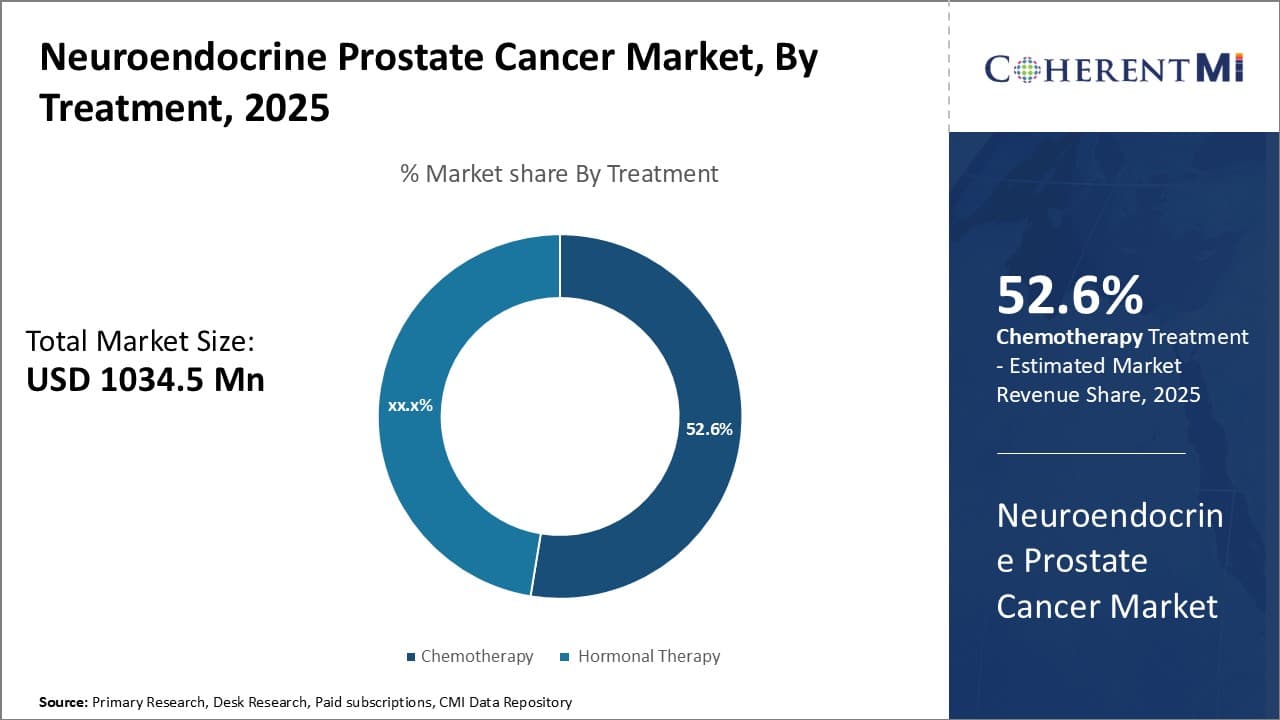
Insights, By Treatment: Chemotherapy's Clinical Efficacy Drives its Market Share
Chemotherapy segment is estimated to hold 52.6% share of the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market in 2025. This is primarily due to its established clinical efficacy compared to other options. Neuroendocrine prostate cancers are often more aggressive and chemotherapy has been shown to be particularly effective against these cancer types.
The chemotherapeutic agents most commonly used for neuroendocrine prostate cancers include docetaxel, cabazitaxel, and etoposide. Docetaxel in particular has a clear role in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) with neuroendocrine differentiation and is now considered the standard first-line chemotherapy. Its success rates in improving overall survival and progression-free survival make it the preferred choice for clinicians and patients alike.
While hormonal therapies may treat localized disease or be used adjuvantly, once the cancer progresses and metastasizes, chemotherapy takes over as the frontline treatment due to its proven ability improve clinical outcomes. The clinical data supporting chemo's effectiveness against these cancers has given it market dominance over less proven alternatives. Continued research into novel combination regimens will further strengthen chemo's share in the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market going forward.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
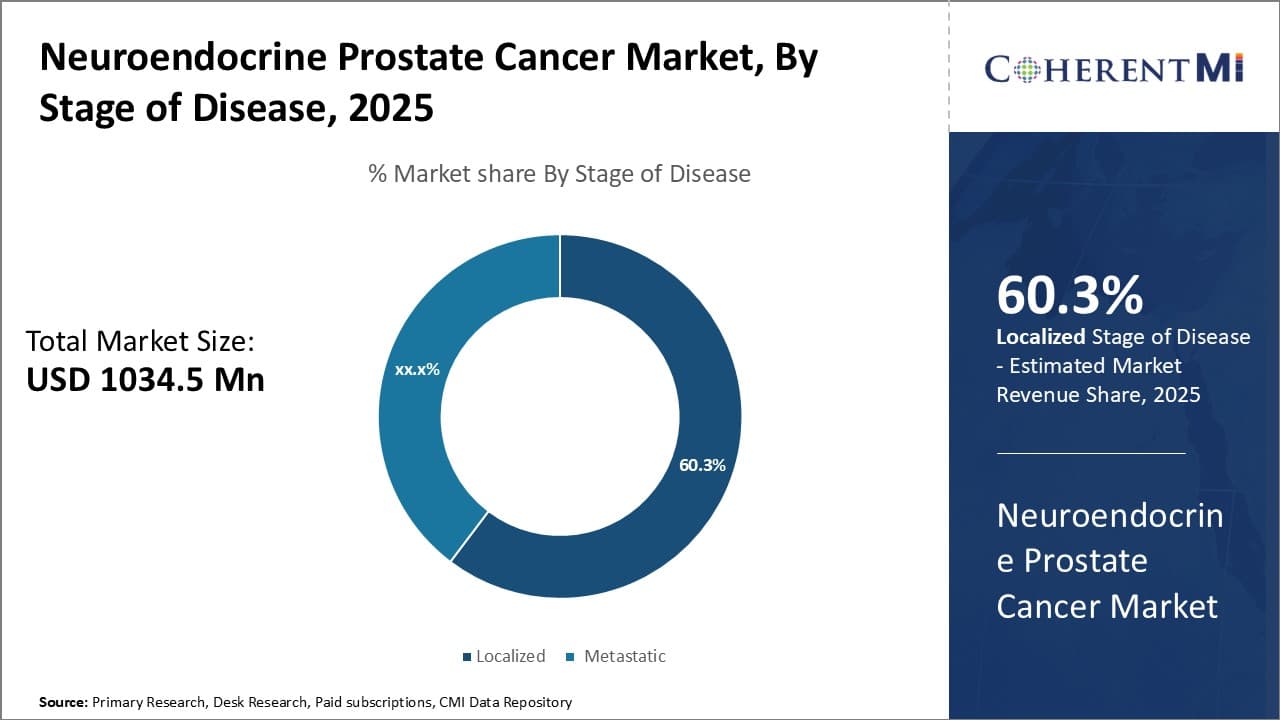
Insights, By Stages of Disease: Higher Incidence of Localized Disease Boosts its Market Share
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Stages of Disease: Higher Incidence of Localized Disease Boosts its Market Share
The localized stage of neuroendocrine prostate cancer is estimated to hold 60.3% share of the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market in 2025, due to its higher prevalence compared to the metastatic stage. Around 70-80% of neuroendocrine prostate cancer cases are diagnosed at the localized stage when the cancer is still contained within the prostate gland. This is because localized disease can go undetected for longer in its early biological stages.
By the time symptoms emerge and a patient seeks medical attention, the cancer has often already spread beyond the prostate in many cases. However, for those that are caught at the localized stage, there is a much higher probability of successful treatment and prolonged remission periods.
As a result, localized disease accounts for a disproportionately larger slice of the overall caseload size and treatment volume. This higher incidence translates directly to increased market demand for diagnostics and therapeutics tailored for early-stage neuroendocrine cancers confined to the primary site.
Insights, By Therapeutics: Immunotherapy's Novel Mechanisms Drive its Market Disruption
The immunotherapy segment dominates neuroendocrine prostate cancer market share due to the exciting novel mechanisms of action it provides. Neuroendocrine prostate cancers have proven notoriously resistant to existing hormonal and cytotoxic therapies.
Immunotherapies like peptide vaccines, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and CAR T-cell therapies tap into the body's own immune defenses in unique ways. They stimulate anti-tumor immune responses and reprogram the tumor microenvironment - mechanisms not explored by historical standard of care options. This gives hope for more durable responses and treatments for patient populations with few remaining options.
The potential for combination regimens only increases novel immunotherapy's appeal further. Their new therapeutic paradigm has lit high hopes in clinicians and is drawing significant research investment - factors that are driving their market disruption in neuroendocrine prostate cancer therapeutics.
Success stories in other cancer types also bolster confidence that immunotherapy can overcome the challenges of these treatment-resistant diseases.
The major players operating in the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market include Amgen, BioXcel Therapeutics, Oric Pharmaceuticals, Xencor, Astellas Pharma/Medivation, Novartis, Pfizer, Amgen, Merck, and Bayer.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer Market is segmented By Treatment (Chemotherapy, Hormonal Therapy), By...
Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer Market
How big is the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market?
The neuroendocrine prostate cancer market is estimated to be valued at USD 1034.5 Mn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 1694.1 Mn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market?
The high cost of treatment and limited accessibility in certain regions and side effects associated with current therapies are the major factor hampering the growth of the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market.
What are the major factors driving the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market growth?
The increasing incidence of neuroendocrine prostate cancer and advancements in targeted and personalized treatment are the major factor driving the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market.
Which is the leading treatment in the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market?
The leading treatment segment is chemotherapy.
Which are the major players operating in the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market?
Amgen, BioXcel Therapeutics, Oric Pharmaceuticals, Xencor, Astellas Pharma/Medivation, Novartis, Pfizer, Amgen, Merck, Bayer are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market?
The CAGR of the neuroendocrine prostate cancer market is projected to be 7.3% from 2025-2032.