

The non muscle invasive bladder cancer market is estimated to be valued at USD 371.1 Mn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 656.9 Mn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% from 2025 to 2032. This represents a significant opportunity for key players in this market as advances in diagnostic methods and treatment options continue to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
The market is expected to witness positive growth over the forecast period due to rising prevalence of bladder cancer worldwide. Additionally, increasing health awareness and favorable reimbursement policies for bladder cancer treatment in developed nations will also contribute to market expansion. However, lack of awareness about bladder cancer in developing regions and high cost of innovative therapies may hamper market growth to some extent over the coming years.
Market Size in USD Mn
CAGR8.5%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 8.5% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Merck & Co., Inc., Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Inc., CG Oncology, Sesen Bio, Inc. and Among Others |
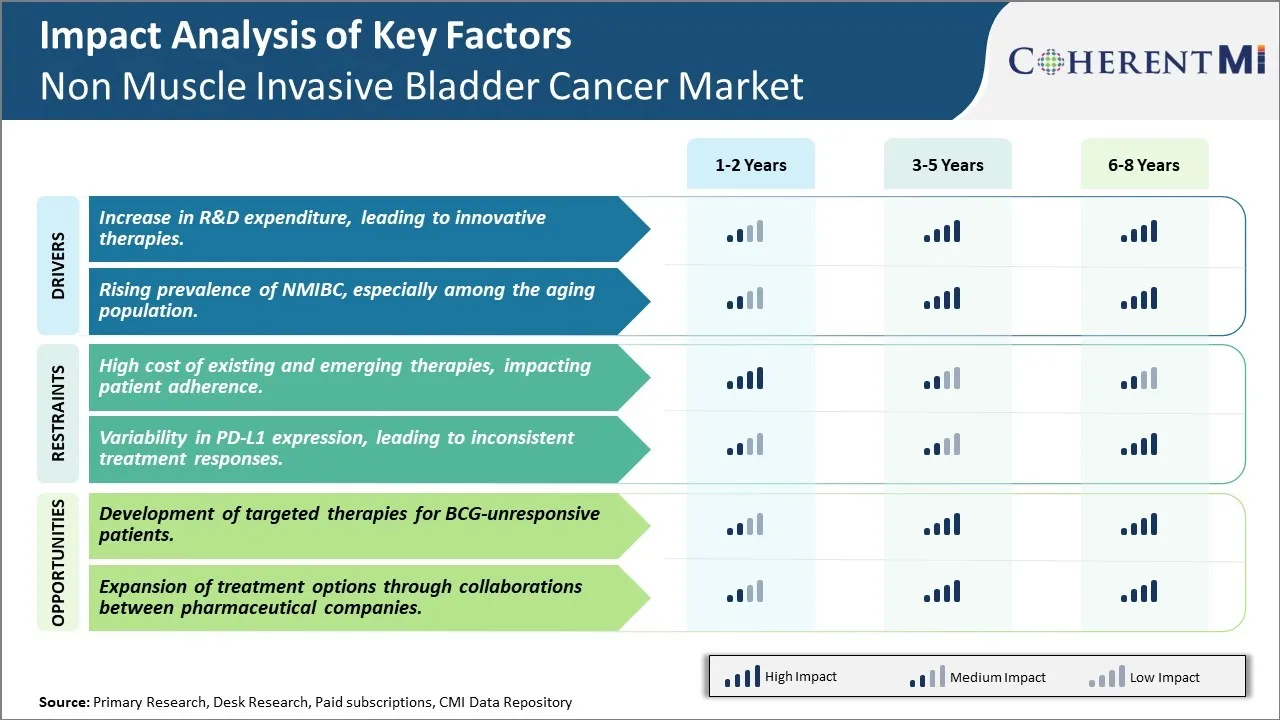
Market Driver - Increase in R&D expenditure, leading to innovative therapies
With increasing awareness about non muscle invasive bladder cancer, major pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies have started allocating large funds towards research and development of advanced targeted therapies. According to our analysis, the global R&D spending on bladder cancer is expected to witness a substantial rise in the coming years. Companies are investing heavily in order to come up with novel drug formulations and combination therapies that can precisely target bladder cancer cells and lower the recurrence rates.
Some of the therapies that are currently being researched include immune checkpoint inhibitors, vaccines, targeted therapies and gene therapy. Immune checkpoint inhibitors like pembrolizumab and atezolizumab target proteins that cancer cells use to hide from the body's immune system are showing promising results in clinical trials. Several neoantigen vaccines are in pipeline to trigger an immune response against tumor-specific antigens. Research is ongoing to identify biomarkers that can predict response to various drug treatments. Companies are collaborating with research institutes to develop advanced targeted therapies that block growth and spread of cancer by interfering with specific molecules involved in tumor growth and progression.
Increased R&D spending is also directing researchers and scientists to explore opportunities around gene therapy and stem cell therapy for bladder cancer. Gene therapies involve modification of existing genes or introduction of new genes inside the body's cells and tissues to fight disease. Some early phase trials have demonstrated potential of gene therapy to treat non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Similarly, stem cell therapy aims to replace damaged or dead cells with new stem cells to trigger body's natural healing response. Considering the growing body of scientific evidence, more private funding is being directed towards translation of these advanced therapies from research labs into practical clinical use. If successful, these new therapeutic strategies promise to disrupt existing treatment paradigms and provide patients with long lasting therapeutic benefits while also addressing shortfalls of current standard of care.
Market Driver - Rising prevalence of NMIBC, especially among the aging population
Another important driver for the non-muscle invasive bladder cancer market is increasing prevalence rates, predominantly due to aging population globally. As per United Nations statistics, the proportion of global population aged over 60 years is projected to nearly double from 12% to 22% between 2015 and 2050. Strong epidemiological evidence suggests that risk of bladder cancer rises steeply with age and majority of cases are diagnosed in people aged 65 years or older. Aging is associated with accumulation of various molecular damage and genetic mutations in tissues over time which can trigger abnormal cell growth.
Older individuals also have higher likelihood of developing multiple chronic conditions simultaneously due to oxidative stress & weakening of immune defenses. Many chronic illnesses and their medications are linked to higher risk of developing bladder cancer. For instance, frequent urinary tract infections from enlarged prostate in aging males can increase bladder cancer probability. Similarly, long term use of analgesic drugs is a known risk factor. Growing prevalence of metabolic conditions worldwide like diabetes and obesity which are risk modulators for bladder cancer also contributes to rising disease incidence. As populations continue to grow older across world regions, these risk factors will become more prominent in the coming decades resulting in explosion of new bladder cancer cases, especially non muscle invasive type.
Early detection capability is also improving continuously with advancements in diagnostic technologies like blue light cystoscopy which allows precise visualization of tumors. This will lead to more NMIBC cases being identified at curable stages. Considering ill effects of aging process on human body and limitations of existing standard therapies, there exists a clear unmet need for novel drugs, procedures and disease modifying agents to effectively treat NMIBC without recurrence in elderly population. These factors will ensure continuous growth for this therapeutics market over long term.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High cost of existing and emerging therapies, impacting patient adherence
One of the major challenges faced in the non-muscle invasive bladder cancer market is the high cost of existing and emerging therapies. Treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer primarily involves transurethral resection of the tumor followed by immunotherapy with bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG). However, BCG therapy faces issues of limited availability and high treatment costs, which can range from $5000 to $15000 per induction course alone. This high financial burden impacts patient adherence to the recommended treatment regimen significantly. Approximately 50% of patients fail to complete the recommended maintenance course of BCG therapy due to reasons of affordability and side effects. The influx of several emerging targeted therapies and combination regimens in the market is expected to further drive up treatment costs. Drugs such as AstraZeneca’s IMFINZI (durvalumab), Roche’s atezolizumab, and Merck’s Keytruda (pembrolizumab) which are approved in advanced settings cost upwards of $12000 per patient annually. This exponential rise in the costs of bladder cancer care poses concerns, especially in developed markets with an aging population where the incidence and recurrence rates are highest. Addressing treatment affordability will be a critical step towards improving patient outcomes in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.
Market Opportunity - Development of targeted therapies for BCG-unresponsive patients
One of the major opportunities in the non-muscle invasive bladder cancer market lies in the development of targeted therapies specifically for patients who fail initial BCG therapy. Approximately 20-30% of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer patients do not respond adequately to the standard BCG treatment regimen and are at high risk of progression to muscle-invasive disease. Currently, there are no established standardized treatment options available for these BCG-unresponsive patients other than early cystectomy. Several biopharma companies are actively conducting clinical trials to evaluate novel targeted drug candidates and combination regimens that could fulfill this unmet need. For example, phase III trials are ongoing to study the safety and efficacy of compounds such as Janssen’s erdafitinib, Seattle Genetics’ enfortumab vedotin, and Mirati Therapeutics’ adagrasib in the BCG-unresponsive setting. Successful approval of targeted drugs specifically approved for this high-risk patient subset can open up a huge market opportunity. It can significantly improve clinical outcomes while generating significant revenues for those companies.
Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) is generally treated based on risk stratification into low, intermediate and high-risk categories. For low-risk NMIBC, the first-line treatment is often transurethral resection of the bladder tumor (TURBT), followed by intravesical immunotherapy with bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG), an immunomodulator drug marketed as TICE BCG.
For intermediate-risk NMIBC, TURBT is again the first treatment option. Prescribers commonly then opt for a 6-week induction course of intravesical chemotherapy using mitomycin C, sold under the brand name Mutamycin. For those who respond poorly, a maintenance regimen of BCG is preferred.
In high-risk NMIBC cases, maximal TURBT is performed where possible. This is typically followed by induction BCG, with 3-year maintenance therapy being the standard practice. For non-responders or those who experience recurrence, prescribers may choose second-line intravesical chemotherapy using drugs like Valrubicin (Valstar) or gemcitabine (Gemzar).
Additional factors influencing prescribers' choice include patient compliance, tolerance to side effects, and disease recurrence/progression rates. BCG is generally preferred over chemotherapy for its higher efficacy. However, chemo drugs gain prominence if a patient is unfit or unwilling for the rigors of BCG therapy. Overall, a personalized risk-benefit approach guides most prescribers.
Companies have invested heavily in R&D to develop novel therapies for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. For example, Roche gained FDA approval for its immunotherapy drug atezolizumab (Tecentriq) in 2021 for previously untreated high-risk NMIBC. This marked the first FDA approval of an immunotherapy for this patient population. Such innovation gives companies a strong competitive edge.
Players make strategic acquisitions and partnerships to enhance their product pipelines and market reach. For instance, in 2018, Merck acquired Peloton Therapeutics to gain access to its FGFR inhibitor therapy for NMIBC. In 2020, Roche partnered with RemeGen to develop and commercialize sitravatinib in China and selected Asia Pacific markets for bladder cancer. This expands their commercial presence.
Large companies spend heavily on marketing and promoting their newly launched therapies. For example, when launching its immunotherapy recently, Roche conducted nationwide marketing campaigns targeting both physicians and patients through medical journals, conferences, and digital platforms. Such promotional activities help generate greater awareness and uptake of new therapies.
As NMIBC incidence is growing in developing countries, companies are expanding their presence globally through setting up infrastructure and registrations. For instance, since 2015, Pfizer has registered and marketed its drug BCG for NMIBC treatment in China, India, and various Latin American countries. This geographic expansion into high growth regions will be key to sustain sales long-term.
Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer is staged as CIS, Ta, T1 or carcinoma in situ. For stage Ta/T1 tumors, the first-line standard of care is transurethral resection of the bladder tumor (TURBT), which aims to surgically remove all visible tumors. For low-risk NMIBC, the primary prevention strategy after TURBT is surveillance with cystoscopy and urine cytology.
For intermediate- and high-risk NMIBC, the preferred adjuvant treatment is intravesical immunotherapy or chemotherapy directly following TURBT to kill any remaining cancer cells. Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) immunotherapy is considered the gold standard, using an attenuated form of the bacterium Mycobacterium bovis. BCG works to trigger an immune response against tumor cells. It is administered weekly for 6 weeks, then patients undergo maintenance doses every 3-6 months for up to 3 years to prevent recurrences.
For patients who experience recurrence after BCG or are BCG-intolerant, options include a second course of BCG, chemotherapy drugs like mitomycin C or valrubicin, or surgical options like cystectomy. Emerging therapies also include intravesical immune checkpoint inhibitors like pembrolizumab and molecular targeted therapies like erdafitinib. The choice depends on each patient's individual risk factors, tolerability of side effects, and physician recommendation. Close surveillance remains important to monitor for disease progression.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy Insights, By Treatment Type: First-line standard treatment benefits of BCG therapy drives the sub-segment growth
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy Insights, By Treatment Type: First-line standard treatment benefits of BCG therapy drives the sub-segment growth
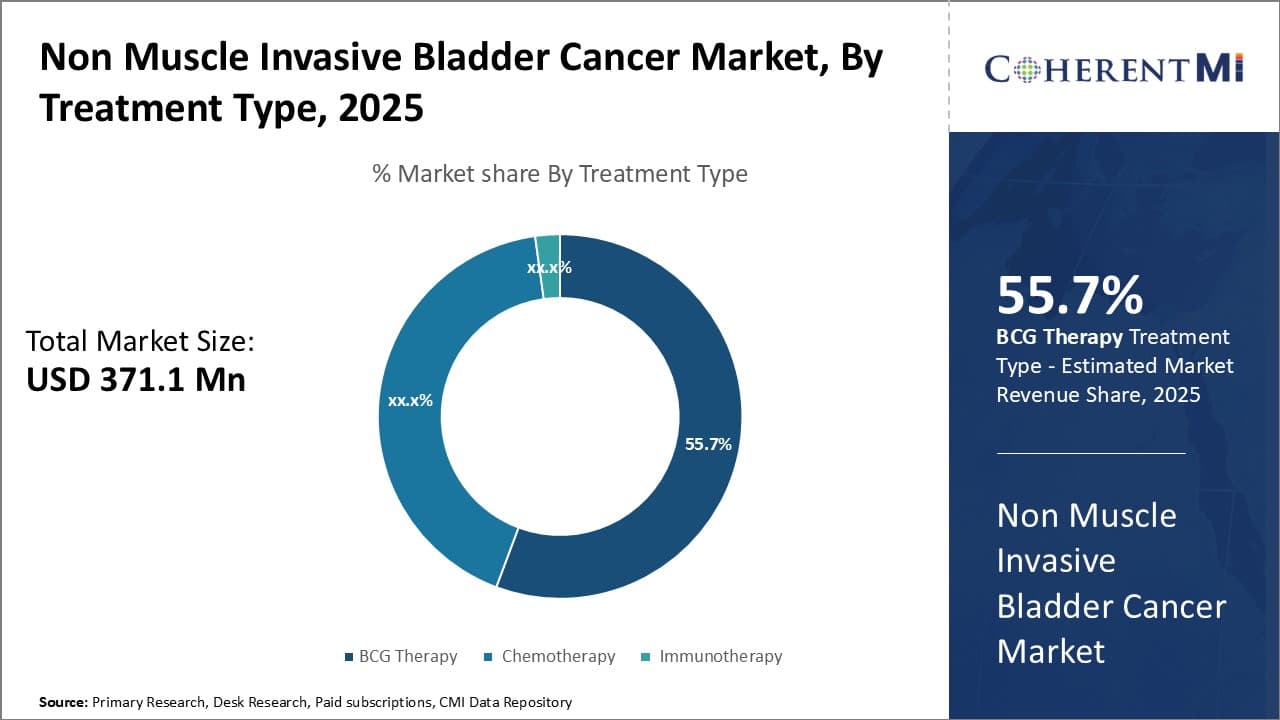
In terms of treatment type, BCG therapy sub-segment contributes the highest share of 55.7% in the market owing to its first-line standard treatment benefits. BCG therapy, also called Bacillus Calmette-Guérin immunotherapy, contributes the largest share in the treatment type segment of the non-muscle invasive bladder cancer market. This is mainly attributable to the fact that BCG therapy has been an established first-line standard treatment option for patients diagnosed with stage Ta, Tis and T1 bladder cancer tumors. Clinical guidelines from major medical organizations like the American Urological Association and National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommend BCG immunotherapy as the preferred treatment choice for high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.
BCG therapy works by boosting the patient's immune response against tumor cells through intravesical administration of live attenuated Mycobacterium bovis bacteria. Numerous randomized controlled trials and long-term follow up data have proven the superior therapeutic efficacy of BCG over other monotherapies like chemotherapy in reducing recurrence rates and delaying disease progression, especially for high-risk cases. Its ability to stimulate localized and systemic anti-tumor immunity gives BCG an advantage over single agent chemotherapy. Additionally, BCG therapy is an outpatient procedure, allowing for convenient administration with minimal disruption to patients' daily lives and work. These favorable clinical benefits have solidified BCG's primacy as the standard first-line option for appropriate non-muscle invasive bladder cancer cases.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
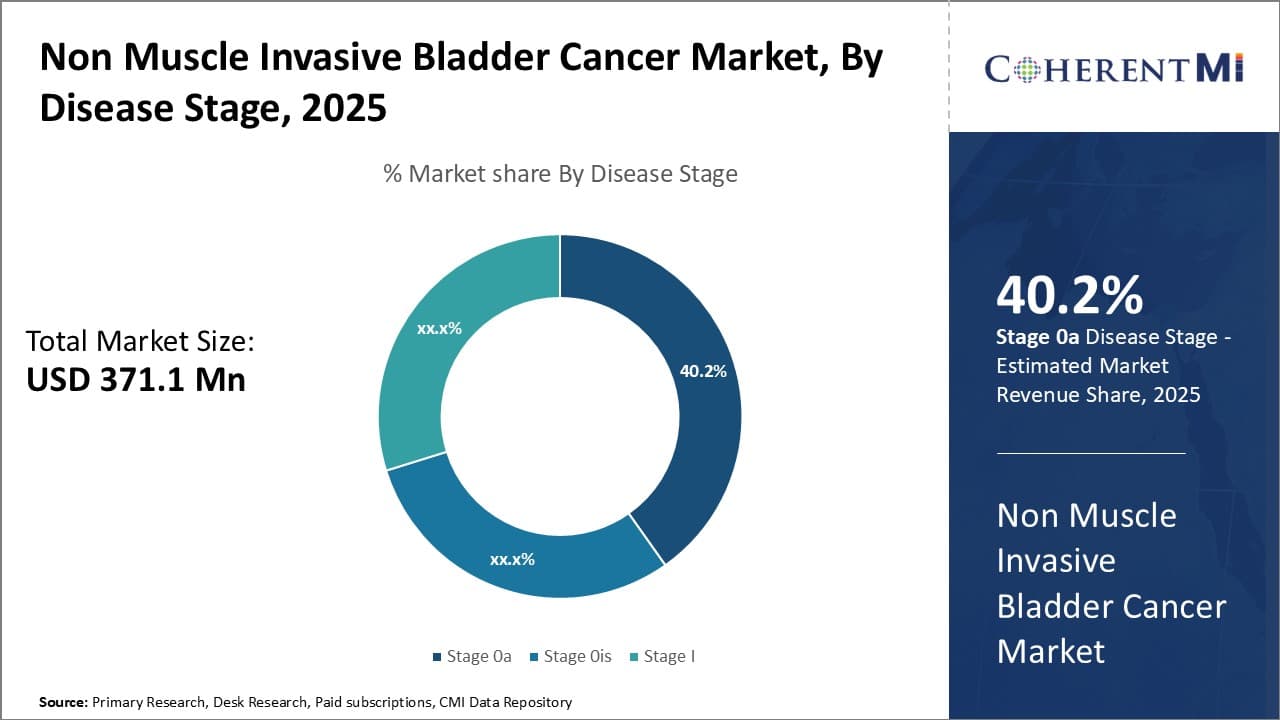
Insights, By Disease Stage: Stage 0a tumors are the most prevalent amongst newly diagnosed non-muscle invasive cases, globally
In terms of disease stage, stage 0a sub-segment contributes the highest share of 40.2% in the market owing to its prevalence as an early tumor stage. Among the disease stage segments in the non-muscle invasive bladder cancer market, Stage 0a accounts for the largest share. This dominant position stems from the fact that Stage 0a represents the earliest form of bladder cancer that is confined to the innermost layer of cells lining the bladder. Globally, Stage 0a tumors are the most prevalent amongst newly diagnosed non-muscle invasive cases. Data from cancer registries and hospital record analyses reveal that approximately 30-40% of incident bladder tumors fall under the Stage 0a classification.
The non-invasive and localized nature of Stage 0a lesions allows for less aggressive treatment approaches with favorable cure rates. Most Stage 0a patients are amenable to transurethral resection of the bladder tumor alone or in conjunction with immunotherapy. Less extensive surgery reduces costs, recovery time and morbidity risks compared to managing more advanced stages. The widespread detection of Stage 0a cancers also points to increased screening and surveillance efforts paying off in the early diagnosis of potentially lethal diseases. Its preponderance in caseloads means more Stage 0a patients entering the treatment system and driving its proportional market size over other stages.
The NMIBC market is undergoing a significant transformation due to the emergence of novel therapies targeting BCG-unresponsive cases. This segment has seen limited advancements over the last 50 years, but recent developments, including gene therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors, are poised to drive substantial growth. Companies like Merck and Ferring are leading the charge with innovative products that offer new hope for patients with limited options. Additionally, the pipeline is robust, with multiple therapies at various stages of development, promising to further diversify and strengthen the treatment landscape over the next decade.
The major players operating in the non muscle invasive bladder cancer market include Merck & Co., Inc., Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Inc., CG Oncology and Sesen Bio, Inc.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Non Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Market is Segmented By Treatment Type (BCG Therapy, Chemotherapy,...
Non Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Market
How big is the Non Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Market?
The Non Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Market is estimated to be valued at USD 371.1 in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 656.9 Million by 2032.
What are the major factors driving the non muscle invasive bladder cancer market growth?
The increase in R&D expenditure, leading to innovative therapies and rising prevalence of NMIBC, especially among the aging population are the major factors driving the non muscle invasive bladder cancer market.
Which is the leading treatment type in the non muscle invasive bladder cancer market?
The leading treatment type segment is BCG therapy.
Which are the major players operating in the non muscle invasive bladder cancer market?
Merck & Co., Inc., Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Inc., CG Oncology, and Sesen Bio, Inc. are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the non muscle invasive bladder cancer market?
The CAGR of the non muscle invasive bladder cancer market is projected to be 8.5% from 2025-2032.