Non-Viral Drug Delivery Systems Market Size - Analysis
The non-viral drug delivery systems market is estimated to be valued at USD 9.23 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 23.10 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.00% from 2025 to 2032. Recent technological advancements have enabled improved targetability and delivery of therapeutics. Furthermore, the growing prevalence of chronic diseases and increasing demand for advanced drug delivery systems are contributing to the growth of the non-viral drug delivery systems market.
The market is witnessing positive trends with the increasing demand for advanced drug delivery systems and investments in R&D activities. The growing need to improve the bioavailability and solubility of drugs is further propelling the demand for non-viral drug delivery systems. Additionally, supportive government policies and emphasis on drug development are expected to contribute to the strong market growth over the forecast period.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR14.00%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 14.00% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Arcturus Therapeutics, Bio-Path Holdings, CureVac, Entos Pharmaceuticals, eTheRNA Immunotherapies and Among Others |
please let us know !
Non-Viral Drug Delivery Systems Market Trends
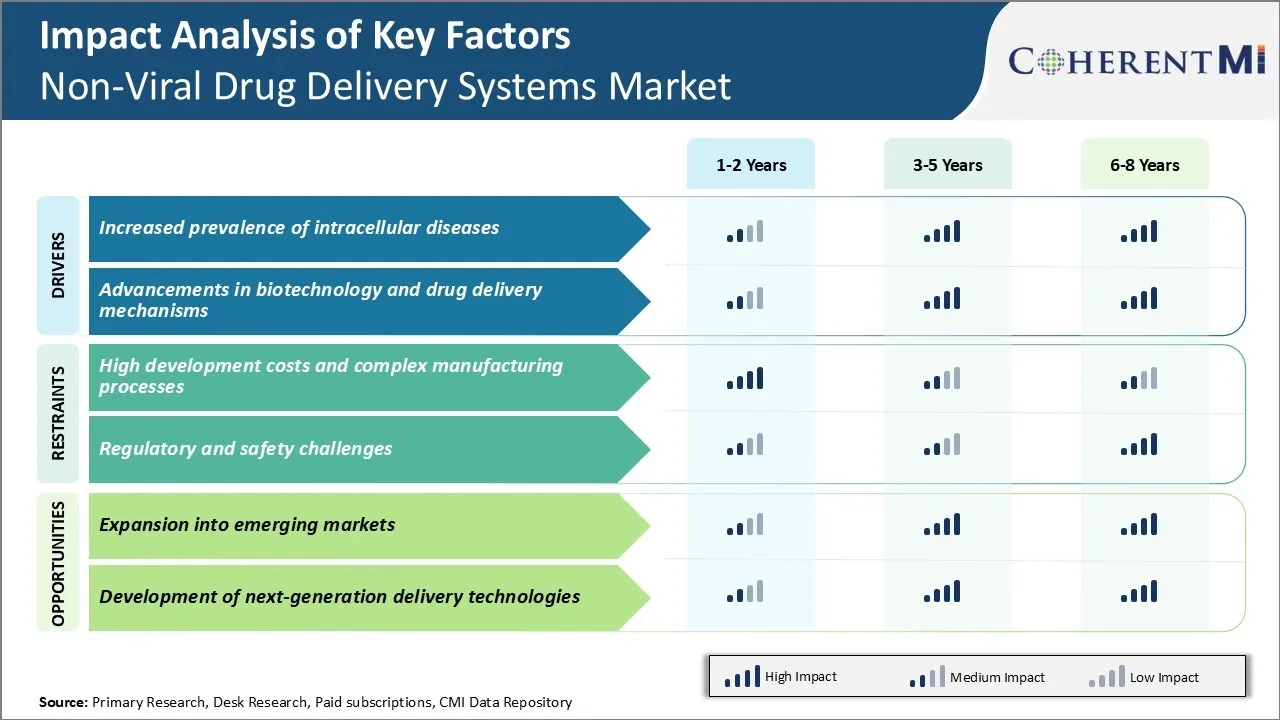
Market Driver - Increased prevalence of intracellular diseases
The advent of various chronic and life-threatening diseases has significantly impacted the non-viral drug delivery systems market in recent years. A major factor driving growth has been the rising incidence of intracellular diseases like cancer, infectious diseases among others. Cancer remains one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide with an estimated 19.3 million new cases and 10 million cancer deaths in 2022. Apart from cancer, intracellular disorders like viral infections caused by HIV, hepatitis, influenza also pose a serious health burden.
Treating such intracellular conditions poses unique challenges as conventional drug delivery methods often struggle to effectively deliver therapeutics inside target cells. Drugs need to cross cell membrane barriers and ensure sufficient intracellular concentrations are achieved at the site of action. Unfortunately, many promising drug candidates fail in clinical trials due to poor intracellular bioavailability. This highlights the need for advanced non-viral delivery systems that can effectively transport therapeutics across cell membranes. Nucleic acid-based therapies also require efficient intracellular delivery for gene expression and therapeutic effect.
The growing diabetes epidemic has also fueled demand. While insulin is administered via injections to regulate blood glucose levels, innovative intracellular delivery approaches could enable oral insulin delivery and enhance patient compliance for diabetes management.
Market Driver - Advancements in biotechnology and drug delivery mechanisms
Significant progress in the fields of biotechnology and material science over the past decade has enabled innovative advancements in non-viral delivery approaches. Continuous refinement of carrier biomaterial properties, conjugation techniques, and fabrication methods have facilitated enhanced intracellular delivery capabilities. Rapid developments in the allied areas of nanotechnology have further accelerated this evolution.
Sophisticated biomimetic particulate carriers have been engineered to overcome multiple physiological barriers and cellular uptake mechanisms; emulating pathogens that host cells have evolved to phagocytose. Specifically, materials inspired by viral capsids demonstrate improved pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Additionally, active targeting ligands such as antibodies are being conjugated to delivery vehicles to induce receptor-mediated endocytosis preferentially in diseased cells overexpressing target antigens.
Advances in production technologies have enabled reproducible, scalable manufacturing of therapeutic nanoparticles with precise control over critical quality attributes like size, surface properties. Continuous manufacturing using microfluidics aids consistent performance batch-on-batch. Such refinements are crucial for regulatory approvals and commercialization. Further, characterization tools continue gaining sensitivity to better understand structure-activity relationships, providing insights to optimize intracellular transport. Cross-disciplinary research involving physics, chemistry and cell biology nurtures a vibrant innovation ecosystem driving more customized carrier designs.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High development costs and complex manufacturing processes
The non-viral drug delivery systems market faces significant challenges due to the high research and development costs associated with manufacturing these systems. Developing an effective non-viral vector requires extensive research to design novel biomaterials that can protect active pharmaceutical ingredients and selectively deliver them to target sites in the body. Extensive pre-clinical testing is needed to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of different vector formulations. Meeting stringent regulatory standards for clinical trials and commercial production further drives up costs. The manufacturing processes for non-viral vectors can also be highly complex due to stringent quality control measures and expertise required for vector self-assembly. Producing vectors at consistent commercial scales demands specialized equipment and facilities. Overall project timelines and costs are difficult to estimate upfront due to challenges in optimizing physiochemical properties of different vector designs. The high financial investment required poses a major hurdle for market participants
Market Opportunity: Expansion into emerging markets
The non-viral drug delivery systems market has significant opportunities to expand into emerging markets. There is high unmet medical need for effective and affordable drug delivery technologies in developing nations which have large patient populations and growing healthcare budgets. Entry into emerging markets allows companies to leverage the relatively lower costs of clinical trials and regulatory approvals. It also offers the opportunity to gain more extensive real-world clinical experience and data that can accelerate approvals in developed markets. With improved access to healthcare and rising incomes, emerging nation patients are increasingly open to innovative treatments. If tailored appropriately for local healthcare systems, non-viral vectors have the potential for widespread adoption. By pre-emptively establishing manufacturing and distribution infrastructure, companies can gain an early-mover advantage in emerging growth markets. This can help offset challenges from high R&D investment required for these delivery technologies.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Non-Viral Drug Delivery Systems Market
Leading players like Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Novartis have heavily invested in nanoparticle-based non-viral delivery systems over the past decade. Nanoparticles can encapsulate drug molecules and carry them into cells via endocytosis. Pfizer's CRLX101, an anti-cancer nanomedicine approved in 2018, uses a dynamic polymeric nanoparticle to deliver camptothecins. In clinical trials, it showed improved efficacy over conventional delivery with fewer side effects.
Players are focusing on ligands and target receptors to functionally decorate delivery vehicles for tissue/cell-specific targeting. In 2015, Novartis received FDA approval for HYQVIA, the first subcutaneous immunoglobulin using HISTAFree lipid nanoparticles targeting FcRn receptors on endothelial cells to boost IgG levels. Clinical trials showed it was as effective as intravenous treatment with less side effects and higher patient compliance.
Leading companies are leveraging existing delivery platforms and modifying them for new drug applications. In 2010, Johnson & Johnson rolled out PREZISTA, a prescription HIV-1 protease inhibitor enhanced through encochleation - a lipid-based self-assembly process. It achieved higher bioavailability than previous protease inhibitors, becoming the standard first-line regimen.
Major players partner or acquire smaller innovative companies to gain access to new delivery technologies. In 2014, Amgen partnered with Isis Pharma to develop AMG 890, an antisense drug for cardiovascular risks delivered with Isis' lipid nanoparticle system. Positive phase 2 trial data led to FDA breakthrough designation in 2017.
Segmental Analysis of Non-Viral Drug Delivery Systems Market
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
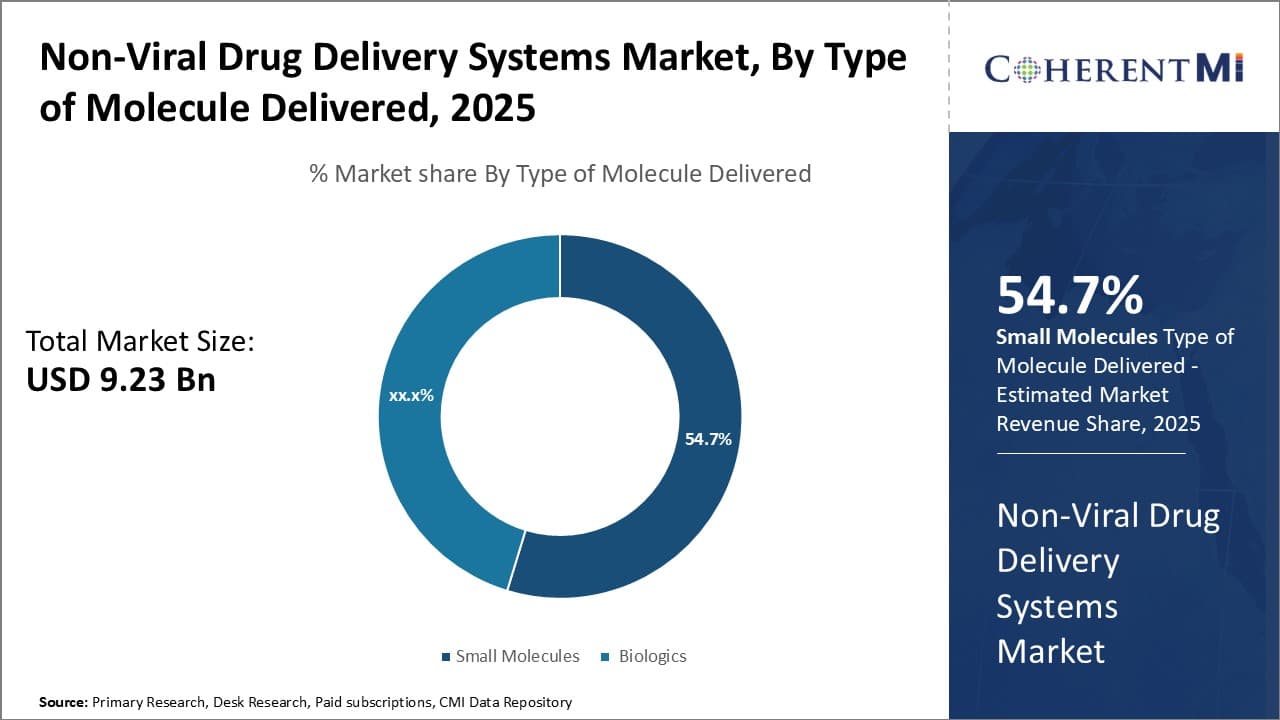
Insights, By Type of Molecule Delivered: Widespread therapeutic applications and advantages over biologics
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Type of Molecule Delivered: Widespread therapeutic applications and advantages over biologics
In terms of type of molecule delivered, small molecules sub-segment contributes the highest share of 54.7% in the non-viral drug delivery systems market owning to their widespread therapeutic applications and advantages over biologics. Small molecule drugs can be efficiently delivered to target tissues through various non-viral methods without the need for complex manufacturing processes. This makes them highly suitable for chronic diseases that require frequent and long-term medication. Their defined chemical structure also allows for better characterization and optimization of delivery properties.
A major factor driving the segment's growth is the large number of small molecule drugs in the pharmaceutical development pipeline. Many novel small molecule candidates for cancer, autoimmune disorders, cardiovascular diseases and other indications are being evaluated using non-viral delivery techniques. This is because non-viral systems offer a safer and more economical alternative to viral vectors for delivering small molecules. Liposomes, nanoparticles, polymeric micelles and other carriers can protect drugs from degradation and control their release kinetics in a customized manner. Successful clinical translation of these candidate drugs will further stimulate demand in this segment.
Another boost comes from the growing interest in combination drug therapies. Non-viral carriers allow co-delivery of multiple small molecule drugs targeting different pathways of a disease in a single formulation. This enhances therapeutic efficacy and overcomes resistance issues. Various academic and industry collaborations are exploring such combination regimens for conditions like cancer. Favorable results from ongoing clinical studies will encourage wider application of combined small molecule therapies mediated by non-viral delivery platforms.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
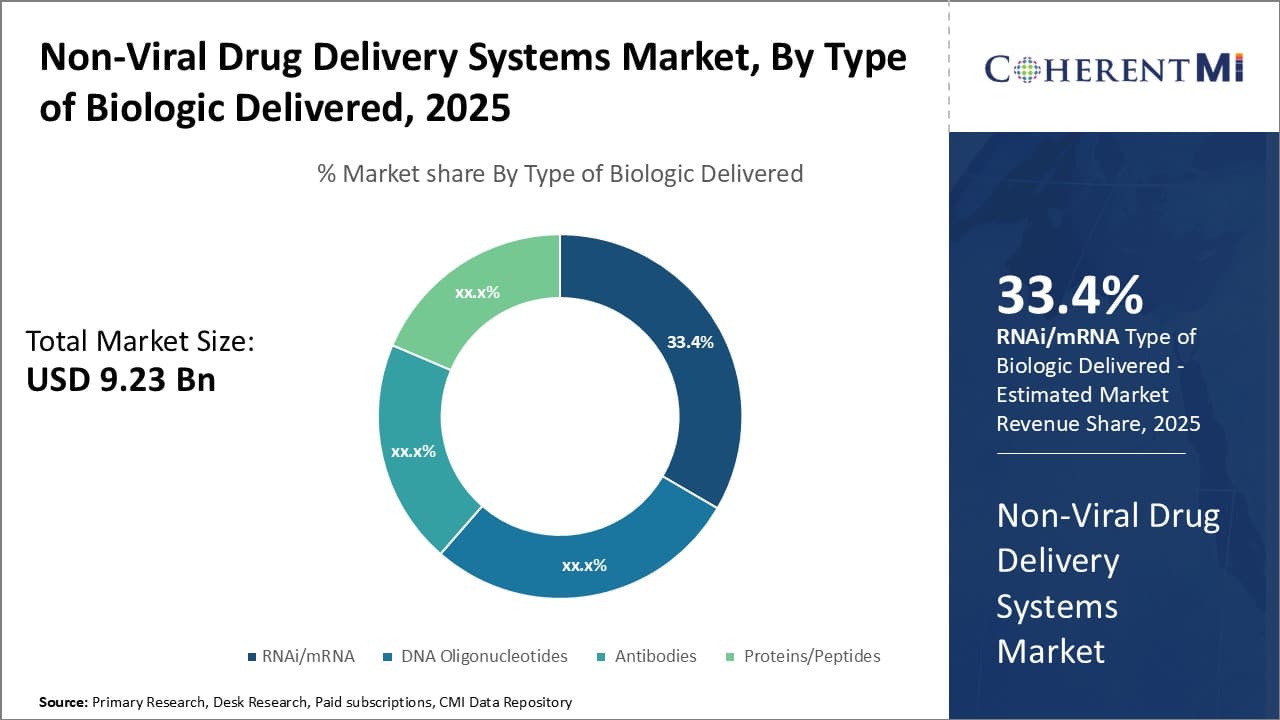
Insights, By Type of Biologic Delivered: RNAi/mRNA drives growth in non-viral biologics delivery segment
Within the biologics segment of non-viral drug delivery systems, RNAi and mRNA contributes the maximum share of 33.4% owing to the enormous therapeutic potential of these nucleic acid based biologics. The non-viral route provides an efficient yet safe means to administer RNAi and mRNA constructs for gene regulation and protein replacement respectively. Without effective delivery methods, these biologics cannot demonstrate their clinical benefits.
A major factor propelling this segment's growth is the strong clinical pipeline of RNAi and mRNA candidates for various genetic and acquired disorders. A multitude of constructs targeting disease-causing genes or encoding crucial proteins are in active development for cancer, respiratory diseases, cardiovascular conditions and more. Their delivery requires biocompatible non-viral carriers that can protect the RNA from degradation and aid cellular internalization for functional output. This clinical validation will justify investments into refining nucleic acid delivery formulations and techniques.
Advanced research into material science and nanotechnology has led to sophisticated polymeric and lipid-based vehicles tailored to the unique requirements of RNAi and mRNA cargos. Properties like endosomolytic ability, controlled unpacking kinetics and cytosolic transport/release are now better understood and replicated in synthetically modified delivery platforms. This level of customization was earlier missing, limiting early nucleic acid biologics. With continuously evolving delivery methods, more RNAi/mRNA molecules may translate from bench to applications.
Additional Insights of Non-Viral Drug Delivery Systems Market
- The non-viral drug delivery systems market is poised for significant growth due to the increasing need for targeted therapies that can efficiently deliver drugs to intracellular spaces. With the limitations of traditional small molecule drugs, especially their inability to selectively bind to a large portion of the human genome, the industry is shifting towards more innovative solutions like gene and mRNA delivery systems.
- Over 20% of the proteome, including oncogenic proteins and signal transduction pathway components, are localized within the cell membrane, making non-viral delivery systems crucial for modern therapeutic interventions.
Competitive overview of Non-Viral Drug Delivery Systems Market
The major players operating in the non-viral drug delivery systems market include Arcturus Therapeutics, Bio-Path Holdings, CureVac, Entos Pharmaceuticals, eTheRNA Immunotherapies, Matinas BioPharma, MDimune and PCI Biotech.
Non-Viral Drug Delivery Systems Market Leaders
- Arcturus Therapeutics
- Bio-Path Holdings
- CureVac
- Entos Pharmaceuticals
- eTheRNA Immunotherapies
Recent Developments in Non-Viral Drug Delivery Systems Market
- In June 2023, The Centre for Process Innovation (CPI) established a new UK Intracellular Drug Delivery Centre to develop new lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations for RNA medicine delivery.
- In May 2023, CPI partnered with Medicines Discovery Catapult, the University of Strathclyde, the University of Liverpool, and Imperial College London to develop novel drug delivery technologies.
- In April 2023, Vitarka Therapeutics raised USD 1.58 million in equity from venture capital firm SOSV to develop combination medicines using RNAi therapies and a non-viral drug delivery platform.
Non-Viral Drug Delivery Systems Market Segmentation
- By Type of Molecule Delivered
- Small Molecules
- Biologics
- By Type of Biologic Delivered
- RNAi / mRNA
- DNA Oligonucleotides
- Antibodies
- Proteins / Peptides
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
