

The Pheochromocytoma treatment market is estimated to be valued at USD 284.66 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 400.55 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.00% from 2025 to 2032. Advances in medical therapies and surgical techniques along with better healthcare infrastructure and investments are fueling the growth of this market.
Pheochromocytoma is a rare, usually benign tumor of the adrenal medulla, characterized by overproduction of catecholamines. Its symptoms include high blood pressure, headaches, palpitations, and sweating. It is often associated with genetic syndromes like MEN2 and von Hippel-Lindau disease. Approximately 25-30% of Pheochromocytoma cases are associated with hereditary syndromes. Diagnosis involves biochemical tests to confirm excessive hormone production and imaging studies to locate the tumor. Surgery remains the primary treatment option, but emerging therapies like EO2401 are exploring non-surgical options, especially for metastatic or inoperable cases.
The market is expected to witness positive growth over the forecast period owing to rising prevalence of pheochromocytoma and increasing R&D investments by key players to develop improved drugs for treatment. Furthermore, growing awareness among patients and clinicians about effective treatment options and early diagnosis of pheochromocytoma is also augmenting the demand for treatment and management of this endocrine disorder across the globe.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR5.00%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 5.00% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Pfizer Inc, Zydus Cadila, Novartis AG, Curium Pharma, AstraZeneca and Among Others |
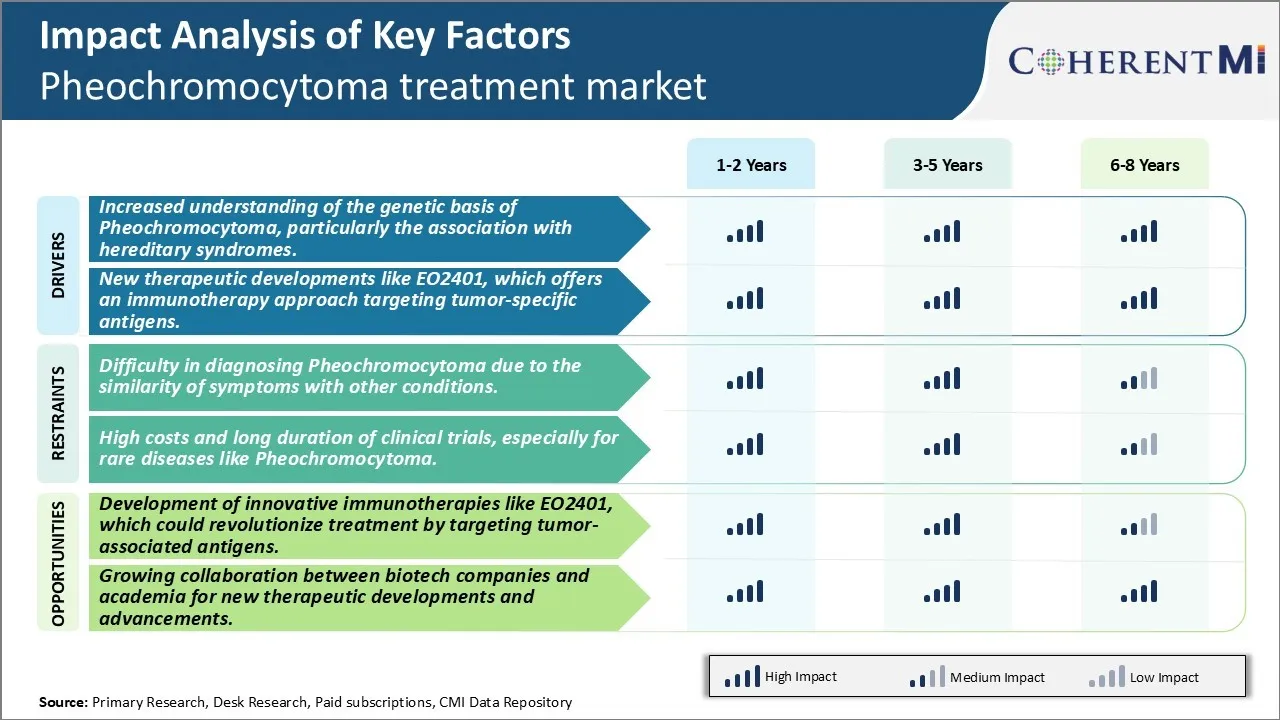
Market Driver - Increased Understanding of The Genetic Basis of Pheochromocytoma, Particularly the Association with Hereditary Syndromes.
As researchers have dug deeper into understanding the root causes of pheochromocytoma, their work has started to shine a light on important genetic components. Around 10% of pheochromocytoma cases are linked to hereditary syndromes passed down through families. Certain gene mutations have been identified that dramatically increase someone's chances of developing this rare tumor later in life. With next-generation sequencing techniques, scientists have mapped out the human genome more comprehensively than ever before.
Through studying large cohorts of patients and their families, tell-tale genetic patterns have emerged that provide important clues. The genes most often implicated include those involved in hereditary paraganglioma-pheochromocytoma syndrome, multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2, Von Hippel-Lindau disease, and neurofibromatosis type 1. Rising public awareness of the hereditary links will also be important for improving diagnostics. Discussing any relevant family medical histories more openly with healthcare providers may help expedite evaluation and diagnosis. With more people recognizing the potential genetic components at play, we expect the rates of early screening and intervention will continue growing over time. Hereditary factors undoubtedly represent an important piece of the puzzle, and deepening insight in this area should enhance care and outcomes for those afflicted with pheochromocytoma.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Driver - New Therapeutic Developments to Boost Industry Growth.
One of the most promising new avenues being explored for more effective pheochromocytoma treatment involves immunotherapy. Several biotechs have been investigating ways to harness the power of the immune system against this rare neuroendocrine tumor. Chief among their projects is a startup company working on EO2401, a first-in-class immunotherapy candidate tailored to this disease. EO2401 works by stimulating an immune response against cancer-specific antigens present on pheochromocytoma cells but not healthy tissues.
Through meticulous research, the developers of EO2401 have identified unique antigen signatures expressed by a majority of patient tumors. Preliminary studies show these antigens are not detected on other major organ types, suggesting the potential for highly targeted treatment with minimal off-target effects. Early data also indicate that when a person's T-cells are exposed to EO2401 outside of the body, it can prime those cells to more aggressively attack pheochromocytoma cells in future encounters. With refined engineering, the hope is this type of “vaccine” could educate the immune system to surveil for and destroy any remaining malignant cells after primary treatment.
As the first drug candidate to take an immunotherapy strategy for pheochromocytoma, EO2401 is seen as a game-changer. It represents the vanguard of a new generation of precision medicines tailored to target the distinct molecular and cellular properties of these rare neuroendocrine tumors. With a growing toolbox of immunotherapies achieving remarkable results against several cancer types, stakeholders have high hopes that EO2401 could transform outcomes for pheochromocytoma patients as well. Ongoing clinical trials will provide important insight into how well it performs in real-world patients.
Market Challenge - Difficulty in Diagnosing Pheochromocytoma Due to The Similarity of Symptoms with Other Conditions.
Accurately diagnosing pheochromocytoma poses a notable challenge for the market. Patients suffering from this condition often present with a variety of nonspecific symptoms that can mimic many other disorders like hypertension, diabetes, and anxiety. Symptoms such as headaches, sweating, heart palpitations and weight loss are common to multiple health issues in addition to pheochromocytoma. This makes clinical diagnosis extremely difficult without specialized tests. Biochemical tests that detect levels of catecholamines and their metabolites in urine or plasma are required but may still yield equivocal results in around 10% of cases. Imaging modalities like CT scans and MRI are also needed to localize the tumor. Even with a combination of testing methods, differentiating pheochromocytoma from other possible conditions can be challenging, leading to delays in confirming diagnoses and initiating proper treatment. This diagnostic difficulty means many cases potentially go undetected or are misdiagnosed initially. Overcoming the lack of pathognomonic symptoms for accurate and timely diagnosis remains a major challenge for the market.
Market Opportunity: Development of Innovative Immunotherapies to Encourage Emergence of Novel Opportunities.
A significant market opportunity exists around the development of novel treatment approaches for pheochromocytoma. One promising area of research is immunotherapy. Immunotherapies like EO2401 aim to trigger an anti-tumor response by targeting tumor-associated antigens found in pheochromocytoma cells. In clinical studies so far, EO2401 has demonstrated an ability to induce immune activation and produce durable anti-tumor effects. This type of targeted immunotherapy could revolutionize pheochromocytoma treatment by providing an alternative to conventional surgery and drug therapies. If successful, EO2401 or related agents would offer patients a non-invasive option for managing their disease long-term. There is also a chance immunotherapy could help improve outcomes when used adjunctively with existing approaches. Significant investment and research into immunotherapies representing a major opportunity for pharmaceutical companies and the market to establish innovative new treatment paradigms for pheochromocytoma.
Pheochromocytoma is typically treated through a multi-staged approach consisting of various pharmacological and surgical options. For early-stage disease, first-line pharmacological treatment involves the use of alpha-adrenergic blockers such as phenoxybenzamine (Dibenzyline) to help control blood pressure spikes. These are prescribed for 2-4 weeks prior to surgery to reduce risks.
The next stage involves surgical resection, with the goal of complete tumor removal. For localized tumors confined to the adrenal gland, laparoscopic adrenalectomy is the standard procedure performed. Larger or metastatic tumors require open adrenalectomy. Pre-surgical control of blood pressure is essential to mitigate risks like hypertensive crisis during the procedure.
For patients where surgery is not possible or the tumor remains incompletely resected, second-line pharmacological options include other alpha-blockers like doxazosin (Cardura) or calcium channel blockers like nifedipine. Third-line treatments involve use of beta-blockers such as propranolol (Inderal) along with alpha-blockers for improved management of symptoms.
Other factors influencing prescriber preferences include tumor size and locations, a patient's comorbidities, and their tolerance to medications. Genetic testing can provide insight into family history and risks of recurrence, guiding longer-term management plans which may involve radiation or chemotherapies like cyclophosphamide in selective cases. Regular follow-ups involving biochemical and radiological testing help track treatment effectiveness.
Pheochromocytoma is usually treated based on the stage and circumstances of the individual patient. Treatment aims to remove the tumor and control excess catecholamine production.
For localized disease that has not spread beyond the adrenal gland (stage I-II), surgery is the primary treatment option. The adrenal gland containing the tumor is removed through an open or laparoscopic procedure. This directly addresses the source of excess catecholamines. For benign tumors, surgery alone may be curative.
If the tumor is too large or otherwise inaccessible, medications may be used pre-operatively to help control blood pressure and prepare the patient. Common options include alpha-blockers like phenoxybenzamine which block adrenaline receptors, and beta-blockers like propranolol which block adrenaline effects. This lowers perioperative risks.
For metastatic or recurrent disease (stage III-IV), a combination of treatments is typically used. Lifelong medications are needed to control catecholamine levels. Common options are calcium channel blockers like amlodipine combined with alpha- and beta- blockers. Radiation therapy may provide palliation for painful bone metastases. Chemotherapy drugs like cyclophosphamide are also sometimes used but provide only limited benefits.
In all stages, lifelong follow-up is required as there is a risk of recurrence even years later. Repeat imaging and biochemical testing helps monitor for new growths. Surveillance and multi-disciplinary care improving the outcomes by enabling early detection and tailored treatment of recurrent or progressive disease.
Investment in Research and Development and Clinical Trials: Leading companies, such as Pfizer, Novartis, and AstraZeneca, are heavily investing in research and development (R&D) to develop new, targeted therapies. This includes drugs like Cabozantinib and Lutathera, which are under clinical trials for advanced or metastatic pheochromocytoma. These targeted therapies focus on inhibiting specific molecular pathways, offering new hope for patients who are not suitable for surgery.
Partnerships and Collaboration: Partnerships between pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are critical for sharing resources and expertise. For example, Novartis has partnered with academic centers to advance the development of personalized treatments through biomarker research and innovative therapeutic approaches.
Market Expansion: Companies are expanding into targeted molecular therapies to manage advanced cases, where surgery is not an option. These therapies aim to block the effects of catecholamines and inhibit tumor growth. The development of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and peptide receptor radionuclide therapies (PRRT) has been particularly noteworthy.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
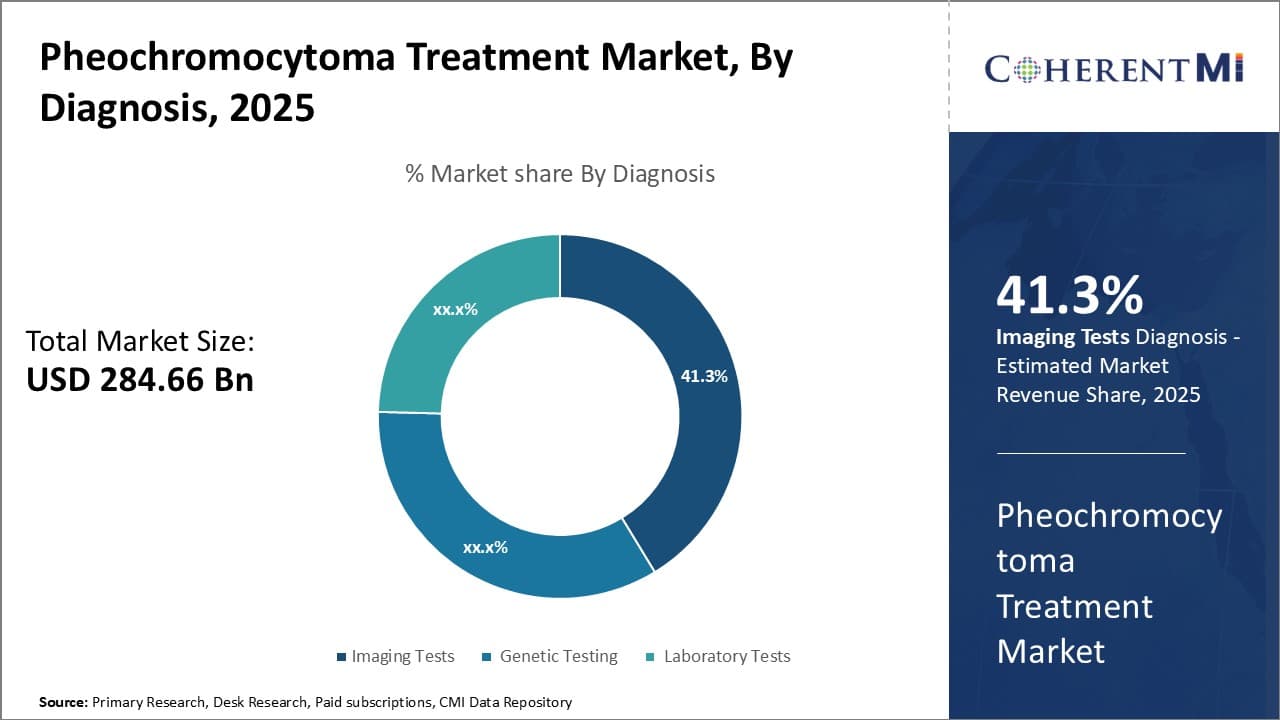
Insights, By Diagnosis: Advanced Imaging Techniques Lead Diagnosis Market.
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Diagnosis: Advanced Imaging Techniques Lead Diagnosis Market.
By diagnosis, imaging tests are expected to contribute 41.3% share of the pheochromocytoma treatment market owing to their high accuracy and non-invasive nature. Advances in imaging technology have revolutionized the diagnosis process for pheochromocytoma. CT scans, MRI scans, PET scans, and ultrasound imaging now allow doctors to detect even small tumors with great precision. This high detection rate helps physicians confidently diagnose patients at earlier stages of the disease.
CT scans are a common first-line test due to their wide availability and ability to identify tumors in the adrenal glands or other organ tissues. Recent developments improving CT scan resolution have increased their utility for locating even tiny pheochromocytomas. MRI scans provide excellent soft tissue contrast and are often used complementary to CT to visualize tumors in more detail. Functional MRI techniques analyzing tissue perfusion and diffusion properties further enhance detection capabilities.
Due to its use of radiolabeled ligands that bind to pheochromocytoma cells, PET scanning has emerged as a very accurate metabolic imaging tool. Integration of PET with CT allows precise anatomic localization in addition to functional evaluation. Several PET tracers like 18F-FDG, 18F-fluorodihydroxyphenylalanine (18F-FDOPA), and 18F-fluorodopamine (18F-DOPA) targeting diverse tumor characteristics are employed to maximize detection. The high sensitivity and specificity of PET scanning has made it a critical part of the imaging diagnostic workflow.
Beyond whole body scans, localized ultrasound is playing a rising role. Its lack of radiation and real-time functionality allows focused evaluation of suspicious lesions found on other modalities. Developments in high frequency transducer technology and Doppler flow imaging aid ultrasound identification of small adrenal tumors. As a complementary follow-up to initial scans, ultrasound provides valuable diagnostic information without additional radiation exposure for patients.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
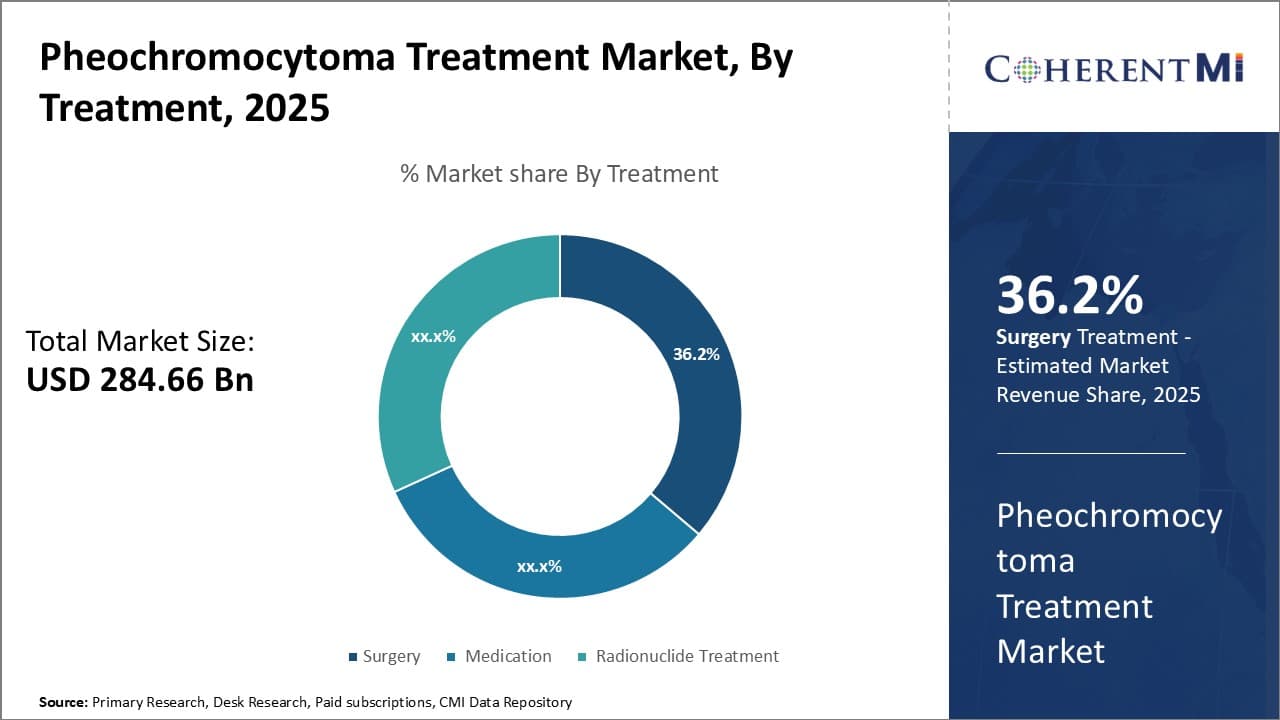
Insights, By Treatment, Surgical Management Remains Cornerstone Treatment.
By Treatment, surgery is expected to contribute 36.2% share in 2025 owing to its curative potential. While medication can control symptoms, complete tumor resection through an operation remains the only approach offering a definitive cure to patients. With evolving surgical techniques and improvements in perioperative care, most localized tumors today are amenable to safe and effective surgical management.
Traditional open adrenalectomies have given way to laparoscopic and robotic-assisted minimally invasive techniques. These approaches provide distinct advantages like reduced blood loss, fewer complications, decreased hospital stays, and faster recovery times compared to open surgeries. As even specialists with extensive open surgery experience embrace the less traumatic options, minimally invasive methods have become the standard of care.
Beyond the approach, refinements to surgical protocols also improve outcomes. Preoperative medical management lowering catecholamine levels helps reduce intraoperative fluctuations. Careful identification and preservation of nearby structures like vessels decreases post-surgical issues. Intraoperative tools like nerve-sparing techniques and ultrasound serve to maximize tumor excision rates while minimizing collateral organ risks. Comprehensive multidisciplinary teams optimally stage and coordinate each surgery to achieve the best possible results.
Insights, By End-user, Research Environment Fuels Academic Progress.
By End-users, Research and Academic Institutes contributes the highest share of the pheochromocytoma treatment market as they are on the forefront of expanding understanding and developing innovations. Their substantial investments in basic science, clinical trials, registries, and education continuously push forward the boundaries of diagnosis and care.
Many of the most prestigious academic medical centers globally dedicated considerable resources towards pheochromocytoma research programs. By leveraging diverse expertise and close industry partnerships, such hubs spearhead projects from fundamental mechanism elucidation to Phase III drug assessments. Pioneering work in genetics, biomarker discovery, and predictive models emerges from these environments to transform practices.
The cooperative, multi-institutional nature of research consortia further strengthens progress. Federally-funded initiatives like the National Institutes of Health's Rare Disease Clinical Research Network galvanize collaboration between leading researchers. Registries pool biospecimen and outcomes data from thousands of participants to identify novel patterns and priorities.
Pheochromocytoma is a rare but potentially dangerous condition due to the overproduction of stress hormones by tumors in the adrenal medulla. These hormones, mainly catecholamines, cause symptoms like severe hypertension, headaches, and heart palpitations, making it crucial for patients to receive an accurate diagnosis and timely treatment. While surgery remains the standard treatment, new therapies like Enterome’s EO2401 are being developed to target malignant or metastatic cases. EO2401 is based on immunotherapy principles, designed to activate the patient’s immune system to recognize and destroy tumor cells. By leveraging microbial-derived OncoMimics™ peptides, EO2401 mimics tumor-associated antigens to trigger a specific immune response. This innovation could change how clinicians approach treatment, especially in cases where surgery is not viable or where the disease has spread.
The major players operating in the Pheochromocytoma treatment market include Pfizer Inc, Zydus Cadila, Novartis AG, Curium Pharma, AstraZeneca, Jubilant Cadista, Mylan N.V., Apotex Inc., Lupin and Glenmark Pharmaceuticals.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Pheochromocytoma Treatment Market is segmented By Diagnosis (Imaging Tests, Genetic Testing, Laborat...
Pheochromocytoma Treatment Market
How Big is the Pheochromocytoma treatment market?
The Global Pheochromocytoma treatment market is estimated to be valued at USD 284.66 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 400.55 Bn by 2032.
What will be the CAGR of the Pheochromocytoma treatment market?
The CAGR of the Pheochromocytoma treatment market is projected to be 4.8% from 2024 to 2031.
What are the major factors driving the Pheochromocytoma treatment market growth?
The increased understanding of the genetic basis of pheochromocytoma, particularly the association with hereditary syndromes and new therapeutic developments like eo2401, which offers an immunotherapy approach targeting tumor-specific antigens, are the major factors driving the Pheochromocytoma treatment market.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the Pheochromocytoma treatment market?
The difficulty in diagnosing pheochromocytoma due to the similarity of symptoms with other conditions, high costs and long duration of clinical trials, especially for rare diseases like pheochromocytoma, are the major factors hampering the growth of the Pheochromocytoma treatment market.
Which is the leading Diagnosis in the Pheochromocytoma treatment market?
The Imaging Tests are the leading diagnosis segment.
Which are the major players operating in the Pheochromocytoma treatment market?
Pfizer Inc, Zydus Cadila, Novartis AG, Curium Pharma, AstraZeneca, Jubilant Cadista, Mylan N.V., Apotex Inc., Lupin, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals are the major players.