

The pneumonia, pneumococcal therapeutic market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.95 Billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 5.26 Billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.6% from 2025 to 2032. The growing geriatric population and increased risk of pneumonia among the elderly is driving the demand. Furthermore, rising pollution levels and environmental factors leading to higher prevalence of respiratory illnesses are also boosting the market growth.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR8.6%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 8.6% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Biotest AG, Vaxcyte, Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc. and Among Others |
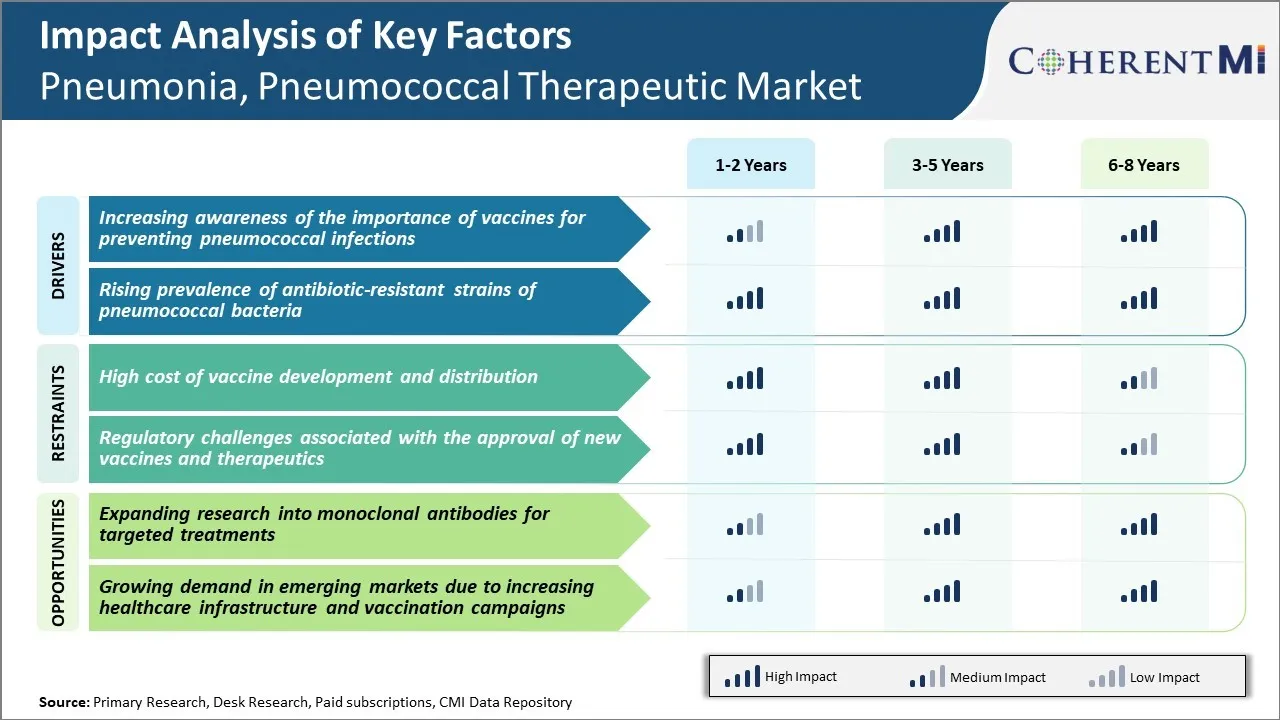
Market Driver - Increasing Awareness of the Importance of Vaccines for Preventing Pneumococcal Infections
More and more people are becoming aware that pneumonia and pneumococcal infections can be prevented through vaccination. Doctors and health organizations have significantly increased their education and counseling efforts regarding pneumococcal vaccines in recent years.
They are informing patients, especially older adults and those with chronic medical conditions, about how the bacteria Streptococcus pneumoniae is one of the leading causes of pneumonia. It can also lead to other serious illnesses like bacteremia and meningitis. With the rise of digital media and social networking, health information is more easily accessible which has contributed to growing knowledge.
Vaccination plays a critical role in protection against pneumococcal diseases. Doctors highlight that vaccines like PCV13 and PPSV23 help build immunity so the body is prepared to fight the infection causing bacteria. They reduce the risk of getting a pneumococcal infection and even if one gets infected after vaccination, the illness is likely to be less severe. With greater understanding of this, more individuals are willing to get recommended pneumococcal vaccines. Public health campaigns have also raised recognition of how vaccinating children provides herd immunity and protects the elderly and high-risk groups.
Market Driver - Rising Prevalence of Antibiotic-resistant Strains of Pneumococcal Bacteria
An ongoing concern globally is the rising threat of antibiotic resistance where bacteria evolve and become impervious to existing drugs. Pneumococcal bacteria have also been developing resistance at an alarming pace. Several antibiotic-resistant strains have emerged and become widespread in communities.
One of the primary reasons is the massive overuse and misuse of antibiotics for viral upper respiratory illnesses that they have no effect against. When antibiotics are indiscriminately prescribed for minor illnesses, it places immense selection pressure on bacteria to mutate their way around these drugs. As a result, resistant forms are selected and then transmit between individuals.
Many routine antibiotics are now ineffective against these ‘superbugs’ making infections much harder to treat. Pneumonia caused by drug-resistant pneumococci also leads to poorer outcomes and increased deaths. The rise in antibiotic-resistant strains is particularly concerning in settings with high HIV and institutions housing elderly or immunocompromised patients.
Facing this growing menace, healthcare providers feel compelled to use newer and often more expensive broad-spectrum antibiotics. Given the greater difficulties in management, it is also driving higher adoption of pneumococcal vaccines aimed at prevention. The escalating antimicrobial resistance seen in pneumococcal bacteria worldwide is a major concern propelling the therapeutic market forward.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High Cost of Vaccine Development and Distribution
One of the major challenges currently faced by players in the pneumonia, pneumococcal therapeutic market is the high costs associated with vaccine development and distribution. Developing an effective vaccine involves extensive research and clinical trials to ensure safety and efficacy. This R&D process requires massive investments and carries a high risk of failure.
Even if a vaccine makes it through all stages of development successfully, the costs of manufacturing, storage, and distribution pose significant financial challenges, especially in developing countries with weaker healthcare infrastructure and lower purchasing power.
Ensuring vaccines reach remote and rural populations further increases expenses. Additionally, vaccine prices must be kept affordable to improve accessibility, yet covering the high development costs within economically viable price points is difficult. Players will need to explore strategies like government subsidies, public-private partnerships, and prioritizing diseases causing the highest mortality burdens to balance profitability with public health goals.
Overall, the high financial outlay required throughout the vaccine value chain remains a major hurdle restricting better prevention against pneumonia globally.
Market Opportunity - Expanding Research into Monoclonal Antibodies for Targeted Treatments
One key opportunity for players in the pneumonia, pneumococcal therapeutic market lies in intensifying research efforts focused on monoclonal antibodies. Monoclonal antibodies have emerged as an important class of targeted biologic therapies with potential applications for both treatment and prevention of infectious diseases.
Compared to vaccines, monoclonal antibodies have advantages such as rapid onset of action, ability to provide short-term protection, and not requiring multiple doses over time for sustained effect. Several monoclonal antibodies are already in clinical trials for treating respiratory infections caused by pathogens like Streptococcus pneumoniae and testing new molecules could unlock new treatment options.
Additionally, monoclonal antibodies may be able to provide temporary protection for high-risk groups like the elderly during pneumonia seasons as an alternative or complement to vaccines. With continued research and development, monoclonal antibodies show promise to expand the product portfolio and address unmet needs in the pneumonia therapeutic space.
The standard line of treatment for Pneumonia, Pneumococcal Infection involves a multi-staged approach based on the severity and progression of symptoms. For mild cases in the early stages, doctors typically prescribe a 5-7 day course of macrolide antibiotics like azithromycin (Zithromax) or clarithromycin (Biaxin). These drugs are effective at targeting the most common strains of bacteria that cause pneumonia.
As the infection progresses and symptoms worsen, prescribers may switch treatment to a respiratory fluoroquinolone like levofloxacin (Levaquin) or moxifloxacin (Avelox). These broad-spectrum antibiotics provide stronger coverage against both typical and atypical pneumonia pathogens. For hospitalized patients with severe pneumonia, the preferred medications are intravenous antibiotics like ceftriaxone (Rocephin) or ampicillin/sulbactam (Unasyn). Treatment duration extends to 7-10 days to ensure the infection fully clears.
Several factors influence antibiotic selection at each disease stage. Prescribers consider the patient's age, underlying health conditions, allergies/intolerances, as well as the likely causative microorganisms based on locale and season. While macrolides typically work well for outpatient cases, fluoroquinolones are favored when risk of complications is higher or mixed bacterial and viral involvement is possible. Overall, the goal is initiating timely, targeted therapy to achieve the best outcomes.
Pneumonia is classified as mild, moderate or severe based on symptoms and test results. For mild pneumonia, over-the-counter medications may be sufficient. Patients are prescribed acetaminophen to reduce fever and cough suppressants. If symptoms persist or worsen after a few days, a doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
For moderate pneumonia, antibiotics are usually required. Common first-line treatments include amoxicillin, doxycycline, or azithromycin, administered orally. These broader-spectrum antibiotics target Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), the leading cause of bacterial pneumonia. Hospitalization isn't required in most moderate cases if symptoms improve within a few days of starting antibiotics.
Severe pneumonia requires hospitalization with intravenous (IV) antibiotics. Common options include ceftriaxone, cefotaxime orampicillin/sulbactam, administered via IV for 5-10 days. For very severe cases, last-line antibiotics like vancomycin or linezolid may be needed. Supplemental oxygen therapy is also given, and patients are monitored closely for complications like empyema (pus in the lungs).
Pneumococcal vaccination reduces infection risk and is recommended for adults over 65, smokers, and those with chronic illnesses. It provides coverage for over 90% of pneumococcal serotypes known to cause invasive disease.Proper treatment selection based on severity is key to resolving pneumonia quickly and preventing escalation to more advanced stages of disease.
Pfizer has been a leader in the pneumococcal vaccine market for decades with its pneumococcal conjugate vaccine Prevenar/Prevnar. In the late 1990s and early 2000s, Pfizer adopted an aggressive vaccination strategy targeting young children. It conducted extensive outreach programs to educate parents and physicians about the dangers of pneumococcal disease. Between 2000-2010, Prevenar usage in children under 2 years increased from 30% to over 90% in the US. This early mover advantage allowed Pfizer to capture over 70% market share.
Sanofi responded with its own pneumococcal conjugate vaccine Prevnar 13 in 2010. It pursued a wide age indication down to 6 weeks, allowing it to also target the large pediatric market. Between 2010-2015, Sanofi ran direct-to-consumer advertising campaigns emphasizing Prevnar 13's coverage of more pneumococcal serotypes compared to Prevenar.
In recent years, Merck has gained ground with its 15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine Vaxneuvance, approved in 2021. Leveraging its strong relationships with pharmacies and wholesale buyers, Merck aggressively discounted Vaxneuvance to gain formulary access. It also recruited respected KOLs and medical experts to publish data demonstrating Vaxneuvance's superiority over Prevnar 13. Within a year of launch, Vaxneuvance captured 10-15% U.S. market share from Pfizer and Sanofi.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
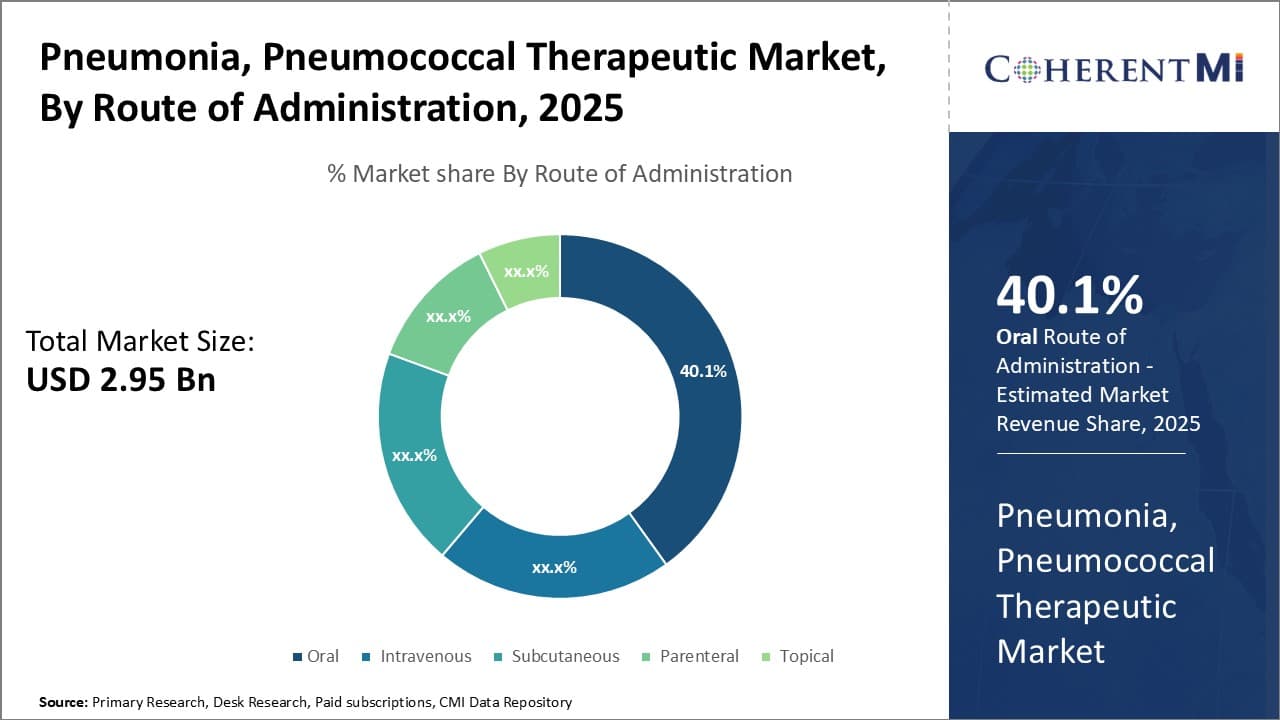
Insights, By Route of Administration: Ease of Self-Administration Drives Oral Segment Dominance
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Route of Administration: Ease of Self-Administration Drives Oral Segment Dominance
The oral route of administration segment currently holds the largest share of the pneumonia, pneumococcal therapeutic market. This dominance can be attributed to the ease of self-administration associated with oral medications. Patients find it much more convenient to simply take pills at home rather than visiting hospitals or clinics for intravenous or parenteral treatments. This leads to better patient compliance which is critical for effectively treating and managing a condition like pneumonia.
Additionally, oral drugs allow for a more gradual and prolonged delivery of the active ingredients over time as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. This sustained release improves bioavailability and ensures therapeutic drug levels are maintained continuously in the body. The non-invasiveness of oral administration further makes it more acceptable and appealing to patients.
Leading pharmaceutical companies have therefore focused on developing novel oral formulations like softgels, granules and extended-release tablets for pneumonia drugs. These enhanced oral delivery systems aim to mask unpleasant tastes, facilitate dosing in pediatric/geriatric patients, and offer site-specific drug targeting in the GI tract for optimized systemic absorption. Several popular brands with oral drug formulations currently dominate the pneumonia market owing to such advantages of the oral route of administration.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
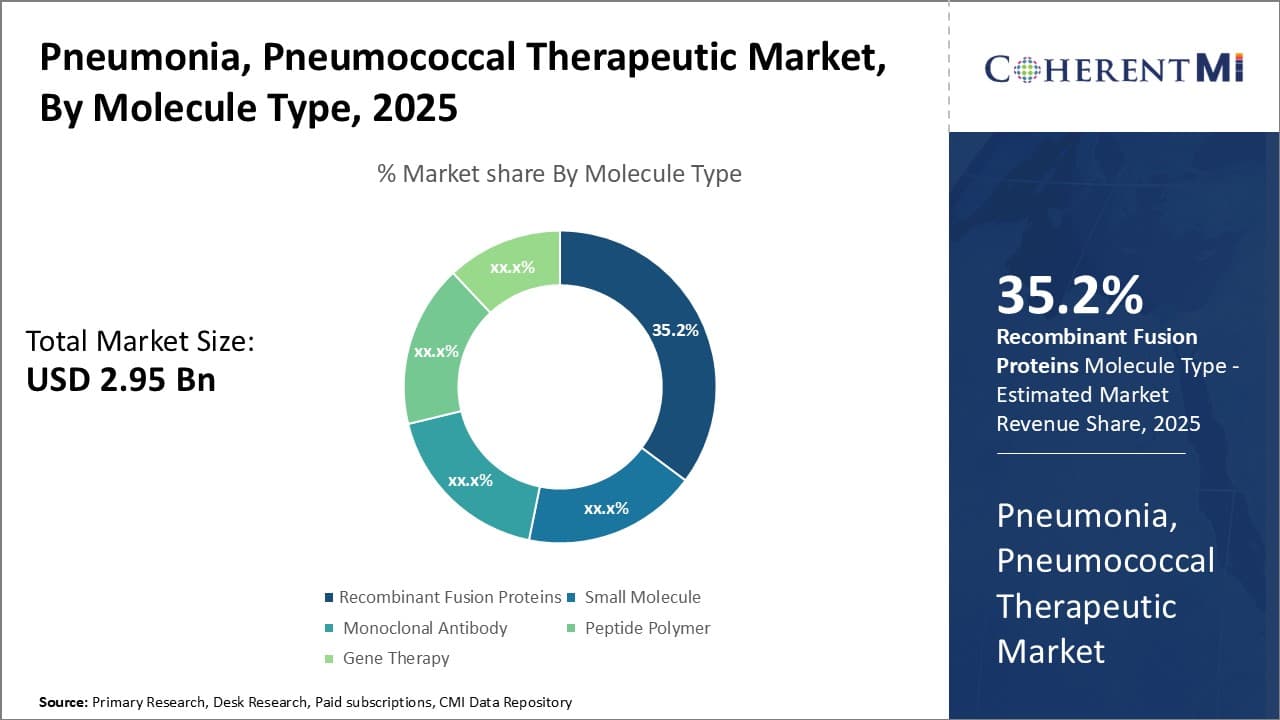
Insights, By Molecule Types: Preference for Targeted Mechanisms Boosts Recombinant Fusion Proteins
Among different molecule types for treating pneumonia, recombinant fusion proteins account for the highest share presently. This segment growth can be attributed to the smart, targeted mechanisms of action associated with these biologics. Recombinant fusion proteins have the ability to selectively bind to specific receptors overexpressed on bacterial or infected cells.
Their high binding affinity and specificity minimizes adverse effects by preventing unwanted interactions with healthy tissues. This precision allows recombinant fusion proteins to eradicate pathogenic organisms more effectively while also reducing the potential for generating antibiotic resistance. The additional merits of long half-life and less frequent dosing requirements through fusion to Fc domains or albumin further support patient compliance.
Leading developers continuously work on enhancing such selectivity and tuning pharmacokinetic profiles of recombinant biologics. Next-generation platforms like domain-antibody fusions and immunoconjugates also expand the toolbox of targeted mechanisms against difficult-to-treat respiratory infections. The clear advantages over small molecules in achieving pathogen clearance through refined selectivity and potency will continue propelling the recombinant fusion protein segment ahead in the pneumonia therapeutic space.
The major players operating in the Pneumonia, Pneumococcal Therapeutic Market include Biotest AG, Vaxcyte, Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc., Sanofi, Johnson & Johnson, Astellas Pharma Inc., CSL Limited, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Bavarian Nordic, and SutroVax, Inc.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
Pneumonia, Pneumococcal Therapeutic Market is segmented By Route of Administration (Oral, Intravenou...
Pneumonia, Pneumococcal Therapeutic Market
How big is the pneumonia, pneumococcal therapeutic market?
The pneumonia, pneumococcal therapeutic market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.95 Billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 5.26 Billion by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the pneumonia, pneumococcal therapeutic market?
The high cost of vaccine development and distribution and regulatory challenges associated with the approval of new vaccines and therapeutics are the major factors hampering the growth of the pneumonia, pneumococcal therapeutic market.
What are the major factors driving the pneumonia, pneumococcal therapeutic market growth?
The increasing awareness of the importance of vaccines for preventing pneumococcal infections and rising prevalence of antibiotic-resistant strains of pneumococcal bacteria are the major factors driving the pneumonia, pneumococcal therapeutic market.
Which is the leading route of administration in the pneumonia, pneumococcal therapeutic market?
The leading route of administration segment is oral.
Which are the major players operating in the pneumonia, pneumococcal therapeutic market?
Biotest AG, Vaxcyte, Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc., Sanofi, Johnson & Johnson, Astellas Pharma Inc., CSL Limited, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Bavarian Nordic, SutroVax, Inc. are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the pneumonia, pneumococcal therapeutic market?
The CAGR of the pneumonia, pneumococcal therapeutic market is projected to be 8.6% from 2025-2032.