

The Rare Kidney Diseases Market is estimated to be valued at USD 4.26 Billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 9.07 Billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.4% from 2025 to 2032. The increasing prevalence of chronic kidney diseases and various types of rare genetic disorders affecting the kidneys are driving the demand for improved diagnostic and treatment options.
The market is witnessing positive trends with the availability of novel drug therapies and new treatment approaches to manage rare kidney conditions. Furthermore, the launch of personalized medicines and recent approvals of orphan drugs to treat specific rare nephropathies are helping boost the clinical outcomes for patients. Increasing R&D investments by pharmaceutical companies in this domain will further fuel market growth during the forecast period.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR11.4%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 11.4% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Seres Therapeutics, Inc., Enterome, 4D pharma plc, International Flavors & Fragrances Inc., OptiBiotix Health Plc and Among Others |
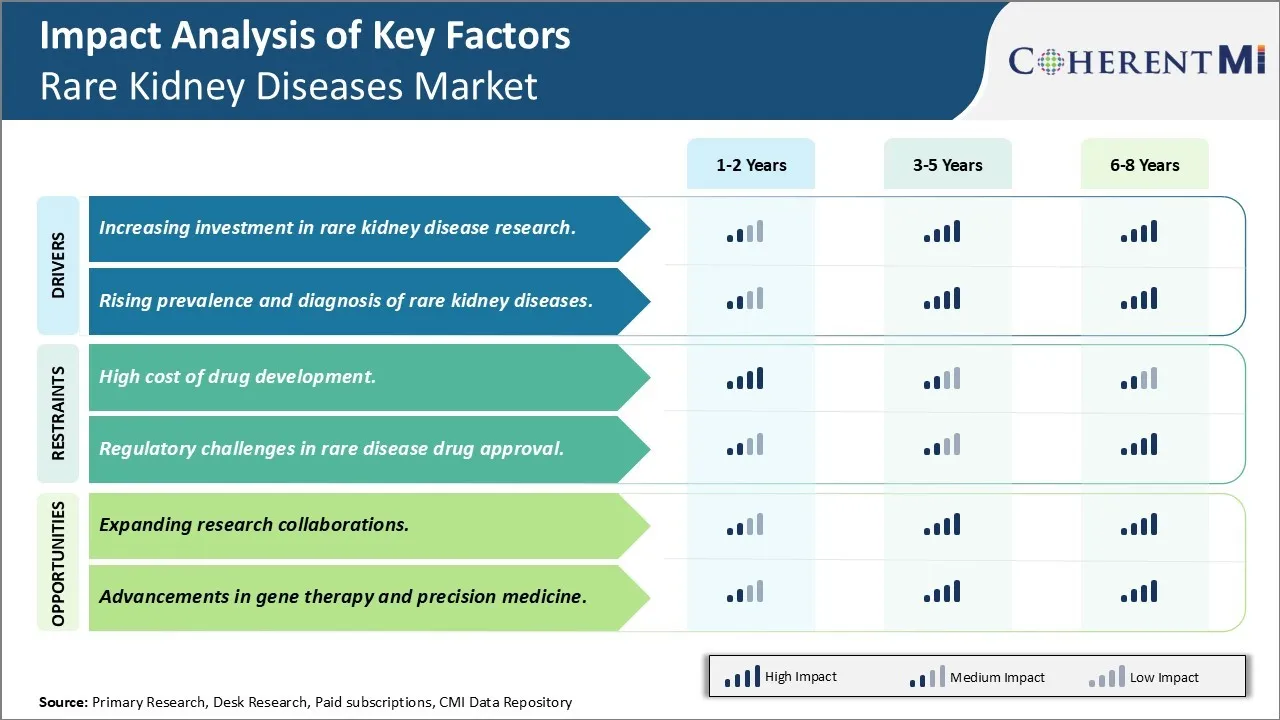
Market Driver - Increasing investment in rare kidney disease research.
The field of rare kidney disease research has seen significant investments over the past decade from both private and public organizations. There is a growing recognition that many of these conditions still lack effective treatment options and our understanding of the underlying biological mechanisms remains limited. Major pharmaceutical companies have started dedicating more funds to developing orphan drugs that target rare kidney diseases. Some of the promising pipelines in clinical trials can potentially transform the lives of patients if approved.
Government agencies and nonprofit foundations have also increased their commitments. For example, the National Institutes of Health has established dedicated grant programs that provide funding exclusively for rare disease studies. Several biotech startups have received venture capital backing to advance new diagnostic tests and therapeutics. Charitable patient advocacy groups are allocating more donations collected through various fund raising efforts into sponsoring research. All of these dedicated investments are helping boost enrollment numbers in clinical studies and drive novel discoveries.
Scientists now have greater access to state of the art research infrastructure and tools to unravel the complex genetics and pathways involved. More specialized rare disease research centers and consortiums have emerged in leading academic medical institutions. International collaborations are allowing researchers to pool resources and gather larger sample sizes which are often difficult for rare conditions. Major technology advancements in areas such as genomic sequencing, stem cell modeling, organ chips and artificial intelligence are fueling new insights at an accelerating pace. With the inflow of capital showing no signs of slowing, we can expect significant progress to be made in identifying targets and developing breakthrough treatments over the coming years.
Rising prevalence and diagnosis of rare kidney diseases
There are multiple factors that are contributing to a growth in prevalence and improved diagnosis of rare kidney diseases globally in recent times. Advances in modern medical technologies have enabled doctors to detect manifestations that were not identifiable before. Next generation sequencing has dramatically improved our ability to pinpoint causal genetic mutations underlying many rare conditions. This is leading to more conclusive diagnoses than ever before. Meanwhile, improved awareness among the healthcare community and public is resulting in enhanced screening efforts and improved identification of at-risk populations.
Higher rates of diagnosis are also a reflection of populations aging in many parts of the world. As lifespan increases, patients now survive long enough for rarer forms of kidney diseases to manifest later in their lifetime. Growing environmental pollutants and toxin exposures pose novel risks that can trigger atypical presentations of rare diseases as well. International travel and migration trends have made it more common for doctors to encounter patient cases originating from diverse ethnic backgrounds with a higher likelihood of certain rare genetic diseases.
Lastly, patients have become more proactive in self-advocating and pioneering the use of online communities to crowdsource information to arrive at the right diagnosis after “doctor shopping” for several years. While not all cases can be identified, the collective efforts of multiple parties are expanding our edges of medical understanding and narrowing the gap between estimated and confirmed prevalence of many under-recognized rare kidney conditions. This momentum will likely continue its positive impact.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Challenge: High cost of drug development
The high cost of drug development is a major challenge for the rare kidney diseases market. Developing drugs to treat rare diseases is very expensive due to the small patient populations and limited market size. This results in pharmaceutical companies lacking sufficient financial incentive to invest resources into researching and developing new treatments. With small target populations, rare disease drug developers are often unable to recoup their high investment costs through product sales alone. It is estimated that developing an orphan drug can cost over $1 billion, while the average drug costs around $800 million to develop. Additionally, clinical trials for rare diseases are challenging due to difficulties finding enough patients to participate. This prolongs development timelines and increases costs further. The high financial risks associated with rare disease drug development may discourage companies from entering this market space. For the rare kidney diseases market to grow, mechanisms need to be established that make drug R&D more financially viable for pharmaceutical companies.
Opportunity: Expanding research collaborations
Expanding research collaborations between pharmaceutical companies, patient advocacy groups, and government agencies presents a major opportunity for growth in the rare kidney diseases market. By collaborating, the different stakeholders are able to pool their resources and expertise to advance drug development at a lower overall cost. For example, patient advocacy groups play an important role by assisting with patient recruitment for clinical trials. They establish networks of potential participants and raise awareness of trial opportunities. Government agencies also offer funding support through public grants as well as incentives such as extended market exclusivity periods for orphan drugs upon approval. This helps boost the potential returns on investment for pharmaceutical developers and share some of the financial risk. Increased partnership between players in the rare disease space is therefore key going forward. It lowers barriers to rare disease drug development and fuels greater investment into new treatments and cures, expanding the rare kidney diseases market overall.
Focus on gene therapy and precision medicines: Many big pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in developing gene therapies and precision/personalized medicines to treat rare kidney diseases. For example, Reata Pharmaceuticals' bardoxolone methyl showed promise in treating Alport syndrome and IgA nephropathy in Phase 2 trials. If approved, it could significantly help patients with limited treatment options. Vertex Pharmaceuticals acquired Exonics Therapeutics in 2021 to gain access to its pipeline of gene therapies for polycystic kidney disease (PKD) and Alport syndrome.
Target underserved patient populations: There is high unmet medical need in developing nations for treating rare kidney diseases. Companies like Travere Therapeutics have focused on expanding access to therapies in Asia, Latin America, Middle East and Africa through partnerships. Its drug sparsentan recently gained approval in China for focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). This strategy helped Travere enter a large patient population at an early stage.
Partner with patient advocacy groups: Having the support of patient groups is crucial for rare disease drugs. Most leading companies regularly partner with advocacy organizations like the PKD Foundation, NephCure Kidney International and Alport Syndrome Foundation on awareness and support programs. This builds goodwill among stakeholders and helps attract patients to clinical trials.
Acquisitions of small biotechs: Large pharmaceutical firms acquire smaller biotechs working on niche rare kidney disease programs. For instance, Sanofi acquired Synthorx in 2020 to gain access to its preclinical autoimmune and kidney disease portfolio. Such deals help companies expand their pipelines and portfolios quickly without spending on early-stage R&D.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
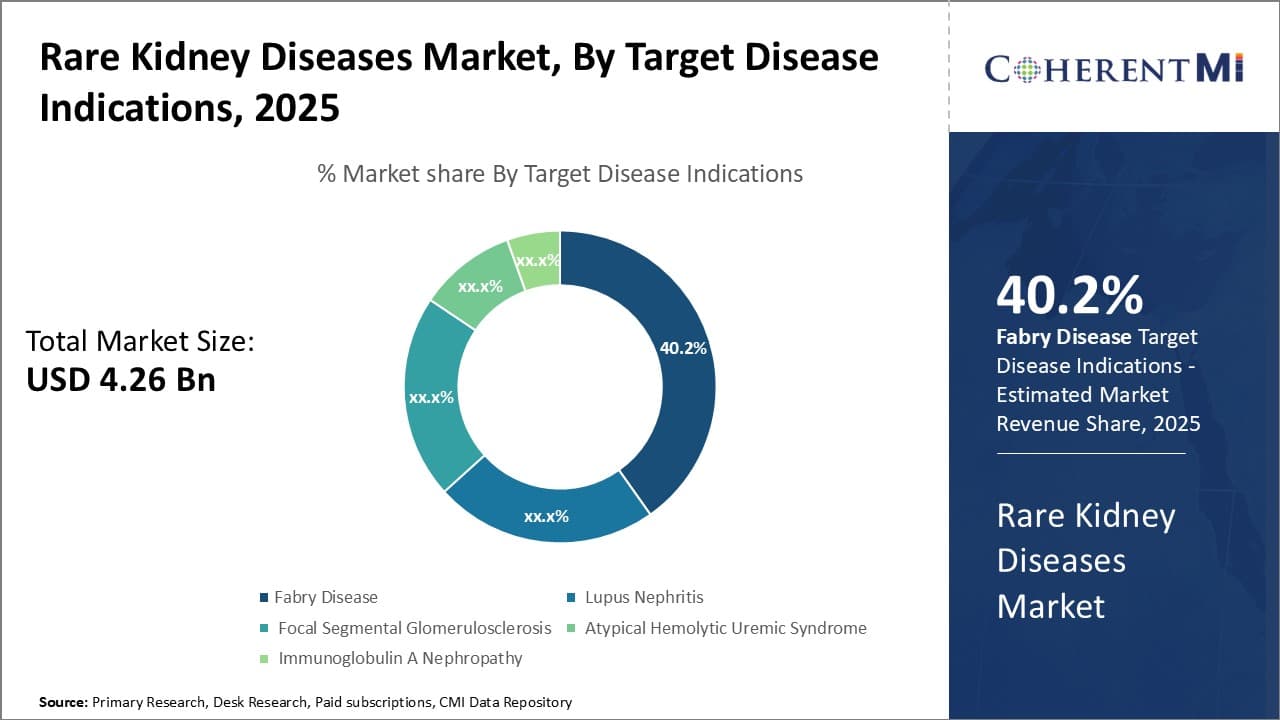
By Target Disease Indications- Increased Awareness and Diagnosis Drives Fabry Disease Segment
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
By Target Disease Indications- Increased Awareness and Diagnosis Drives Fabry Disease Segment
In terms of Target Disease Indications, Fabry Disease contributes the highest share of the market owing to growing awareness and improved diagnosis rates. Fabry disease is an inherited lysosomal storage disorder caused by deficient activity of the enzyme alpha-galactosidase A. For many years it went under-diagnosed due to its non-specific symptoms. However, heightened screening efforts by patient advocacy groups and support from pharmaceutical companies have enabled widespreadcascade screening of at-risk family members. This has led to identification of many undiagnosed patients. Further, advancement in techniques like newborn screening has allowed early detection before symptom onset, improving treatment outcomes.
Growing patient numbers have supported market uptake of enzyme replacement therapies for Fabry disease. Drugs like Agalsidase alfa and Agalsidase beta enjoy favorable reimbursement coverage for treating classic Fabry disease. Their administration through intravenous infusions requires specialized healthcare resources. However, availability of supportive programs and home healthcare has made long-term treatment more feasible. Novel oral therapies currently in late stage trials also hold promise to drive better adherence if approved. Overall, increasing public knowledge about the condition alongside effective diagnosis tools has enabled significant growth of the Fabry disease segment.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
By Molecule Type:- Rising Incidence Drives Lupus Nephritis Segment
In terms of Target Disease Indications, Lupus nephritis also captures a sizable portion of the rare kidney diseases market. The incidence and prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), of which lupus nephritis is a serious complication, has been rising globally over the past few decades. Africa and Asia Pacific regions in particular have witnessed growth rates higher than western countries. Improved survival of SLE patients and lack of a cure means more people are living with the condition and at risk of developing kidney damage. Early diagnosis through renal biopsy has allowed for timely immunosuppressive therapy in lupus nephritis cases.
Biologics dominate treatment of proliferative lupus nephritis owing to their potent immunomodulating effects. Drugs like Belimumab specifically target B-cell mediated immune responses implicated in SLE and lupus nephritis pathology. Mycophenolate is commonly used as standard of care to complement corticosteroids. Furthermore, research efforts are ongoing to develop novel strategies targeting specific immune pathways and biomarkers to achieve remission with reduced toxicity. Industry partnerships with clinical research consortiums actively enroll SLE patients to test new therapies. Therefore, increasing disease incidence, aggressive treatment approaches and robust pipeline support consistent uptake in the lupus nephritis segment.
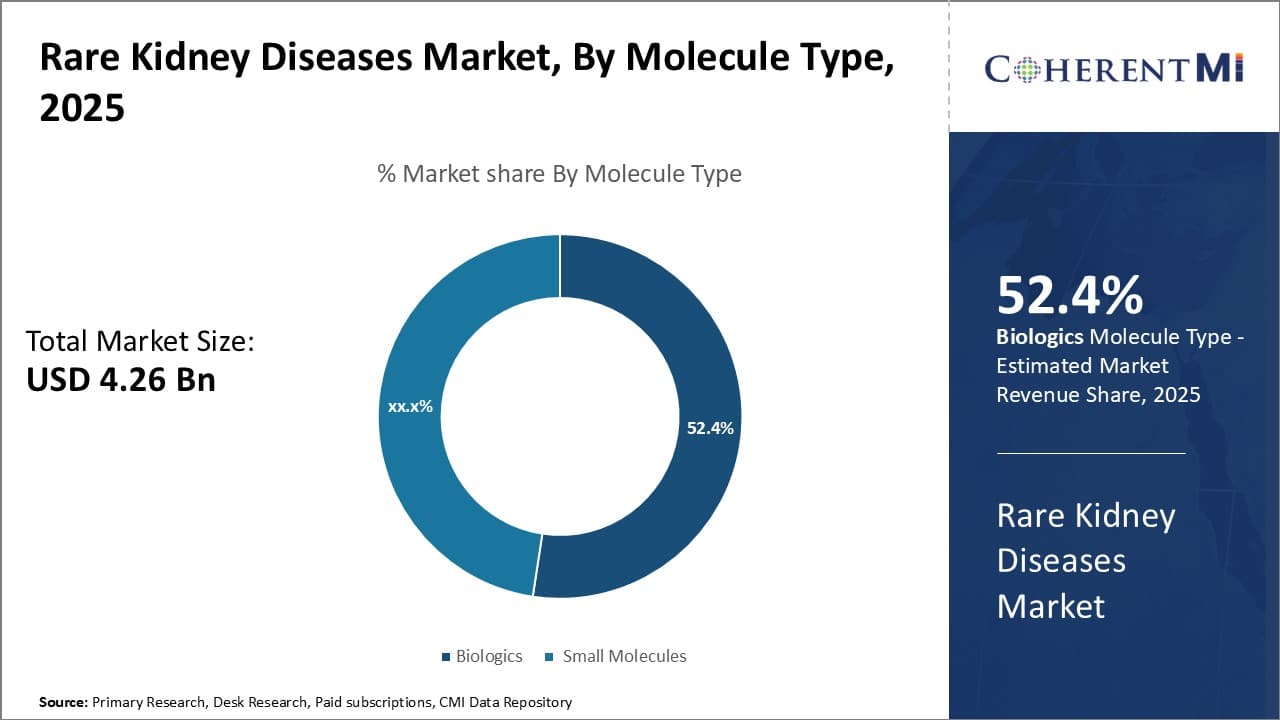
By Route of Administration- Ease of Oral Administration Boosts Small Molecule Dominance
By Route of Administration, the oral route captures the leading segment within the rare kidney diseases therapeutics market. The dominance of the oral route can be attributed to the widespread availability of effective small molecule therapies that are convenient for long-term use. Many diseases like Fabry disease, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) commonly employ orally-dosed small molecule therapies as first-line options due to their ease of use compared to injectables.
For example, corticosteroids remain a backbone treatment for IgAN and FSGS despite adverse effects, due their effectiveness when taken orally. Research has focused on developing targeted oral agents with improved tolerability profiles. Drugs likeFinerenone for FSGS have established oral formulations as an inducement for patient adherence. Furthermore, new pipeline candidates for Fabry disease like gene editing therapies aim for simplified dosing to drive compliance to management regimens spanning decades. Home healthcare programs also contribute by providing administration support and monitoring adherence for those on oral therapies. Together, oral drugs address an important unmet need for convenience in chronic rare kidney disease management.
The major players operating in the Rare Kidney Diseases Market include Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Synlogic, Inc., Second Genome, Inc., Vedanta Biosciences, Inc., YSOPIA Bioscience, FlightPath Biosciences, Inc., Finch Therapeutics Group, Inc., AOBiome Therapeutics, BioGaia, Quantbiome, Inc., Viome Life Sciences, Inc., BIOHM Health, DayTwo, Atlas Biomed and Gnubiotics Sciences.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
Rare Kidney Diseases Market is Segmented By Target Disease Indications (Fabry Disease, Lupus Nephrit...
Rare Kidney Diseases Market
How big is the Rare Kidney Diseases Market?
The Rare Kidney Diseases Market is estimated to be valued at USD 4.26 in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 9.07 Billion by 2032.
What are the major factors driving the Rare Kidney Diseases Market growth?
The increasing investment in rare kidney disease research. and rising prevalence and diagnosis of rare kidney diseases. are the major factor driving the Rare Kidney Diseases Market.
Which is the leading Target Disease Indications in the Rare Kidney Diseases Market?
The leading Target Disease Indications segment is Fabry Disease.
Which are the major players operating in the Rare Kidney Diseases Market?
Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Synlogic, Inc., Second Genome, Inc., Vedanta Biosciences, Inc., YSOPIA Bioscience, FlightPath Biosciences, Inc., Finch Therapeutics Group, Inc., AOBiome Therapeutics, BioGaia, Quantbiome, Inc., Viome Life Sciences, Inc., BIOHM Health, DayTwo, Atlas Biomed, Gnubiotics Sciences are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the Rare Kidney Diseases Market?
The CAGR of the Rare Kidney Diseases Market is projected to be 11.4% from 2025-2032.