RNA Targeted Therapeutics Market Size - Analysis
The RNA targeted therapeutics market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.81 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 15.10 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 35.4% from 2025 to 2032.
The market is witnessing positive trends owing to rising prevalence of target medical conditions and increasing number of RNA therapeutics under clinical trials. There has been a considerable increase in research and development activities for RNA therapeutics over the past decade. Many biopharma companies are actively working on RNA interference technologies to develop treatment for cancer, genetic diseases, and infectious diseases. Recent regulatory approvals and successful commercialization of few RNA therapeutics have boosted confidence in this platform. If upcoming clinical trial results are positive, it may lead to approval and commercialization of more RNA drugs in the near future. This will upsurge demand and drive higher market revenues during the forecast period.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR35.4%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 35.4% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Abivax, AC Immune, Arrakis Therapeutics, eFFECTOR Therapeutics, Eloxx Pharmaceuticals and Among Others |
please let us know !
RNA Targeted Therapeutics Market Trends
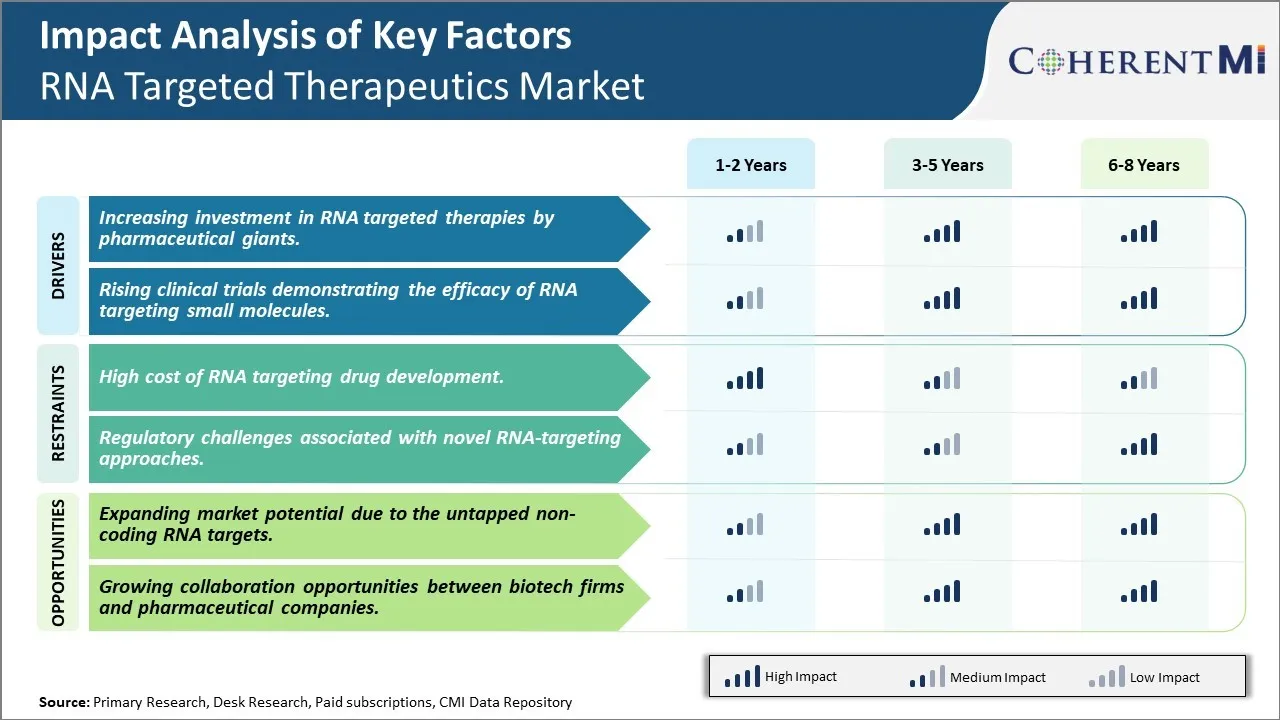
Market Driver - Increasing investment in RNA targeted therapies by pharmaceutical giants
The pharmaceutical industry has recognized the immense potential of RNA targeted therapeutics and has been steadily increasing investments in this promising area of drug development. Many big pharma companies are now dedicating large portions of their research & development budgets to further our understanding of RNA biology and develop novel RNA targeting molecules.
Some of the major players leading this transition include Pfizer, Roche, Merck & Co., Johnson & Johnson and AstraZeneca. In the last 5 years, these companies have significantly ramped up their RNA focused programs by acquiring smaller biotech firms working in this domain, partnering with academic labs, and setting up large RNA research centers. For instance, Pfizer recently spent over $600 million to acquire Trillium Therapeutics, a pioneer in immuno-oncology therapies utilizing cytokine therapies. Similarly Roche, who is a front-runner in cancer immunotherapies, has committed well over $1 billion since 2018 to build its RNA capabilities organically as well as inorganically through partnerships.
The strategic vision behind this investment trend is clear. Large pharmaceutical firms realize that RNA offers unprecedented potential for developing truly transformative therapies across disease areas. By modulating gene expression and protein levels, RNA targeted drugs have the ability to treat conditions previously believed to be "undruggable". This promises to open up whole new treatment paradigms and multi-billion dollar markets. The first wave of promising clinical RNA candidates validates this perception, with RNA interference and antisense oligonucleotide based medicines already demonstrating efficacy against cancer, neurological disorders as well as rare genetic diseases. With more investment pouring in, rapid scientific progress is expected to make RNA drugs a mainstay of treatment in the near future. This investment momentum is thus a major driver propelling the RNA targeted therapeutics market to new heights.
Market Driver - Rising clinical trials demonstrating the efficacy of RNA targeting small molecules
Another encouraging development driving significant growth in the RNA therapeutics field is the rising success of clinical trials evaluating novel RNA targeting small molecule candidates. Over the past decade, researchers have developed diverse classes of small molecule RNA targeting agents like siRNA, oligonucleotides, aptamers and small activating RNAs (saRNAs). These molecules offer several advantages compared to larger biologics like better tissue distribution, oral availability and lower costs of manufacturing and delivery.
Clinical validation of these small molecule therapies has been rising steadily. For example, recent late phase studies showed that inclisiran, a small interfering RNA targeting PCSK9, can safely and effectively lower cholesterol and reduce cardiovascular events when dosed just twice a year. Patisiran, an interfering RNA targeting transthyretin achieved overwhelmingly positive results for treating hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis in phase 3 trials. Eplontersen, an antisense oligonucleotide is demonstrating efficacy in phase 3 for treating spinal muscular atrophy. Even in oncology, clinical studies indicate that mRNA encoded vaccines can generate robust antitumor immune responses.
As more molecules clear clinical efficacy and safety hurdles, pharmaceutical companies and venture investors are gaining confidence that RNA targeting therapies can indeed become mainstream treatment options. The high success rates of ongoing trials signify that scientists have overcome many delivery challenges and gained deeper understanding of RNA pharmacology. This clinical proof-of-concept gives tremendous validation to the field and reassures stakeholders to commit greater resources. With a strong pipeline of new candidates in various disease areas, the positive outcomes from RNA therapeutic clinical programs are sure to significantly accelerate the commercialization and adoption of RNA targeted medicines in the years to come.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High cost of RNA targeting drug development
One of the major challenges facing the RNA targeted therapeutics market is the high cost associated with developing RNA targeting drugs. Developing RNA targeting therapies is an intricate process that requires significant investments in research and clinical trials. Designing siRNA, antisense, and aptamer therapeutics that can safely and effectively regulate RNA function with minimal off-target effects is a major scientific hurdle. Extensive research needs to be conducted to identify RNA targets linked to disease pathways and design oligonucleotides or other molecules that can modulate those targets without causing toxicity or unwanted immune reactions. Additionally, clinical trials involving RNA targeting drugs tend to be complex and lengthy due to safety and delivery challenges. Companies need to incur substantial costs for conducting multiple phases of clinical trials to prove drugs' safety, efficacy, and obtain regulatory approvals before commercialization. The high risk of failure and lengthy development timelines add to the overall costs. This makes it difficult for smaller companies and startups to independently develop RNA drugs and bring them to market. The high costs involved create barriers for further innovation and commercialization in the field of RNA targeting therapies.
Market Opportunity - Expanding market potential due to the untapped non-coding RNA targets
One of the key opportunities for growth in the RNA targeted therapeutics market is the expanding market potential resulting from the untapped class of non-coding RNA targets. While developments so far have majorly focused on targeting messenger RNA (mRNA) to block the translation of disease-causing proteins, recent research has revealed that non-coding RNAs like microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs) also play vital roles in various disease pathways. Non-coding RNAs have emerged as crucial regulators of gene expression and several diseases have been linked to their dysregulation. However, compared to mRNA targeting, relatively few therapies aiming to modulate non-coding RNAs are under development. As research progresses in understanding the roles and functions of non-coding RNAs, several novel targets for conditions like cancer, neurological disorders, and metabolic diseases are expected to be identified. This opens up a huge opportunity for companies to develop innovative non-coding RNA targeting therapies. Targeting these untapped spaces has the potential to expand the current applications and market size of RNA drugs.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of RNA Targeted Therapeutics Market
In 2020, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals partnered with Regeneron Pharmaceuticals to develop RNAi therapeutics for eye diseases. This allows both companies to leverage their expertise and resources to accelerate the development of RNAi therapies for ocular conditions.
In 2018, Ionis Pharmaceuticals partnered with Biogen to develop novel antisense drugs for neurological disorders. This 10-year strategic collaboration allows the companies to share research and development costs, with Biogen paying Ionis over $1 billion in upfront payment.
In 2021, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals acquired Takeda's pipeline of RNAi therapeutics to enhance its portfolio of RNA-based drugs. This added multiple clinical stage programs to Arrowhead's pipeline.
In 2019, Roche acquired Spark Therapeutics for $4.3 billion to gain access to its gene therapy platform and pipeline including investigational Hemophilia A treatment.
Segmental Analysis of RNA Targeted Therapeutics Market
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
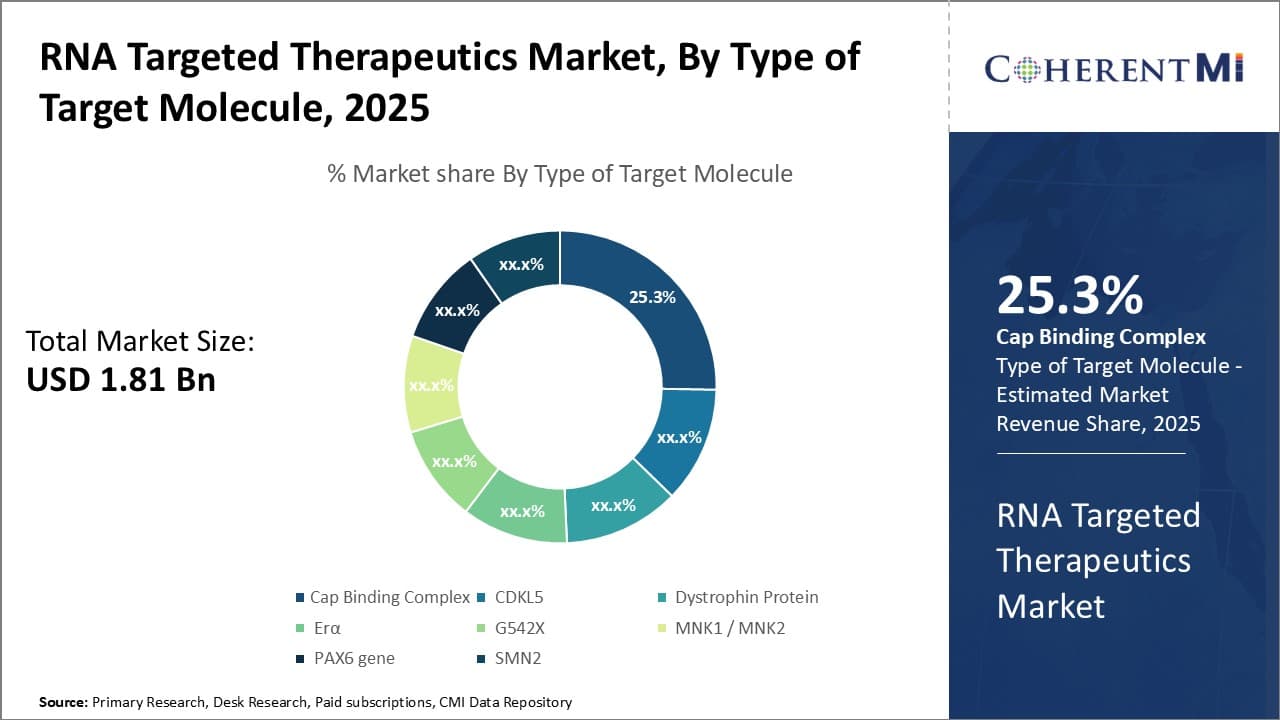
Insights, By Type of Target Molecule: Cap complex leads targeted therapeutics owing to its central role in translation
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Type of Target Molecule: Cap complex leads targeted therapeutics owing to its central role in translation
The cap binding complex sub-segment dominated the RNA targeted therapeutics market with a share of 25.3% in terms of target molecule type. This is due to the central role the Cap Binding Complex plays in initiating mRNA translation. The cap binding complex recognizes the 5' cap structure found in eukaryotic messenger RNAs and recruits the large ribosomal subunit to begin protein synthesis. By disrupting the interaction between the Cap Binding Complex and the mRNA cap, translation can be halted for genes of interest. Many diseases are caused by aberrant expression of certain genes. Targeting the cap binding complex allows for precise control over translation and offers a promising approach for developing therapies.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
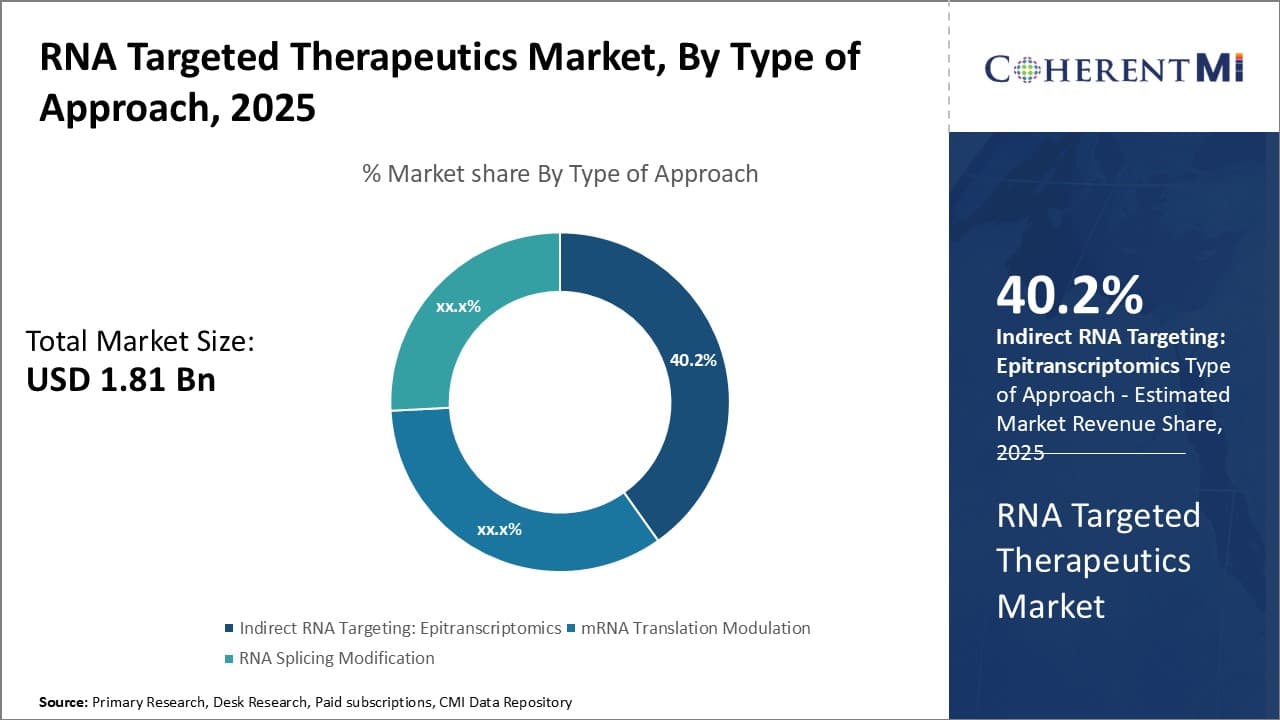
Insights, By Type of Approach: Epitranscriptomics sub-segment at the forefront of indirect targeting
Within the approach type segment of the RNA targeted therapeutics market, indirect targeting through epitranscriptomics held the leading share of 40.2%. Epitranscriptomics refers to reversible chemical modifications on RNA molecules, distinct from changes in the nucleic acid sequence. These modifications influence key properties of RNAs like stability, localization, and interactions with other molecules to regulate gene expression. Emerging evidence indicates RNA modifications play important roles in various biological processes and human diseases. Being able to target the enzymes responsible for installing or removing epitranscriptomic marks offers an indirect yet effective way to modulate gene expression for therapeutic benefit. Many companies are investing in developing therapies focused on epitranscriptomic enzymes given its potential for treatments across multiple disease areas.
Additional Insights of RNA Targeted Therapeutics Market
The RNA targeted therapeutics market is rapidly expanding due to its potential in treating previously untreatable conditions by focusing on non-coding RNAs. Over the last five years, significant investments have been made, and multiple small biotech companies have emerged as pioneers in this field, developing innovative RNA-targeting technologies. The market is expected to witness robust growth, with key players driving advancements in oncological and non-oncological therapeutic areas.
Competitive overview of RNA Targeted Therapeutics Market
The major players operating in the RNA targeted therapeutics market include Abivax, AC Immune, Arrakis Therapeutics, eFFECTOR Therapeutics, Eloxx Pharmaceuticals, H3 Biomedicine, PTC Therapeutics, Ribometrix, Skyhawk Therapeutics and STORM Therapeutics.
RNA Targeted Therapeutics Market Leaders
- Abivax
- AC Immune
- Arrakis Therapeutics
- eFFECTOR Therapeutics
- Eloxx Pharmaceuticals
Recent Developments in RNA Targeted Therapeutics Market
- In March 2023, SiSaf partnered with the University of Leipzig to develop bio-courier targeted miRNA for treating pancreatic cancer. This collaboration aims to enhance targeted delivery methods, potentially improving therapeutic outcomes for pancreatic cancer patients.
- In February 2023, ReviR Therapeutics and Asieris initiated a research agreement to develop treatments for genitourinary tumors using RNA-targeted technologies, marking significant progress in addressing serious diseases within the genitourinary field.
RNA Targeted Therapeutics Market Segmentation
- By Type of Target Molecule
- Cap Binding Complex
- CDKL5
- Dystrophin Protein
- Erα
- G542X
- MNK1 / MNK2
- PAX6 gene
- SMN2
- By Type of Approach
- Indirect RNA Targeting: Epitranscriptomics
- mRNA Translation Modulation
- RNA Splicing Modification
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
