Robotic Welding Market Trends
Market Driver - Rising Demand for Automation to Enhance Productivity and Reduce Errors
Over the past few decades, manufacturers have been increasingly looking to automate various processes on their production floors to boost productivity and prevent human errors. One area that has seen significant uptake of robotics is welding. With robotics, manufacturers are able to automate repetitive welding tasks and achieve finer precision and consistency compared to manual welding.
The reduced dependency on skilled labor has also helped many companies cope with acute shortages of welders. This is particularly for specialized welding types that require extensive training and experience. Given current demographic trends, shortages are expected to worsen in the coming years, further driving the demand for robotic welding solutions.
From an operational perspective, robotic welding cells are highly configurable and modular. Additional robots can be added or removed easily based on changing production volumes without disrupting the workflow. This makes robotic welding highly scalable compared to manual lines that need to be expanded or reconfigured.
Market Driver - Reduction in Labor Costs through Robotic Efficiency and Scalability
Alongside the productivity and quality benefits, a key factor driving wider uptake of robotic welding solutions is the reduction in long-term labor costs for manufacturers. The initial capital outlay for robotics welding system installation is high. However, manufacturers realize significant savings in labor costs within a few years of deployment through greater efficiency and scalability. Robotic welders can complete welding tasks much faster compared to manual methods as they are not bound by human constraints and can work continuously.
Another major cost advantage stems from the multi-tasking capability of robots. Advanced welding robots today can perform complex welding sequences involving different joint types, materials, and positions in a single operation. It replaces the need for multiple dedicated manual welding stations.
Lastly, robotic systems provide scalability in production without additional labor requirements. As volumes fluctuate, manufacturers can simply activate or deactivate robots as needed rather than hiring and training new welders or laying them off during downturns. All these factors contribute to robotic welding market’s growth.
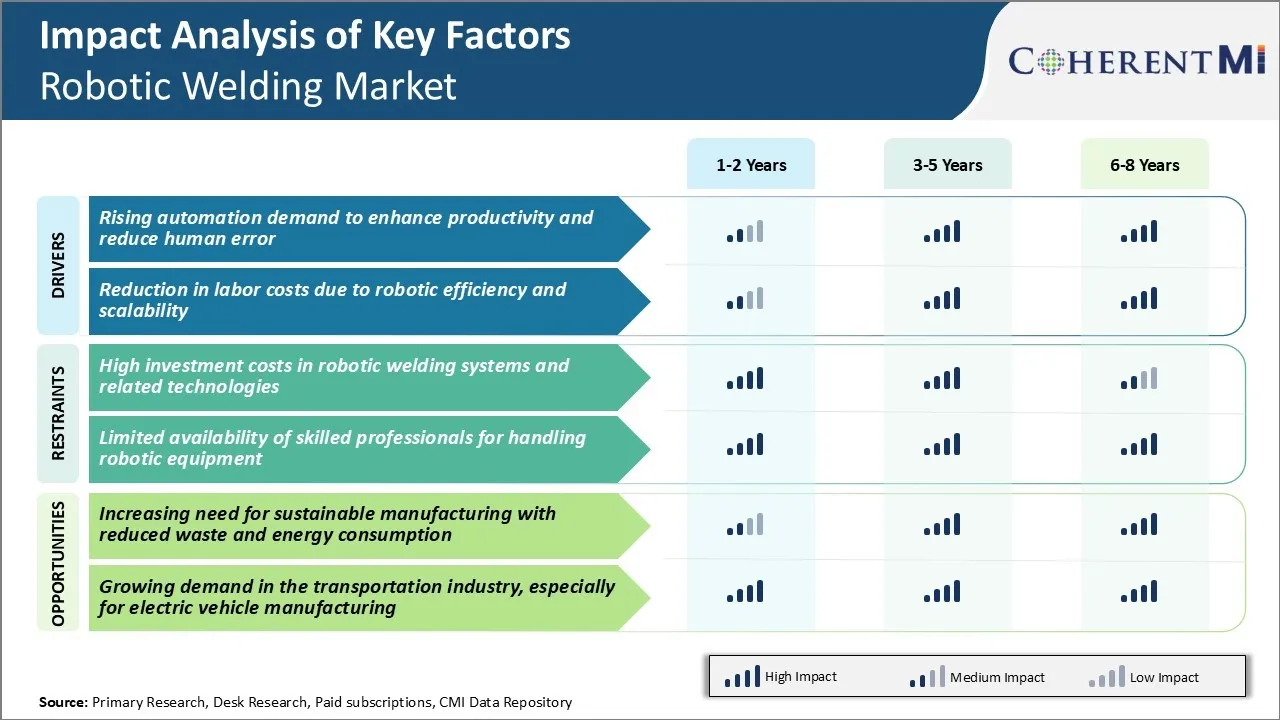
Market Challenge - High Investment Costs in Robotic Welding Systems and Related Technologies
The initial investment required for robotic welding systems and related technologies presents a major challenge for widespread expansion of the robotic welding market. The high capital expenditure discourages many small and medium enterprises from automating their welding processes. Robotic cells can range in price from tens of thousands to over a million dollars depending on the type, payload capability and complexity of operations.
Additional costs are incurred for system integration, tooling, safety enclosures and operator training. Financing options from equipment suppliers and the complexity of ROI calculations also pose challenges. Given the technical sophistication of these systems, high maintenance and support costs further impact the total cost of ownership over the lifecycle.
With competitive pressures to reduce costs and maximize margins, many manufacturers are reluctant to make such sizable investments unless optimal capacity utilization levels can be assured over several years to properly amortize the costs.
Market Opportunity - Increasing Need for Sustainable Manufacturing with Reduced Waste and Energy Consumption
There is a rising need among manufacturers to reduce the environmental impact of their operations and transition to more sustainable production methods. Robotic welding market presents promising opportunities in this area by enabling waste reduction techniques and improving energy efficiency compared to manual welding.
Properly programmed robots can achieve critical seam quality consistently with little to no defects or rework. This significantly lowers metal waste generation which would otherwise require re-melting and reprocessing. Their precision also supports the use of narrower weld joints and grades of material.
Additionally, robotic welding processes such as laser welding use less energy than arc welding, resulting in lower carbon footprint and utility costs for manufacturers. With sustainable manufacturing gaining importance, these advantages of robotic systems provide a compelling business case for players in the robotic welding market.