

The Global Systemic Amyloidosis Therapeutic Market is estimated to be valued at USD 6.69 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 11.54 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.1% from 2025 to 2032.
The market has been witnessing positive trends in the recent past due to high prevalence of systemic amyloidosis across the globe and increasing research for developing novel therapeutics for the treatment of the disease. Development of targeted therapies holds promise for better management of systemic amyloidosis. Moreover, several pipeline drugs are under clinical trials that could potentially enter the market in the coming years. With increasing awareness about the disease and supportive government initiatives, the systemic amyloidosis therapeutic market is expected to witness significant growth over the forecast period. However, high cost of treatment and lack of effective treatment remain major challenges for the market.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR8.1%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 8.1% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | AstraZeneca, Attralus, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Prothena Biosciences, Alexion Pharmaceuticals and Among Others |
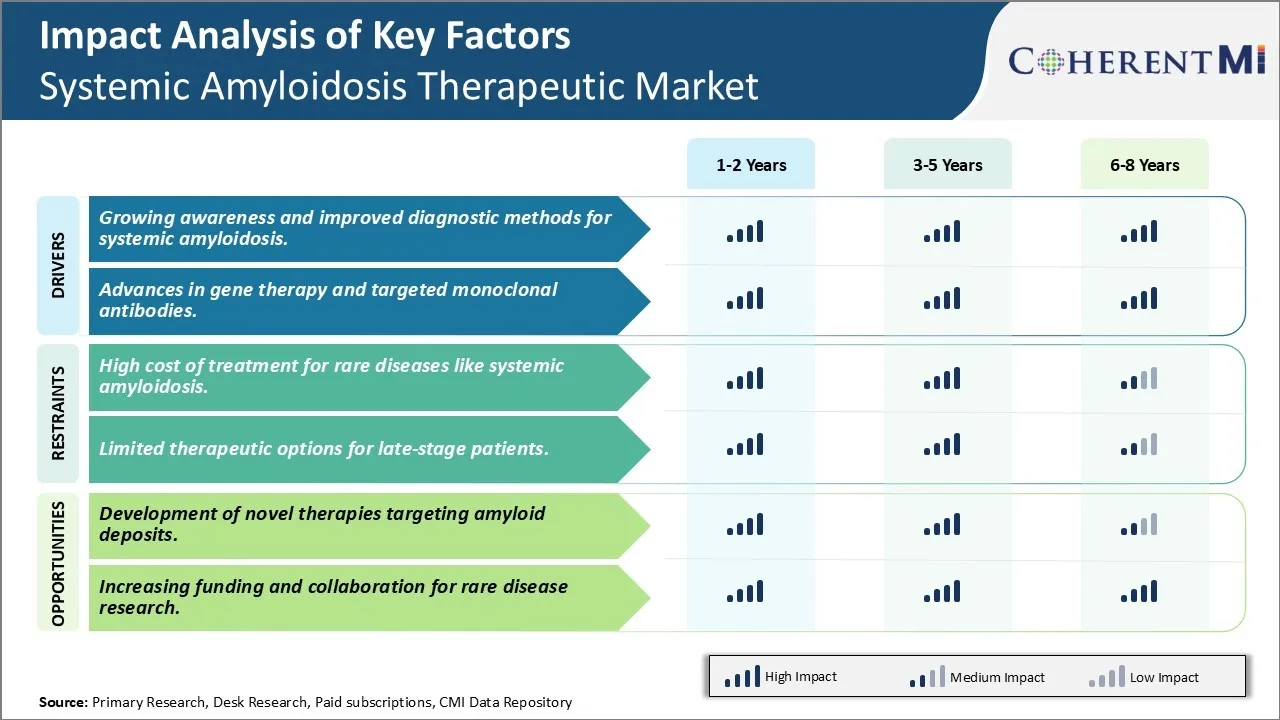
Market Driver - Growing Awareness and Improved Diagnostic Methods for Systemic Amyloidosis
With advancements in research and development, awareness about systemic amyloidosis as a disease condition has increased significantly over the past decade. Various non-profit organizations and patient advocacy groups across the globe are educating people about its symptoms and importance of early diagnosis. This has motivated many high-risk individuals to get relevant medical tests done.
At the same time, diagnostic methods for detecting systemic amyloidosis have also witnessed major enhancements. Newer imaging techniques such as nuclear medicine scans, along with biochemical tests and tissue biopsy are helping physicians arrive at confirmatory diagnosis faster than before. Some hospitals have even established dedicated amyloidosis centers with specialized pathologists and staff. This is limiting the dependency on overseas medical centers for biopsy analysis. Additionally, biomarkers are being studied which can potentially rule out amyloidosis or flag a positive case through simple blood or urine screening.
The collective effect of these trends has been higher diagnosis rates globally. Whereas previously many patients would remain unaware about having amyloidosis for years, today majority of those at risk are empowered to proactively check for it. Furthermore, physicians can now examine patient samples more accurately than relying on indirect clinical signs alone. As more cases come to light, it is reinforcing calls for improved treatments. Pharmaceutical companies will see this growing diagnosed patient pool as a strong driving factor to accelerate R&D of novel therapeutic solutions.
Market Driver - Advances in Gene Therapy and Targeted Monoclonal Antibodies to Encourage Market Developments
Significant progress is occurring in unravelling the genetic origins of different types of amyloidosis. Researchers have identified numerous gene mutations responsible for hereditary forms as well as acquired ones associated with aging. This expanding genetic knowledge is opening up avenues for targeted therapeutic approaches.
Gene silencing techniques hold promise for halting overexpression of abnormal proteins at the root cause. Trials involve delivering custom designed genetic material or viral vectors to switch off the faulty genes. Challenges remain in ensuring specificity and sustained activity but initial results have been encouraging.
Monoclonal antibodies represent another exciting area of investment. These labengineered proteins can bind precisely to amyloid deposits or protein precursors in the bloodstream and enable their removal from the body. Some antibodies are proving highly effective in animal studies at clearing or preventing amorphous clumps from accumulating in vital organs over time.
Combination strategies fusing gene therapies and antibody drugs are under active consideration. The hope is to address systemic amyloidosis at the genetic, protein and organ levels simultaneously for optimal outcomes. While more research is still to be done, medical innovations centered on genes and targeted molecules are without a doubt revolutionizing treatment outlook for this previously difficult to handle disease.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High Cost of Treatment for Rare Diseases Like Systemic Amyloidosis
One of the major challenges faced in the systemic amyloidosis therapeutic market is the high cost of treatment for these rare diseases. Systemic amyloidosis is a group of rare disorders caused by aggregation of misfolded proteins that are deposited abnormally in tissues and organs. With no approved disease-modifying treatments available, management of amyloidosis mainly involves alleviating symptoms through expensive strategies like chemotherapy, stem cell transplants, and organ transplantation. Due to the low prevalence of these conditions, pharmaceutical companies have little incentive to invest heavily in research and development of new therapies. Further, the small patient populations also result in high per-patient drug development costs that get reflected in the final price of approved therapies. This makes treatment unaffordable for many patients. Even developed healthcare markets often lack specialized programs and funding to support patients with these rare illnesses. Overall, the orphan drug designation does not entirely resolve the financial challenges involved in developing and accessing therapies for systemic amyloidosis and similar rare diseases.
Market Opportunity: Development of Novel Therapies Targeting Amyloid Deposits
One of the major opportunities in the systemic amyloidosis therapeutic market lies in the development of novel therapies that can directly target the amyloid deposits causing organ damage. Currently, stem cell transplants and liver transplantation are the only treatments that mobilize amyloid deposits in specific types of amyloidosis. However, these are highly invasive procedures associated with life-threatening risks. Pharmaceutical companies are now exploring new mechanisms to disrupt amyloid formation or enhance clearance of existing deposits through oral small molecule drugs or monoclonal antibodies. Some of the approaches under investigation include antibodies against amyloidogenic proteins, small molecules inhibiting amyloid precursor protein processing, and therapies promoting amyloid degradation. Success in any of these novel drug development programs can help manage the underlying disease pathology instead of just symptoms. This can potentially improve treatment outcomes while also making therapies more accessible through oral administration and less intensive care requirements.
Systemic amyloidosis is a progressive disease characterized by the buildup of abnormal amyloid protein deposits in vital organs. Prescribers' treatment approaches vary depending on the type and stage of amyloidosis.
For early-stage AL amyloidosis, the first-line treatment is often a chemotherapy combination such as bortezomib (Velcade) and dexamethasone. For patients able to tolerate intensive therapy, autologous stem cell transplants using melphalan (Alkeran) conditioning are sometimes utilized.
As the disease advances, options may include lenalidomide (Revlimid) either alone or with dexamethasone. For those with more severe accumulation, especially affecting the heart, carfilzomib (Kyprolis) or daratumumab (Darzalex) based regimens present alternative options.
In AA amyloidosis associated with inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, treating the underlying condition aggressively takes priority. Prescribers may rely on immunosuppressants like corticosteroids along with disease-modifying drugs. For partial organ involvement, liver or kidney transplants may be considered.
Hereditary forms like ATTR amyloidosis associated with specific gene mutations are typically managed via supportive care due to lack of effective treatment. However, tafamidis (Vyndaqel) and inotersen (Tegsedi) have shown promise in halting neurologic decline for specific mutations and are increasingly prescribed earlier.
Overall treatment approaches vary considerably based on amyloid type, organ involvement severity, and individual prognostic factors. A multidisciplinary care team approach including cardiac and renal specialists is also important to address secondary organ damage.
Systemic amyloidosis has four main stages - early, intermediate, advanced and end-stage disease. Treatment depends on the type and stage of amyloidosis.
In early-stage AL amyloidosis, the primary treatment is chemotherapy with bortezomib (Velcade)-based regimens in combination with dexamethasone. This helps suppress the abnormal plasma cells that deposit amyloid fibrils. For early stage ATTR amyloidosis, tafamidis (Vyndaqel) is recommended to stabilize the amyloidogenic transthyretin tetramer.
As the disease progresses to intermediate stage, chemotherapy continues to be the mainstay for AL amyloidosis. Regimens combining bortezomib with cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone are commonly used. For intermediate ATTR amyloidosis, inotersen (Tegsedi) or patisiran (Onpattro) are preferred as they interfere with transthyretin production.
Advanced stage amyloidosis sees reduced organ function. At this stage, stem cell transplant may be considered for eligible AL patients who are transplant candidates. For ATTR, tafamidis or RNAi therapies continue to be used along with supportive care.
In end-stage disease, treatment shifts to palliative care focusing on symptom relief. Liver transplantation is sometimes considered for hereditary ATTR amyloidosis to replace the mutated transthyretin gene. Overall, treatment continuously adapts based on amyloid type and stage to suppress protein deposition and improve quality of life.
Collaborations and Acquisitions: Many players have focused on collaborations and acquisitions to gain access to new drug candidates and strengthen their pipeline. For example, in 2018, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals acquired a clinical-stage RNAi therapeutics company, Dicerna Pharmaceuticals, to gain access to their pipeline of RNAi therapies for treating amyloidosis. This strengthened Alnylam's presence in this market.
Focus on Orphan Drugs: Most companies are targeting rare or orphan indications like amyloidosis which have higher chances of favorable regulatory designations and pricing.
Late-Stage Pipeline and Approvals: Players with drugs in late-stages of development or recent approvals have seen success.
Expanded Targets: Companies are also looking to expand the target population for existing drugs through additional indications. For instance, on the back of Onpattro's approval, Alnylam initiated several studies to evaluate patisiran for ATTR amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy and for hereditary and wild-type ATTR neuropathy. This could potentially increase the eligible patient pool.
These examples of strategies clearly show how collaborations, focus on orphan drugs, late-stage successes and expanded pipelines have helped key players gain significant leadership positions and maximize revenues in this market.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
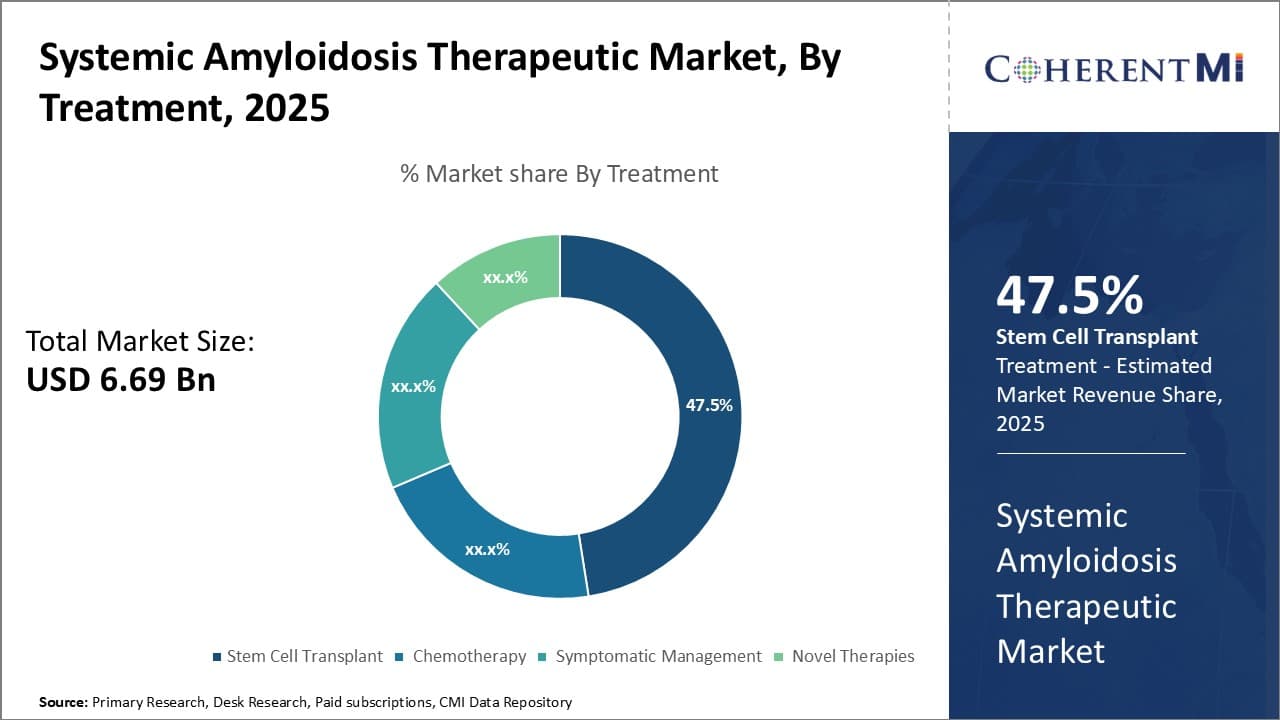
Insights, By Treatment, Stem Cell Transplant is the Leading Segment Throughout the Forecast Period
By Treatment, Stem Cell Transplant is expected to contribute 47.5% markets share in 2025 due to growing adoption as a viable cure. The systemic amyloidosis therapeutic market has seen stem cell transplant emerge as the leading treatment segment. This is owing to the growing adoption of stem cell transplant as a viable cure for certain types of amyloidosis.
Stem cell transplant provides patients with a replacement set of healthy bone marrow, thereby essentially curing the disease. It has proven effective in conditions like AL amyloidosis where stem cells from a donor can target the aberrant plasma cells producing abnormal light chains. The success rates for stem cell transplants in AL amyloidosis have increased over the last decade, making it an attractive option for eligible patients.
Additionally, recent advances have expanded the pool of eligible patients. Improvements in related procedures like reduced-toxicity conditioning have allowed even elderly or debilitated patients to undergo transplantation. Umbilical cord blood is also being increasingly utilized as a stem cell source. This has addressed the issue of finding a suitable donor match.
Furthermore, greater awareness among physicians has led to more prompt diagnoses and timely referrals for stem cell transplant evaluation. Several clinical studies have highlighted transplant as the treatment of choice in suitable AL amyloidosis cases, strengthening its position as the go-to option when viable. Stem cell transplant being a one-time curative approach versus lifelong management with other therapies, along with the promising success rates, has contributed to its rising preference among AL amyloidosis patients and clinicians. This is expected to further increase its share in the systemic amyloidosis therapeutic market over the coming years.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
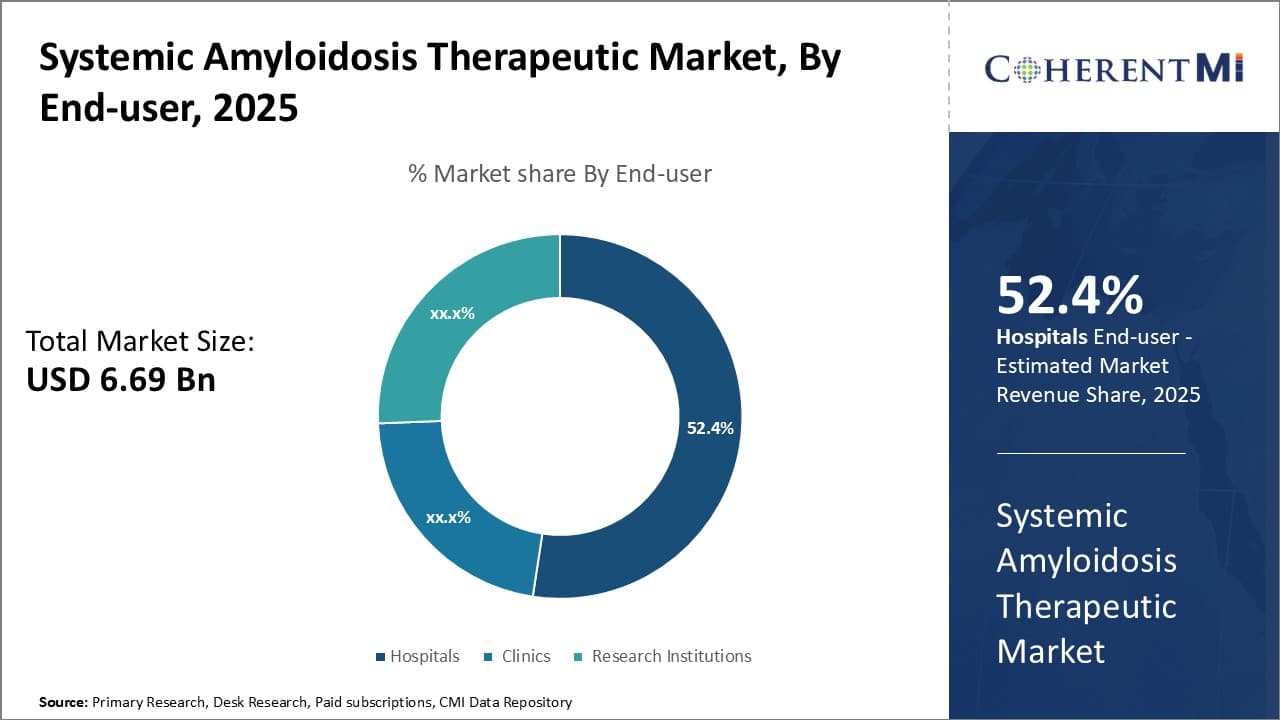
Insights, By End-user Hospitals Lead Throughout the Forecast Period
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By End-user Hospitals Lead Throughout the Forecast Period
By End-user, hospitals are expected to contribute 52.4% market share in 2025 owing to central role in treatment. The end-user segment of the systemic amyloidosis therapeutic market is dominated by hospitals, which account for the largest share. This is attributed to the central role hospitals play at various stages of amyloidosis treatment and management. As amyloidosis often requires multidisciplinary care, hospitals serve as the primary treatment hub coordinating inputs from different specialists. Being equipped with advanced diagnostic facilities, they allow for prompt diagnosis and subtype classification vital for effective therapy.
Further, hospitals have the requisite infrastructure and medical expertise to deliver intensive treatments like stem cell transplant. The complex nature of these procedures necessitates in-patient hospitalization, positioning hospitals at the forefront of specialized amyloidosis care.
Management of amyloidosis also largely takes place on an out-patient basis at hospitals through frequent follow-up visits. This is essential for monitoring disease progression as well as treatment effectiveness and side effects. The outcomes data collected aids clinical research. Lastly, amyloidosis patients tend to suffer numerous systemic complications that may require emergency admissions. Hospitals are well-equipped to handle such complications with round-the-clock amenities and intensive care facilities if needed. This makes hospitals the preferred End-user relied upon at different junctures.
Systemic amyloidosis is a rare but potentially life-threatening disorder caused by the deposition of misfolded proteins in vital organs. The disorder’s heterogeneity complicates diagnosis and treatment, with types like AL amyloidosis commonly seen in conjunction with plasma cell disorders. Novel approaches, such as monoclonal antibodies and gene therapies, are transforming the treatment landscape. AstraZeneca's CAEL-101 and Attralus' AT-02 represent key developments in amyloid removal, showing potential in ongoing clinical trials. Despite progress, challenges remain, including the high cost of treatment and limited therapeutic options for advanced-stage patients. Continued investment in research and collaborations between academic and industry players are crucial to addressing unmet needs in this field. The future of systemic amyloidosis treatment lies in precision medicine and personalized therapies that target specific amyloid subtypes, improving survival rates and quality of life for affected individuals.
The major players operating in the Systemic Amyloidosis Therapeutic Market include AstraZeneca, Attralus, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Prothena Biosciences, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Eidos Therapeutics, GSK Plc, Novartis Plc, Sanofi SA, Akcea Therapeutics and Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
Systemic Amyloidosis Therapeutic Market is segmented By Treatment (Stem Cell Transplant, Chemotherap...
Systemic Amyloidosis Therapeutic Market
How Big is the Systemic Amyloidosis Therapeutic Market?
The Global Systemic Amyloidosis Therapeutic Market is estimated to be valued at USD 6.69 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 11.54 Bn by 2032.
What will be the CAGR of the Systemic Amyloidosis Therapeutic Market?
The CAGR of the Systemic Amyloidosis Therapeutic Market is projected to be 7.9% from 2024 to 2031.
What are the major factors driving the Systemic Amyloidosis Therapeutic Market growth?
The growing awareness and improved diagnostic methods for systemic amyloidosis, advances in gene therapy and targeted monoclonal antibodies, are the major factors driving the Systemic Amyloidosis Therapeutic Market.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the Systemic Amyloidosis Therapeutic Market?
The high cost of treatment for rare diseases like systemic amyloidosis and limited therapeutic options for late-stage patients are the major factor hampering the growth of the Systemic Amyloidosis Therapeutic Market.
Which is the leading Treatment in the Systemic Amyloidosis Therapeutic Market?
Stem Cell Transplant is the leading Treatment segment.
Which are the major players operating in the Systemic Amyloidosis Therapeutic Market?
AstraZeneca, Attralus, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Prothena Biosciences, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Eidos Therapeutics, GSK Plc, Novartis Plc, Sanofi SA, Akcea Therapeutics, Janssen Pharmaceuticals are the major players.