Tendonitis Drugs Market Size - Analysis
The tendonitis drugs market is estimated to be valued at USD 234.81 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 306.92 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.9% from 2025 to 2032. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) currently dominate the tendonitis drugs market and are expected to continue to do so through the forecast period due to their cost effectiveness and ease of administration compared to other therapies.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR3.9%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 3.9% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | MiMedex Group Inc., MEDRx USA Inc., Cerimon Pharmaceuticals, InGeneron Inc., ZetrOZ Inc and Among Others |
please let us know !
Tendonitis Drugs Market Trends
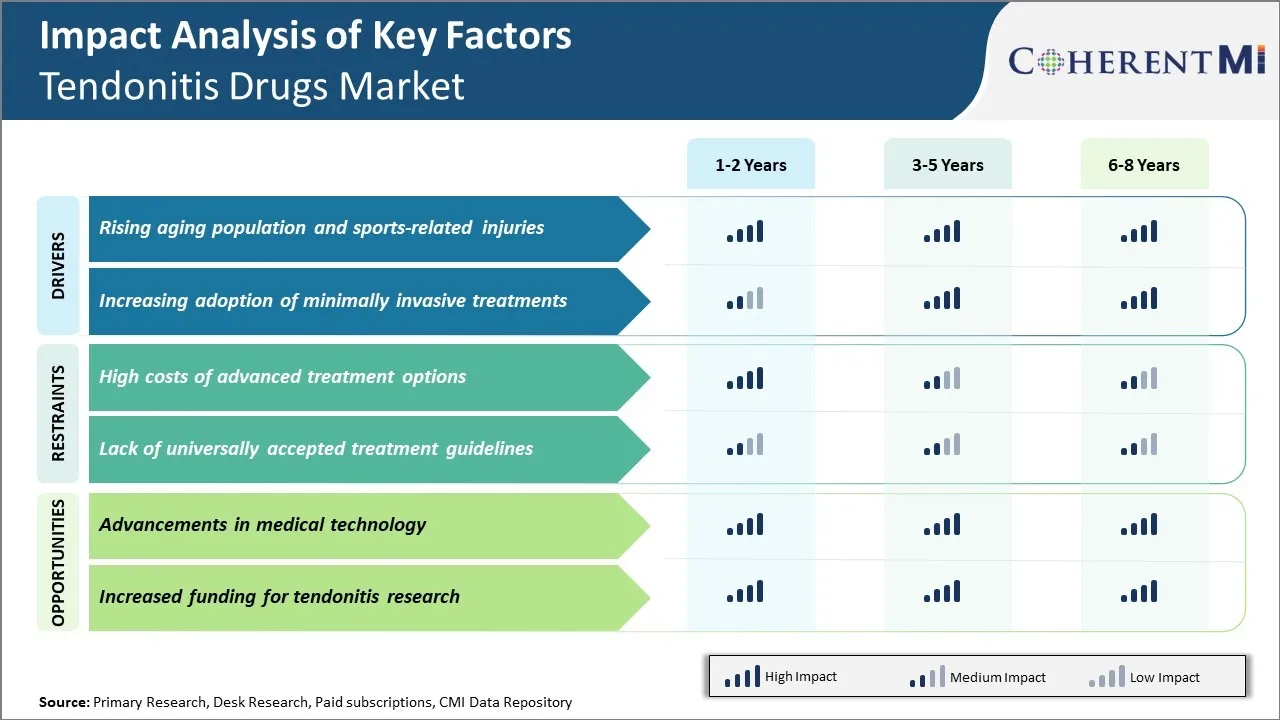
Market Driver - Rising Aging Population and Sports-related Injuries
As the overall population is aging worldwide and people are living longer lives compared to past decades, age-related health issues are rising as well. Tendonitis or tendon injury/damage occurs more commonly among the elderly due to gradual wear and tear of tendons over time.
The degeneration of tendon tissue makes the tendons weaker and prone to inflammation or tears. With sedentary lifestyle and less physical activity, tendons do not get proper exercise and strength training which exacerbates tendon-related issues.
In sports as well, where there is sudden force or repetitive motion applied, tendons undergo significant stress and strain which increases chances of damage. Younger population engaged in various recreational sports and physical activities are also reporting rise in tendon injuries like tennis elbow, jumper's knee etc. Certain high-impact sports like basketball, rugby, football put increased load on tendons which when combined with improper warming up or cooling down can cause micro-tears.
With greater focus on health and fitness globally, participation in sports has surged but without adequate preventive measures, so have sports injuries. Both aging population demographic and sports involvement demographic are expected to drive increased demand for tendonitis drugs in coming years.
Market Driver - Increasing Adoption of Minimally Invasive Treatments
The pharmaceutical industry is continuously researching and developing less invasive treatment options for various medical conditions. For tendon injuries and strains, traditionally physiotherapy and rest/immobilization were the main treatment protocols.
However, these conservative treatment methods require longer recovery time which impacts daily lifestyle and productivity. With advancement in understanding of tendon anatomy and physiology, new drug formulations are emerging that can help relieve pain and swelling more effectively with minimally invasive administration.
Options like injections and topical gels allow targeted drug delivery directly into or around the injured tendon site. This leads to faster healing compared to oral medications which have larger dosage and more systemic effects. Also, injections eliminate issues with oral drug absorption and ensure higher concentration reaches the tendon tissue.
Many new drugs are also designed to reduce inflammation more quickly and strengthen tendon matrix to prevent re-injury. As patients demand options allowing them to resume normal activities sooner with less disruption, adoption of minimally invasive tendonitis drugs is on the rise. This shift in treatment preference will augment the future growth of this drug segment.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High Costs of Advanced Treatment Options
One of the major challenges faced by the tendonitis drugs market is the high costs associated with advanced treatment options such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy and stem cell therapy. These innovative techniques have shown promising results in treating chronic tendonitis by reducing inflammation and promoting healing.
However, the equipment and infrastructure required for PRP preparation and stem cell extraction, processing, and implantation drives up the procedure costs significantly.
A typical PRP therapy costs between $500-$1000 per treatment, while a single stem cell therapy procedure may exceed $10,000. This makes these advanced options unaffordable for many patients and pushes the demand towards conventional drug therapies. The high entry costs also create barriers for wider adoption of these emerging treatments across healthcare providers.
Unless protocol and equipment costs are reduced substantially, innovative non-drug therapies are likely to have limited penetration in the overall tendonitis drugs market.
Market Opportunity - Advancements in Medical Technology
The tendonitis drugs market is poised to witness numerous growth opportunities arising from continued advancements in medical technologies. Researchers are working on developing novel drug delivery systems such as sustained-release injectable formulations and bioabsorbable drug-eluting sutures that can control drug levels at the tendon site for extended periods. This can help reduce frequency of dosing and improve patient compliance.
Technology companies are also investing in formulations that leverage nanotechnology and proprietary lipid-based constructs to enhance cellular uptake of corticosteroids and other anti-inflammatories at the target tissues. Such advanced formulations are expected to demonstrate higher efficacy with lower drug concentrations.
Furthermore, new technologies for PRP preparation are being designed to automate the entire process and minimize batch-to-batch variability. Companies are working on single-use, pre-filled syringe systems for Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy that can make the procedure simpler and more affordable.
As these innovative product developments cater to the unmet needs in tendon treatment, they are likely to open promising growth opportunities for players in the tendonitis drugs market.
Prescribers preferences of Tendonitis Drugs Market
Tendinitis is typically treated through a stepped approach depending on the severity and stages of the condition. For mild cases, prescribers will often recommend over-the-counter oral NSAIDs like ibuprofen (Advil) or naproxen (Aleve) to help reduce inflammation and pain. Physical therapy focusing on stretching and strengthening exercises is also usually suggested.
If symptoms don't improve with conservative treatment, prescribers may prescribe slightly stronger oral or topical NSAIDs such as diclofenac (Voltaren) gel. Cortisone injections containing corticosteroids like triamcinolone acetonide (Kenalog) directly into the affected tendon may provide relief for more persistent cases. These aim to reduce swelling and pain.
For patients who do not get adequate relief from medication and injections, prescribers may recommend focused shock wave therapy to stimulate healing of the tendon.
Brand options include OssaTron and DolorClast machines. Some also use platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections containing concentrations of a patient's own growth factors to accelerate healing.
Surgical treatment is typically a last resort if all conservative options fail. Common procedures include debridement to remove damaged tissue or repair the tendon using grafts.
Treatment Option Analysis of Tendonitis Drugs Market
For mild tendonitis, initial treatment focuses on rest, ice therapy, and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medicines like ibuprofen to reduce pain and swelling. Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises help prevent further damage as the tendon heals.
Moderate cases may involve physical therapy. Under a therapist's guidance, exercises target mobilizing the tendon and strengthening muscles around the affected area. Modalities like ultrasound therapy and electric stimulation help reduce inflammation.
If conservative care proves inadequate, corticosteroid injections directly into the tendon can provide powerful anti-inflammatory effects. However, frequent injections are not advisable long-term due to risk of tendon damage.
For persistent or worsening tendonitis unresponsive to other options, a platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injection may offer relief. PRP contains concentrations of growth factors that help accelerate healing. Brands like Puregraft PRP use the patient's own blood for minimally invasive treatment.
In severe, untreatable cases where function is impaired, surgery may be required to repair or decompress the tendon. Arthroscopic techniques minimize scarring and downtime. Post-surgical rehab focuses on regaining full motion and strength.
Treatment selection depends on symptoms, examination findings, and specialist evaluation. A multidisciplinary approach combining different options often provides best results for returning to normal activity.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Tendonitis Drugs Market
Adopt combination therapy approach: Some companies like AbbVie have adopted the strategy of developing combination therapies instead of single molecule drugs. For example, their drugVimovo combines a NSAID with a proton pump inhibitor to address both pain and risk of stomach ulcer. This holistic approach helps address multiple patient needs and has seen good success.
Shift to specialty indication focus: Earlier many companies aimed for broad tendonitis treatment but have shifted to specializing in specific tendon indications like shoulder, knee, elbow etc which have bigger market potential. For example, Bayer divested its broad pain portfolio to focus only on shoulder tendonitis drugs where it dominates with drugs like Durolane seeing over $100 million in annual sales.
Capitalize on non-surgical preference: Studies show many patients prefer non-surgical options due to risk and downtime of surgery. Companies promote their drugs as effective alternatives to procedures. For example, Abbott highlights how its Cortisone injections like Kenalog can help delay potential surgery needs for some patients. This helps create stickiness for pharmaceutical solutions.
Segmental Analysis of Tendonitis Drugs Market
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
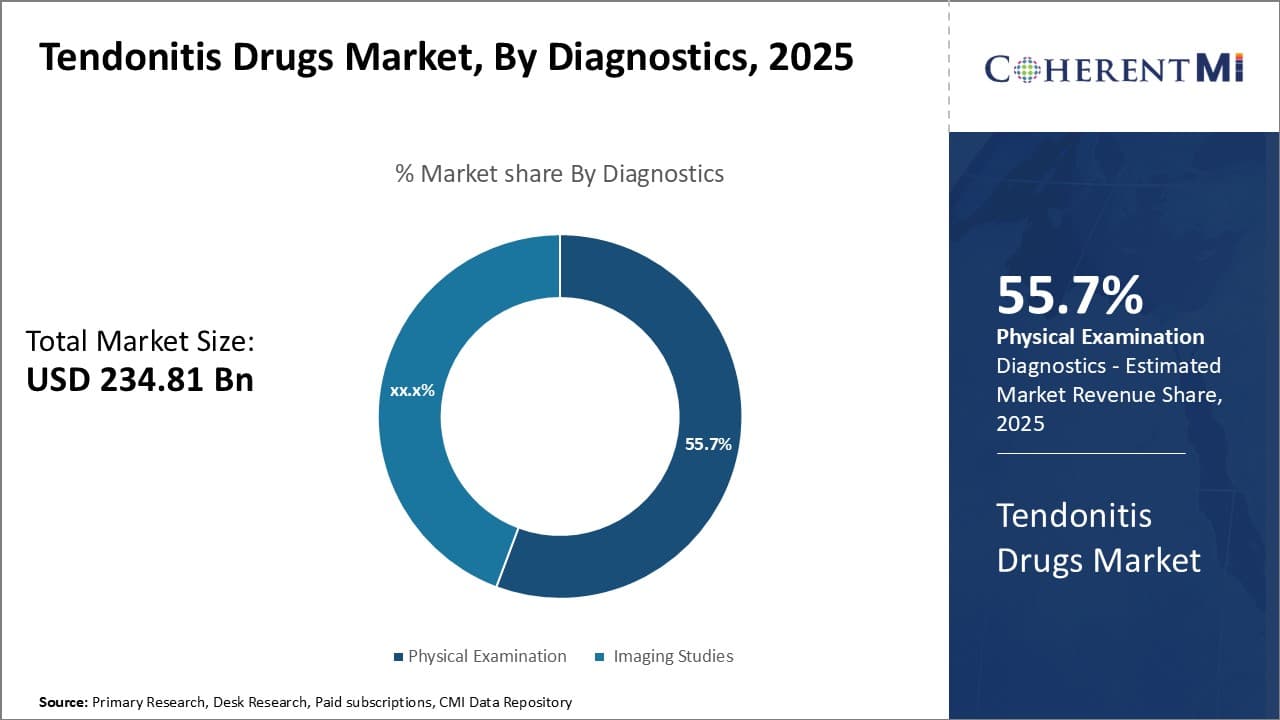
Insights, By Diagnostics: Physical Examination Remains the Most-preferred Diagnostic Approach
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Diagnostics: Physical Examination Remains the Most-preferred Diagnostic Approach
In terms of diagnostics, physical examination contributes the highest share of the market owning to its accessibility and low cost. Physical examination allows doctors to determine the location and severity of tendonitis through touch and motion tests.
By feeling the affected tendon area for swelling, tenderness, or nodules, and having the patient perform movements to assess limited range of motion or painful resisted motions, physicians can diagnose tendonitis without expensive imaging tests. This hands-on approach is suitable for primary care facilities and allows for a quick diagnosis during initial patient visits.
As many cases of tendonitis are mild to moderate, physical examination alone is sufficient for treating and monitoring the majority of patients. Its affordability makes it preferable to insurance providers and cost-conscious consumers as the first-line diagnostic method.
Furthermore, physical therapists and chiropractors heavily rely on hands-on techniques for tendonitis screening and treatment monitoring. Their recommendation of physical examination as the primary assessment tool contributes to its widespread use.
Overall, the convenience, low cost, and effectiveness of physical examination in identifying the signs and symptoms of tendonitis have allowed it to capture the largest diagnostic segment share.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
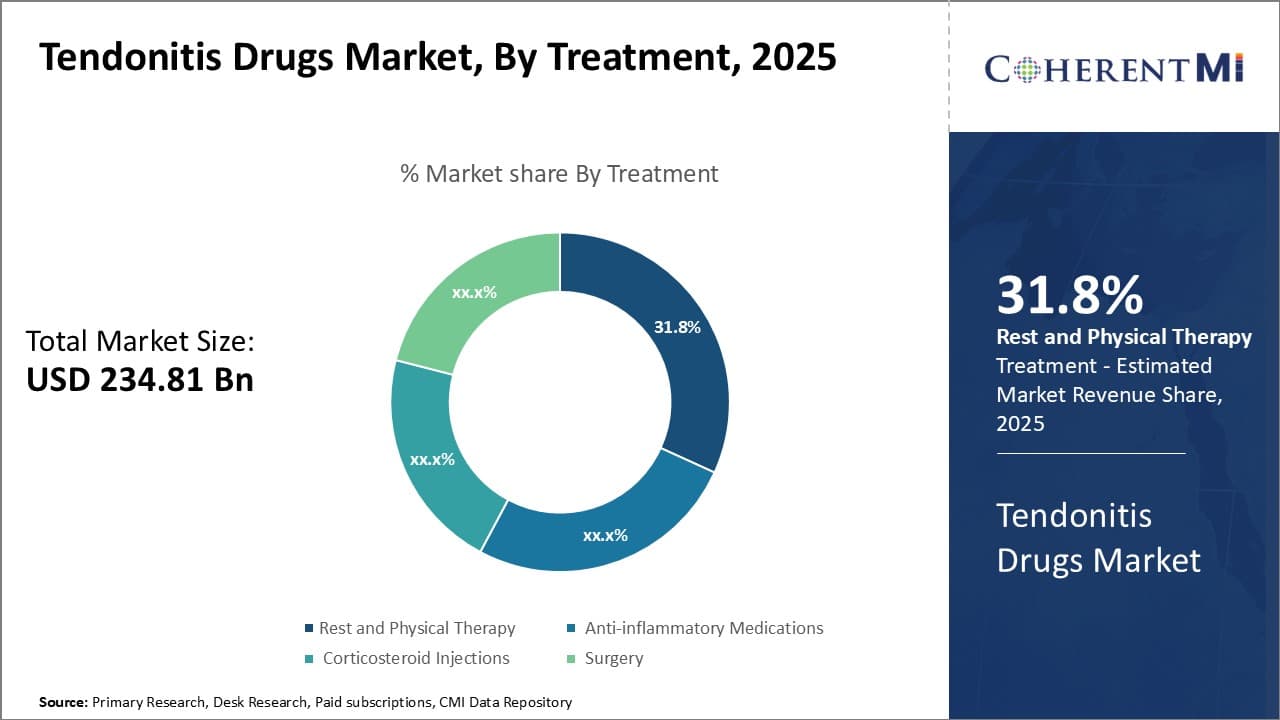
Insights: By Treatment: Rest and Therapy Dominates Treatment Segment
In terms of treatment, rest and physical therapy contributes the highest share of the market owning to its position as the first-line approach. For mild to moderate tendonitis, rest and physical therapy are clinically recommended as the standard initial treatment before consideration of medications or more invasive procedures.
Resting the affected tendon area by avoiding aggravating activities or positions allows it to begin healing. Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises administered through physical therapy then helps reduce tendon inflammation and scar tissue while improving range of motion and tendon gliding function.
As most tendonitis cases respond well to this conservative treatment path when followed consistently, it prevents unnecessary medication use or progression to chronic stages requiring surgery. Its status as the guideline-recommended starting treatment makes it covered by most insurance providers without hassle.
Furthermore, as rest and therapy can usually be fully administered in an outpatient setting, it imposes lower direct and indirect costs compared to options like surgeries or costly biologic medications. These factors of clinical guidelines support, cost-effectiveness, and functionality as a front-line approach have allowed rest and physical therapy to rise as the leading segment in tendonitis drugs market by treatment.
Additional Insights of Tendonitis Drugs Market
- The global prevalence of tendonitis is rising, particularly in aging populations across the U.S., EU, and Japan. This is attributed to lifestyle factors, increasing sports participation, and a focus on quicker recovery treatments.
Competitive overview of Tendonitis Drugs Market
The major players operating in the tendonitis drugs market include MiMedex Group Inc, MEDRx USA Inc, Cerimon Pharmaceuticals, InGeneron Inc, ZetrOZ Inc, ZARS Pharma Inc, Smith & Nephew Inc., and Stryker.
Tendonitis Drugs Market Leaders
- MiMedex Group Inc.
- MEDRx USA Inc.
- Cerimon Pharmaceuticals
- InGeneron Inc.
- ZetrOZ Inc
Recent Developments in Tendonitis Drugs Market
- MiMedx Group focuses on regenerative therapies, particularly using placental biologics to improve patient outcomes. The company is a leader in the development of placental tissue-based allografts, such as EPIFIX®, which are used for wound healing and reducing scarring in chronic wounds like diabetic foot ulcers. MiMedx's proprietary methods, including the PURION® process, are key to their regenerative medicine approach.
- In September 2021, Stryker's Trauma and Extremities division introduced the Citrelock Tendon Trauma Fixation Device System. This advanced system offered surgeons a unique design featuring a tendon thread made from proprietary resorbable technology. The launch not only provided an innovative solution for tendon repair but also strengthened Stryker’s orthopedic surgery portfolio by expanding its offerings in the trauma and extremities sector.
Tendonitis Drugs Market Segmentation
- By Diagnostics
- Physical Examination
- Imaging Studies
- By Treatment
- Rest and Physical Therapy
- Anti-inflammatory Medications
- Corticosteroid Injections
- Surgery
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Ghanshyam Shrivastava - With over 20 years of experience in the management consulting and research, Ghanshyam Shrivastava serves as a Principal Consultant, bringing extensive expertise in biologics and biosimilars. His primary expertise lies in areas such as market entry and expansion strategy, competitive intelligence, and strategic transformation across diversified portfolio of various drugs used for different therapeutic category and APIs. He excels at identifying key challenges faced by clients and providing robust solutions to enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. His comprehensive understanding of the market ensures valuable contributions to research reports and business decisions.
Ghanshyam is a sought-after speaker at industry conferences and contributes to various publications on pharma industry.
