Thyroid Eye Disease TED Market Size - Analysis
The Global Thyroid Eye Disease (TED) Market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.71 Billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 4.10 Billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1% from 2025 to 2032. The increasing prevalence of Graves' disease and hyperthyroidism across the globe is expected to drive the market growth during the forecast period.
The rising awareness about the condition and its treatment options along with increasing healthcare expenditure is further augmenting the market growth. Additionally, the expanding R&D activities for development of novel drug candidates for treatment of TED is also contributing to the increasing demand. Various pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in clinical trials to develop effective therapeutic solutions for better management of TED symptoms.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR6.1%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 6.1% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Horizon Therapeutics, Immunovant, Viridian Therapeutics, Novartis, Apitope and Among Others |
please let us know !
Thyroid Eye Disease TED Market Trends
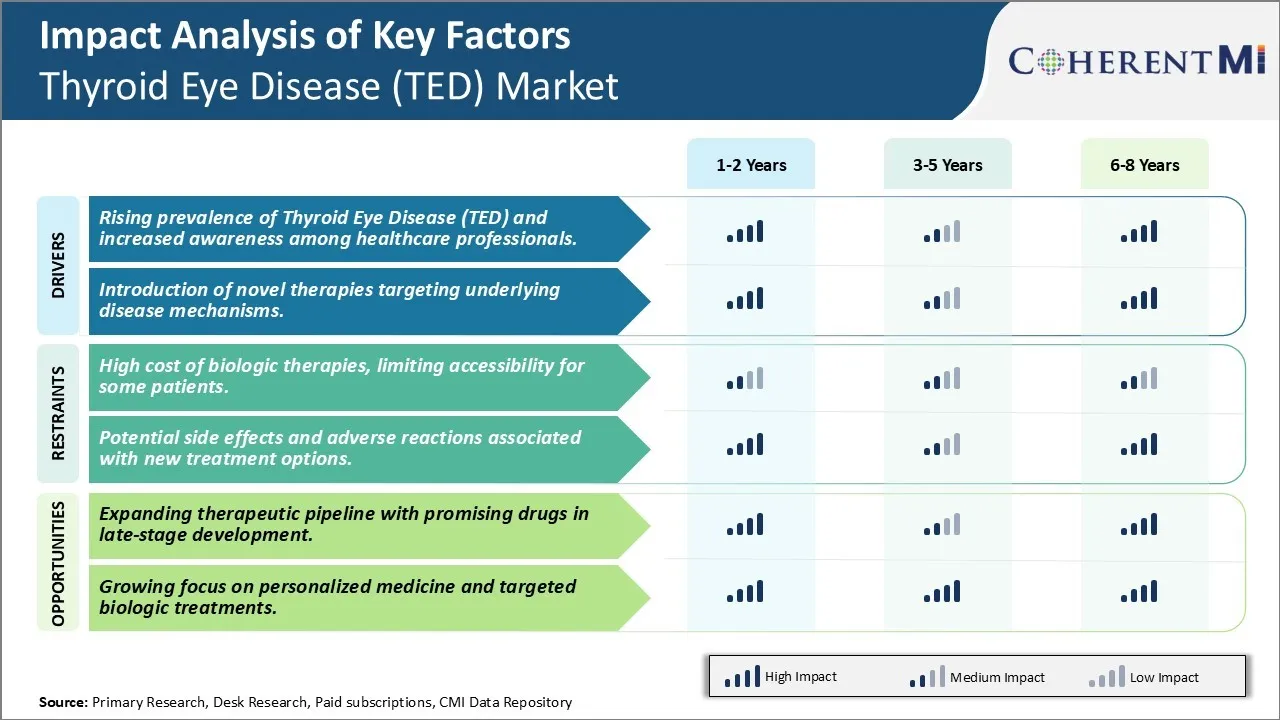
Market Driver - Rising prevalence of Thyroid Eye Disease (TED) and increased awareness among healthcare professionals.
The rising prevalence of Thyroid Eye Disease or Graves’ ophthalmopathy is one of the primary drivers propelling the growth of this market. TED is an autoimmune disorder affecting the muscles and fatty tissues behind the eyes. It is usually associated with Graves' disease, an autoimmune condition of the thyroid gland. With increasing instances of Graves' disease worldwide due to factors such as genetic predisposition, changing lifestyle habits, and environmental influences, the number of TED cases is also growing substantially. For example, epidemiological studies have found the prevalence of Graves' disease to be anywhere between 0.5% to 3% of the general population. Moreover, up to 25% of Graves’ disease patients ultimately develop TED over their lifetime.
What's more, enhanced awareness among physicians and healthcare practitioners regarding early identification and management of TED signs and symptoms has encouraged more patients to seek timely medical intervention. Doctors are now more capable of distinguishing TED from other ocular problems based on its characteristic clinical features. Even minor symptoms are brought to medical attention to prevent long-term complications. Several educational campaigns by support organizations in the recent years have highlighted the importance of prompt treatment. As a result of combined efforts made on the epidemiological as well as awareness front, people with TED are getting appropriately diagnosed and referred to ophthalmologists at earlier stages for evaluation and treatment if required. This is expected to fuel the demand for relevant drugs and medical technologies within the forecast period.
Market Driver - Introduction of Novel Therapies Targeting Underlying Disease Mechanisms.
The second major driver driving growth in this domain is the ongoing research into novel treatment paradigms that delve deeper into disease biology. Several biologics targeting specific immunopathogenic pathways implicated in TED pathogenesis are either in clinical trials or nearing commercial approval worldwide. For instance, significant funding is currently directed towards teprotumumab, the first FDA-approved monoclonal antibody for TED management. By inhibiting the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R), it showed promising efficacy in phase 3 studies, achieving substantially superior outcomes than conventional alternatives. Meanwhile, other biologics neutralizing autoantibodies, inflammatory cytokines, and immune cell subsets are progressing well in clinical development.
Additionally, gene therapies hold immense potential to cure TED at its genetic source. Scientists are working on developing gene therapy vectors to directly modify genetic mutations and correct the abnormal immune responses driving the condition. Coupled with advanced delivery methods, they may revolutionize patient care. Such a paradigm shift from symptom management to root cause treatment bodes well for long-term health improvements and sustainability in the market. The influx of groundbreaking pharmacological innovations aligned with ongoing progress in gene-based options is anticipated to open up lucrative prospects through 2030 and beyond.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High Cost of Biologic Therapies, Limiting Accessibility For Some Patients.
One of the major challenges for the Thyroid Eye Disease (TED) market is the high cost of biologic therapies which limits their accessibility for some patients. Biologic therapies such as TEPEZZA (teprotumumab) and HUMIRA (adalimumab) have demonstrated efficacy in treating the symptoms of TED. However, their high list prices, sometimes over USD10,000 per treatment course, makes them unaffordable for many patients. This is a significant barrier as TED is generally not considered a life-threatening condition and private and public drug plans may be reluctant to pay for such expensive therapies. While treatment is important to improve quality of life and vision for patients with TED, the high drug prices can leave patients having to make difficult financial choices. Pharmaceutical companies will need to consider strategies for increasing accessibility of these novel biologics, such as outcome-based contracting, patient assistance programs, or structured discount programs, in order to help more patients gain treatment access. If costs remain prohibitively high, many patients may have to rely only on supportive eye care and steroid treatments which have more limited efficacy in addressing the inflammation and swelling associated with TED.
Market Opportunity- Expanding Therapeutic Pipeline with Promising Drugs in Late-Stage Development.
One key opportunity for future growth is the expanding therapeutic pipeline with several promising drugs currently in late-stage development. For example, brontictuzumab, a monoclonal antibody being developed by Brontic, has shown positive Phase 2 results for reducing proptosis and eye swelling in TED patients. Additionally, Novartis' brolucizumab, an anti-VEGF agent, is in Phase 3 trials and has potential as an alternative or addition to steroid therapies. These new pipeline drugs provide hope that patients will gain access to more efficacious and targeted treatment options beyond existing biologics. If successful in completing clinical trials, they could capture significant market share and increase treatment rates for TED in the coming years. A diversifying product landscape would give physicians and patients more treatment choices based on individual disease characteristics and needs. This expanding pipeline represents an opportunity to improve patient outcomes and drive future revenue growth.
Prescribers preferences of Thyroid Eye Disease TED Market
Thyroid eye disease typically progresses through mild, moderate and severe stages. For mild disease, prescribers commonly recommend intravenous corticosteroids such as methylprednisolone to reduce inflammation and swelling. If symptoms worsen despite corticosteroids, orbital radiotherapy may be considered as the next line of treatment.
In moderate cases where proptosis and diplopia are present, oral corticosteroids like prednisone are often prescribed. Some prescribers also use immunosuppressants, with mycophenolate mofetil (Cellcept) being a preferred option. Biological agents may be utilised if patients do not respond to standard therapies. Teprotumumab (Tepezza), a fully human monoclonal antibody, has gained popularity as an effective second-line treatment. For severe, active TED marked by significant proptosis, optic nerve dysfunction and extraocular muscle restriction, some prescribers turn immediately to biologicals due to patients' compromised vision and quality of life. These include teprotumumab and rituximab (Rituxan), a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting B-cells. Orbital decompression surgery may also be considered for cases with optic nerve compression or disfigurement. Cost of treatment strongly influences prescribing decisions, especially for newer and expensive drugs. Responses to initial therapies also impact whether prescribers switch treatment strategies or dosing regimens for a given stage of disease.
Treatment Option Analysis of Thyroid Eye Disease TED Market
TED can be classified into 4 stages based on severity - mild, moderate, severe and decompensated. For mild disease, the preferred initial treatment is oral medications like steroids. Prednisone is commonly prescribed due to its potent anti-inflammatory effects. It is usually taken for 6-8 weeks at a starting dose of 30-60 mg per day to reduce eye bulging and discomfort. For patients with moderate to severe TED, intravenous steroids may be used if oral steroids are not effective. Methylprednisolone administered intravenously in pulsed doses of 500-1000 mg per week works better than oral steroids for more advanced stages. It provides higher levels of the drug directly to tissues and fluids around the eyes.
In cases where steroids do not suffice or cannot be used due to intolerance, a biologic agent like Tepezza (teprotumumab) may be prescribed. It is a recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor antibody that selectively targets the IGF-1R pathway causal to TED. Tepezza administered via infusion every 3 weeks for 24 weeks has shown significantly better outcomes than steroids for active, moderate-to-severe TED by halting the autoimmune process leading to ocular swelling.
Orbital decompression surgery is the preferred treatment for patients with severe, inactive TED and those with optic neuropathy or corneal problems from prolonged proptosis. It helps reduce pressure inside the orbit and symptoms like vision issues by resecting bony structures.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Thyroid Eye Disease TED Market
Focus on Innovation - Leading companies like Horizon Therapeutics, Bausch & Lomb, and Pfizer have invested heavily in R&D to develop novel drugs and treatment approaches for TED.
Acquisitions for Product Portfolio Expansion - Companies have made strategic acquisitions to expand their TED treatment offerings. For instance, in 2020, AbbVie acquired Allergan, primarily to gain access to Allergan's leading portfolio of ophthalmic products including Restasis, a first-line treatment for TED. This acquisition strengthened AbbVie's position in the USD1.24 billion global thyroid eye disease (TED) market.
Aggressive Marketing Campaigns - Large pharma companies aggressively promote newly launched drugs through extensive direct-to-consumer advertising campaigns as well as promotional packages for doctors. For example, after Tepezza's approval, Horizon launched a large patient education and awareness program called "TED Talks" along with promotional materials for ophthalmologists. TUSDhese efforts boosted Tepezza sales to USD 376 million in its first full year.
Targeting Undertreated Patient Segments - Companies seek to identify undertreated patient subpopulations and launch awareness programs. Many patients overlook mild TED symptoms which can worsen without treatment. By informing such patients, companies attract new customers. For example, Horizon conducted surveys finding many mild TED patients were untreated, and then increased outreach to ophthalmologists on this opportunity.
Segmental Analysis of Thyroid Eye Disease TED Market
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
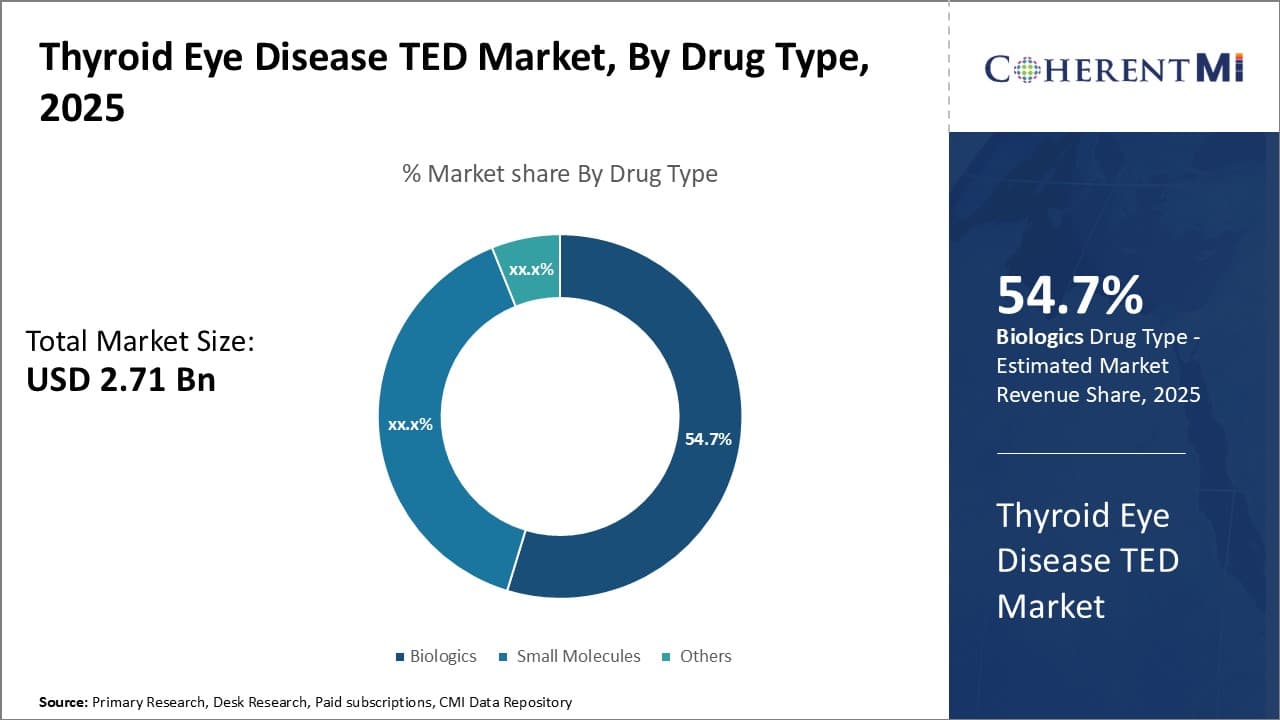
Insights, By Drug Type: Innovation in Biologics Drives Market Growth
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Drug Type: Innovation in Biologics Drives Market Growth
By Drug Type, Biologics contributes the highest market share at 54.70% in 2025 owing to continuous innovation and development of new and improved biologic drugs for treatment of Thyroid Eye Disease (TED). Biologics such as recombinant human thyroid-stimulating hormone (rhTSH), have revolutionized treatment paradigm by selectively targeting immune cells and inflammatory pathways involved in the pathogenesis of TED. Their high specificity, efficacy and tolerability have made biologics first choice of treatment over other drug types. Biologics in development pipelines indicate higher affinity and specificity to thyroid receptors and signaling proteins, which holds promise to arrest or even reverse progression of eye bulging and associated symptoms with minimal side effects. Ongoing research to repurpose approved biologics also expand treatment options.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
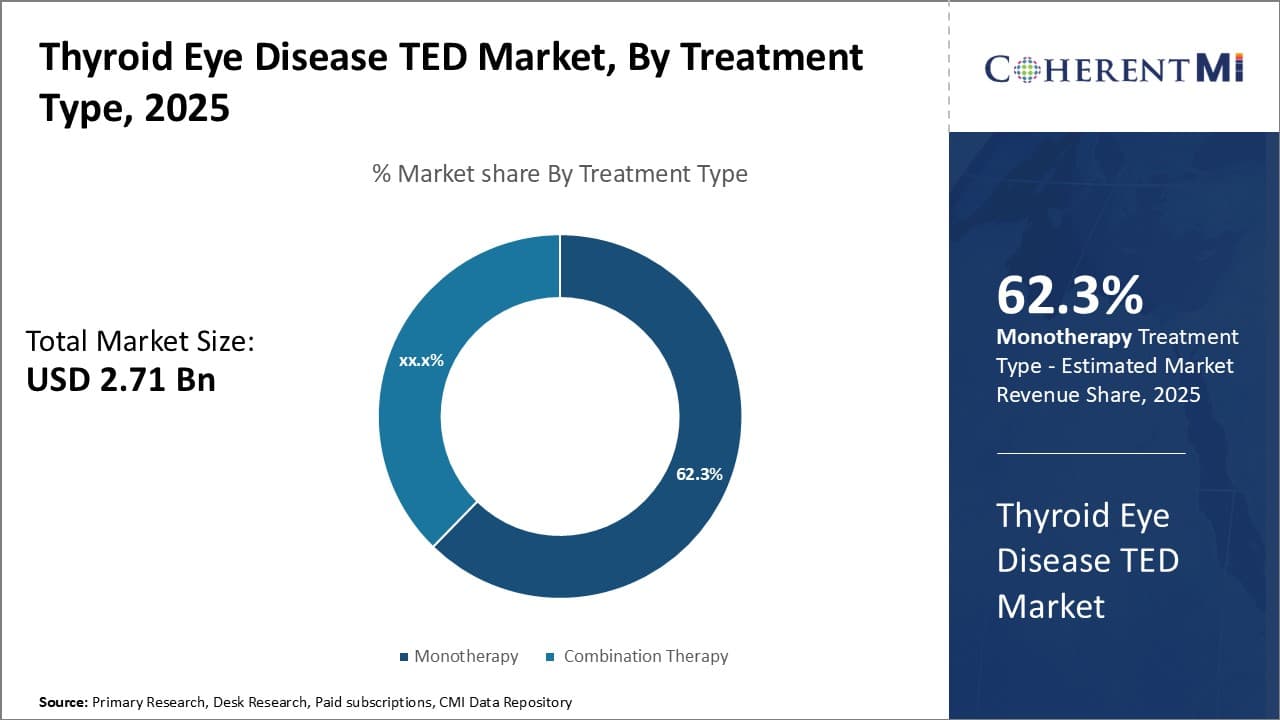
Insights, By Treatment Type, Efficacy Drives Monotherapy adoption
By Treatment Type, Monotherapy contributes the highest share 62.70% in 2025 due to demonstrated higher efficacy compared to Combination Therapy. Monotherapy involves administration of a single drug that comprehensively targets key inflammatory mechanisms underlying TED symptoms. Drugs like high dose oral prednisone are preferred as first line monotherapy due to fast response rates and ability to significantly relieve proptosis and diplopia when given alone. Combination therapies necessitate complex dosing with increased risk of drug interactions and adverse effects from multiple medications. Growing understanding of disease pathways stimulates focus on precision monotherapies that hit select nodes for maximum benefit with minimal toxicity.
Insights, By Route of Administration, Patient Convenience Driving Oral Route Preference
By Route of Administration, Oral route contributes the highest share owing to convenience and flexibility it offers patients over Intravenous or Subcutaneous modes. Given the chronic nature of TED, oral drugs can be self-administered at home on an outpatient basis without need for hospital visits or specialized healthcare environment. This minimizes disruption to daily lives and reduces healthcare costs associated with repeated infusions or injections. Ensuring medication adherence becomes easier with oral consumption compared to invasive parenteral routes. Oral drugs also allow for flexible dose titration based on individual response and tolerability. New research aims at developing highly bioavailable sustained release formulations for round the clock symptom management through oral delivery.
Additional Insights of Thyroid Eye Disease TED Market
The Thyroid Eye Disease (TED) market is poised for transformative growth, driven by increasing awareness, advances in biologic therapies, and ongoing clinical trials exploring novel treatment approaches. The introduction of targeted biologics, such as Tepezza, represents a major shift in managing TED, offering patients an effective, non-surgical option that addresses the underlying disease mechanism. Despite these advances, there are still challenges, including high treatment costs and accessibility issues that limit patient access to the latest therapies. Additionally, the need for long-term safety data and the development of alternative treatment modalities continues to be critical areas of focus. The market landscape is evolving rapidly with multiple late-stage clinical programs, which, upon successful completion, could significantly expand the therapeutic arsenal available for TED management. The growing emphasis on personalized treatment strategies tailored to individual patient profiles further underscores the market's dynamic nature and the potential for substantial growth in the coming years.
Competitive overview of Thyroid Eye Disease TED Market
The major players operating in the Thyroid Eye Disease (TED) Market include Horizon Therapeutics, Immunovant, Viridian Therapeutics, Novartis, Apitope, IONIS Pharmaceuticals, Sobi (Swedish Orphan Biovitrum), River Vision Development Corp. and Diurnal Group Plc.
Thyroid Eye Disease TED Market Leaders
- Horizon Therapeutics
- Immunovant
- Viridian Therapeutics
- Novartis
- Apitope
Recent Developments in Thyroid Eye Disease TED Market
- January 2022: Horizon Therapeutics announced promising results from a long-term follow-up study of Tepezza, indicating sustained efficacy in treating Thyroid Eye Disease, which could further solidify its position as the leading therapy.
- June 2021: Immunovant initiated Phase II trials for IMVT-1401, a fully human monoclonal antibody targeting the neonatal Fc receptor, aimed at reducing disease severity in TED patients.
Thyroid Eye Disease TED Market Segmentation
- By Drug Type
- Biologics
- Small Molecules
- Others
- By Treatment Type
- Monotherapy
- Combination Therapy
- By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
- Subcutaneous
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
