

The viral vaccine cell culture media market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.91 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 2.87 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.00% from 2025 to 2032. This steady growth can be attributed to factors such as the increasing prevalence of diseases such as influenza and COVID-19 worldwide, along with rising investments from public and private bodies in vaccine development.
The viral vaccine cell culture media market is expected to witness positive growth over the forecast period. Concerns regarding disease outbreaks and pandemics have boosted research and development for viral vaccines. Additionally, advancement of cell culture techniques for efficient and large scale production of viral vaccines will support the market growth.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR6.00%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 6.00% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Merck, Sartorius, Creative Biolabs, Xell and Among Others |
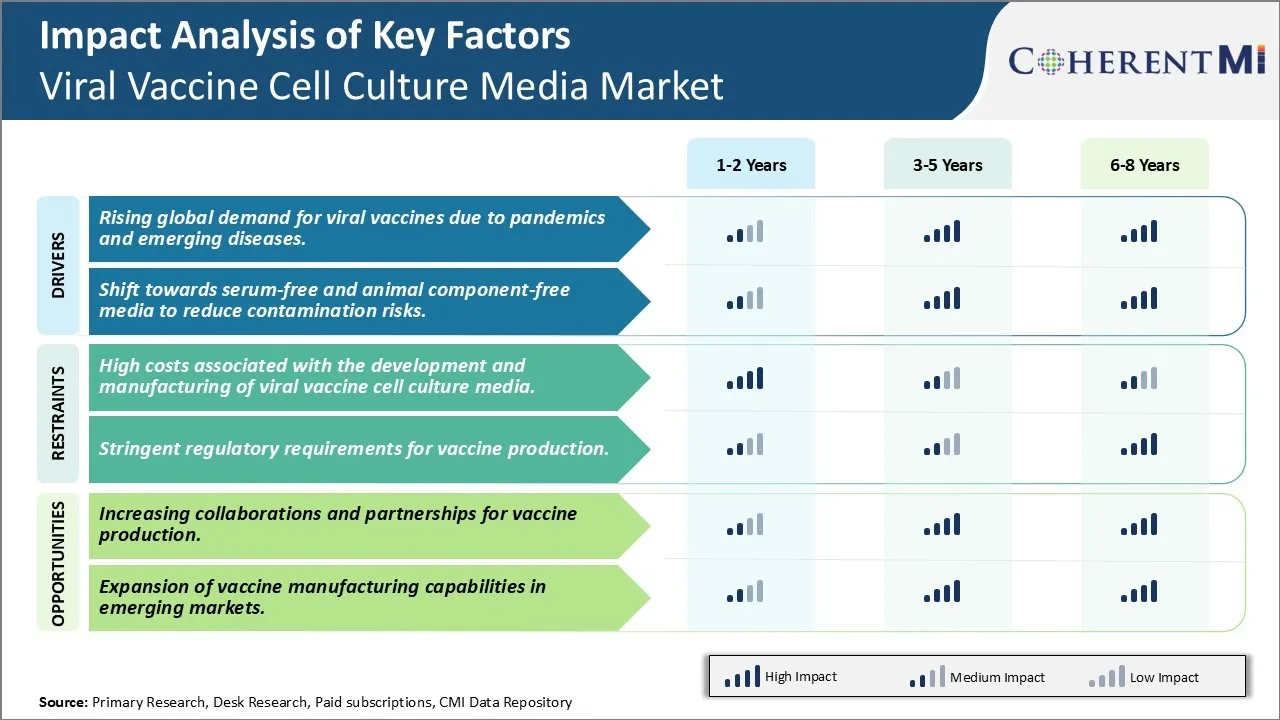
Market Driver - Rising global demand for viral vaccines due to pandemics and emerging diseases
The ever-increasing prevalence of viral infections and pandemics worldwide has led to a significant rise in the demand for viral vaccines over the recent past. The outbreak of Covid-19 pandemic in particular has highlighted the importance of vaccination in curbing the spread and severity of such respiratory viral diseases. Development of effective vaccines requires efficient production through cell culture media which serves as a growth environment for virus production.
As vaccine manufacturers aim to scale up supply and expand access to meet the massive global demand generated through vaccination programs, the requirement for cell culture media is growing substantially. Establishment of new production facilities and incremental capacities by leading vaccine companies is further propelling media demand. Additionally, constant efforts towards the development of vaccines for emerging diseases such as Zika, Ebola and Nipah viruses require continuous investments in research involving optimization of cell culture conditions and media formulations.
Rising government focus on immunization globally through initiatives like GAVI and recommendations for booster doses has also contributed to strong off-take of viral vaccines in recent times. The growing elderly population worldwide makes them more susceptible to infectious diseases and necessitates newer vaccine targets. This augurs well for the long term prospects of both viral vaccine development and mammalian cell culture media production. Overall, the critical role played by cell culture media in the large-scale commercial manufacture of all modern viral vaccines through robust and standardized processes is likely to drive significant consumption in the forthcoming years.
Market Driver - Shift towards serum-free and animal component-free media
With increasing regulatory pressures and industry move towards cleaner production methods, serum-free and animal origin raw material-free cell culture media formulations have gained widespread acceptance in recent years. Traditional serum-supplemented media cultivation relies on animal-sourced raw materials like fetal bovine serum which are associated with batch-to-batch inconsistency and risk of pathogen transmission. This necessitates extensive characterization and testing during production adding to costs.
In contrast, defined media with documented composition offer higher consistency and safety by removing animal-derived components and serum from the process altogether. Advanced serum-free media featuring protein-free and chemically-defined formulations facilitate robust viral replication without the concern for adventitious agents. Their utilization enables adherence to quality and biocontainment standards demanded by regulatory bodies. Furthermore, they improve downstream process efficiency by eliminating unnecessary purification steps for removal of animal proteins.
Leading vaccine makers worldwide have proactively invested in understanding cell behavior in absence of serum to come up with optimized chemically-defined and xeno-freemedia platforms. This shift supports reliable commercial-scale manufacturing while ensuring biosafety. With greater emphasis on process analytical technology and real-time material attribute monitoring, advanced animal-free media are likely to emerge as the production system of choice; thereby accelerating market growth over the coming years.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High costs associated with the development and manufacturing of viral vaccine cell culture media
The development and manufacturing of viral vaccine cell culture media requires high capital investments and operational expenditures. Manufacturers have to invest heavily in biosafety cabinets, bioreactors, media formulation equipment and facilities that meet rigorous quality and regulatory standards. They also need to utilize premium quality raw materials in the media formulation process to ensure optimal cell growth and virus replication. This makes the media production a costly affair. Additionally, regulations demand strict quality control testing at various stages of manufacturing that increases the production costs. The low volumes and specialized nature of viral vaccine cell culture media compared to other cell culture products also do not allow economies of scale, further bumping up the per unit costs. The high costs involved pose a major challenge for biopharmaceutical companies and may delay the development of new vaccines, especially for diseases prevalent in low and middle income countries.
Market Opportunity - Increasing collaborations and partnerships for vaccine production
The viral vaccine manufacturing landscape is witnessing growing instances of collaborations between research institutes, global health organizations and manufacturers. This is helping pool resources as well as expertise for more efficient and affordable vaccine production. For example, the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization (GAVI) is supporting several collaboration initiatives between manufacturers from developing and developed countries for transferring technologies and strengthening local vaccine manufacturing capabilities. Many manufacturers are also signing material transfer agreements, licensing deals and contract manufacturing partnerships with emerging contract development and manufacturing organizations from Asia and Latin America. This allows tapping their comparatively lower-cost infrastructure and skilled workforce. Such partnerships enable greater capacity utilization of existing vaccine production facilities and shared risks of investments. In the long run, they are expected to bolster global vaccine supplies and drive down costs through economies of scale, which would facilitate increased immunization in low and middle-income regions.
The treatment of viral disease typically follows a step-wise approach based on the stage of the infection. For initial symptomatic treatment at early stages, over-the-counter antiviral medications like Acetaminophen or Ibuprofen are commonly prescribed to reduce fever and body aches.
As the disease progresses, prescribers often recommend branded oral antivirals such as Tamiflu (oseltamivir) for high-risk patients within 48 hours of symptom onset. For cases involving secondary bacterial infections, antibiotics like Azithromycin (Zithromax) may be prescribed. In more severe stages, intravenous antivirals and steroids are used. Intravenous Peramivir (Rapivab) and Dexamethasone (Decadron) help control virus replication and modulate inflammatory response.
Hospitalization is recommended for elderly patients or those with existing medical conditions like lung/heart disease which increased risk of complications. During these stages, strong antivirals combined with supportive care help manage symptoms and prevent organ damage. Favipiravir (Avigan) and Remdesivir (Veklury) are two newer broad-spectrum antivirals gaining prominence.
Factors like co-morbidities, stage and severity of infection, risk profile, and availability of new drugs in the region influence prescriber decisions. Close patient monitoring along with combination therapies is common during critical stages to optimize outcomes.
Lung cancer is typically diagnosed in one of four main stages - stage I through stage IV - depending on how far the cancer has spread. For early stage lung cancers (stage I-II), surgery is often the primary treatment option with the goal of removing the cancer from the lungs. For patients whose cancer is not surgically removable or who cannot undergo surgery, stereotactic radiotherapy or hypofractionated radiotherapy are preferred to precisely deliver high doses of radiation directly to the tumor.
For more advanced lung cancers (stage III-IV), chemotherapy is generally recommended. Platinum-based doublet chemotherapy using drugs like cisplatin or carboplatin combined with other chemotherapy drugs such as paclitaxel, docetaxel or pemetrexed is the standard first-line treatment. For non-small cell lung cancer, immune checkpoint inhibitors like pembrolizumab, nivolumab or atezolizumab are often added to chemotherapy based on the expression of PD-L1 on tumor cells. Second-line treatments may include monotherapy immune checkpoint inhibitors, ALK/EGFR inhibitors such as alectinib, crizotinib or osimertinib based on the presence of genetic mutations. For select patients with no driver mutations and good performance status, chemotherapy regimens like docetaxel or pemetrexed are utilized. These tailored multi-modal therapies offer the best chances of overall response and improved survival.
Companies like Thermo Fisher Scientific have significantly invested in R&D to develop newer and more advanced cell culture media formulations that support high viral yields. In 2018, Thermo launched ExpiSfTM Expression Medium, an animal component-free chemically defined media for suspended cell cultures. This media has helped manufacturers scale-up production of viral vaccines effectively.
To expand their cell culture media offerings, many players have pursued acquisitions. For example, in 2020, Merck KGaA acquired Atlanta Biologicals, a leader in serum-free and animal-origin free cell culture media. This strengthened Merck's media portfolio and capabilities in viral vaccine production.
Media manufacturers form key partnerships with vaccine producers to support their R&D and commercial production needs. For example, in 2015, Sartorius partnered with Sanofi Pasteur, supporting their development and production of live attenuated influenza vaccine with its Sartorius cell culture media.
To ensure leadership in the high-growth viral vaccine market, players like Thermo Fisher have invested in large scale production plants. For example, its 400,000 sq. ft facility in Burlington, NC manufactures serum-free and chemically defined media at an industrial scale. This strategy ensures adequate media supply to the market.
Media companies also adopt the strategy of offering customized and application-specific media formulations. For example, Irvine Scientific’s viral production media are optimized and custom formulated for specific viruses like viral vectors and respiratory viruses. This targeted approach helps improve client retention and satisfaction.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
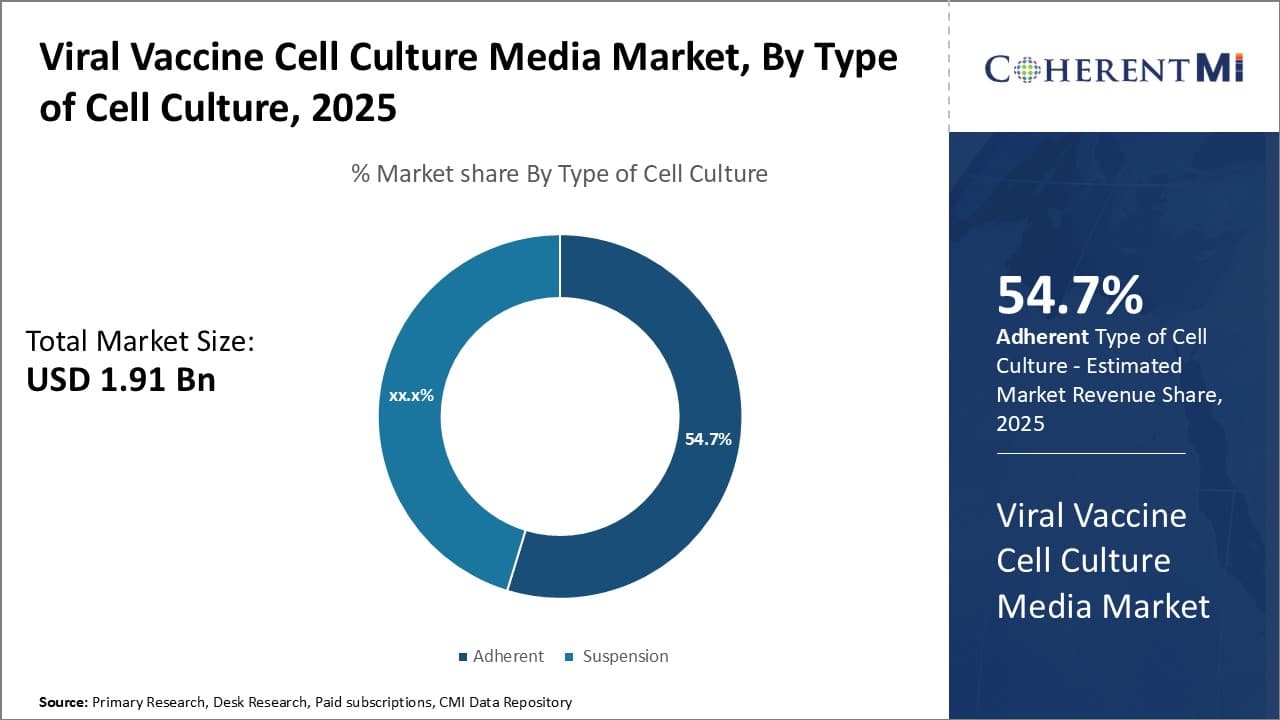
Insights, By Type of Cell Culture: Ease of cell adherence drives growth of adherent cell culture segment
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Type of Cell Culture: Ease of cell adherence drives growth of adherent cell culture segment
The adherent sub-segment contributes the largest share of 54.7% in the viral vaccine cell culture media market due to the inherent advantages of adherent cell growth techniques. Adherent cell lines naturally attach and grow on the surface of culture vessels, flasks, or plates. This ease of cell adherence eliminates the need for specialized equipment or techniques required for suspension cell culture. As a result, adherent cell culture is more straightforward and affordable to set up and maintain in a clinical or research laboratory setting.
The straightforward nature of adherent cell culture allows for high cell yields that are crucial for effective viral vaccine production. Adherent cells readily multiply directly on the surface area provided by culture vessels. This facilitates dense monolayers of actively growing and dividing cells. The direct contact of adherent cells with the culture surface maximizes surface area available for cellular activities and proliferation. As a result, adherent cell culture is highly productive and efficient at generating the vast numbers of cells necessary for viral vaccine development and manufacture.
Adherent cell culture is also well-suited to the versatile techniques employed in viral vaccine development. Cells can be easily observed, manually passed, harvested or treated while attached to surfaces. This permits adherent cells to be used effectively in basic research applications like transfection, infection or analysis using microscopy. It also enables adherent cells to be adapted to large-scale industrial processes like bioreactor suspension or microcarrier culture with relative ease. The flexibility of adherent cell culture to multiple techniques and scales of application reinforces its dominant position in the viral vaccine cell culture media market.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
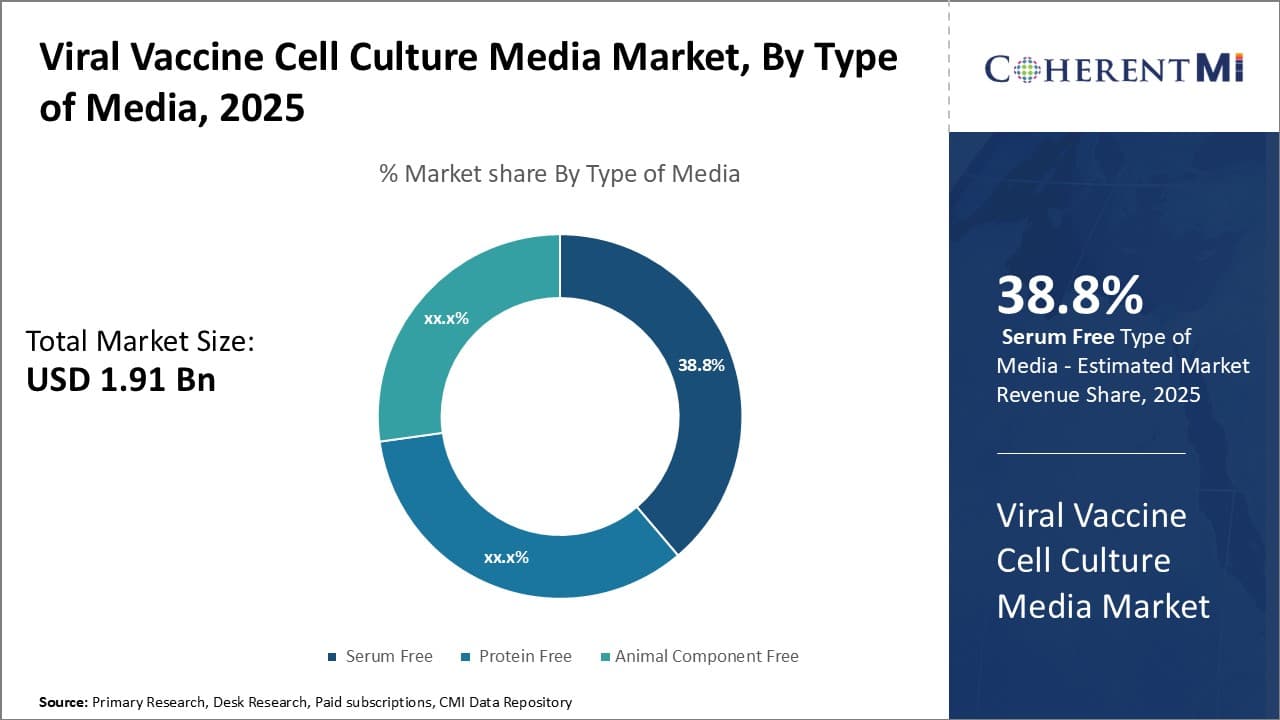
Insights, By Type of Media: Demand for animal-free products boosts serum-free media sub-segment
The serum-free sub-segment holds a sizable share of 38.8% in the viral vaccine cell culture media market due to increased demand for animal-free bioproduction. Serum supplements like fetal bovine serum contain non-human proteins and growth factors that can transmit potential contaminants to human viral vaccine products. Regulatory bodies have strengthened requirements to remove animal-derived components from manufacturing processes.
This has led biopharmaceutical firms to adopt serum-free media for viral vaccine production. Serum-free formulations precisely control cellular nutrient and growth factor inputs without unnecessary animal proteins. These animal-free conditions provide a defined, reproducible environment preferred for consistent high-quality vaccine lot production. Absence of animal serum also avoids potential purity, efficacy and safety issues from unknown contaminants.
Demand has also increased as ethically-conscious consumers seek vaccines developed without animal exploitation. Highly-purified serum-free media addresses these ethical considerations while still enabling efficient cell culture and vaccine manufacture. Leading biopharmas now exclusively use optimized, animal-free media to meet both regulatory compliance and consumer values regarding animal welfare in their immunization products.
The major players operating in the viral vaccine cell culture media market include Thermo Fisher Scientific, Merck, Sartorius, Creative Biolabs, Xell, Jianshun Biosciences, ATZ labs and OPM Biosciences.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Vipul Patil is a dynamic management consultant with 6 years of dedicated experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Known for his analytical acumen and strategic insight, Vipul has successfully partnered with pharmaceutical companies to enhance operational efficiency, cross broader expansion, and navigate the complexities of distribution in markets with high revenue potential.
Viral Vaccine Cell Culture Media Market is segmented By Type of Cell Culture (Adherent, Suspension),...
Viral Vaccine Cell Culture Media Market
How big is the Viral Vaccine Cell Culture Media Market?
The Viral Vaccine Cell Culture Media Market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.91 in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 2.87 Billion by 2032.
What are the major factors driving the viral vaccine cell culture media market growth?
The rising global demand for viral vaccines due to pandemics and emerging diseases and shift towards serum-free and animal component-free media to reduce contamination risks are the major factors driving the viral vaccine cell culture media market.
Which is the leading type of cell culture in the viral vaccine cell culture media market?
The leading type of cell culture segment is suspension.
Which are the major players operating in the viral vaccine cell culture media market?
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Merck, Sartorius, Creative Biolabs, Xell, Jianshun Biosciences, ATZ labs, and OPM Biosciences are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the viral vaccine cell culture media market?
The CAGR of the viral vaccine cell culture media market is projected to be 6.00% from 2025-2032.